The following article comes from what you can call my brother Cai, the author Daocai
Today, let's learn (RE) selenium, a library that simulates the running of browsers. It is a tool for Web application testing. Selenium tests run directly in the browser, just like real users. Supported browsers include IE (7, 8, 9, 10, 11), Mozilla, Firefox, Safari, Google Chrome, Opera and Edge.
Here, I will take Chrome as an example to demonstrate the function of Selenium~
0. Preparation
Before starting the follow-up function demonstration, we need to install the Chrome browser and configure the chrome driver. Of course, we also need to install the selenium library!
0.1. Install selenium Library
pip install selenium
0.2. Install browser driver
In fact, there are two ways to install browser drivers: one is common manual installation, and the other is automatic installation using a third-party library.
The following premise: everyone has installed Chrome browser
Manual installation
Check the local Chrome browser version first: (either way)
- Type C in the address bar of the browser hrome://version , you can view the browser version number
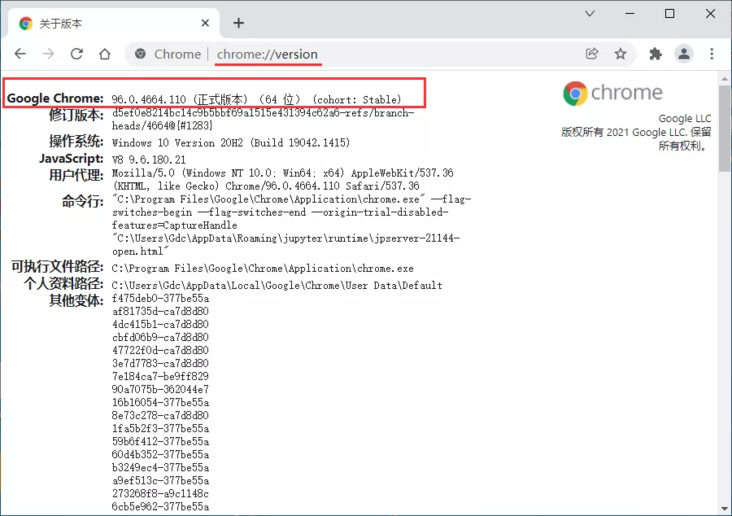
- Or click chrome menu help → about Google Chrome to view the browser version number
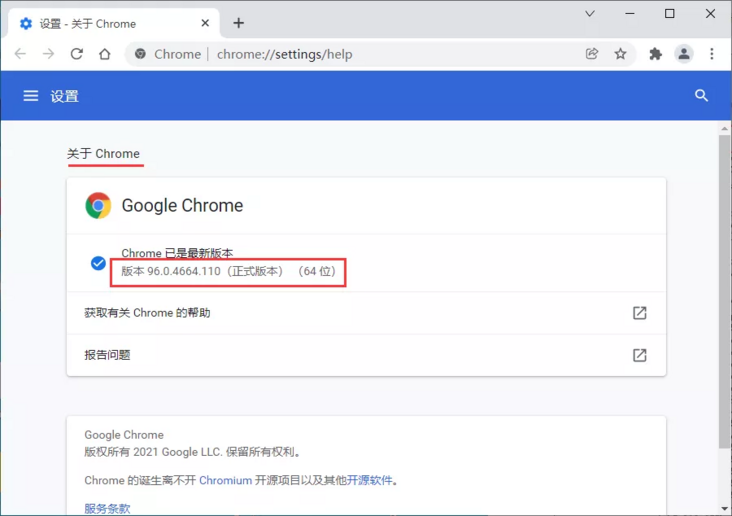
Then select the driver version corresponding to the version number
Download address: https://chromedriver.storage....
Finally, configure the environment variables, that is, the corresponding ChromeDriver executable file ChromeDriver Drag the EXE file to the Scripts directory of Python.
Note: of course, you can not do this, but specify chromedriver when calling Exe absolute path can also be used.
Automatic installation
The third-party library webdriver is required for automatic installation_ Manager, first install the library, then call the corresponding method.
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys
from webdriver_manager.chrome import ChromeDriverManager
browser = webdriver.Chrome(ChromeDriverManager().install())
browser.get('http://www.baidu.com')
search = browser.find_element_by_id('kw')
search.send_keys('python')
search.send_keys(Keys.ENTER)
# Close browser
browser.close()In the above code, chrome drivermanager () The install () method is to automatically install the driver. It will automatically obtain the version of the current browser and download the corresponding driver to the local.
====== WebDriver manager ====== Current google-chrome version is 96.0.4664 Get LATEST chromedriver version for 96.0.4664 google-chrome There is no [win32] chromedriver for browser in cache Trying to download new driver from https://chromedriver.storage.googleapis.com/96.0.4664.45/chromedriver_win32.zip Driver has been saved in cache [C:\Users\Gdc\.wdm\drivers\chromedriver\win32\96.0.4664.45]
If the browser channel already exists locally, it will be prompted that it already exists.
====== WebDriver manager ====== Current google-chrome version is 96.0.4664 Get LATEST driver version for 96.0.4664 Driver [C:\Users\Gdc\.wdm\drivers\chromedriver\win32\96.0.4664.45\chromedriver.exe] found in cache
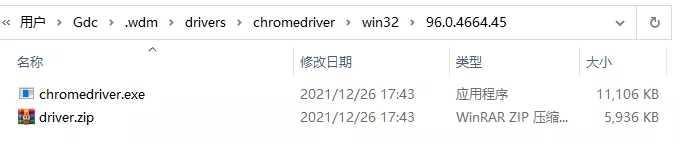
After completing the above preparations, we can begin to learn the formal content of this article~
1. Basic usage
In this section, we will start from the basic operations such as initializing browser objects, accessing pages, setting browser size, refreshing pages and moving forward and backward.
1.1. Initialize browser object
In the preparation part, we mentioned the need to add the browser channel to the environment variable or specify the absolute path. The former can be initialized directly, while the latter needs to be specified.
from selenium import webdriver # Initialize browser to chrome browser browser = webdriver.Chrome() # How to specify an absolute path path = r'C:\Users\Gdc\.wdm\drivers\chromedriver\win32\96.0.4664.45\chromedriver.exe' browser = webdriver.Chrome(path) # Close browser browser.close()
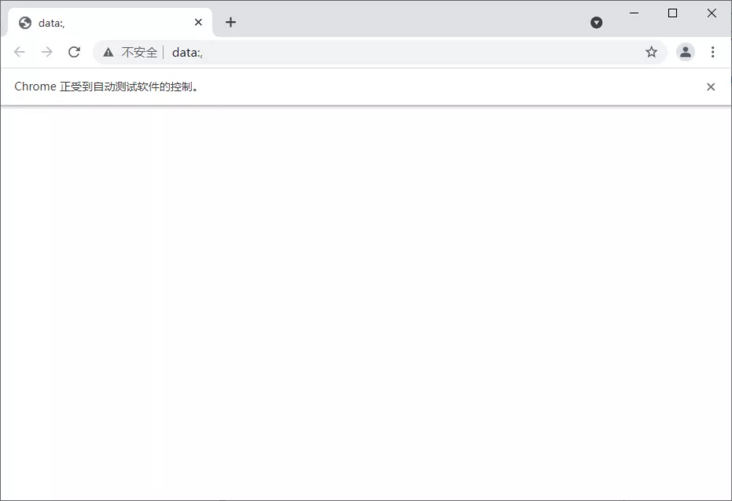
You can see that the above is a browser with interface. We can also initialize the browser to a browser without interface.
from selenium import webdriver
# Browser without interface
option = webdriver.ChromeOptions()
option.add_argument("headless")
browser = webdriver.Chrome(options=option)
# Visit Baidu Homepage
browser.get(r'https://www.baidu.com/')
# Screenshot Preview
browser.get_screenshot_as_file('screenshot.png')
# Close browser
browser.close()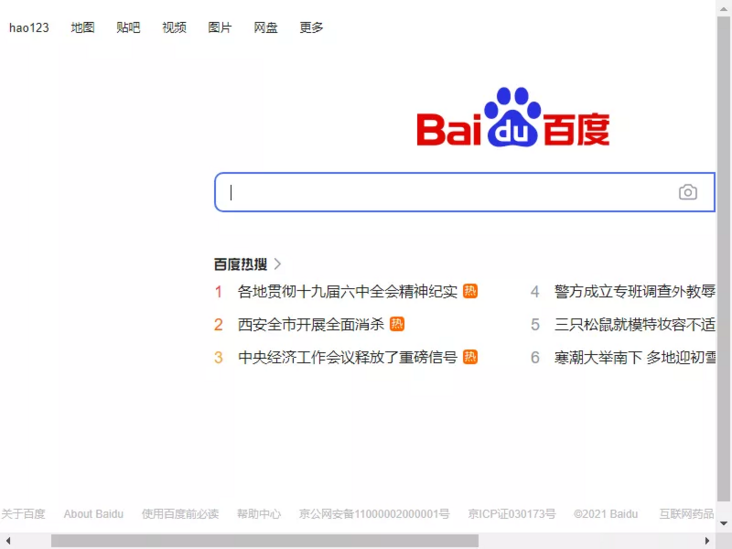
After the initialization of the browser object is completed and assigned to the browser object, we can call the browser to perform various methods to simulate the operation of the browser.
1.2. Access page
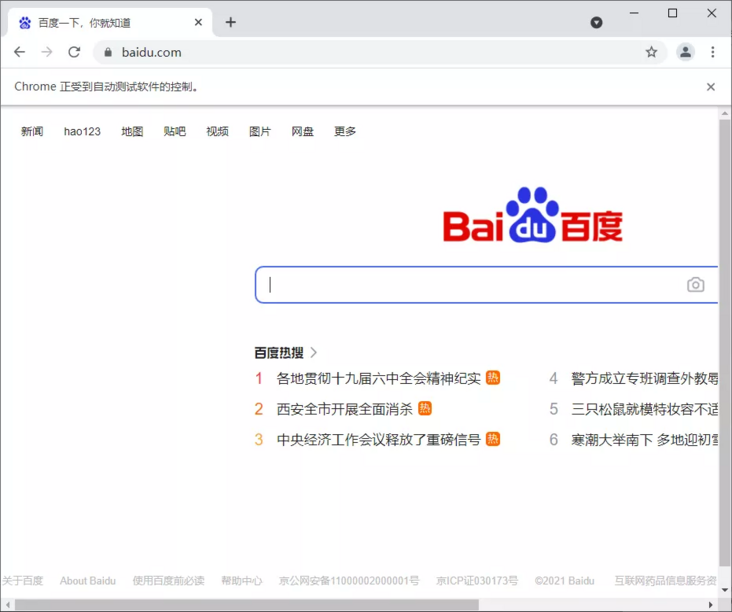
The get method is used for page access, and the incoming parameter is the URL address of the page to be accessed.
from selenium import webdriver # Initialize browser to chrome browser browser = webdriver.Chrome() # Visit Baidu Homepage browser.get(r'https://www.baidu.com/') # Close browser browser.close()
1.3. Set browser size
set_ window_ The size () method can be used to set the browser size (that is, the resolution), and maximize_window is to set the browser to full screen!
from selenium import webdriver import time browser = webdriver.Chrome() # Set browser size: full screen browser.maximize_window() browser.get(r'https://www.baidu.com') time.sleep(2) # Set resolution 500 * 500 browser.set_window_size(500,500) time.sleep(2) # Setting resolution 1000 * 800 browser.set_window_size(1000,800) time.sleep(2) # Close browser browser.close()
There are no screenshots here. Let's demonstrate the effect by ourselves~
1.4. Refresh page
Refreshing the page is a very common operation when we operate the browser. Here, the refresh() method can be used to refresh the browser page.
from selenium import webdriver
import time
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
# Set browser full screen
browser.maximize_window()
browser.get(r'https://www.baidu.com')
time.sleep(2)
try:
# Refresh page
browser.refresh()
print('Refresh page')
except Exception as e:
print('refresh failed')
# Close browser
browser.close()We also demonstrate the effect by ourselves. It is the same as the F5 shortcut key.
1.5. Forward and backward
Forward and backward are also very common operations when we use the browser. Here, the forward() method can be used to achieve forward and back() can be used to achieve backward.
from selenium import webdriver import time browser = webdriver.Chrome() # Set browser full screen browser.maximize_window() browser.get(r'https://www.baidu.com') time.sleep(2) # Open Taobao page browser.get(r'https://www.taobao.com') time.sleep(2) # Back to Baidu page browser.back() time.sleep(2) # Forward Taobao page browser.forward() time.sleep(2) # Close browser browser.close()
2. Get page basic properties
When we open a page with selenium, there are some basic attributes, such as web page title, web address, browser name, page source code and so on.
from selenium import webdriver browser = webdriver.Chrome() browser.get(r'https://www.baidu.com') # Page title print(browser.title) # Current web address print(browser.current_url) # Browser name print(browser.name) # Web source code print(browser.page_source)
The output is as follows:
Baidu once, you will know https://www.baidu.com/ chrome <html><head><script async="" src="https://passport.baidu.com/passApi/js/wrapper.js?cdnversion=1640515789507&_=1640515789298"></script><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html;charset=utf-8"><meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge,chrome=1"><meta content="always" name="referrer"><meta name="theme-color"..."
It should be noted that the page source code here can be parsed and extracted with tools such as regular expression, Bs4, xpath and pyquery.
3. Locate page elements
When we actually use the browser, very important operations include entering text, clicking OK and so on. Selenium provides a series of methods to facilitate the above operations. Let's demonstrate the eight common operation modes of locating page elements one by one!
We take the search box node on baidu home page as an example to search python
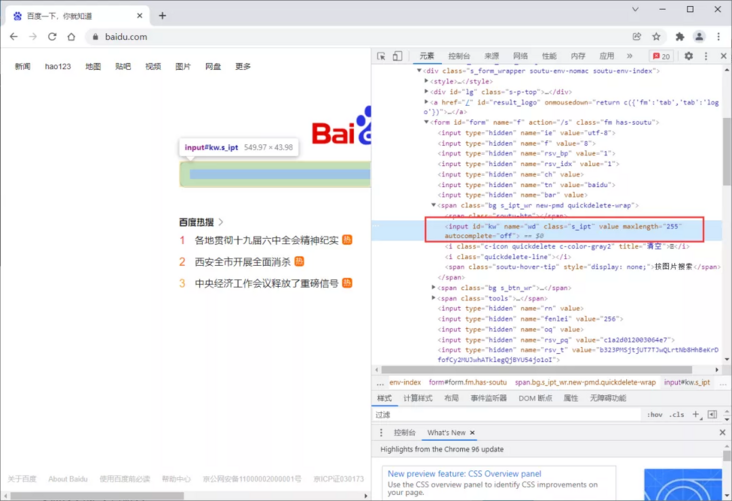
html structure of search box:
<input id="kw" name="wd" class="s_ipt" value="" maxlength="255" autocomplete="off">
3.1. id location
find_element_by_id() is obtained according to the id attribute, where the id attribute is kw
from selenium import webdriver
import time
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
browser.get(r'https://www.baidu.com')
time.sleep(2)
# Enter python in the search box
browser.find_element_by_id('kw').send_keys('python')
time.sleep(2)
# Close browser
browser.close()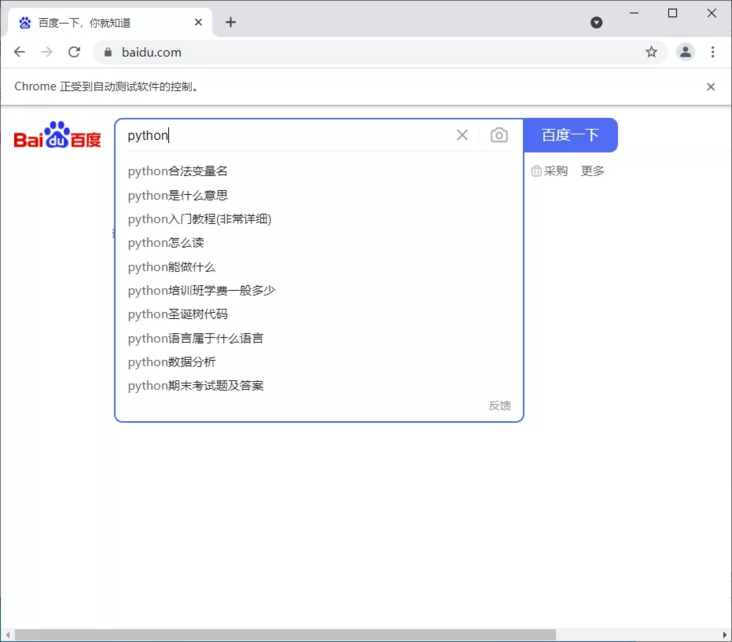
3.2. name positioning
find_element_by_name() is obtained according to the name attribute, where the name attribute is wd
from selenium import webdriver
import time
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
browser.get(r'https://www.baidu.com')
time.sleep(2)
# Enter python in the search box
browser.find_element_by_name('wd').send_keys('python')
time.sleep(2)
# Close browser
browser.close()3.3. class positioning
find_element_by_class_name() is obtained according to the class attribute, where the class attribute is s_ipt
from selenium import webdriver
import time
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
browser.get(r'https://www.baidu.com')
time.sleep(2)
# Enter python in the search box
browser.find_element_by_class_name('s_ipt').send_keys('python')
time.sleep(2)
# Close browser
browser.close()3.4. tag positioning
We know that HTML defines functions through tags, such as input, table and so on. Each element is actually a tag. A tag is often used to define a kind of function. When we look at the HTML code of Baidu home page, we can see that there are many similar tags, so it is difficult to distinguish different elements through tags.
find_element_by_tag_name()
from selenium import webdriver
import time
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
browser.get(r'https://www.baidu.com')
time.sleep(2)
# Enter python in the search box
browser.find_element_by_tag_name('input').send_keys('python')
time.sleep(2)
# Close browser
browser.close()Because there are multiple input s, the above code will report an error.
3.5. link location
As the name suggests, this method is used to locate text links, such as the classification module link at the top of Baidu home page.
find_element_by_link_text()
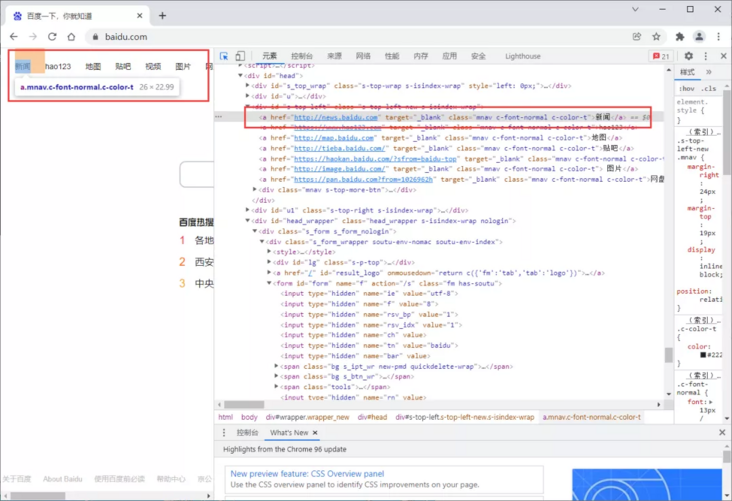
Take news as an example
from selenium import webdriver
import time
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
browser.get(r'https://www.baidu.com')
time.sleep(2)
# Click the news link
browser.find_element_by_link_text('Journalism').click()
time.sleep(2)
# Close all browser pages
browser.quit()3.6. partial positioning
Sometimes the text of a hyperlink is very long. If we input all of it, it will be troublesome and the code looks very ugly. At this time, we can intercept only part of the string and use this method to blur the matching.
find_element_by_partial_link_text()
from selenium import webdriver
import time
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
browser.get(r'https://www.baidu.com')
time.sleep(2)
# Click the news link
browser.find_element_by_partial_link_text('smell').click()
time.sleep(2)
# Close all browser pages
browser.quit()3.7. xpath positioning
The above described positioning methods are ideal and have a certain scope of use, that is, in the current page, each element has a unique attribute of id or name or class or hyperlink text, so we can locate them through this unique attribute value.
However, it is not so beautiful in actual work, so we can only locate it through xpath or css at this time.
find_element_by_xpath()
from selenium import webdriver
import time
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
browser.get(r'https://www.baidu.com')
time.sleep(2)
# Enter python in the search box
browser.find_element_by_xpath("//*[@id='kw']").send_keys('python')
time.sleep(2)
# Close browser
browser.close()3.8. css positioning
This method is simpler and faster than xpath.
find_element_by_css_selector()
from selenium import webdriver
import time
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
browser.get(r'https://www.baidu.com')
time.sleep(2)
# Enter python in the search box
browser.find_element_by_css_selector('#kw').send_keys('python')
time.sleep(2)
# Close browser
browser.close()# Import By class before use
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By# Import By class before use
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By3.9. find_ By positioning of element
In addition to the above eight positioning methods, Selenium also provides a general method, find_element(), this method has two parameters: location method and location value.
# Before using, import the by class from selenium webdriver. common. by import By
The above operations can be equivalent to the following:
browser.find_element(By.ID,'kw') browser.find_element(By.NAME,'wd') browser.find_element(By.CLASS_NAME,'s_ipt') browser.find_element(By.TAG_NAME,'input') browser.find_element(By.LINK_TEXT,'Journalism') browser.find_element(By.PARTIAL_LINK_TEXT,'smell') browser.find_element(By.XPATH,'//*[@id="kw"]') browser.find_element(By.CSS_SELECTOR,'#kw')
3.10. Multiple elements
If there is more than one target element in the web page, you need to use find_elements, the result will be in the form of a list. In short, the plural identifier s is added after element, and other operations are consistent.
4. Get page element attributes
Since we have many ways to locate the elements of the page, we can consider obtaining the attributes of the following elements, especially when using Selenium for web crawler.
4.1. get_attribute get attribute
Take the logo of Baidu home page as an example to obtain the relevant attributes of logo
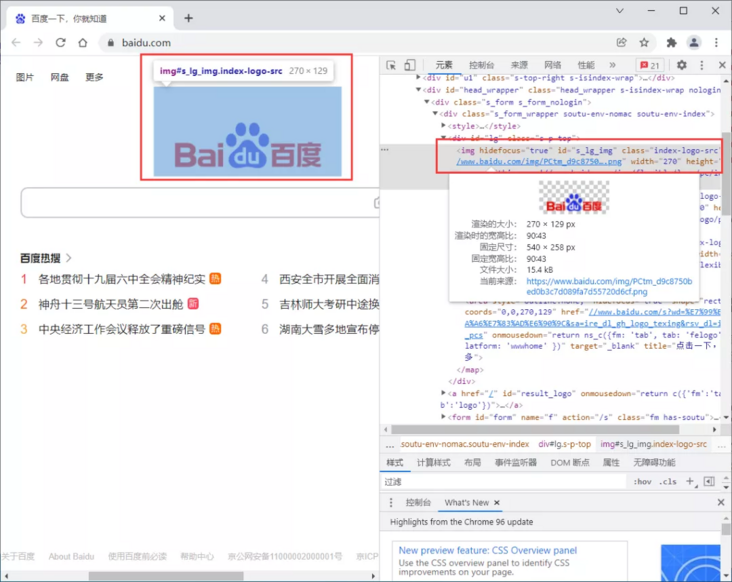
<img hidefocus="true" id="s_lg_img" class="index-logo-src" src="//www.baidu.com/img/PCtm_d9c8750bed0b3c7d089fa7d55720d6cf.png" width="270" height="129" onerror="this.src='//www.baidu.com/img/flexible/logo/pc/index.png';this.onerror=null;" usemap="#mp">
Get the picture address of the logo
from selenium import webdriver
import time
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
browser.get(r'https://www.baidu.com')
logo = browser.find_element_by_class_name('index-logo-src')
print(logo)
print(logo.get_attribute('src'))
# Close browser
browser.close()Output:
<selenium.webdriver.remote.webelement.WebElement (session="e95b18c43a330745af019e0041f0a8a4", element="7dad5fc0-610b-45b6-b543-9e725ee6cc5d")> https://www.baidu.com/img/PCtm_d9c8750bed0b3c7d089fa7d55720d6cf.png
4.2. Get text
Take the hot list as an example to get the hot list text and links
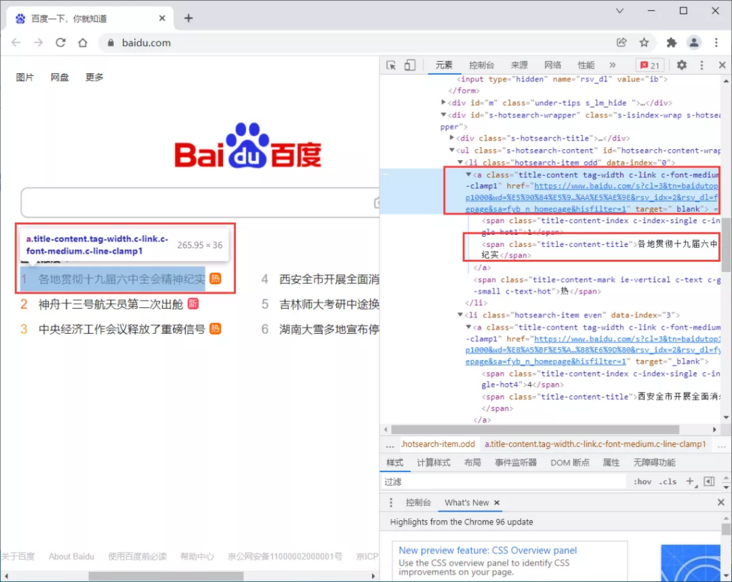
<a class="title-content tag-width c-link c-font-medium c-line-clamp1" href="https://www.baidu. com/s? cl=3& tn=baidutop10& fr=top1000& wd=%E5%90%84%E5%9C%B0%E8%B4%AF%E5%BD%BB%E5%8D%81%E4%B9%9D%E5%B1%8A%E5%85%AD%E4%B8%AD%E5%85%A8%E4%BC%9A%E7%B2%BE%E7%A5%9E%E7%BA%AA%E5%AE%9E& rsv_ idx=2& rsv_ dl=fyb_ n_ homepage& sa=fyb_ n_ homepage& hisfilter=1" target="_ Blank "> span class =" title content index c-index-single c-index-single-hot1 "> 1 < / span > < span class =" title content title "> documentary on the implementation of the spirit of the Sixth Plenary Session of the 19th CPC Central Committee < / span ></a>
Get the text of the hot list. Use the text attribute and call it directly
from selenium import webdriver
import time
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
browser.get(r'https://www.baidu.com')
logo = browser.find_element_by_css_selector('#hotsearch-content-wrapper > li:nth-child(1) > a')
print(logo.text)
print(logo.get_attribute('href'))
# Close browser
browser.close()Output:
1 Documentary on the implementation of the spirit of the Sixth Plenary Session of the 19th CPC Central Committee https://www.baidu.com/s?cl=3&tn=baidutop10&fr=top1000&wd=%E5%90%84%E5%9C%B0%E8%B4%AF%E5%BD%BB%E5%8D%81%E4%B9%9D%E5%B1%8A%E5%85%AD%E4%B8%AD%E5%85%A8%E4%BC%9A%E7%B2%BE%E7%A5%9E%E7%BA%AA%E5%AE%9E&rsv_idx=2&rsv_dl=fyb_n_homepage&sa=fyb_n_homepage&hisfilter=1
4.3. Get other properties
In addition to attributes and text values, there are attributes such as id, location, tag name, and size.
from selenium import webdriver
import time
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
browser.get(r'https://www.baidu.com')
logo = browser.find_element_by_class_name('index-logo-src')
print(logo.id)
print(logo.location)
print(logo.tag_name)
print(logo.size)
# Close browser
browser.close()Output:
6af39c9b-70e8-4033-8a74-7201ae09d540
{'x': 490, 'y': 46}
img
{'height': 129, 'width': 270}5. Page interaction
Page interaction refers to various operations in the browser, such as entering text, clicking links, etc. as demonstrated above, as well as clearing text, entering confirmation, radio box and multi box selection, etc.
5.1. Enter text
In fact, we used this operation in the previous section.
send_keys()
from selenium import webdriver
import time
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
browser.get(r'https://www.baidu.com')
time.sleep(2)
# Locate search box
input = browser.find_element_by_class_name('s_ipt')
# Enter python
input.send_keys('python')
time.sleep(2)
# Close browser
browser.close()5.2. click
Similarly, we have used this click operation.
click()
from selenium import webdriver
import time
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
browser.get(r'https://www.baidu.com')
time.sleep(2)
# Select the news button
click = browser.find_element_by_link_text('Journalism')
# Click it
click.click()
time.sleep(2)
# Close all browser pages
browser.quit()5.3. Clear text
Since there is input, there is clear text here.
clear()
from selenium import webdriver
import time
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
browser.get(r'https://www.baidu.com')
time.sleep(2)
# Locate search box
input = browser.find_element_by_class_name('s_ipt')
# Enter python
input.send_keys('python')
time.sleep(2)
# Clear python
input.clear()
time.sleep(2)
# Close browser
browser.close()5.4. Enter to confirm
For example, enter the text python in the search box, and then press enter to display the query results.
submit()
from selenium import webdriver
import time
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
browser.get(r'https://www.baidu.com')
time.sleep(2)
# Locate search box
input = browser.find_element_by_class_name('s_ipt')
# Enter python
input.send_keys('python')
time.sleep(2)
# Enter query
input.submit()
time.sleep(5)
# Close browser
browser.close()5.5. Single choice
Radio selection is easy to operate. First locate an element that needs radio selection, and then click it.
5.6. Multiple choice
Multi selection seems to be easier. Locate the elements to be selected in turn and click.
5.7. Drop down box
The operation of the drop-down box is relatively complex and requires the Select module.
Import this class first
from selenium.webdriver.support.select import Select
In the select module, there are the following positioning methods
'''1,Three ways to select an option''' select_by_index() # Locate by index; Note: > index starts with "0". select_by_value() # Locate the value through the value, VA > Lue tag attribute value. select_by_visible_text() # Locate through the text value, that is, display the value displayed in the drop-down box. '''2,Three kinds of return options Information method''' voptions # Returns the options of all > of the select element all_selected_options # Returns the selected option in the select element first_selected_options # Returns the first option in the Select > in the select element '''3,Four ways to uncheck items''' deselect_all # Cancel all selected items deselect_by_index # Cancels the selected index entry deselect_by_value # Uncheck the selected value deselect_by_visible_text # Cancels the selected text value
Let's demonstrate a wave. Because I haven't found a suitable web page for the time being, I wrote a simple web page local test here (the file is saved as handsome. html)
<html> <body> <form> <select name="handsome guy"> <option value="Brother CAI">Brother CAI</option> <option value="Xiao Ming" selected="">Xiao Ming</option> <option value="Xiaohua">Xiaohua</option> <option value="Grass ">Grass</option> </select> </form> </body> </html>
Then, demonstrate the different selection methods of the drop-down box
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.support.select import Select
import time
url = 'file:///C:/Users/Gdc/Desktop / handsome guy html'
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
browser.get(url)
time.sleep(2)
# Select by index
Select(browser.find_element_by_name("handsome guy")).select_by_index("2")
time.sleep(2)
# Select according to value
Select(browser.find_element_by_name("handsome guy")).select_by_value("Grass ")
time.sleep(2)
# Select according to text value
Select(browser.find_element_by_name("handsome guy")).select_by_visible_text("Brother CAI")
time.sleep(2)
# Close browser
browser.close()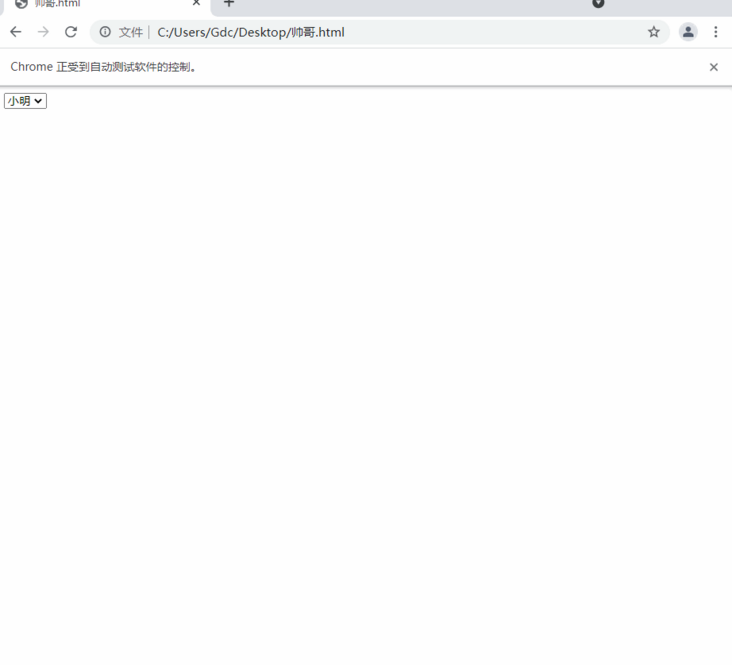
6. Multi window switching
For example, the node element acquisition operation of different sub pages of the same page, the switching operation between different tabs and between different browser windows, and so on.
6.1. Frame switching
After Selenium opens a page, it operates on the parent page by default. At this time, if the page has sub pages, you need to switch to the sub page to erase the node element information of the sub page. At this time, switch_to.frame() is coming. If you want to go back to the parent page, use switch_to.parent_frame().
6.2. Tab switching
When we visit the web page, we will open many pages. Selenium provides some methods to facilitate us to operate these pages.
current_window_handle: get the handle of the current window.
window_handles: returns the handles of all windows in the current browser.
switch_to_window(): used to switch to the corresponding window.
from selenium import webdriver
import time
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
# Open Baidu
browser.get('http://www.baidu.com')
# Create a new tab
browser.execute_script('window.open()')
print(browser.window_handles)
# Jump to the second tab and open Zhihu
browser.switch_to.window(browser.window_handles[1])
browser.get('http://www.zhihu.com')
# Go back to the first tab and open Taobao (the original Baidu page is changed to Taobao)
time.sleep(2)
browser.switch_to.window(browser.window_handles[0])
browser.get('http://www.taobao.com')7. Simulate mouse operation
Since it is to simulate browser operations, it is natural to simulate some mouse operations. Here, you need to import ActionChains class.
from selenium.webdriver.common.action_chains import ActionChains
7.1. Left key
This is actually the click() operation in page interaction.
7.2. Right click
context_click()
from selenium.webdriver.common.action_chains import ActionChains
from selenium import webdriver
import time
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
browser.get(r'https://www.baidu.com')
time.sleep(2)
# Navigate to the element you want to right-click and select the news link here
right_click = browser.find_element_by_link_text('Journalism')
# Right click operation
ActionChains(browser).context_click(right_click).perform()
time.sleep(2)
# Close browser
browser.close()In the above operation
ActionChains(browser): call ActionChains() class and pass browser driven browser as parameter
context_click(right_click): simulate double clicking with the mouse, and you need to pass in the specified element positioning as a parameter
perform(): execute all the operations stored in ActionChains(), which can be regarded as executing the previous series of operations
7.3. double-click
double_click()
from selenium.webdriver.common.action_chains import ActionChains
from selenium import webdriver
import time
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
browser.get(r'https://www.baidu.com')
time.sleep(2)
# Navigate to the element you want to double-click
double_click = browser.find_element_by_css_selector('#bottom_layer > div > p:nth-child(8) > span')
# double-click
ActionChains(browser).double_click(double_click).perform()
time.sleep(15)
# Close browser
browser.close()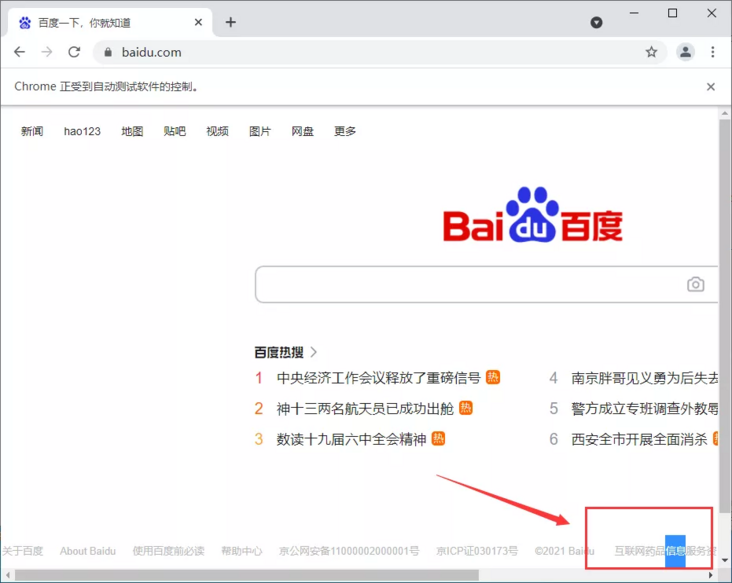
7.4. Drag
drag_ and_ For the drop (source, target) drag operation, the start position and end position need to be specified. This is often used for the operation of slider verification code.
We use a case of rookie tutorial to demonstrate
https://www.runoob.com/try/tr...
from selenium.webdriver.common.action_chains import ActionChains
from selenium import webdriver
import time
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
url = 'https://www.runoob.com/try/try.php?filename=jqueryui-api-droppable'
browser.get(url)
time.sleep(2)
browser.switch_to.frame('iframeResult')
# Start position
source = browser.find_element_by_css_selector("#draggable")
# End position
target = browser.find_element_by_css_selector("#droppable")
# Drag and drop elements
actions = ActionChains(browser)
actions.drag_and_drop(source, target)
actions.perform()
# Drag
time.sleep(15)
# Close browser
browser.close()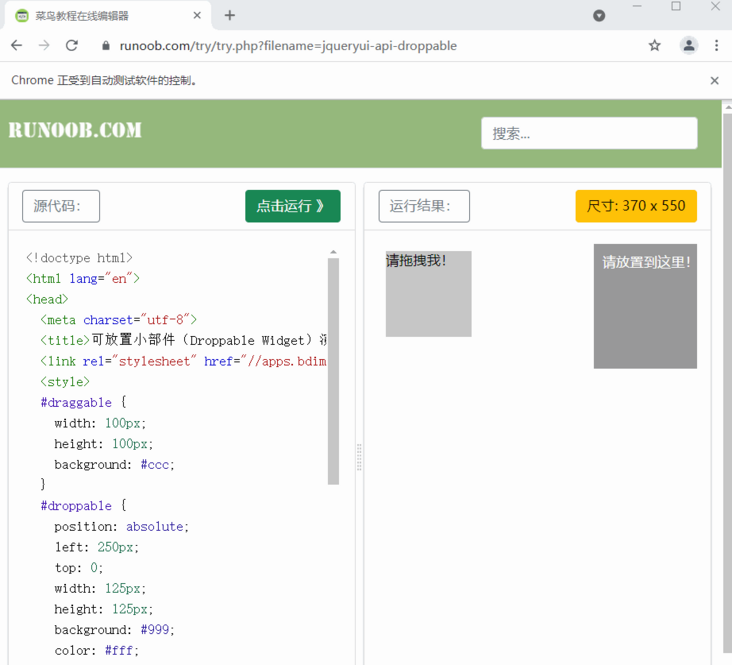
7.5. hover
move_to_element()
from selenium.webdriver.common.action_chains import ActionChains
from selenium import webdriver
import time
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
url = 'https://www.baidu.com'
browser.get(url)
time.sleep(2)
# Position hover
move = browser.find_element_by_css_selector("#form > span.bg.s_ipt_wr.new-pmd.quickdelete-wrap > span.soutu-btn")
# Hover operation
ActionChains(browser).move_to_element(move).perform()
time.sleep(5)
# Close browser
browser.close()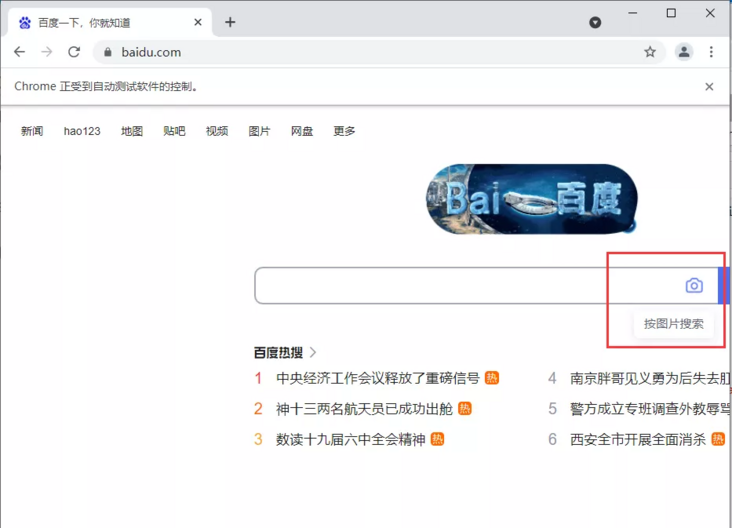
8. Simulate keyboard operation
The Keys() class in selenium provides most of the keyboard operation methods through send_keys() method to simulate the keys on the keyboard.
Introduce the Keys class
from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys
Common keyboard operations
send_keys(Keys.BACK_SPACE): delete keys (BackSpace)
send_keys(Keys.SPACE): Space
send_keys(Keys.TAB): tab
send_keys(Keys.ESCAPE): Escape
send_keys(Keys.ENTER): Enter
send_keys(Keys.CONTRL,'a'): select all (Ctrl+A)
send_keys(Keys.CONTRL,'c'): copy (Ctrl+C)
send_keys(Keys.CONTRL,'x'): cut (Ctrl+X)
send_keys(Keys.CONTRL,'v'): paste (Ctrl+V)
send_keys(Keys.F1): keyboard F1
.....
send_keys(Keys.F12): keyboard F12
Example operation demonstration:
Locate the element to be operated, and then operate it!
from selenium.webdriver.common.keys import Keys
from selenium import webdriver
import time
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
url = 'https://www.baidu.com'
browser.get(url)
time.sleep(2)
# Locate search box
input = browser.find_element_by_class_name('s_ipt')
# Enter python
input.send_keys('python')
time.sleep(2)
# enter
input.send_keys(Keys.ENTER)
time.sleep(5)
# Close browser
browser.close()9. Delay waiting
If you encounter a web page loaded with ajax, the page elements may not be loaded at the same time. At this time, try to obtain the web page source code when the get method is completed, which may not be the page completely loaded by the browser. Therefore, in this case, it is necessary to set a delay for a certain time to ensure that all nodes are loaded.
There are three ways to play: forced waiting, implicit waiting and explicit waiting
9.1. Forced waiting
It's very simple, direct time Sleep (n) forces a wait of N seconds, which is executed after the get method is executed.
9.2. Implicit waiting
implicitly_wait() sets the waiting time. If an element node is not loaded at the time, an exception will be thrown.
from selenium import webdriver
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
# Implicit wait, wait time 10 seconds
browser.implicitly_wait(10)
browser.get('https://www.baidu.com')
print(browser.current_url)
print(browser.title)
# Close browser
browser.close()9.3. Explicit wait
Set a waiting time and a condition. Within the specified time, check whether the condition is true every other period of time. If it is true, the program will continue to execute, otherwise a timeout exception will be thrown.
from selenium import webdriver
from selenium.webdriver.support.wait import WebDriverWait
from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as EC
from selenium.webdriver.common.by import By
import time
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
browser.get('https://www.baidu.com')
# Set the waiting time 10s
wait = WebDriverWait(browser, 10)
# Set judgment condition: wait for the element with id='kw 'to load
input = wait.until(EC.presence_of_element_located((By.ID, 'kw')))
# Enter in keyword: Keyword
input.send_keys('Python')
# Close browser
time.sleep(2)
browser.close()Parameter description of WebDriverWait:
WebDriverWait(driver,timeout,poll_frequency=0.5,ignored_exceptions=None)
Driver: Browser driver
Timeout: timeout, the longest waiting time (taking into account the hidden waiting time)
poll_frequency: the interval between each detection. The default is 0.5 seconds
ignored_exceptions: exception information after timeout. NoSuchElementException is thrown by default
until(method,message='')
Method: during the waiting period, call the incoming method at regular intervals until the return value is not False
Message: if timeout occurs, TimeoutException will be thrown and message will be passed in as an exception
until_not(method,message='')
until_not is the opposite of until. Until is to continue to execute when an element appears or any condition is true. until_not means to continue execution when an element disappears or any condition is not true, and the parameters are the same.
Other waiting conditions
from selenium.webdriver.support import expected_conditions as EC # Judge whether the title is consistent with the expectation title_is # Determine whether the title contains the expected string title_contains # Determine whether the specified element is loaded presence_of_element_located # Judge whether all elements are loaded presence_of_all_elements_located # Determines whether an element is visible Visible means that the element is not hidden, and the width and height of the element are not equal to 0. The incoming parameter is a locator of tuple type visibility_of_element_located # Judge whether the element is visible. The passed in parameter is the positioned element WebElement visibility_of # Determine whether an element is invisible or does not exist in the DOM tree invisibility_of_element_located # Determines whether the text of the element contains the expected string text_to_be_present_in_element # Determine whether the value of the element contains the expected string text_to_be_present_in_element_value #Judge whether the frame can be cut in. You can pass in the locator tuple or directly pass in the location method: id, name, index or WebElement frame_to_be_available_and_switch_to_it #Judge whether alert appears alert_is_present #Determine whether the element can be clicked element_to_be_clickable # To judge whether an element is selected, it is generally used in the drop-down list to pass in the WebElement object element_to_be_selected # Judge whether the element is selected element_located_to_be_selected # Judge whether the selected state of the element is consistent with the expectation. Pass in the parameter: for the elements after positioning, return True if they are equal, otherwise return False element_selection_state_to_be # Judge whether the selected state of the element is consistent with the expectation. Pass in the parameter: the positioning of the element. If it is equal, return True; otherwise, return False element_located_selection_state_to_be #Judge whether an element is still in the DOM. Pass in the WebElement object to judge whether the page has been refreshed staleness_of
10. Others
Add some
10.1. Run JavaScript
There are also some operations, such as pulling down the progress bar, simulating javaScript and using execute_script method.
from selenium import webdriver
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
# Zhihu discovery page
browser.get('https://www.zhihu.com/explore')
browser.execute_script('window.scrollTo(0, document.body.scrollHeight)')
browser.execute_script('alert("To Bottom")')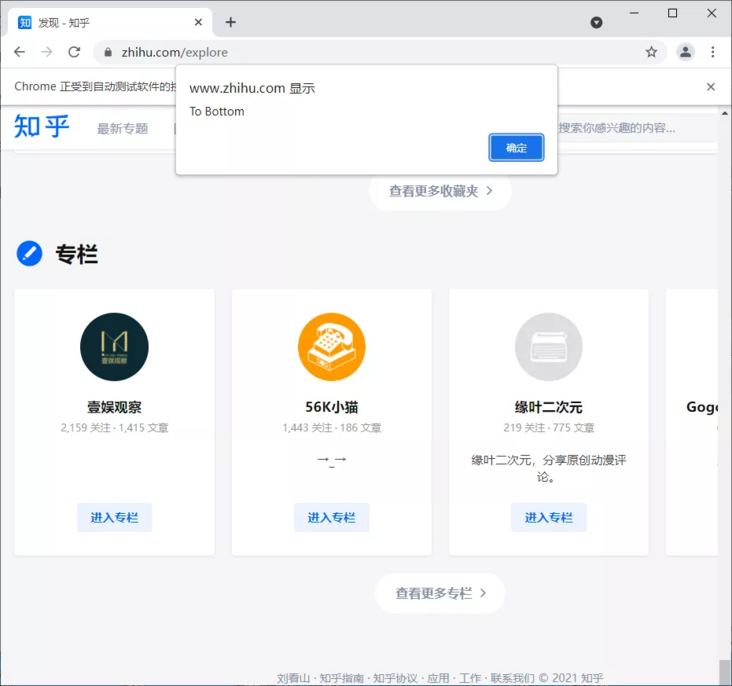
10.2. Cookie
During the use of selenium, it is also convenient to obtain, add and delete cookies.
from selenium import webdriver
browser = webdriver.Chrome()
# Zhihu discovery page
browser.get('https://www.zhihu.com/explore')
# Get cookie
print(f'Cookies Value of:{browser.get_cookies()}')
# Add cookie
browser.add_cookie({'name':'Brother CAI', 'value':'handsome guy'})
print(f'After adding Cookies Value of:{browser.get_cookies()}')
# delete cookie
browser.delete_all_cookies()
print(f'After deletion Cookies Value of:{browser.get_cookies()}')Output:
Cookies Value of:[{'domain': '.zhihu.com', 'httpOnly': False, 'name': 'Hm_lpvt_98beee57fd2ef70ccdd5ca52b9740c49', 'path': '/', 'secure': False, 'value': '1640537860'}, {'domain': '.zhihu.com', ...]
After adding Cookies Value of:[{'domain': 'www.zhihu.com', 'httpOnly': False, 'name': 'Brother CAI', 'path': '/', 'secure': True, 'value': 'handsome guy'}, {'domain': '.zhihu.com', 'httpOnly': False, 'name': 'Hm_lpvt_98beee57fd2ef70ccdd5ca52b9740c49', 'path': '/', 'secure': False, 'value': '1640537860'}, {'domain': '.zhihu.com',...]
After deletion Cookies Value of:[]10.3. Anti shielding
I found that meituan was directly blocked by Selenium. I don't know what to do!!
The above is all the content of this time. If you think it is helpful, please like it and watch it!
GitHub home page link:
https://github.com/SeleniumHQ...
Open source outposts share popular, interesting and practical open source projects on a daily basis. Participate in maintaining the open source technology resource library of 100000 + Star, including Python, Java, C/C + +, Go, JS, CSS and node js,PHP,. NET, etc.