preface
This article comes from the Vue3 + Ts course of teacher coderwhy
Attach link: https://ke.qq.com/course/3453141
Who can refuse a teacher who is 100% praised and adds classes
catalogue
Declarative programming and imperative programming
Meet Vue
-
vue is the same as view
-
Progressive: embed vue as part of your application
-
What is Vue's current position at the front end?
-
At present, the three most mainstream front-end frameworks are Vue, React and Angular
-
-
How to import Vue
-
CDN introduction
-
CDN is called Content Delivery Network or Content Distribution Network (abbreviated as CDN)
-
It refers to the use of servers closest to each user through interconnected network systems;
-
Send music, pictures, videos, applications and other files to users faster and more reliably;
-
To provide high-performance, scalability and low-cost network content delivery to users;
-
-
code:
<body> <div id="app"></div> <script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script> <script> const mjjh = { template: '<h2>Hellow World</h2>' } const app = Vue.createApp(mjjh); app.mount("#app") </script> </body>
-
-
local import
-
Import directly after downloading
-
code:
<body> <div id="app"></div> <script src="../js//Vue.js"></script> <script> const app = Vue.createApp({ template: '<h2>Hellow World</h2>' }).mount("#app") </script> </body>
-
Vue Beginner - counter case
-
js native
<body> <h2 class="counter"></h2> <button class="increment">+1</button> <button class="decrement">-1</button> <script> const conterEl = document.querySelector('.counter') const incrementEl = document.querySelector('.increment') const decrementEl = document.querySelector('.decrement') let counter = 100; conterEl.innerHTML = counter; incrementEl.addEventListener("click",() =>{ counter += 1; conterEl.innerHTML = counter }) decrementEl.addEventListener("click",() =>{ counter -= 1; conterEl.innerHTML = counter }) </script> </body> -
Vue
<body> <div id="app"></div> <script src="../js//Vue.js"></script> <script> Vue.createApp({ template: ` <div> <h2>{{message}}</h2> <h2>{{counter}}</h2> <button @click='increment'>+1</button> <button @click='decrement'>-1</button> </div> `, data: function(){ return{ message:"Hello World", counter: 100 } }, methods: { increment(){ this.counter++ }, decrement(){ this.counter-- } } }).mount("#app") </script> </body>
Declarative programming and imperative programming
-
We will find that the modes and characteristics of native development and Vue development are completely different. In fact, there are two different programming paradigms: imperative programming and declarative programming
-
Imperative programming focuses on "how to do", while declarative programming focuses on "what to do". The framework (machine) completes the process of "how"
MVVM model
-
MVC and MVVM are both software architectures
-
MVC iS the abbreviation of model view controller. It iS a very framework architecture mode used in the early stage, such as iS and front end
-
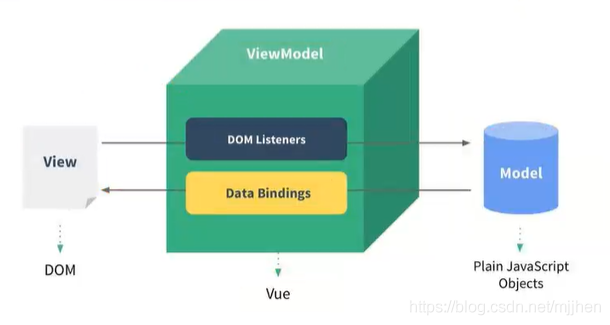
MVVM is the abbreviation of model view - viewmode. It is a very popular architecture mode at present
-
-
In general, we often call vue an MVVM framework
vue officials have stated that although vue does not fully comply with the MVVM model, the whole design is inspired by it
template attribute
-
When using createApp, we pass in an object. Next, we will analyze in detail the meaning of the previously passed in attributes.
-
Template attribute: indicates the template information Vue needs to help us render
-
At present, we can see that there are a lot of HTML tags in it. These tags will replace the innerHTML of the elements we mount (such as d IV V with id app)
-
There are some strange syntax in the template, such as {}, such as @) click. These are the unique syntax of the template, which we will talk about later
-
-
However, the writing method of this template is a little too awkward, and the IDE may not have any prompts, which hinders the efficiency of our programming
-
vue provides two ways:
-
Method 1: use script tag and mark its type as X-template;
<body> <div id="app">hhhh</div> <script type="x-template" id="why"> <div> <h2>{{message}}</h2> <h2>{{counter}}</h2> <button @click='increment'>+1</button> <button @click='decrement'>-1</button> </div> </script> <script src="../js//Vue.js"></script> <script> Vue.createApp({ template: '#why', data: function(){ return{ message:"Hello World", counter: 100 } }, methods: { increment(){ this.counter++ }, decrement(){ this.counter-- } } }).mount("#app") </script> </body> -
Method 2: use any label (usually template label, because it will not be rendered by the browser) and set the ID; The V template element is a mechanism for saving client-side content that is not rendered when the page is reloaded, but can then be instantiated at run time using JavaScript
<body> <div id="app"></div> <template id="why"> <div> <h2>{{message}}</h2> <h2>{{counter}}</h2> <button @click='increment'>+1</button> <button @click='decrement'>-1</button> </div> </template> <script src="../js//Vue.js"></script> <script> Vue.createApp({ template: '#why', data: function(){ return{ message:"Hello World", counter: 100 } }, methods: { increment(){ this.counter++ }, decrement(){ this.counter-- } } }).mount("#app") </script> </body>-
Useless tips: you can also use boxes such as div, but div will be loaded by the browser, so two boxes will be displayed
-
-
data attribute
-
The data attribute is passed into a function, and the function needs to return an object
-
In Vue2x, you can also pass in an object (although the official recommendation is a function);
-
In Vue3x, you must pass in a function, otherwise you will directly report an error in the browser
-
-
The object returned in data will be hijacked by the responsive system of vue, and then the modification or access to the object will be processed in hijacking
-
Therefore, we can access counter through {counter} in the template to obtain data from the object
-
Therefore, when we modify the value of counter, {counter) in the template will also change;
-
methods property (emphasis)
-
The methods attribute is an object. Usually, we will define many methods in this object
-
These methods can be bound to the template template;
-
In this method, we can use this keyword to directly access the properties of the object returned in data;
-
-
Problem: the official document has this description, that is, the arrow function cannot be used
-
Why not use the arrow function (VUE3.0)?
-
In methods, we want to use data to return the data in the object:
-
Then this must have a value, and it should be possible to obtain the data in the data return object through this.
-
-
So can this be a window?
-
It can't be window, because we can't get the data in the data return object in window;
-
But if we use the arrow function, this will be window;
-
-
Why window?
-
Here, the arrow function uses the search rule of this, which will act on its own upper layer to find this;
-
Finally, we just found this in the script, so it is window;
-
-
How does this find and bind?
-
-
What exactly does this point to without using the arrow function
-
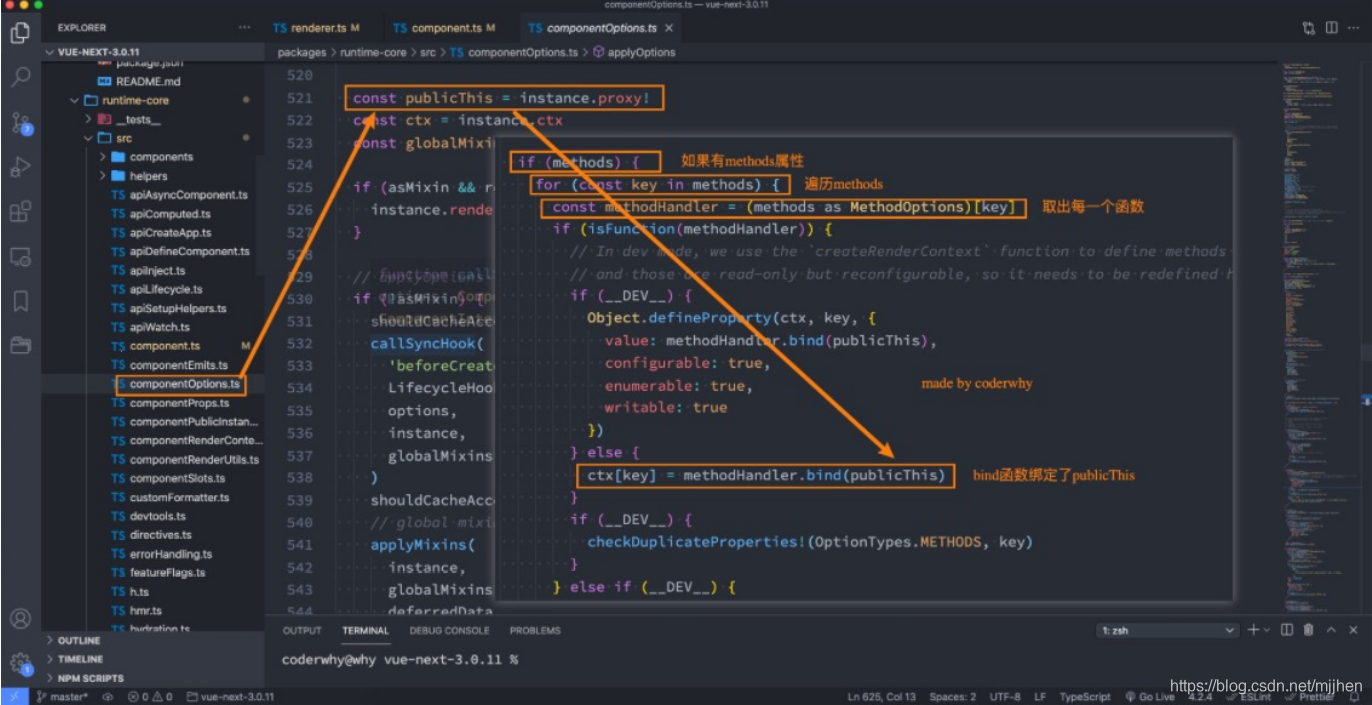
In fact, Vue's source code traverses all functions in methods and binds this through bind
-
How to read Vue source code
-
Required environment npm, yarn
-
Operation steps
-
Install yarn npm install yarn -g
-
Configure yarn install in the project
-
Add -- sourcemap after dev in package.json
-
Package the project yarn dev (there are two files in the vue/dist folder, vue.global.js and vue.global.js.map)
-
Create your own folder and test demo in Vue / example
-
Set a breakpoint in the demo - debugger
-
Open the debugging panel in the browser and select the source panel to view and execute the corresponding source code
-