Classification of 0 sort
- Stability and Instability: Is the Relative Position of Equal Numbers Changing
- Internal and External Sorting: Whether to Use External Storage
1 insertion sort
Ideas:
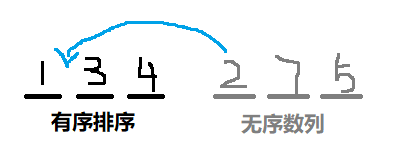
- Starting with the first element, build an ordered ordering
- Find the right place to insert one by one in the ordered order ahead
Time complexity:
- Best case: order T=O(n)T=O(n)T=O(n) T = O (n)
- Worst case: reverse order T=O(n2)T=O(n^2)T=O(n2)
Classification: stable, internal ranking
// Insertion sort void insertion_sort(int data[], int len){ // If length <= 1, exit without sorting if( len <= 1 ){ return; } // Number of comparisons and exchanges int compareCount = 0; int swapCount = 0; // sort int i,j; // Insert the preceding ordered array from the second bit, with the subscript of 1 for ( i=1; i<len; i++){ int tmp = data[i]; // The first of an unordered array for ( j=i-1; j>=0; j-- ){ compareCount++; if(data[j] <= tmp){ break; }else{ data[j+1] = data[j]; } } swapCount++; data[j+1] = tmp; } printf("Number of insert sort comparisons:%d\n", compareCount); printf("Insert Sort Exchange Number:%d\n", swapCount); }
2 Bubble Sorting
Ideas:
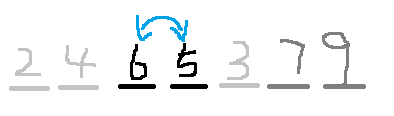
- Starting from the first number each time, the adjacent elements are compared in turn, the order is unchanged, and the reverse order is exchanged.
- The largest number must be in the last place. Next time, compare it with the first one.
- break a process without exchange order
Time complexity:
- Best case: order T=O(n)T=O(n)T=O(n) T = O (n)
- Worst case: reverse order T=O(n2)T=O(n^2)T=O(n2)
Classification: stable, internal ranking
// Exchange function, C language needs to pass in pointer to exchange void swap(int *a, int *b){ int tmp; tmp = *a; *a = *b; *b = tmp; }
// Bubble sort void Bubble_sort(int data[], int len){ int k = 0; int compareCount = 0; // Record the number of comparisons int swapCount = 0; // Record Exchange Number while(1) { bool done = false; // Determine if there is at least a sequential exchange in the loop int i; for( i=0; i<len-1-k; i++ ){ compareCount++; // Number of comparisons + 1 if( data[i] < data[i+1]){ continue; } swap(&data[i], &data[i+1]); // Need to change the incoming address swapCount++; // Exchange times + 1 done = true; } if(!done){ break; } k++; } printf("Bubble sort comparison times:%d\n", compareCount); printf("Bubble Sort Exchange Number:%d\n", swapCount); }
3 Hill Sorting
Optimized version of insert sort
Ideas:
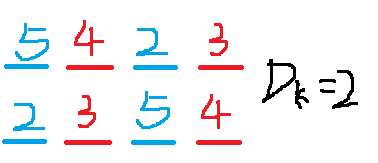
- Define the decrement sequence D1>D2>...> D k>...> D n = 1D_1> D_2>...> D_k>...> D_n = 1D1 > D_2 > Dk > Dn = 1
- Insert and sort subcolumns in the list with intervals of DkD_kDk in turn
Time complexity:
Influenced by interval selection
Classification: Unstable, Internal Sorting
// The insertion sort of the subcolumn, which considers D as 1, is the normal insertion sort. // Input: starting point, number of nodes, spacing void Insert_sort(int data[], int len, int D){ // Determine whether insertion sort is needed if ( len <= 1 ){ return; } // Insert Sort: Ordered + Unordered // Each subcolumn int i; for(i=D; i<len*D; i+=D){ int j, tmp = data[i]; // Unordered insertion order (reverse comparison from ordered tail) for (j=i-D; j>=0; j-=D){ if (data[j] <= tmp ){ break; } data[j+D] = data[j]; } data[j+D] = tmp; } }
// Shell Sort void Shell_sort(int data[], int len ){ /* Determine whether insertion sort is needed */ if ( len <= 1 ){ return; } /* Partition subcolumn */ int D; // interval for (D=len/2; D>0; D/=2){ // Operations on different subcolumns in turn int k; for (k=0; k<D; k++){ Insert_sort(data+k, len/D, D); } } }
4 Selective Sorting
Ideas:
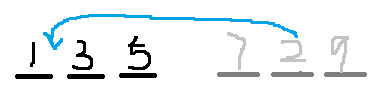
- Starting from the first place, always choose the smallest number to put in
Time complexity:
T=O(n2)T=O(n^2)T=O(n2)
// exchange void swap(int *a, int *b){ int tmp = *a; *a = *b; *b = tmp; }
// Selective Sorting void Selection_sort(int data[], int len){ int compareCount = 0; int swapCount=0; int i; for( i=0; i<len; i++ ){ int minIndex = i; int j; for ( j=i+1; j<len; j++ ){ compareCount++; if( data[j] < data[minIndex] ){ minIndex = j; } } // Insert the smallest into the corresponding position swapCount++; swap(&data[i], &data[minIndex]); } printf("The number of comparisons in the selection order:%d\n", compareCount); printf("Select the number of swaps for sorting:%d\n", swapCount);
5 Quick Sorting
Thought: Recursion
- Find a fulcrum position
- Initialization: iii is at the top of the column to be sorted, and jjj is at the end of the column to be sorted
- Comparing the number of iii and j j j positions from right to left, order j_1j-1j_1, reverse order exchange
- Comparing the number of jjj and I I I positions from left to right, order i+1i+1i+1, reverse order exchange
- I & lt; Ji & lt; Ji < j, return to the position of the central axis
- Line up the left side - go back to step 1
- Line up the right side - go back to step 1
Time complexity: T=O(nlog(n))T=O(nlog(n))T=O(nlog(n)) T = O (nlog (n))
Classification: instability
// Commutative function void swap(int *a, int *b){ int tmp = *a; *a = *b; *b = tmp; }
/* partition */ int Partition(int data[], int len){ // Determine whether the length needs to be executed if (len <= 1){ return 0; } int i = 0; // Initial i is at the head of the column to be sorted int j = len-1; //Initial j is at the end of the column to be sorted while(i<j){ // Comparing the number of positions i and j from right to left, order j-1, reverse order exchange while(data[i]<=data[j] && i<j){ j--; // Sequence j-1 } swap(&data[i], &data[j]); // Inverse Sequence Exchange // Comparing the number of positions i and j from left to right, order i+1, reverse order exchange while(data[i]<=data[j] && i<j){ i++; // Sequence i+1 } swap(&data[i], &data[j]); // Inverse Sequence Exchange } return i; // Return to the center axis = Left Length }
// Recursive execution partition void Quick_sort(int data[], int len){ // Determine whether the length needs to be executed if (len <= 1){ return; } // Recursive execution partition int pivot = Partition(data, len);// partition Quick_sort(data, pivot); Quick_sort(data+pivot+1, len-pivot-1); }