1. Review of Knowledge Points
1. Comparison of Arrays and Objects
Arrays store the same type of data
Objects store different types of data, out of order, descriptions of one type of thing
2. Object is of reference data type
3. Deep and Shallow Copies of Objects
4. Traversal of object for(var key in obj) where key is a string
var cat = new Object() ;
cat.name = 'cat';
cat.age = 2 ;
cat.say = function(){
console.log('Miao');
}
var cat = {
// Key name: key value
name : 'cat',
age : 2 ,
say :function(){
console.log('Miao');
}
}
var obj = {
0 : 1 ,
1 : 2 ,
2 : 3 ,
Name : 'array',
}
console.log(obj['Name']);
2. Deep copy of multidimensional arrays
The idea is to iterate through a multidimensional array until each data is not an array, then place it in a new empty array.
var arr = [1,2,3,4,[5,6,[7,8]]];
var arr2 = arr.slice();
function deepArr(arr){
var newArr = [];
for(var i = 0 ; i < arr.length ; i++){
// newArr.push(arr[i])//this arr[i] may or may not be an array
if(Array.isArray(arr[i])){
// Continue traversing the array or get an array
var list = deepArr(arr[i]);
// Place the resulting array in newArr
newArr.push(list)
}
else{
newArr.push(arr[i])
}
}
return newArr
}
// console.log(deepArr([1,2,3,4,[5,6]]));
var res = deepArr(arr);
res[4].push('a');
console.log(res);
console.log(arr);3. Strings
1. There are 2 ways to create strings
var str = 'hello'; // string
var str2 = new String('hello');
console.log(typeof str2); // object2. Angle scale and length
var str = 'hello'; // string
console.log(str.length); // 5
console.log(str[0]); // h3. String length and labels can only be read, not overridden
// Str[5] ='w'; // invalid
var str = 'hello'; // string
str += 'w';
console.log(str); // hellow
4. Method of string
includes determines whether a value exists in a character
indexOf determines whether a value exists in a string, returns a corner if it exists, and returns -1 if it does not exist
lastIndexOf determines if a value exists in the array and returns the last subscript
concat string stitching
slice intercepts some of the values in the array and returns a new array package before and after
charAt() accesses the value corresponding to the corner label
charCodeAt() accesses the ASCII value of the value corresponding to the corner label
String.fromCharCode() converts an ASCII value to a corresponding character
substring(i,i) intercept (1,2) corners Second to Third
substr(i, quantity) (2, 2) The second start truncates 2
trim() removes the first and last characters
split() cuts a string into an array
replace(old,new) Replace (only the first will be replaced by default)
toUpperCase() uppercase
ToLowerCase
var str = 'hello';
console.log(str.includes('o')); // true
console.log(str.indexOf('lo')); // 3
var str2 = 'world';
console.log(str.concat(str2)); // helloworld
console.log(str[0]); // h
console.log(str.charAt(0)); // h Access Corner Corresponding Value
console.log(str.charCodeAt(0)); //The ASCII value of the value corresponding to the 104 access angle label
console.log(String.fromCharCode(97)); // a Converts the ASCII value to the corresponding character
console.log(str.slice(0,2)); // he intercepts packages before and after
console.log(str.substring(1,2)); // e After intercepting packages 2 to 3
console.log(str.substr(1,2)); // el intercept starts at 2 and truncates 2
var str = ' fvg 3ff l ';
console.log(str.trim()); // Fvg 3ff l removes first and last spaces
var str = 'day day up' ;
var arr = str.split('');
console.log(arr); // ['d','a','y', '','d','a','y','', '','u','p'] Cut the string into an array
var str = 'What the fuck,String This Simple,What the fuck';
var res = str.replace('What the fuck','**')
document.write(res) //Replace bug s can only be replaced once
// **, string is simple, bedroom
var str = 'hello' ;
var str2 = 'HELLO';
// Change case to uppercase or lowercase before comparing
if(str.toLowerCase() === str2.toLowerCase()){
alert(666)
}
5. Random Authentication Code
Ideas: 1. Write four array numbers first, lowercase, uppercase, all;
2. Encapsulate random numbers Encapsulate get method
3. Encapsulate Random Authentication Code function randCode(){}
3.1. Get the first, second, third, and remaining digits (default minimum 4 digits n= n || 4)
3.2 Unordering strings - > Turn strings into arrays var res = res.split(');
3.3 Exchange Order - > Traverse Array Traverse in
3.4 Turn the array back to the string res = arr.join(');
4. Binding Click Event - > Verification Code Refresh Effect
5. The first time a web page opens, it will display get('code').innerHTML = randCode()
6. Binding Click Event - > Verification Code
6.1 Get the value of the input box Get the value of the verification code (inner.HTML)
6.2 if to determine if the two values are equal (validation codes are case-insensitive)
* Equal ->Validation Passed
Unequal - > Authentication Code Refresh Input Box Empty
* Validation failed
<input type="text" id="inp">
<span id="code">dwef</span>
<span id="msg">Verification codes are case insensitive</span>
<br>
<button id="btn">Verification</button>
<script>
var numArr = [] ;
for(var i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++){
numArr.push(i + '');
}
var smallArr = [] ;
for(var i = 97 ; i <= 122 ; i++){
smallArr.push(String.fromCharCode(i))
// Convert ASCII code to corresponding character
}
var bigArr = [];
for(var i = 65 ; i <= 90 ; i++){
bigArr.push(String.fromCharCode(i))
} // Convert ASCII code to corresponding character
var allArr = numArr.concat(smallArr,bigArr);
// The first parameter is the maximum value, the second parameter is the minimum value, and the minimum value defaults to 0
function rand(max,min){
min = min || 0 ;
return parseInt(Math.random()*(max - min)+ min)
}
// Random Generation of Verification Codes
function randCode(n){
n = n || 4 ;
var res = '' ;
//The first digit is taken in the number array
res += numArr[rand(numArr.length)];
//The second digit is taken in a lowercase letter
res += smallArr[rand(smallArr.length)];
//The third digit is taken in a capital letter
res += bigArr[rand(bigArr.length)];
//Get the rest in the allArr array
for(var i = 0 ; i < n -3 ; i++){
res += allArr[rand(allArr.length)];
}
console.log(res); //9mXn
// Want to shuffle the order of strings--strings cannot be assigned values
// Convert String to Array
var arr = res.split('');
// console.log(arr);
//['9', 'm', 'X', 'n']
// Traverse this array
for(var i in arr){
// Change of position
var index = rand(arr.length);
var t = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[index];
arr[index] = t ;
}
// Turn Array Back to String
res = arr.join('');
// console.log(res); Xmn9
return res
}
// Encapsulate get method to get elements
function get(id){
return document.getElementById(id)
}
// Show the verification code on the page
get('code').innerHTML = randCode()
//Bind Click Event
get('code').onclick = function(){
get('code').innerHTML = randCode()
}
// Verification
get('btn').onclick = function(){
//Get the value of the input box
var str = get('inp').value;
//Get the verification code displayed
var str2 = get('code').innerHTML;
if(str.toLowerCase() === str2.toLowerCase()){
get('msg').innerHTML = 'Verification Passed';
get('msg').style.color = 'green'
}else{
get('code').innerHTML = randCode()
get('inp').value = '' // Refresh
get('msg').innerHTML = 'Validation failed';
get('msg').style.color = 'red'
}
}
</script>6. Registration Verification
Ideas: 1. Encapsulate rand get validation code function
2. Get the desired object by the get method, for example: var oUser = get('user');
3. Create four arrays
4. Binding Click Event - > Verification Code Refresh
5. The first time a web page opens, it will display get('code').innerHTML = randCode()
6. Bind Click Event - > Validation
6.1 User Name Verification
6.11 Remove the leading and trailing spaces var username = oUser.value.trim()
6.12 judged empty
6.13 Verification Length (Length must be in 3-6 digits)
If (numArr.includes (username.charAt(0)) verify the number (cannot start with a number) at 6.14
6.15 Verify illegal characters (cannot contain illegal characters) if (allArr.includes (username[i])
6.16 User Name Verification Successful oUserSpan.innerHTML =''
* 6.2 Password Verification
6.21 Remove the leading and trailing spaces var password = oPwd.value.trim()
6.22 judged null
6.23 Verification Length (Length must be in 3-6 digits)
If (numArr.include (password.charAt(0)) verify the number (cannot start with a number) at 6.24
6.25 Verify illegal characters (cannot contain illegal characters)
6.26 Intensity validation for pure numbers and weak letters; Combining letters with numbers is strong
* Password validation succeeded at 6.27 * oPwdSpan.innerHTML =''
6.3 Authentication Code
Get the value of the input box at 6.31 to get the value of the verification code
6.32 to determine if the two values are equal (validation codes are case-insensitive)
* Equal ->Validation Passed
* Not Equal - > Authentication Code Refresh Input Box Empty
Validation failed
7. Registration succeeds if all three of the username password validation codes succeed
<script>
//Take Object
var oUser = get('user');
var oUserSpan = get('userSpan')
var oPwd = get('pwd')
var oPwdSpan = get('pwdSpan')
var oYzm = get('yzm')
var oCode = get('code')
var oMsg = get('msg')
var oBtn = get('btn')
var oStrong = get('strong')
var numArr = [];
for(var i= 0 ; i < 10 ; i++){
numArr.push(i + '');
}
var smallArr = [];
for(var i = 97 ; i <= 122 ; i++){
smallArr.push(String.fromCharCode(i))
//Convert ASCII code to corresponding character
}
var bigArr = [];
for(var i = 65 ; i <= 90 ; i++){
bigArr.push(String.fromCharCode(i))
}
var allArr = numArr.concat(smallArr,bigArr);
oCode.innerHTML = randCode();
//Authentication Code Refresh
oCode.onclick = function(){
oCode.innerHTML = randCode()
}
//Verification
oBtn.onclick = function(){
// Verify user name first--remove leading and trailing spaces
var username = oUser.value.trim();
// Judge as null
if( username.length === 0){
oUserSpan.innerHTML = 'Input cannot be empty'
oUserSpan.style.color = 'red'
//Direct End Function`
return
}
//Verify Length
if(username.length < 3 || username.length > 6){
oUserSpan.innerHTML = 'Length should be 3-6 Within bits'
oUserSpan.style.color = 'red'
return ;
}
//Verify Number
if(numArr.includes(username.charAt(0))){
oUserSpan.innerHTML = 'Cannot start with a number'
oUserSpan.style.color = 'red'
return
}
// Cannot include illegal characters
for(var i = 0 ; i < username.length ; i++){
if(!allArr.includes(username[i])){
oUserSpan.innerHTML = 'User name can only be a number or a letter'
oUserSpan.style.color = 'red'
return
}
}
oUserSpan.innerHTML = '√'
oUserSpan.style.color = 'green'
// Password verification
// Remove first and last spaces
var password = oPwd.value.trim();
// Judge as null
if(password.length === 0){
oPwdSpan.innerHTML = 'Input cannot be empty'
oPwdSpan.style.color = 'red'
return
}
// Verify Length
if(password.length < 3 || password.length > 6){
oPwdSpan.innerHTML = 'Length must be 3-6 Within bits'
oPwdSpan.style.color = 'red'
return
}
// Verify Number
if(numArr.includes(password.charAt(0))){
oPwdSpan.innerHTML = 'Cannot start with a number'
oPwdSpan.style.color = 'red'
return
}
// Cannot include illegal characters
for(var i = 0 ; i < password.length ; i++){
if(!allArr.includes(password[i])){
oPwdSpan.innerHTML = 'Passwords can only be numbers or letters'
oPwdSpan.style.color = 'red'
return
}
}
//Strength verification
// for(var i = 0 ; i < password.length;i++){
// if(!numArr.includes(password[i]) || !smallArr.includes(password[i]) || !bigArr.includes(password[i])){
// oStrong.innerHTML ='Weak'
// oStrong.style.color = 'grey'
// }else{
// if(numArr.includes(password[i]) && smallArr.includes(password[i]) && bigArr.includes(password[i])){
// oStrong.innerHTML ='strong'
// oStrong.style.color = 'goldenrod'
// }
// }
// }
for(var i = 0 ; i < password.length;i++){
if(numArr.includes(password[i]) && smallArr.includes(password[i]) && bigArr.includes(password[i])){
oStrong.innerHTML = 'strong'
oStrong.style.color = 'goldenrod'
}else{
oStrong.innerHTML = 'weak'
oStrong.style.color = 'grey'
}
}
oPwdSpan.innerHTML = '√'
oPwdSpan.style.color = 'green'
// Verification Code
var str = oYzm.value;
var str2 = oCode.innerHTML;
if(str.toLowerCase() === str2.toLowerCase()){
oMsg.innerHTML = 'Verification Passed'
oMsg.style.color = 'green'
}else{
oCode.innerHTML = randCode();
oYzm.value = ''
oMsg.innerHTML = 'Validation failed'
oMsg.style.color = 'red'
}
}
7. Cutting the Address Bar
Purpose: To get the format of a two-dimensional array
[
['username' , 'wy'],
['password','123456'],
['email','wuyi@qq.com']
]
Ideas: 1. Cut var arr= URL by question mark. Split ('?');
2. The first step cuts into two arrays and we want to get the second var str = arr[1];
3. Press & cut var arr = str.split ('&');
4. Press=Cut and use map function to implement two-dimensional array
Purpose: To get the format of objects in the array
[
{'username' , 'wy'},
{'password','123456'},
{'email','wuyi@qq.com'}
]
Ideas: On the above basis.
1. Declare an empty object
2. Press = Cut
3. Object Key Name=Key Value
4. Encapsulate the above with map functions
var url = 'file:///C:/Users/Administrator/Desktop/h5_2114/%E4%BA%8C%E9%98%B6%E6%AE%B5/day_10/%E4%BD%9C%E4%B8%9A-2.%E5%88%87%E5%89%B2%E5%9C%B0%E5%9D%80%E6%A0%8F.html?username=wuyi&password=123456&email=wuyi%40qq.com'
//Expect
// [
// ['username' , 'wy'],
// ['password','123456'],
// ['email','wuyi@qq.com']
// ]
var str = url.split('?')[1];
var arr = str.split('&')
console.log(arr);
var res = arr.map(function(v){
return v.split('=')
})
console.log(res);
//Expect
// [
// {'username' , 'wy'},
// {'password','123456'},
// {'email','wuyi@qq.com'}
// ]
var res = arr.map(function(v){
var obj ={}
var list = v.split('=')
obj[list[0]] = list[1];
return obj
} )
console.log(res);8. Filtering data
Thought: Filter with a filter var res = arr.filter(function(v){})
var arr = ['hello','hi','hei','hehe','xixi','pupu'];
// Found containing h
var res = arr.filter(function(v){
return v.includes('h')
})
console.log(res);
var data = [
{
img :"https://img.alicdn.com/bao/uploaded/i1/3951599478/O1CN01WX3jUn2JsyXfgVnxC_!!0-item_pic.jpg_468x468q75.jpg_.webp",
title : 'Piglet 1**',
content : 'Cute Piggy**',
price : 100
},
{
img : "https://img.alicdn.com/bao/uploaded/i1/3951599478/O1CN01WX3jUn2JsyXfgVnxC_!!0-item_pic.jpg_468x468q75.jpg_.webp",
title : 'Piglet 2**',
content : 'Cute Piggy**',
price : 200
},
{
img : "https://img.alicdn.com/bao/uploaded/i1/3951599478/O1CN01WX3jUn2JsyXfgVnxC_!!0-item_pic.jpg_468x468q75.jpg_.webp",
title : 'Piglet 2**',
content : 'Cute Piggy**',
price : 300
}
]
var res2 = data.filter(function(v){
return v.title.includes('1')
})
console.log(res2);
9. Date Object
Date object: record time
Regional Time
Inside js. 1970.1. 1 0:0:0 Standard Time
Creation of date objects
Create --- Get the current time of the computer
* Number single parameter creation, milliseconds 1s = 1000ms
Multiple parameters create year, month, day, hour and second
Note: Month starts at 0 and time can be calculated automatically
String Single Parameter Creation Year [-*,]Month [-*,]DayTime: Minutes: Seconds
Time is normal and cannot be calculated automatically
var date = new Date();
console.log(date); // Get the current time of your computer
var date2 = new Date(0);
console.log(date2); // Thu Jan 01 1970 08:00:00 GMT+0800 (China Standard Time)
var date3 = new Date(1000);
console.log(date3); // Thu Jan 01 1970 08:00:01 GMT+0800 (China Standard Time)
var date4 = new Date(2020,13,1,1,1,1);
console.log(date4); //Mon Feb 01 2021 01:01:01 GMT+0800 (China Standard Time) 13 months is February
var date5 = new Date('2021-1-1 1:1:1');
console.log(date5); // Fri Jan 01 2021 01:01:01 GMT+0800 (China Standard Time)
var date6 = new Date(date2);
console.log(date6); // date6 === date210. Days of last month
var date = new Date();
// Day 0 of this month is also the last day of last month
date.setDate(0); //Last day of last month
console.log(date);11. Obtain specific dates
function formatDate() {
var date = new Date() ;
var year = date.getFullYear();
var month = date.getMonth() +1 ;
var day = date.getDate();
var week = date.getDay();
var hour = date.getHours();
var minute = date.getMinutes();
var second = date.getSeconds();
var arr = ['Sunday' , 'Monday' ,'Tuesday' ,'Wednesday' ,'Thursday' ,'Friday' ,'Saturday'] ;
return year + '-' + month + '-' + day + ' ' + hour + ':' + minute + ':' + second + ' ' + arr[week]
}
var date = formatDate()
document.write(date);12. Setting time
var date = new Date() ;
date.setFullYear(2020); // 2020
// Time can be calculated automatically
date.setMonth(12) // January
date.setDate(10) // 10 days
date.setHours(10) // 10 o'clock
date.setMinutes(10) // 10 points
date.setSeconds(1000) // 1000 seconds
// Date. SetDay (4); Err week cannot be set
console.log(date);13. Days of the Month
function currentMonth(){
var date = new Date();
date.setMonth(date.getMonth());
// Date. SetMonth(12)// January
// Date. GetMonth(11)// December
console.log(date);
return date
}
var res = currentMonth()
document.write(res)14. Timer
Timer: Repeated alarm clock
Do one thing every once in a while
Delayer: one-time alarm clock
After a while, do one thing
setInterval(fn , time)
When using variables to store timers, variables store the last timer on the page
Note:
Timer is asynchronous (not until all synchronous code is executed)
* Synchronous and asynchronous
Listen asynchronously while typing code (doing a lot of things at the same time)
Boil water before soaking noodles synchronously (dry first, dry then dry - queue)
Single-threaded and multi-threaded
Single-threaded: Do one thing at a time
Multithreaded: Do many things at once
* js a single-threaded language
* js is primarily tagging (tags cannot be deleted while modifying them)
* js Code Execution Order
1 Execute synchronous code on the main thread first, encounter asynchronous, put in task queue
2 After all synchronization is completed, if time has elapsed in the task queue, it can be executed. (This task can be executed on the main thread)
var t = setInterval(function(){
console.log(666);
},0)
var t2 = setInterval(function(){
console.log(777);
},2000)
document.onclick = function(){
console.log(999);
}
console.log(1);
console.log(2);15. Page dwell time
<body>
<h1 id="time"></h1>
<script>
var oH1 = document.getElementById('time');
var count = 0 ;
oH1.innerHTML = 'You stopped on the page' + count + 's'
setInterval(function(){
count++ ;
oH1.innerHTML = 'You stopped on the page' + count + 's'
},1000)
</script>
</body>The results are as follows:

16. Moving time
Idea: Use timer effect to achieve.
Get information such as minutes, seconds, and hours of the current year, month, day, and so on through the date function.
Detail handling: In bits per second, by string stitching, in the first zero such as 9 is 09
Turn week from array to week**
// Zero Complement
var oH1 = document.getElementById('time');
var res = formatDate();
oH1.innerHTML = res;
setInterval(function(){
var res = formatDate();
oH1.innerHTML = res;
},1000)
function formatDate(){
var date = new Date();
var year = date.getFullYear();
var month = date.getMonth() + 1;
var day = date.getDate();
var week = date.getDay();
var hour = date.getHours();
var minute = date.getMinutes();
var second = date.getSeconds();
if(hour < 10 && hour >= 0){
hour = '0'+ hour
}
if(minute < 10 && minute >= 0){
minute = '0'+ minute
}
if(second < 10 && second >= 0){
second = '0'+ second
}
var arr = ['Sunday','Monday','Tuesday','Wednesday','Thursday','Friday','Saturday'];
return year + '-' + month + '-' + day +' ' + hour + ':' + minute + ':' + second + ' ' + arr[week]
}17. Countdown
Ideas: 1. get method gets element oTime, oH1
2. Declare a future time (time you want to count down, like tomorrow)
3. Start encapsulating functions
3.1 var gap = future time - present time
Subtraction of 3.2 gives gap s in milliseconds, so conversion is required.
3.21 allSeconds = parseInt(gap/1000)
Change var h = parseInt(allSeconds / 3600) at 3.22 seconds
var m = parseInt(allSeconds % 3600 / 60)
var s = allSeconds % 60
3.3 if judges that allSeconds less than or equal to 0 will expire
3.4 Output oTime. InnerHTML = H +': '+ m +':' + s;
4. Start writing timer var t = setInterval(function(){}, 1000)
4.1 Execute the function showDate(tt)
4.2 Timer time is cleared if it is less than 0. *
if(allSeconds <= 0){
clearInterval(t)
}
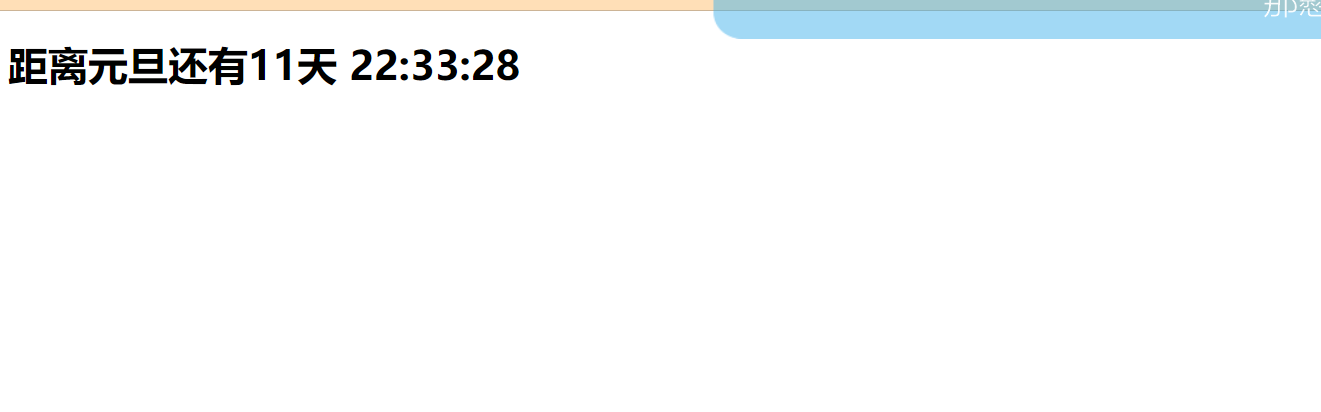
<body>
<h1 id="h1">There's still time to finish<span id="time"></span></h1>
<script>
var oTime = document.getElementById('time');
var oH1 = document.getElementById('h1');
var tt = new Date('2021-12-20 0:49:0')
showDate(tt)
function showDate(tt){
var future = new Date(tt);
var now = new Date();
// Time can be subtracted--you get milliseconds
var gap = future - now;
allSeconds = parseInt(gap/1000)
//Declare allSeconds as a global variable
console.log(allSeconds);
if(allSeconds <= 0){
oH1.innerHTML = 'Time has expired'
return
}
var h = parseInt(allSeconds / 3600)
var m = parseInt(allSeconds % 3600 / 60)
var s = allSeconds % 60 ;
oTime.innerHTML = h + ':' + m + ':' + s;
}
// The third parameter of setInterval, including the following parameters, is for the first function
// var t = setInterval(showDate,1000,tt)
var t = setInterval(function(){
showDate(tt)
if(allSeconds <= 0){
clearInterval(t)
}
},1000)
</script>
</body>The results are as follows: