Articles Catalogue
- 1. Introduction of Bidirectional, Leading and Circulating Link List
- 2. Bidirectional Link List Structure and Common Function Interface
- 3. Implementation of Bidirectional Link List Interface
- 3.1 Establishing New Nodes
- 3.2 Initialization
- 3.3 Destruction
- 3.4 tail insertion
- 3.5 End Deleted
- 3.6 pins
- 3.7 deletions
- 3.8 Find Node x
- 3.9 Insert Nodes Before a Given Position
- 3.10 Delete a given location node
- 3.11 Delete a given value node
- 3.12 Returns bi-directional list size
- 3.13 Judging whether a two-way list is empty
- 3.14 Print Two-way Link List
1. Introduction of Bidirectional, Leading and Circulating Link List
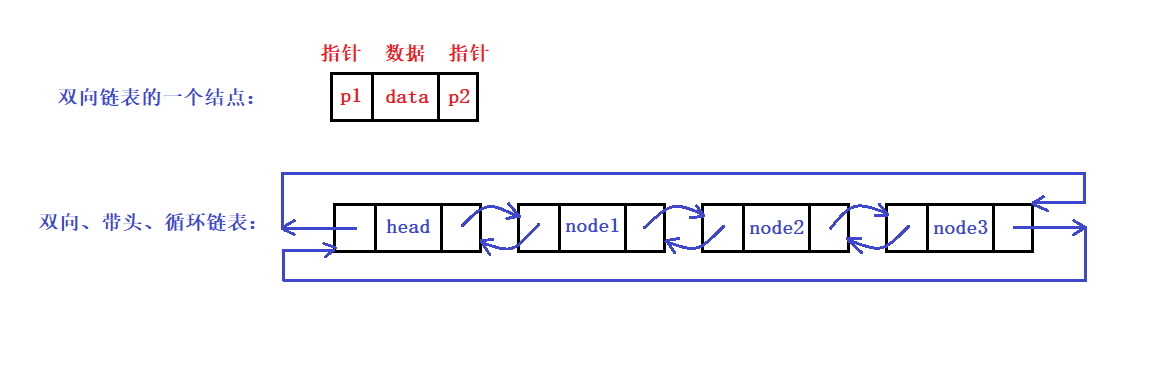
Leading bidirectional circular linked list: The structure is the most complex, but the interface is relatively simple, generally used to store data separately. Most of the linked list data structures used in practice are bi-directional circular linked lists.
2. Bidirectional Link List Structure and Common Function Interface
// Two-way, Leading, Circulation typedef int LTDataType; typedef struct ListNode { // A Node of Bidirectional Linked List struct ListNode* _prev; LTDataType _val; struct ListNode* _next; }ListNode; typedef struct List { ListNode* _head; // Head pointer }List;
_defines two structures. The first structure is the node of the bidirectional linked list (precursor pointer, data field, successor pointer), and the second structure defines the pointer to the head of the bidirectional linked list.
Function interface of single linked list:
ListNode* BuyListNode(LTDataType x);// Establishing New Nodes void ListInit(List* plt);// Initialization void ListDestroy(List* plt);// Destruction void ListPushBack(List* plt, LTDataType x);// Tail insertion void ListPopBack(List* plt);// Tail deletion void ListPushFront(List* plt, LTDataType x);// Head insertion void ListPopFront(List* plt);// Header deletion ListNode* ListFind(List* plt, LTDataType x); // Find node X and return the pointer to node x void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x); // Insert node x in front of pos void ListErase(ListNode* pos);// Delete the node of pos location void ListRemove(List* plt, LTDataType x);// Delete node x int ListSize(List* plt);//Size of bidirectional linked list int ListEmpty(List* plt);//Judging whether a two-way linked list is empty void ListPrint(List* plt);// Printing
3. Implementation of Bidirectional Link List Interface
3.1 Establishing New Nodes
When building a new node, malloc first creates a new node space, then assigns the given value to the data domain of the new node, and finally empties the front and back pointers of the new node.
ListNode* BuyListNode(LTDataType x)// Establishing New Nodes { ListNode* node = (ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(ListNode)); node->_val = x; node->_prev = NULL; node->_next = NULL; return node; }
3.2 Initialization
First call the BuyListNode function to apply for a header node, because it is a circular list, so all pointers point to itself.
void ListInit(List* plt)// Initialization { assert(plt); ListNode* head = BuyListNode(-1); // plt->_head->_next = plt->_head; // It should point to the first node, but there is no first node and no last node. // It points to itself, so simplify it as follows: head->_prev = head; head->_next = head; plt->_head = head; }
3.3 Destruction
Define a pointer to the first node (the first node is not the head node), iterate through it, release it in turn, and point the pointer to the next location to be released. At the end of the cycle, the head node needs to be released separately and the head pointer is empty.
void ListDestroy(List* plt)// Destruction { assert(plt); if (plt->_head == NULL) { return 0; } ListNode* cur = plt->_head->_next;//cur is a pointer to the first element while (cur != plt->_head) // Notice the end condition of this loop { ListNode* next = cur->_next; free(cur); cur = next; } free(plt->_head);//Release head node plt->_head = NULL;//Head Node Pointer Empty }
3.4 tail insertion
Find the last node according to the precursor pointer of the head node, connect the new node to the last node, and change the direction of the four pointers before the head node.
void ListPushBack(List* plt, LTDataType x)// Tail insertion { assert(plt); ListNode* head = plt->_head; ListNode* tail = head->_prev; ListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x); tail->_next = newnode; // Connect the new node to the back of the last node newnode->_prev = tail; head->_prev = newnode; // Connect the new node to the front of the head node newnode->_next = head; }
3.5 End Deleted
Define two pointers, find the penultimate node and the last node, connect the penultimate node and the head node directly, release the last node.
void ListPopBack(List* plt)// Tail deletion { assert(plt); if (plt->_head == NULL || plt->_head->_next == plt->_head) { return 0; } // Guarantee at least one node ListNode* cur = plt->_head->_prev; // cur must not be empty ListNode* prev = cur->_prev; // Find the penultimate node prev->_next = plt->_head; plt->_head->_prev = prev; free(cur); cur = NULL; }
3.6 pins
Define a pointer to the first node, connect the new node with the first node, and change the direction of the four pointers.
void ListPushFront(List* plt, LTDataType x)// Head insertion { assert(plt); ListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x); // Apply for a new node if (plt->_head->_next == plt->_head) { // Chain list is empty, head insert is equivalent to tail insert ListPushBack(&plt, x); return 0; } ListNode* first = plt->_head->_next; // Point to the first node plt->_head->_next = newnode; // Head Node and New Node Connection newnode->_prev = plt->_head; first->_prev = newnode; // First node and new node connection newnode->_next = first; }
3.7 deletions
Define two pointers, point to the first node and the second node respectively, then connect the head node and the second node, release the first node.
void ListPopFront(List* plt)// Header deletion { assert(plt); ListNode* head = plt->_head; if (plt->_head->_next == plt->_head) { // Only Head Node return 0; } ListNode* first = head->_next; // Point to the first node ListNode* second = first->_next; // Point to the second node free(first); // Release the first node head->_next = second; // Connect second->_prev = head; }
3.8 Find Node x
Define a pointer, look it up from the beginning of the node, and find the pointer that points back to the value. Pay attention to the conditions for the end of the cycle.
ListNode* ListFind(List* plt, LTDataType x) // Find node X and return the pointer to node x { assert(plt); ListNode* cur = plt->_head->_next; while (cur != plt->_head) // Termination Conditions { if (cur->_val == x) { return cur; } cur = cur->_next; } return NULL; }
3.9 Insert Nodes Before a Given Position
First, apply for a new node, define a pointer to find the previous node of pos, connect the former node and the new node of pos, and finally connect POS and the new node.
void ListInsert(ListNode* pos, LTDataType x) // Insert node x in front of pos { assert(pos); ListNode* newnode = BuyListNode(x); // Apply for a new node ListNode* prev = pos->_prev; // The previous node of pos prev->_next = newnode; // Connect the previous node and the new node of pos newnode->_prev = prev; pos->_prev = newnode; // Connect pos and new nodes newnode->_next = pos; }
3.10 Delete a given location node
Define two pointers, point to the front and back nodes of pos, connect the front and back nodes, release the POS nodes.
void ListErase(ListNode* pos) // Delete the node of pos location { assert(pos); ListNode* prev = pos->_prev; // pos pioneer ListNode* next = pos->_next; // pos Succession prev->_next = next; // Precursor Connection Succession next->_prev = prev; free(pos); }
3.11 Delete a given value node
Generally defined a pointer, traverse to find the node, call the ListErase function to delete directly; you can also use the ListFind function to find the node, and then call the ListErase function to delete directly.
void ListRemove(List* plt, LTDataType x)// Delete node x { // General methods: //assert(plt); //ListNode* cur = plt->_head->_next; //while (cur != plt->_head) //{ // if (cur->_val == x) // { // ListErase(cur); // return 0; // } //} // More convenient: assert(plt); ListNode* tmp = ListFind(plt, 1); if (tmp) { ListErase(tmp); } }
3.12 Returns bi-directional list size
Define a counter, start counting from the first node, pay attention to the end of the loop condition (not counting the first node).
int ListSize(List* plt)//Size of bidirectional linked list { assert(plt); ListNode* cur = plt->_head->_next; // Start with the first node int count = 0; while (cur != plt->_head) { ++count; cur = cur->_next; } return count; }
3.13 Judging whether a two-way list is empty
Generally, it is judged whether the pointer of the header node points to itself, and if so, the list is empty.
Or you can use the ListSize function to determine the size of the linked list more directly.
int ListEmpty(List* plt)//Judging whether the two-way list is empty, empty is 0, non-empty IS-1 { assert(plt); // General judgment conditions: //if (plt->_head->_next == plt->_head) //{ // return 0; //} //else return -1; // More directly: return ListSize(plt) == 0 ? 0 : -1; }
3.14 Print Two-way Link List
There is no special requirement for the printing format. It's simple and clear.
void ListPrint(List* plt)// Printing { assert(plt); if (plt->_head == NULL) { printf("NULL\n"); return 0; } ListNode* cur = plt->_head->_next; printf("<==>head<==>"); while (cur != plt->_head) { printf("%d<==>", cur->_val); cur = cur->_next; } printf("\n"); }