1. Vim automatically adds annotations and intelligently changes lines
#vi ~/.vimrc
set autoindent
set tabstop=4
set shiftwidth=4
function AddTitle()
call setline(1,"#!/bin/bash")
call append(1,"#====================================================")
call append(2,"# Author: lizhenliang")
call append(3,"# Create Date: " . strftime("%Y-%m-%d"))
call append(4,"# Description: ")
call append(5,"#====================================================")
endf
map <F4> :call AddTitle()<cr>
//After opening the file, pressing F4 automatically adds comments, saving a lot of time: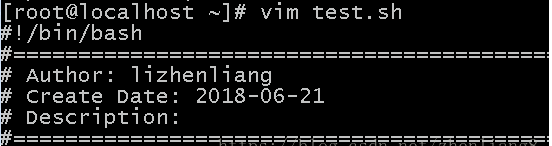
2. Find and delete files created 7 days ago in the / data directory
#find /data -ctime +7 -exec rm -rf {} \;
#find /data -ctime +7 | xargs rm -rf3. tar command compression excludes a directory
#tar zcvf data.tar.gz /data --exclude=tmp #-- exclude parameter does not contain a directory or file, and can be followed by more than one
4. View the tar package archive file without decompressing
#tar tf data.tar.gz #t is to list the directories of archived files and f is to specify the archived files.
5. Use the stat command to view the properties of a file
Access, Modification, Change
stat index.php
Access: 2018-05-10 02:37:44.169014602 -0500
Modify: 2018-05-09 10:53:14.395999032 -0400
Change: 2018-05-09 10:53:38.855999002 -0400
6. Batch decompression tar.gz
Method 1: find. - name "*. tar. gz" - exec tar zxf {}
Method 2: For tar in *. tar. gz; do tar zxvf $tar; do tar
Method 3: ls *.tar.gz | xargs -i tar zxvf {} 7. Screen out the comments and spaces in the document
Method 1: grep-v "^#" httpd.conf | grep-v "^$" Method 2: sed -e'/^$/d'- e'/^ #/d' httpd.conf > http.conf or # sed-e'/^ #/d; /^$/d' e executes multiple sed commands Method 3: awk'/^[^#]/|/"^$"'httpd.conf or # awk'!/^# |$/'httpd.conf
8. Screen all users in / etc/passwd file
Method 1: cat/etc/passwd | cut-d: -f1
Method 2: awk-F ":'{print $1}'/etc/passwd9. iptables website jump
First turn on routing forwarding:
Echo "1">/proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward\ Provisional Effectiveness
Intranet access to the public network ():
iptables - t nat -A POSTROUTING -s [Intranet IP or segment] - j SNAT --to [Public IP]
# Intranet server should point to firewall Intranet IP as gateway
Public Access Intranet (DNA T) (Public Port Mapping Intranet Port):
iptables - t nat -A PREROUTING -d [External IP] - P TCP - dport [External Port] - J DNA T -- to [Intranet IP: Intranet Port]
# Intranet servers should configure firewall Intranet IP as gateway, otherwise data packets can not come back. In addition, there is no need to configure SNAT here, because the system service will return according to the source of the data package.10. iptables forward local port 80 to local port 8080
iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-ports 8080
11. find command finds files and copies them to / opt directory
Method 1: find/etc-name httpd.conf-exec cp-rf {}/opt/;;: exec executes the following command, {} represents the result of the previous output, \
Method 2: find/etc-name httpd.conf | xargs-i CP {}/ opt#-i indicates that the output result is replaced by {}12. View files larger than 1G in the root directory
find / -size +1024M #The default unit is b, and other units such as C, K, M can be used.
13. View the number of server IP connections
netstat -tun | awk '{print $5}' | cut -d: -f1 |sort | uniq -c | sort -n
-tun: -tu It's display. tcp and udp Connect, n So IP address display
cut -d: -f1: cut Is a content command that selectively displays a line.-d Specify: as a delimiter,-f1 Displays the first field after the delimiter.
uniq -c: Reporting or deleting duplicate lines in the text,-c Add the number of occurrences before the output line
sort -n: Sort according to different types. The default sort is ascending.-r Change the parameter to descending order.-n It is sorted according to the size of the values.14. Insert a line to 391 lines, including the special symbol "/"
sed -i "391 s/^/AddType application\/x-httpd-php .php .html/" httpd.conf
15. List the top 10 IP accesses to nginx logs
Method 1: awk'{print $1}'access. log | sort | uniq - C | sort - NR | head - N 10
Sort: sort uniq-c: merge duplicate rows and record the number of duplicates sort-nr: sort by number in descending order
Method 2: awk'{a [$1]+} END {for (v in a) print v, a [v] | "sort-k2-nr | head-10"} access.log16. Top 10 IP with the largest number of visits per day for displaying nginx logs
awk '$4>="[16/May/2017:00:00:01" && $4<="[16/May/2017:23:59:59"' access_test.log |sort |uniq -c |sort-nr |head -n 10
awk '$4>="[16/Oct/2017:00:00:01" && $4<="[16/Oct/2017:23:59:59"{a[$1]++}END{for(i in a){print a[i],i|"sort -k1 -nr |head -n 10"}}' access.log17. Get log access one minute before the current time
date=`date +%d/%b/%Y:%H:%M --date="-1 minute"` ; awk -vd=$date '$0~d{c++}END{print c}' access.log
date=`date +%d/%b/%Y:%H:%M --date="-1 minute"`; awk -vd=$date '$4>="["d":00" && $4<="["d":59"{c++}END{print c}' access.log
grep `date +%d/%b/%Y:%H:%M --date="-1 minute"` access.log |awk 'END{print NR}'
start_time=`date +%d/%b/%Y:%H:%M:%S --date="-5 minute"`;end_time=`date +%d/%b/%Y:%H:%M:%S`;awk -vstart_time="[$start_time" -vend_time="[$end_time" '$4>=start_time && $4<=end_time{count++}END{print count}' access.log18. Find integers between 1 and 255
Method 1: ifconfig | grep-o'[0-9]+' matches the previous character one or more times Method 2: ifconfig | egrep-o' ([1-9] | [1-9] [0-9] | 1 [0-9] [0-9] | 2 [0-4] [0-9] | 25 [0-5] \>
19. Find IP Address
ifconfig |grep -o '[0-9]\{1,3\}\.[0-9]\{1,3\}\.[0-9]\{1,3\}\.[0-9]\{1,3\}' #- o Displays only matched characters20. Adding beginning and ending information to the document
awk 'BEGIN{print "Start by displaying information"}{print $1,$NF} END{print "Show information at the end"}'/etc/passwd
awk 'BEGIN{printf " date ip\n------------------\n"} {print $3,$4} END{printf "------------------\nend...\n"}' /var/log/messages
date ip03:13:01 localhost 10:51:45 localhost
end...
21. View Network Status Command
netstat -antp #View all network connections netstat -lntp #View only listened port information lsof -p pid #View process open file handle lsof -i:80 #See which process is occupying the port
22. Generating 8-bit random strings
Method 1: echo $RANDOM | md5sum | cut-c 1-8 Method 2: OpenSSL rand-base 64 4 Method 3: cat / proc / sys / kernel / random / uuid| cut-c 1-8
23. while Dead Cycle
while true; do #Conditions are exact equal to true, or they can be directly used as conditions ["1"== "1"]. Conditions are always true.
ping -c 2 www.baidu.com
done24.awk formatted output
Align text columns left or right.
Left alignment:
awk '{printf "%-15s %-10s %-20s\n",$1,$2,$3}' test.txt
Right alignment:
awk '{printf "%15s %10s %20s\n",$1,$2,$3}' test.txt25. Integer operations preserve decimal points
Method 1: echo'scale = 2; 10/3;'| BC # scale parameter represents decimal point number
Method 2: awk BEGIN'{printf"%. 2f n, 10/3}" 26. Number summation
cat a.txt
10
23
53
56
//Method 1:
#!/bin/bash
while read num;
do
sum=`expr $sum + $num`
done < a.txt
echo $sum
//Method 2:
cat a.txt |awk '{sum+=$1}END{print sum}'27. Determine whether it is a number (as is string judgment)
[[ $num =~ ^[0-9]+$ ]] && echo yes || echo no #[[]] is more general than [] and supports wildcards for pattern matching=~and string comparison` ^ $: From the beginning to the end, the number satisfies the condition. =~: An operator that indicates whether the left side satisfies the right (as a pattern) regular expression
28. Delete newline characters and replace spaces with other characters
cat a.txt |xargs echo -n |sed 's/[ ]/|/g' #- n No line change cat a.txt |tr -d '\n' #Delete line breaks
29. View 20 to 30 lines of text (a total of 100 lines)
Method 1: awk'{if (NR > 20 & & NR < 31) print $0}'test. TXT
Method 2: sed-n'20,30p'test.txt
Method 3: head-30 test.txt | tail30. Replacement of two columns in text
cat a.txt
60.35.1.15 www.baidu.com
45.46.26.85 www.sina.com.cn
awk '{print $2"\t"$1}' a.txt31. Monitor directory, add the newly created file name to the log
#To install the inotify-tools package
#!/bin/bash
MON_DIR=/opt
inotifywait -mq --format %f -e create $MON_DIR |\
while read files; do
echo $files >> test.log
donefind finds multiple specified file types at a time
find ./ -name '*.jpg' -o -name '*.png' find ./ -regex ".*\.jpg\|.*\.png"
33. String Splitting
echo "hello" |awk -F '' '{for(i=1;i<=NF;i++)print $i}'
echo "hello" |sed 's/./&\n/g'
echo "hello" |sed -r 's/(.)/\1\n/g'34. Running results of real-time monitoring commands
`watch -d -n 1 'ifconfig'`
35. Solving the problem of messy mail code
echo `echo "content" | iconv -f utf8 -t gbk` | mail -s "`echo "title" | iconv -f utf8 -t gbk`" xxx@163.com Note: Converting content character sets through iconv tools
36. Add a newline or content every three lines in the text
sed '4~3s/^/\n/' file
awk '$0;NR%3==0{print "\n"}' file
awk '{print NR%3?$0:$0 "\n"}' file37. Delete matching rows and subsequent or previous rows
sed '/abc/,+1d' file #Delete the matching line and the following line
sed '/abc/{n;d}' file #Delete the last line
tac file |sed '/abc/,+1d' |tac #Delete the previous line38. Statistical total rows
Efficiency 1 # wc-l file
Efficiency 2 # grep-c. file
Efficiency 3 # awk'END {print NR}'file
Efficiency 4 # sed-n'$='File39. Remove the space at the beginning and end of the text
sed -i 's/^[ \t]*//;s/[ \t]*$//' file
40. Add single quotation marks to a single IP
echo '10.10.10.1 10.10.10.2 10.10.10.3' |sed -r 's/[^ ]+/"&"/g'
echo '10.10.10.1 10.10.10.2 10.10.10.3' |awk '{for(i=1;i<=NF;i++)printf "\047"$i"\047"}' 41. Print waiting time in script
wait(){
echo -n "wait 3s"
for ((i=1;i<=3;i++)); do
echo -n "."
sleep 1
done
echo
}
wait42. Delete the specified row
awk 'NR==1{next}{print $0}' file #$0 can be omitted
awk 'NR!=1{print}' file
awk 'NR!=1{print $0}' Or delete matching rows: awk '!/test/{print $0}'
sed '1d' file
sed -n '1!p' file43. Add a line before and after the specified line
Add one line before the second line txt:
awk 'NR==2{sub('/.*/',"txt\n&")}{print}' a.txt
sed'2s/.*/txt\n&/' a.txt
//Add txt after the second line:
awk 'NR==2{sub('/.*/',"&\ntxt")}{print}' a.txt
sed'2s/.*/&\ntxt/' a.txt44. Getting the Network Card Name through IP
ifconfig |awk -F'[: ]' '/^eth/{nic=$1}/192.168.18.15/{print nic}'45. Floating-point arithmetic (number 46 retains decimal points)
# awk 'BEGIN{print 46/100}'
0.46
# echo 46|awk '{print $0/100}'
0.46
# awk 'BEGIN{printf "%.2f\n",46/100}'
0.46
# echo 'scale=2;46/100' |bc|sed 's/^/0/'
0.46
# printf "%.2f\n" $(echo "scale=2;46/100" |bc)
0.4646. Floating point comparison
Method 1:
if [ $(echo "4>3"|bc) -eq 1 ]; then
echo yes
else
echo no
fi
//Method 2:
if [ $(awk 'BEGIN{if(4>3)print 1;else print 0}') -eq 1 ]; then
echo yes
else
echo no
fi47. Replace line breaks with commas
cat a.txt
1:
2
3
//Replacement: 1, 2, 3
//Method 1:
$ tr '\n' ',' < a.txt
$ sed ':a;N;s/\n/,/;$!b a' a.txt
$ sed ':a;$!N;s/\n/,/;t a' a.txt :
//Method 2:
while read line; do
a+=($line)
done < a.txt
echo ${a[*]} |sed 's/ /,/g'
//Method 3:
awk '{s=(s?s","$0:$0)}END{print s}' a.txt
#Trinomial operator (a?b:c), the first s is a variable, s?s"," s? S "," $0: $0,: s? S "," $0: $0,, the first processing 1, the s variable does not assign false, the result print 1, the second processing 2, the s value is 1, true, the result 1, 2. By analogy, parentheses can be omitted.
awk '{if($0!=3)printf "%s,",$0;else print $0}' a.txt48. Removal of hidden formats from text in windows to linux
Method 1: Open the file and enter it :set fileformat=unix Method 2: Open the file and enter it :% s/r*$/M can be replaced byr Method 3: Sed-i's/^M//g'a.txt#^M's input mode is ctrl+v, and then ctrl+m Method 4: dos2unix a.txt
49. Using xargs skillfully
xargs -n1 #Consider a single field as a row # cat a.txt 1 2 3 4 # xargs -n1 < a.txt 1 2 3 4
xargs -n2 #Take two fields as a row $ cat b.txt string number a 1 b 2 $ xargs -n2 < a.txt string number a 1 b 2
50. Statistics the total size of files ending in. html in the current directory
Method 1:
find . -name "*.html" -maxdepth 1 -exec du -b {} \; |awk '{sum+=$1}END{print sum}'
//Method 2:
for size in $(ls -l *.html |awk '{print $5}'); do
sum=$(($sum+$size))
done
echo $sum
//Recursive statistics: find. - name "*. html" - exec Du - K {};; | awk'{sum += $1} END {print sum}'