Golang also provides reflection mechanism, like Java, which obtains information about objects at run time and updates their internal state; Golang obtains object types, field types and values, calls struct instance methods, updates instance values, and so on.
_Go Gos The two most important objects and functions related to reflection in the reflect package are Type and Value.
_Gos provides the following two functions, which are the core of Gos reflection;
_Reflect.TypeOfReturns the type of the target object
_Reflect.ValueOfReturn value The value of the target object
t:=1 fmt.Println(reflect.TypeOf(t), reflect.ValueOf(t)) //Output: int 1
Operating Struct by Reflection
type Demo struct {
Id int
Name string
}
func (d *Demo) Back() {
fmt.Println("Call Method Back")
}
func (d *Demo) Add(a, b int) int {
return a + b
}
Gets the name and value of each member variable in the structure:
d := &Demo{Id: 2, Name: "test"}
getValue(d)
//Output: Id: 2
Name : test
func getValue(v interface{}) {
t := reflect.TypeOf(v)
o := reflect.ValueOf(v)
if t.Kind() == reflect.Ptr {
t = t.Elem() //Gets the type in the type pointer
}
if o.Kind() == reflect.Ptr {
o = o.Elem() //Get the value in the value address
}
num := t.NumField() //Get the number of fields
for i := 0; i < num; i++ {
f := o.Field(i) //Get the value of the field
fieldName := t.Field(i).Name //Get the field name
switch f.Kind() {
case reflect.Int:
fmt.Println(fieldName, ": ", f.Int())
case reflect.String:
fmt.Println(fieldName, ": ", f.String())
default:
fmt.Println("Type not supported")
}
}
}
_Use for reference typesReflect.TypeOfReturns a pointer of this type.Reflect.ValueOfReturns the value address of that type; therefore, the Elem() function is called to get the true type and value for all operations related to the reference type.
_Call the NumField function of a Type or Value object to get the number of fields in the structure
_Call Field(i) of the Value object to get the value of the field;
_Call the Kind() function of the Value object to get the type of field;
_The value corresponds to the type of call to the corresponding function to get the corresponding value, if the type is inconsistent it will be thrown:panic: reflect: call ofReflect.Value.XxxOn int Value;
Modify the value of each member variable in the structure:
d := new(Demo)
setValue(d)
fmt.Println(d)
//Output: &{88 Test}
func setValue(v interface{}) {
t := reflect.TypeOf(v)
o := reflect.ValueOf(v)
if t.Kind() == reflect.Ptr {
t = t.Elem()
}
if o.Kind() == reflect.Ptr {
o = o.Elem()
}
num := t.NumField()
for i := 0; i < num; i++ {
f := o.Field(i)
switch f.Kind() {
case reflect.Int:
f.SetInt(88) //Set a value to this field
case reflect.String:
f.SetString("Test") /Set a value to this field
default:
fmt.Println("Type not supported")
}
}
}
_Modify the field value as you get the value, the type must be consistent, if inconsistency throws an exception, if int type calls SetString to set value: panic: reflect: call ofReflect.Value.SetStringOn int Value;
Invoke the parameterless method of the structure:
d := new(Demo)
callMethod(d)
//Output: Call method Back
func callMethod(v interface{}) {
o := reflect.ValueOf(v)
o.MethodByName("Back").Call(nil)
}
_Call MethodByName to get the method by name, Call to call the method;
Parameter methods that call structs:
d := new(Demo)
callMethodParam (d)
//Output: 3
func callMethodParam(p interface{}) {
o := reflect.ValueOf(p)
args:=[]reflect.Value{reflect.ValueOf(1), reflect.ValueOf(2)}
v:= o.MethodByName("Add").Call(args)
fmt.Println(v[0])
}
More commonly used methods are:
_Get members of a structure by name
Refletct.ValueOf(*e).FieldByName("Name")
_Get json tag information for structure members
reflect.TypeOf(s) . Field(0).Tag.Get("key")
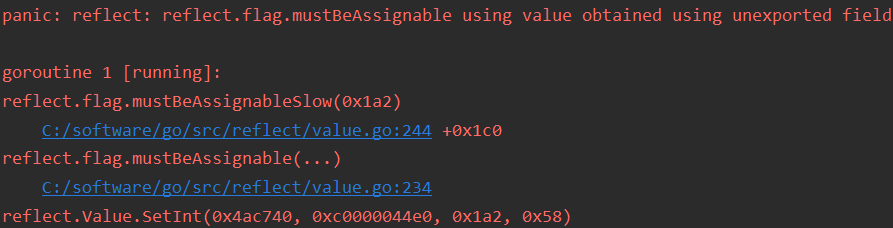
_Golang's reflection also follows the GoLanguage rules. Reflection cannot modify private objects in the structure, cannot call private private methods, can access private members, modifying private members will throwReflect.flag.mustBeAssignableExceptions;
Article starting address: Solinx
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/W0UVbFxMMeXA5HuNNZlK-A