I
1. Give the source code and screenshot of task1.asm
assume cs:code, ds:data data segment x db 1,9,3 len1 equ $ - x ; symbolic constants , $Refers to the offset address of the next data item. In this example, it is 3 y dw 1, 9, 3 len2 equ $ - y ; symbolic constants , $Refers to the offset address of the next data item. In this example, it is 9 data ends code segment start: mov ax, data mov ds, ax mov si, offset x ; Take symbol x Corresponding offset address 0 -> si mov cx, len1 ; From symbol x Number of consecutive byte data items at the beginning -> cx mov ah, 2 s1: mov dl, [si] or dl, 30h int 21h mov dl, ' ' int 21h ; Output space inc si loop s1 mov ah, 2 mov dl, 0ah int 21h ; Line feed mov si, offset y ; Take symbol y Corresponding offset address 3 -> si mov cx, len2/2 ; From symbol y Number of consecutive word data items started -> cx mov ah, 2 s2: mov dx, [si] or dl, 30h int 21h mov dl, ' ' int 21h ; Output space add si, 2 loop s2 mov ah, 4ch int 21h code ends end start

2. Answer question ①
line27, when the assembly instruction loop s1 jumps, it jumps according to the displacement. Check the machine through debug disassembly
What is the jump displacement of the code? (the displacement value is answered in decimal) from the perspective of CPU, it is explained
How to calculate the offset address of the instruction after the jump label s1.
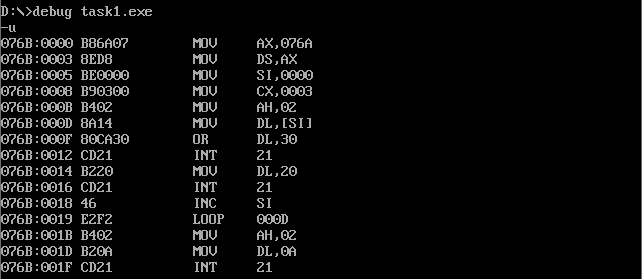
The behavior of loop s1 is 076B:0019, the machine code is E2F2, E2 is loop, F2 is the displacement complement 11110010, which is converted to decimal system as - 14.
According to the loop instruction, the jump address = current ip + offset
Current ip=001b, decimal is 27, 27-14 = 13, so jump to 000d.
3. Answer questions ②
line44. When the assembly instruction loop s2 jumps, it jumps according to the displacement. Check the machine through debug disassembly
What is the jump displacement of the code? (the displacement value is answered in decimal) from the perspective of CPU, it is explained
How to calculate the offset address of the instruction after the jump label s2.
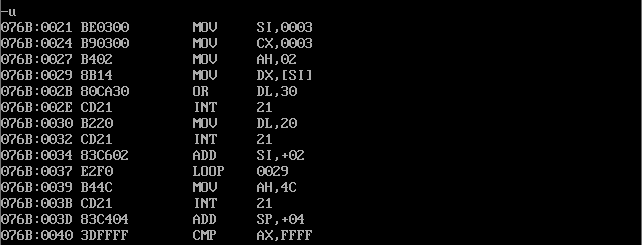
The behavior of loop s2 is 076B:0037. The machine code is E2F0, E2 is loop, and F0 is the displacement complement 11110000, which is converted to decimal - 16.
Current ip=0039, decimal 57, 57-16 = 41, so jump to 0029.
4. Question ③
Attach the disassembly screenshot of debugging observation in debug during the above analysis
II
1. Give the program task2.asm source code.
assume cs:code, ds:data data segment dw 200h, 0h, 230h, 0h data ends stack segment db 16 dup(0) stack ends code segment start: mov ax, data mov ds, ax mov word ptr ds:[0], offset s1 mov word ptr ds:[2], offset s2 mov ds:[4], cs mov ax, stack mov ss, ax mov sp, 16 call word ptr ds:[0] s1: pop ax call dword ptr ds:[2] s2: pop bx pop cx mov ah, 4ch int 21h code ends end start
2. After analysis, debugging and verification, register (ax) =? (bx) = (cx) =? Attach the screenshot of the debugging result interface
① According to the jump principle of call instruction, it is analyzed theoretically that the register (ax) before the program execution to exit (line31)=
? register (bx) =? Register (cx) =?
ax=0021h,bx=0026h,cx=076c
② Assemble and link the source program to get the executable program task2.exe. Use debug to debug, observe and verify debugging
Whether the results are consistent with the theoretical analysis results.
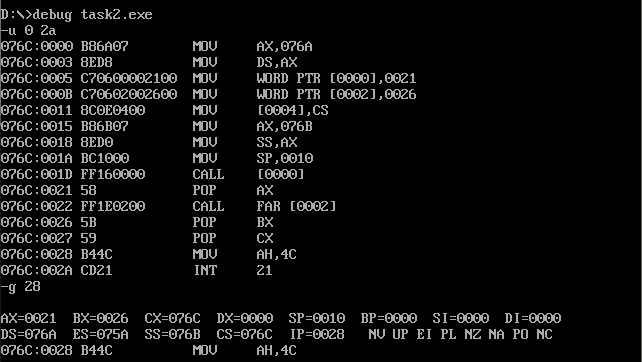
Consistent with conjecture.
III
1. Give the program source code task3.asm
assume ds:data, cs:code, ss:stack
data segment
x db 99, 72, 85, 63, 89, 97, 55
len equ $ - x
data ends
stack segment
dw 16 dup(?)
stack ends
code segment
start:
mov ax, data
mov ds, ax
mov ax, stack
mov ss, ax
mov sp, 32
mov cx, len ;Because the data are byte type,therefore len Is the number of data
print: ;print loop: Print all numbers in sequence
mov ah, 0 ;The data has only one byte,First ah Set 0,The division in a subfunction is ax As divisor
mov al, byte ptr ds:[di] ;Put data into al
inc di ;di Pointer backward
push cx ;hold cx Save it, It will be modified in the subroutine cx value
call printNumber ;Print numbers
call printSpace ;Print spaces
pop cx ;recovery cx
loop print
mov ah, 4ch
int 21h
printNumber:
mov bx, 0 ;The number of digits before getting is 0
;Get numbers bit by bit
getEach: ;getEach loop: Get every bit,Then push it into the stack
mov dl, 10
div dl ;Divide data by 10
push ax ;Push numbers onto the stack(ah Remainder in ax Inside)
inc bx ;digit+1
mov ah, 0 ;ah Is the remainder,After setting 0 ax Represents the result of division
mov cx, ax ;Division result assigned to cx, If the result is 0, all digits are obtained
inc cx ;because loop Time meeting-1,Here first+1,Prevent negative numbers
loop getEach
mov cx, bx ;First bx The number of digits stored is assigned to cx
printEach: ;printEach loop: Take the numbers from the stack in turn,Print bit by bit
pop ax ;Take out one digit
add ah, 30h ;ah Is the remainder of the division just now,That is, the number of digits to be obtained,+30h Is converted to the corresponding character
mov dl, ah ;put to dl, For printing
mov ah, 2 ;call int 21h Subroutine 2 printing
int 21h
loop printEach
ret
printSpace:
mov ah, 2
mov dl, 20h
int 21h
ret
code ends
end start
2. Screenshot of running test

IV
1. Give the program source code task4.asm
assume cs:code, ds:data, ss:stack
data segment
str db 'try'
len = $ - str
data ends
stack segment
dw 2 dup(?)
stack ends
code segment
start:
mov ax, data
mov ds, ax
mov ax, stack
mov ss, ax
mov sp, 2
mov cx, len ;cs: String length
mov ax, 0
mov si, ax ;si: 0
;Print green characters at the top
mov bl, 0Ah ;bl: colour(Background black+Highlight +green:0 000 1 010)
mov bh, 0 ;bh: Line number(Line 1)
call printStr
;Print red characters at the bottom
mov bl, 0Ch ;bl: colour(Background black+Highlight +green:0 000 1 100)
mov bh, 24 ;bh: Line number(Line 25)
call printStr
mov ah, 4ch
int 21h
printStr:
mov al, bh ;Put the line number in al
mov dl, 0A0h ;160 bytes per line,Put on dl in
mul dl ;Multiply by the line number to get the starting address of the line, al The row start address is stored in the
mov di, ax ;di Starting address of deposit line
mov ax, 0b800h
mov es, ax ;Video memory segment address
push si ;Save first si, So we can use it next time
push cx ;preservation cx, For next use
s0:
mov al, ds:[si]
mov es:[di], al ;hold ds:[si]Put new characters in es:[di]
mov es:[di+1], bl ;Add color
inc si
add di, 2
loop s0
pop cx ;recovery cx
pop si ;recovery si
ret
code ends
end start
2. Screenshot of running test
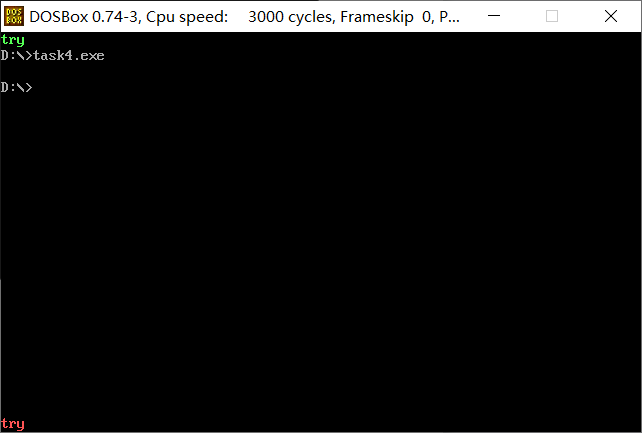
V
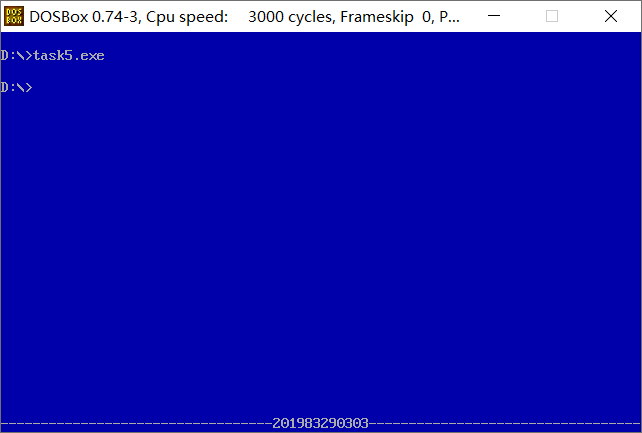
1. Give the program source code task5.asm
assume cs:code, ds:data
data segment
stu_no db '201983290303'
len = $ - stu_no
data ends
code segment
start:
mov ax, data
mov ds, ax
mov di, 0
call printStuNum ; Call print subroutine
mov ah, 4ch
int 21h
printStuNum:
mov ax, 0b800h
mov es, ax ; Control video memory area segment pointer
mov si, 1 ; Display area column pointer
; First print the background of the first 24 lines of the screen in blue
mov al, 24 ; First 24 lines
mov dl, 80 ; Each line of 80 characters needs to change the color
mul dl ; 24*80, Gets the number of characters that need to be filled in blue
mov cx, ax
printBlue:
mov al, 17h ; Blue background+White words:0 001 0 111 -> 17h
mov es:[si], al ; Fill the color in place
add si, 2 ; Move back 2
loop printBlue
sub si, 1 ; Pointer fallback one, Start at the beginning of the last line
; Print last line
mov ax, 80
sub ax, len ; 80 column - Student number length
mov dl, 2
div dl ; (80 - len)/2, That is, the left and right sides of the student number need to be filled'-'Length of
mov dx, ax ; use dx preservation'-'Length of
; Call print'-'Subroutine, Print the to the left of the student number'-'
mov cx, dx
call printSeparator
; Print student number string
mov cx, len
printNumber:
mov al, ds:[di] ; The lower order is a character
mov ah, 17h ; High is color
mov word ptr es:[si], ax ; Put by word
inc di
add si, 2
loop printNumber
; Call print again'-'Subroutine, Print the to the right of the student number'-'
mov cx, dx
call printSeparator
ret
printSeparator:
mov al, '-'
mov ah, 17h
mov word ptr es:[si], ax
add si, 2
loop printSeparator
ret
code ends
end start
2. Screenshot of running test