Reference blog: https://clockworkbird9.wordpress.com/2016/09/
[ 2.824545] VFS: Mounted root (ext4 filesystem) readonly on device 179:1. [ 2.833446] Freeing unused kernel memory: 244K (84733000 - 84770000) [ 3.006884] init: Console is alive [ 3.011436] init: - watchdog - [ 3.329383] init: - preinit - [ 6.570976] mount_root: mounting /dev/root [ 6.579281] EXT4-fs (mmcblk0p1): re-mounted. Opts: (null) [ 6.596450] procd: - early - [ 6.599817] procd: - watchdog - [ 7.301153] procd: - ubus - [ 7.362047] procd: - init -
It is obvious that the procd process took over the init process
1 start up process
- u-boot
It configures low-level hardware, loads Linux kernel imag and device tree blob, and finally uses kernel cmdline to jump to the Linux kernel image in RAM; - Kernel -> Hareware
Linux Kernel initialization Hareware - Kernel -> filesystem
The root file system will be mounted - Kernel -> Init Process (PID 1)
Kernel initialization process - Openwrt -> Preinit
openwrt initializes the process. Note that this is the Preinit function, not a script - Openwrt - > procd, perinit (script)
procd goes back and calls / etc / RC d
After preinit initialization is complete. The initialization process is over
2 Preinit
2.1 /etc/preinit
OpenWRT will inject the OpenWRT initialization process preinit into the kernel initialization process list (kernel_init).
At this time, the device will execute / etc/preinit, which is located in package / base files / etc/
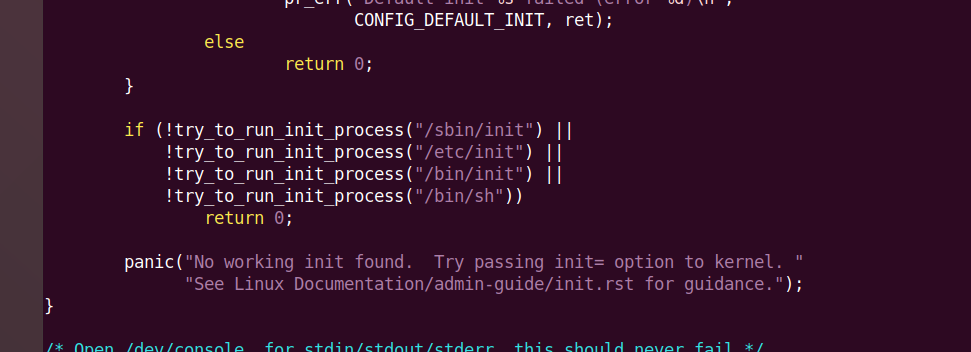
#!/bin/sh # Copyright (C) 2006-2016 OpenWrt.org # Copyright (C) 2010 Vertical Communications ### When the device executes for the first time, the PREINIT parameter is undefined, so / sbin/init will be executed ### Therefore, / sbin/init is the first initialization process of the device [ -z "$PREINIT" ] && exec /sbin/init export PATH="%PATH%" . /lib/functions.sh . /lib/functions/preinit.sh . /lib/functions/system.sh ### boot_hook_init in / lib / functions / Preinit Defined in Sh boot_hook_init preinit_essential boot_hook_init preinit_main boot_hook_init failsafe boot_hook_init initramfs boot_hook_init preinit_mount_root ### Execute all scripts under / lib/preinit / for pi_source_file in /lib/preinit/*; do . $pi_source_file done boot_run_hook preinit_essential pi_mount_skip_next=false pi_jffs2_mount_success=false pi_failsafe_net_message=false boot_run_hook preinit_main
/sbin/init is procd / init d/init. C compiled executable.
int
main(int argc, char **argv)
{
pid_t pid;
//Open log
ulog_open(ULOG_KMSG, LOG_DAEMON, "init");
//Set signal
sigaction(SIGTERM, &sa_shutdown, NULL);
sigaction(SIGUSR1, &sa_shutdown, NULL);
sigaction(SIGUSR2, &sa_shutdown, NULL);
/* early
* |->early_mounts
* | |-> mount
* | |->early_dev Setting environment variables
* |->LOG("Console is alive")
*/
early();
/* cmdline
* |-> get init_debug Get init_debug level
*/
cmdline();
/* watchdog_init
* |->LOG("- watchdog -")
*/
watchdog_init(1);
pid = fork();
if (!pid) {
/* /sbin/kmodloader
* |-> /etc/modules-boot.d Load driver
*/
char *kmod[] = { "/sbin/kmodloader", "/etc/modules-boot.d/", NULL };
if (debug < 3)
patch_stdio("/dev/null");
execvp(kmod[0], kmod);
ERROR("Failed to start kmodloader\n");
exit(-1);
}
if (pid <= 0) {
ERROR("Failed to start kmodloader instance\n");
} else {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 1200; i++) {
if (waitpid(pid, NULL, WNOHANG) > 0)
break;
usleep(10 * 1000);
watchdog_ping();
}
}
uloop_init();
/* preinit
* |-> LOG("- preinit -")
* |-> fork->procd
* |-> setenv("PREINIT", "1", 1)
* |-> fork->sh /etc/preinit
*/
preinit();
uloop_run();
return 0;
}
initd/preinit.c
void
preinit(void)
{
// perinit script
char *init[] = { "/bin/sh", "/etc/preinit", NULL };
// procd
char *plug[] = { "/sbin/procd", "-h", "/etc/hotplug-preinit.json", NULL };
int fd;
LOG("- preinit -\n");
/* Note that this is a callback function
*/
plugd_proc.cb = plugd_proc_cb;
plugd_proc.pid = fork();
if (!plugd_proc.pid) {
/* plug "/sbin/procd", "-h", "/etc/hotplug-preinit.json"
* Execute procd first, and the input parameter is - H / etc / hotplug Preinit json
*/
execvp(plug[0], plug);
ERROR("Failed to start plugd: %m\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if (plugd_proc.pid <= 0) {
ERROR("Failed to start new plugd instance: %m\n");
return;
}
uloop_process_add(&plugd_proc);
setenv("PREINIT", "1", 1);
fd = creat("/tmp/.preinit", 0600);
if (fd < 0)
ERROR("Failed to create sentinel file: %m\n");
else
close(fd);
preinit_proc.cb = spawn_procd;
preinit_proc.pid = fork();
if (!preinit_proc.pid) {
/* init "/bin/sh", "/etc/preinit
* Then execute preinit. The input parameter is - H / etc / hotplug preinit json
*/
execvp(init[0], init);
ERROR("Failed to start preinit: %m\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if (preinit_proc.pid <= 0) {
ERROR("Failed to start new preinit instance: %m\n");
return;
}
uloop_process_add(&preinit_proc);
DEBUG(4, "Launched preinit instance, pid=%d\n", (int) preinit_proc.pid);
}
Callback function: the difference between a callback function and an ordinary function is that in the callback function, the main program will transfer the callback function to the storage function like a parameter
fork procd process, specifying hotplug Preinit JSON, so hotplug will be executed_ run
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int ch;
char *dbglvl = getenv("DBGLVL");
int ulog_channels = ULOG_KMSG;
if (dbglvl) {
debug = atoi(dbglvl);
unsetenv("DBGLVL");
}
while ((ch = getopt(argc, argv, "d:s:h:S")) != -1) {
switch (ch) {
case 'h':
/* Establish netlink communication mechanism, complete kernel interaction and listen for uevent events
*/
return hotplug_run(optarg);
case 's':
ubus_socket = optarg;
break;
case 'd':
debug = atoi(optarg);
break;
case 'S':
ulog_channels = ULOG_STDIO;
break;
default:
return usage(argv[0]);
}
}
ulog_open(ulog_channels, LOG_DAEMON, "procd");
setsid();
uloop_init();
procd_signal();
if (getpid() != 1)
procd_connect_ubus();
else
/* State machine processing, the actual effect is as follows
* [ 6.596450] procd: - early -
* [ 6.599817] procd: - watchdog -
* [ 7.301153] procd: - ubus -
* [ 7.362047] procd: - init -
*/
procd_state_next();
uloop_run();
uloop_done();
return 0;
}
procd_ state_ After next processing the status, the device will execute to RCS c
int rcS(char *pattern, char *param, void (*q_empty)(struct runqueue *))
{
runqueue_init(&q);
q.empty_cb = q_empty;
q.max_running_tasks = 1;
// This is where our common self starting scripts are
// You should know that the files starting with K are stop and the files starting with S are start
return _rc(&q, "/etc/rc.d", pattern, "*", param);
}
Others' illustrations are quoted here
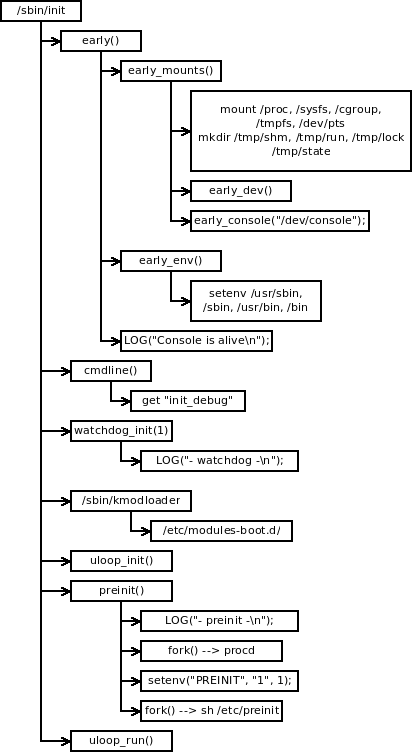
1. early() is the first function in init. It has four main tasks:
- early_mounts(): mount /proc, /sysfs, /dev, /tmp;
- early_env(): Use / usr/sbin: / sbin: / usr/bin: / bin to set the PATH parameter;
- Initialize / dev/console;
- Print the first message from init: "the console is a live", as shown above;
2. cmdline() is the second function that reads the kernel boot command line from / proc/cmdline and parses init_debug parameter;
3,watchdog_init() initializes the monitor / dev/watchdog and prints the second message "- Monitor -" as shown above;
4. fork a new thread and let / sbin/kmodloader load / etc / modules boot D / device drivers;
5,uloop_init() initializes uloop, which is an event loop implementation. Later procd and sh /etc/preinit will be managed by uloop;
6. preinit() has four main tasks:
- Print the third message: "- preinit -", as shown above;
- fork() a new thread to execute sh /etc/preinit. This will be the second time this initialization script is executed. One is called spawn_ The callback function of procd() will be executed after sh /etc/preinit is completed.
Note: spawn_procd() will read the system debug level from / TMP / debugllevel and set it to env DBGLVL. It also sets the watchdog fd to env WDTFD. Finally, it forks the real / sbin/procd as a deamon. - set env variable PREINIT with setenv ("PREINIT", "1", 1);
- fork() is a new thread that executes the / sbin/procd program with the parameter - H / etc / hotplug Preinit json.
- Note: this new thread will pass through uloop_process_add() and a callbakc function are added to uloop as the callback function plugd when / sbin/procd – h is completed_ proc_ cb()