Mode 1: prototype chain inheritance
Tricks
- Define the parent type constructor
- Add a method to the prototype of the parent type
- Define a constructor for a subtype
- Create prototype of parent type object assignment to child type
- Set the construction property of a subtype prototype to a subtype
- Add method to subtype prototype
- Create object of subtype: method of parent type can be called
crux
- The prototype of the subtype is an instance object of the parent type
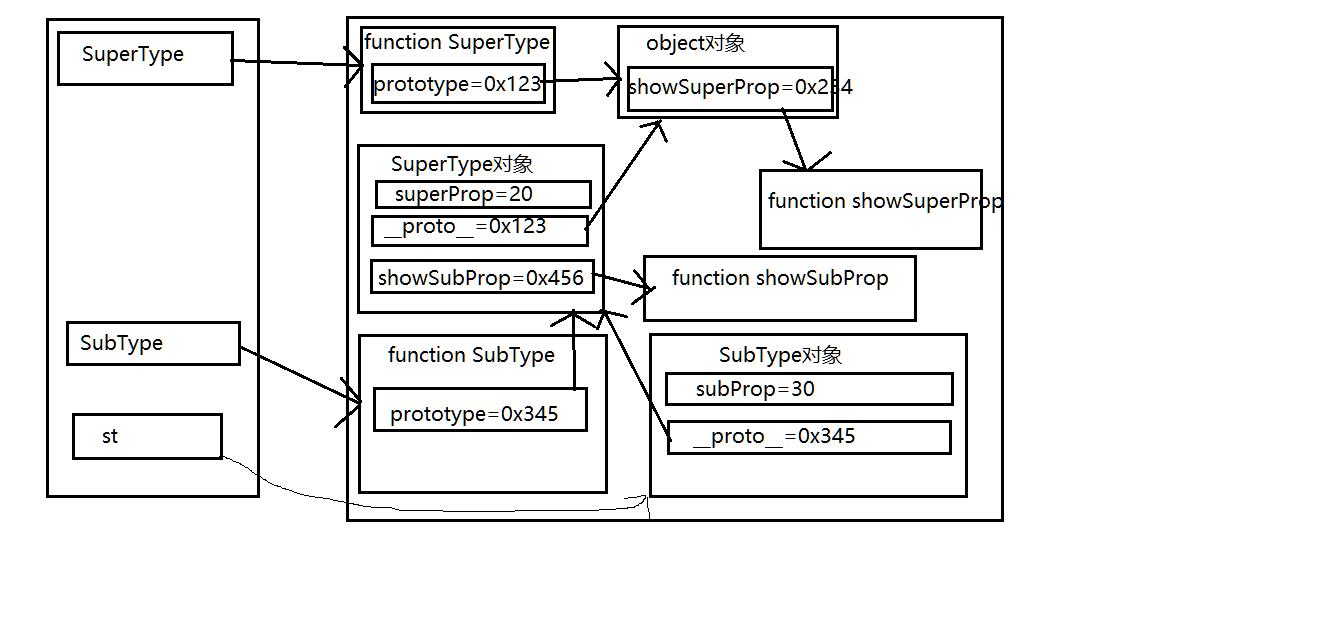
//Parent type
function Supper() {
this.supProp = 'Supper property'
}
Supper.prototype.showSupperProp = function () {
console.log(this.supProp)
}
//Subtype
function Sub() {
this.subProp = 'Sub property'
}
// The prototype of the subtype is an instance object of the parent type
Sub.prototype = new Supper()
// Let the constructor of the prototype of the subtype point to the subtype
Sub.prototype.constructor = Sub
Sub.prototype.showSubProp = function () {
console.log(this.subProp)
}
var sub = new Sub()
sub.showSupperProp()
// sub.toString()
sub.showSubProp()
console.log(sub) // Sub
Mode 2: borrow constructor inheritance (false)
tricks:
- Define the parent type constructor
- Define subtype constructor
- Call parent type construction in child type constructor
Key:
- In the subtype constructor, general super() calls the parent type constructor
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
function Student(name, age, price) {
Person.call(this, name, age)
// Equivalent to: this.Person(name, age)
/*this.name = name
this.age = age*/
this.price = price
}
var s = new Student('Tom', 20, 14000)
console.log(s.name, s.age, s.price)
Mode 3: combination inheritance of prototype chain + borrowing constructor
- Using prototype chain to realize method inheritance to parent type object
- Using super() to build function with parent type to initialize the same property
function Person(name, age) {
this.name = name
this.age = age
}
Person.prototype.setName = function (name) {
this.name = name
}
function Student(name, age, price) {
Person.call(this, name, age) // To get attributes
this.price = price
}
Student.prototype = new Person() // In order to see the method of the parent type
Student.prototype.constructor = Student //Fix constructor property
Student.prototype.setPrice = function (price) {
this.price = price
}
var s = new Student('Tom', 24, 15000)
s.setName('Bob')
s.setPrice(16000)
console.log(s.name, s.age, s.price)