1, String
Overview: string is the most basic type of redis. It can store up to 512MB of data. String type is binary secure, that is, it can store any data, such as numbers, pictures, serialized objects, etc
① append
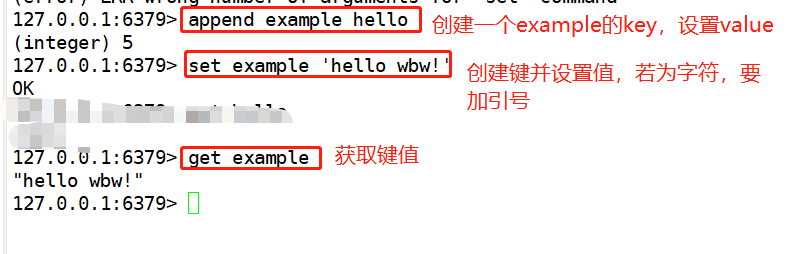
1,append #The append command of Redis is to append value to a key. If there is no key, create one and set value Example: redis-cli exists color append blue 1 append blue red get color

② set
2,SET #The command format is get key Example: set blue 'hello lic!' get blue
③ strlen
3,strlen #Gets the character length of the specified Key Example: strlen example

④ incr,decr,incrby,decrby
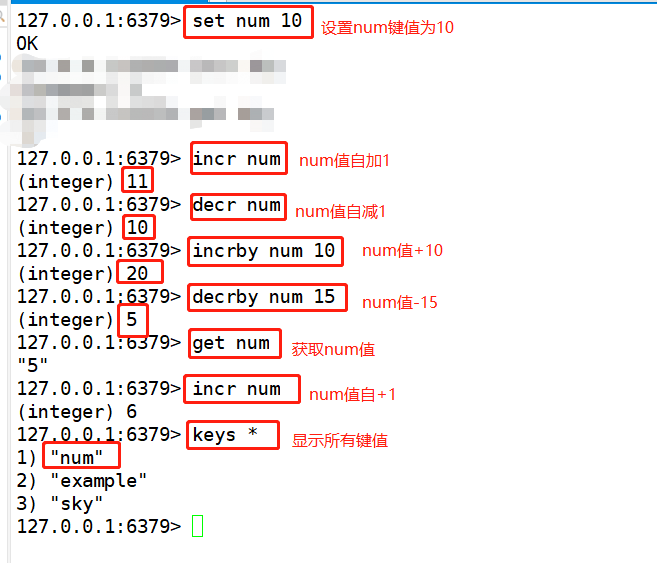
4,incr #The value of the Key is incremented by 1 decr #The value of the Key is decremented by 1 incrby #Increments the specified integer decrby #Decrements the specified integer example: set num 10 incr num decr num incrby num 10 decrby num -20 get num del num keys * incr num keys * set num white get num incr num

⑤ getset
getset #While getting the original value of the counter and setting it to the new value, the two operations are completed atomically at the same time Example: incr white getset white 0 get white

⑥ setex
setex #Set the expiration time of the specified Key to xx seconds ttl key #View the remaining lifetime of the key Example: setex white 20 'wbw' ttl white get white Wait 20 s get white ttl white set white 'wbw' ttl white

⑦ setnx
setnx #Create the specified key. If the key exists, it will not be executed. If it does not exist, it will be executed Example: del white setnx white lic setnx white kiki get white

⑧ mset,mget,msetnx
mset #Value of batch setting key mget #Batch get key values msetnx #Set key values in batch. If there are existing keys, they will not be executed Example: mset k1 1 k2 2 mget k1 k2 msetnx k2 5 k3 6 keys k* msetnx k4 3 k3 4 keys k*

2, List
summary:
The element type of the list is string, sorted according to the insertion order, and elements are added at the head or tail of the list
① lpush,lpushx,lrange
lpush #The command will create the key and its associated List, and then insert the values in the parameter into the header from left to right lpushx #This command inserts the value value into the header only when the key exists lrange #Returns the elements within the specified interval in the list. 0 represents the first element and 1 represents the second element example: lpush num a b c d lrange num 0 -1 lpushx num e keys c* lpushx num e lrange num 0 -1

② lpop,llen
lpop #Remove and return the first element, starting from scratch llen #View the number of elements in the list

③ lrem,lset,lindex,ltrim
lrem #Delete two elements with a value equal to a from the left variable list to the right variable list, and the return value is the actual deleted quantity lset #Set the element value with index value xxx to the new value xxx lindex #Gets the element value with index value xxx. ltrim #Only elements with index values xxx to xxx are retained Example: del num lpush num a b c b b a lrange num 0 -1 lrem num 2 b lrange num 0 -1 lset num 1 b lrange num 0 -1 lindex num 3 ltrim num 0 2 lrange num 0 -1

④ linsert
linsert #Insert a new element before and after the xxx element of the key Example: del num lpush num a b c d e lrange num 0 -1 linsert num before a 0 linsert num after e 1 lrange num 0 -1

⑤ rpush,rpushx
rpush #Insert values from left to right at the end of the table rpushx #Execute when the specified key exists, otherwise do not execute Example: rpush key1 a b c d e lrange key1 0 -1 rpushx key1 f rpushx key2 f keys key?

⑥ rpop,rpoplpush
6,rpop #Removes and returns the first element of the key, starting at the end rpoplpush #Pop up the element xxx at the end of key 1 and insert it into the head of key 2 (atomically complete these two steps) Example: rpop key1 lrange key1 0 -1 rpoplpush key1 key2 keys key? lrange key2 0 -1 lrange key1 0 -1 rpoplpush key1 key1 lrange key1 0 -1

3, Hash
summary:
hash is used to store objects. This naming method can be adopted: the object category and ID constitute the key name, the field is used to represent the attribute of the object, and the field value stores the attribute value. For example, store the car object with ID 2.
If the Hash contains few fields, this type of data will also take up very little disk space. Each Hash can store 4294967295 key value pairs.
① hset,hget,hdel,hexists,hlen,hsetnx
1,hset #Set the field to xxx and the value to xxx for the xxx key hget #Get the xxx key, and the field is the value of xxx hdel #Delete the xxx field of the xxx key, and 1 is returned successfully hexists #Judge whether the xxx field in the xxx key exists, and return 1 if it exists hlen #Gets the number of fields for the xxx key hsetnx #To add a new field to the xxx key, whether to execute or not is based on whether this field exists. No matter whether the key exists or not, a return of 1 indicates that the execution is successful Example: hset hash field1 a field2 b field3 c hget hash field1 hdel hash field2 hexists hash field2 hlen hash hsetnx hash1 field3 d keys has* hsetnx hash field3 d

② hincrby
2,hincrby #Add x to the xxx field value of the xxx key Example: hincrby hash3 field1 5 hincrby hash3 field1 -71

③ hmset,hmget,hgetall,hkeys,hvals
3,hmset #Create fields and assign values for xxx keys in batches hmget #Gets or specifies multiple field values hgetall #Returns all fields and their values of the xxx key, listed pair by pair hkeys #Only get all field names in xxx key hvals #Get only the values of all fields in the xxx key example: hmset hash4 field1 hello field2 world hmget hash4 field1 field2 hkeys hash4 hvals hash4 hset hash5 field1 hello field2 wbw hget hash5 field1 field2 hmget hash5 field1 field2 hkeys hash5 hvals hash5

4, set
summary:
Overview: unordered collection. The element type is String. The element is unique. Duplicate members are not allowed. Union, intersection and difference operations can be performed among multiple set types.
Application scope:
1) It can be used for the leaderboard of a large online game. Whenever the player's score changes, you can execute the ZADD command to update the player's score, and then obtain the user information of the score TOP10 through the ZRANGE command. Of course, we can also use the ZRANK command to obtain the ranking information of players through username. Finally, we will combine the ZRANGE and ZRANK commands to quickly obtain the information of other users with similar points to a player.
2) The sorted set type can also be used to build index data.
① sadd,smembers,scard,sismember
sadd #If one or more member elements are added to the collection, the member elements that already exist in the collection will be ignored. If the collection key does not exist, create a collection containing only the added elements as members smembers #View the insertion results through the smembers command. The order of output is independent of the insertion order scard #Gets the number of members in the collection sismember #Judge whether the xxx member in the key exists. Return 0 to indicate that it does not exist and 1 to indicate that it exists Example: sadd myset a b c d e smembers myset scard myset sismember myset c sismember myset f

② spop,srem,srandmember,smove
spop #Randomly remove and return a member of the key srem #Remove xxx, xxx and xxx members from the key and return the number of removed members srandmember #This command returns a member randomly smove #Moving the xxx member of key 1 to key 2 returns 1 for success and 0 for failure example: del myset sadd myset a b c d e spop myset smembers myset srem myset a b c smembers myset srandmember myset smove myset myset1 e keys myse*

5, Sorted Set
summary:
1. Ordered collection. The element type is String. The element is unique and cannot be repeated.
2. Each element is associated with a score of double type (representing weight), which can be sorted by the size of weight, and the scores of elements can be the same.
Application scope:
1) It can be used for the leaderboard of a large online game. Whenever the player's score changes, you can execute the ZADD command to update the player's score, and then obtain the user information of the score TOP10 through the ZRANGE command. Of course, we can also use the ZRANK command to obtain the ranking information of players through username. Finally, we will combine the ZRANGE and ZRANK commands to quickly obtain the information of other users with similar points to a player.
2) The sorted set type can also be used to build index data.
① zadd,zcard,zcount,zrem,zincrby,zscore,zrank
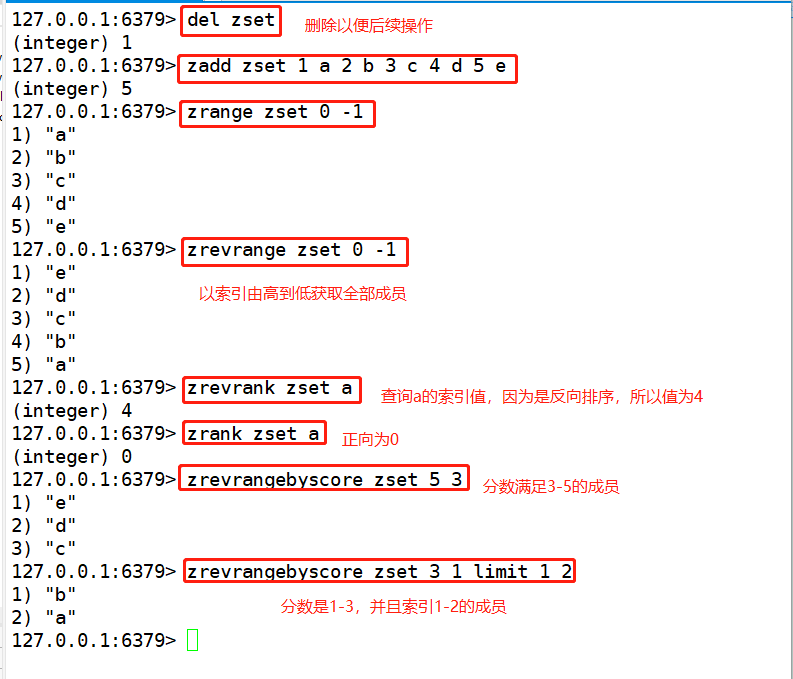
zadd #Add one or more member elements and their fractional values to the ordered set zcard #Gets the number of members in the key zcount #Number of members whose score satisfies the expression x < = score < = x zrem #Delete members xxx and xxx, and return the actual number of deleted members zincrby #If the member xxx does not exist, the zincrby command will add the member and assume its initial score is 0 zscore #Get the score of member xxx zrank #Gets the location index value of member xxx Example: zadd zset 1 a 2 b 3 c 4 d 5 e zrange zset 0 -1 zrange zset 0 -1 withscores zrank zset e zcard zset zcount zset 2 4 zrem zset a b zcard zset zscore zset d zincrby zset 2 a zincrby zset -1 a


② zrangebyscore,zremrangebyrank,zremrrangebyscore
zrangebyscore #Gets the member whose score satisfies the expression x < = score < = X zremrangebyrank #Delete members whose positional index satisfies the expression x < = rank < = X. zremrrangebyscore #Delete members whose scores satisfy the expression x < = score < = x, and return the actual deleted quantity. Example: del zset zadd zset 1 a 2 b 3 c 4 d 5 e zrangebyscore zset 2 4 zrangebyscore zset -inf +inf limit 2 3 zremrangebyscore zset 1 3 zrange zset 0 -1 zremrangebyrank zset 1 2 zrange zset 0 -1

③ zrevrange,zrevrangebyscore,zrevrank
zrevrange #Get and return the members in this interval from high to low by location index zrevrangebyscore #Get the members whose scores satisfy the expression x > = score > = x and output them in the order from high to bottom. zrevrank #Get member index Example: del zset zadd zset 1 a 2 b 3 c 4 d 5 e zrange zset 0 -1 zrevrange zset 0 -1 zrevrank zset a zrank zset a zrevrangebyscore zset 5 3 zrevrangebyscore zset 3 1 limit 1 2