# 0x00 Preface
Android application reinforcement technology is developed with Android application cracking technology. Reinforcement technology is divided into shell protection and disassembly protection. The mature firms on the market usually use shell protection technology and disassembly technology to reinforce Android applications.
The summary of Android disassembly technology will be discussed in detail in another blog of mine.
http://...
The development of Android shell technology can be divided into the following generations:
The first generation shell, dynamic loading shell, obfuscates and encrypts Dex, so and resources of the client, decrypts them at run time, and loads source APK dynamically by customizing ClassLoader.
Second Generation Shell-Code Extraction Shell: The implementation code of the method in Dex is encrypted and stored in the client side. APK runtime calls the shell's Native method to decrypt the encrypted method in Dex, and then decrypts it after execution.
The third generation shell-code obfuscation shell: instruction transformation, flower instruction obfuscation, instruction expansion, code flow obfuscation, etc.
# 0x01 First Generation Shell
I. Dex and so confusion
1. Code obfuscation
Modify the class name and method name in source code into the form of a, b and c(), so that it can not be easily found/guessed by class name and method name, thus increasing the difficulty of reverse analysis.
2. Compile-time confusion
If APK is compiled using LLVM compiler suite at the time of development, the code can be confused during compilation. It is divided into front-end confusion and IR confusion.
Front-end obfuscation: The obfuscation technique adopted by the compiler front-end in native code analysis
IR obfuscation: A technique for obfuscating the generated intermediate code IR when compiling native code
3. Binary confusion
After APK files are generated, the binary files are extracted, and then the binary files are confused. Typical technology is Dex secondary obfuscation, which is to decompile the generated Dex files and then confuse them. This obfuscates Dex's execution process and strings.
1 //Take string obfuscation as an example
2
3 //Before confusion
4 void methodA()
5 {
6 clz.method1("abc");
7 clz.method3(clz.method2("def"),"ghi");
8 }
9
10 //The disassembly code after code obfuscation using ProGuard may be as follows
11 void methodA()
12 {
13 a.a("abc");
14 a.aaa(a.aa("def"),"ghi");
15 }
16
17 //The disassembly code after code obfuscation using DexGuard may be as follows, b.a() method
18 void methodA()
19 {
20 a.a(b.a("xxxxxxxxx"));
21 a.aaa(a.aa(b.a("yyyyyyyyy")),b.a("zzzzzzzzz"));
22 }
2. Dex Encryption
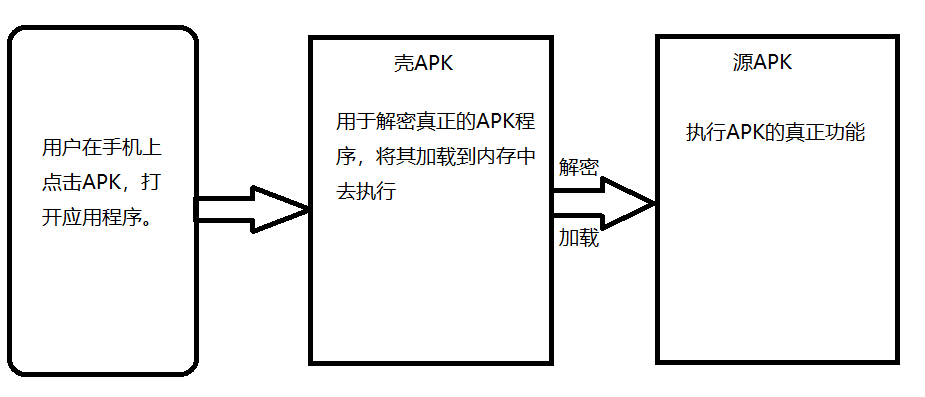
Dex encryption refers to a protection technology that encrypts the DEX files of APK, then decrypts and loads them into memory to execute at run time, so as to prevent the Dex files from being reversed.
The execution process of Dex Encryption APK is as follows:
Reinforcement process:
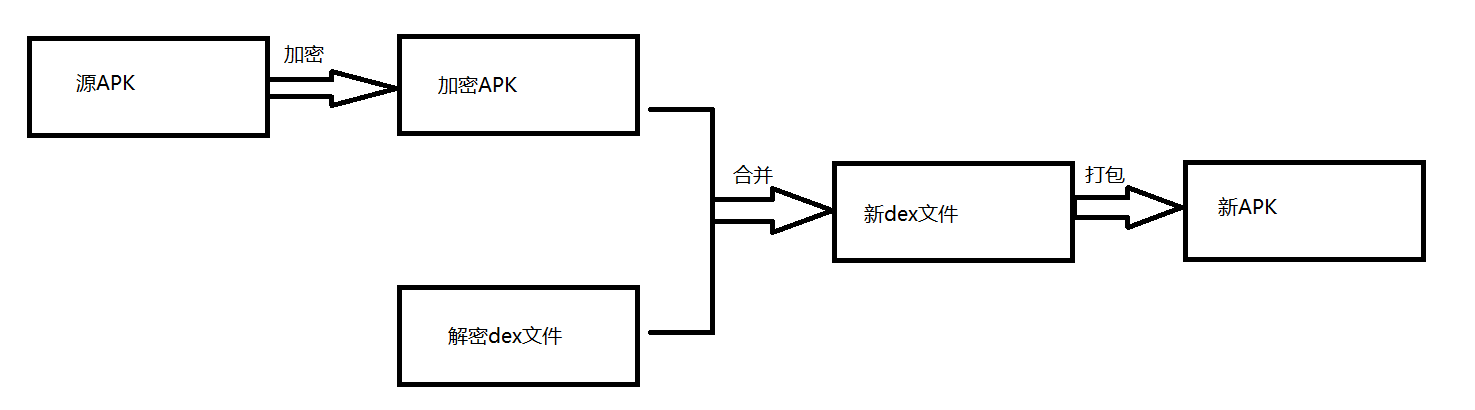
1. Three projects need to be prepared:
(1) Source APK (true APK program)
(2) shell program (Java project, used to encrypt the source APK and merge the encrypted source APK with the dex of the shell program)
(3) Shell program (Android project, used to decrypt encrypted source APK files and load them into memory)
2. The shell program encrypts the source APK into APK files that cannot be read correctly by all operating systems.
3. The classes.dex file of the decrypted APK is extracted from the shell program, and the dex file of the shell program is merged with the encrypted source APK to get a new dex file.
4. Add a 4-bit field at the end of the new dex file to identify the size of the encrypted apk
5. Modify the three header fields of the new dex file: checksum, signature and file_size to ensure the correctness of the new dex file
6. Generate a new classes.dex file, package it, and generate a hardened APK
The flow chart of source APK encryption principle is as follows:
The main logic code analysis of Shell-Adding program:
1 public static void main(String args[]) 2 { 3 try 4 { 5 //---------get files------------------------------------------- 6 //Get the source that needs to be encrypted apk program 7 File payloadSrcFile = new File("xxxx/abc.apk"); 8 System.out.println("SrcAPK size:"+payloadSrcFile.length()); 9 //Acquire shelling(Decrypt)programmatic DEX file,Need to advance the shelling procedure DEX Unzip the file 10 File unshellDexFile = new File("yyyy/classes.dex"); 11 12 //---------Encryption Source apk file---------------------------------------- 13 /* 14 Read apk in binary form and encrypt it into payload Array array 15 readFileBytes Read files in binary form 16 encrpt()Is a custom function for encrypting binary streams 17 */ 18 byte[] payloadArray = encrpt(readFileBytes(payloadSrcFile)); 19 //Reading Shell in Binary Form dex 20 byte[] unshellDexArray = readFileBytes(unshellDexFile); 21 22 //---------merge------------------------------------------------ 23 //***1.Calculate the new Dex Total length of file 24 int payloadLen = payloadArray.length(); //encryption APK Length 25 int unshellDexLen = unshellDexArray.length(); //Shelling Dex Length 26 int totalLen = payloadLen+unshellDexLen=4 //New Dex File length, last+4 For storage payloadLen Valued 27 //***2.Definition New dex file 28 //Define NEW dex Length of file 29 byte[] newDex = new byte[totalLen]; 30 //***3.Start merging 31 //Shell dex Write the contents of the file to the new dex 32 System.arraycopy(unshellDexArray,0,newDex,0,unshellDexLen); 33 //Encrypted source APK Content links at the back 34 /* 35 arraycopy(arr1,x,arr2,y,m)Represents the element that starts arr1 with an index of x, duplicates m elements into arr2, and pastes from the y index of arr2 36 */ 37 System.arraycopy(payloadArray,0,newDex,unshellDexLen,payloadLen); 38 //Finally, the encrypted apk Length recorded in the new dex end of file 39 /* 40 intToByte()Converting int-type data to Byte 41 total It's type int, and newDex is type Byte 42 total It's the shelled dex length + the encrypted apk length + 4, so the payload length is finally written from the total-4 index of newDex 43 A byte is one byte, or eight bits; an int is four bytes, or 32 bits; so the last four represents the four elements written to intToByte (payload Len). 44 */ 45 System.arraycopy(intToByte(payloadLen),0,newDex,totalLen-4,4); 46 47 //---------Modify the new dex Header information of files---------------------------------- 48 //modify file_size field 49 fixFileSizeHeader(newDex); 50 //modify signature field 51 fixSHA1Header(newDex); 52 //modify checksum field 53 fixCheckSumHeader(newDex); 54 55 //---------Generate NEW dex file------------------------------------------ 56 //Define the path and name of the file to be generated and create an empty file 57 String str = "zzzz/classes.dex"; 58 File file = new File(str); 59 if (!file.exists()) 60 { 61 file.createNewFile(); 62 } 63 //Write merged data to a file 64 FileOutputStream localFileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(str); 65 localFileOutputStream.write(newDex); 66 localFileOutputStream.flush(); 67 localFileOutputStream.close(); 68 }catch (Exception e) { 69 e.printStackTrace(); 70 } 71 } 72 73 //Encryption function encrpt()Definition 74 private static byte[] encrpt(byte data[]) 75 { 76 //Encryption algorithm implementation, do not write here 77 return data; 78 }
The principle flow chart of shelling is as follows:
Users implement hardened APP, in fact, they enter the code of the shelled APK. The shelled APK extracts and decrypts the real APK first, but at this time the real APK is not loaded into the memory of the mobile phone. Therefore, it is necessary to extract the real APK decryption and load it into memory before the user interface enters the shell APK at an appropriate time. When is the real APK extracted, decrypted and loaded? The optimal timing is shown in the following analysis:
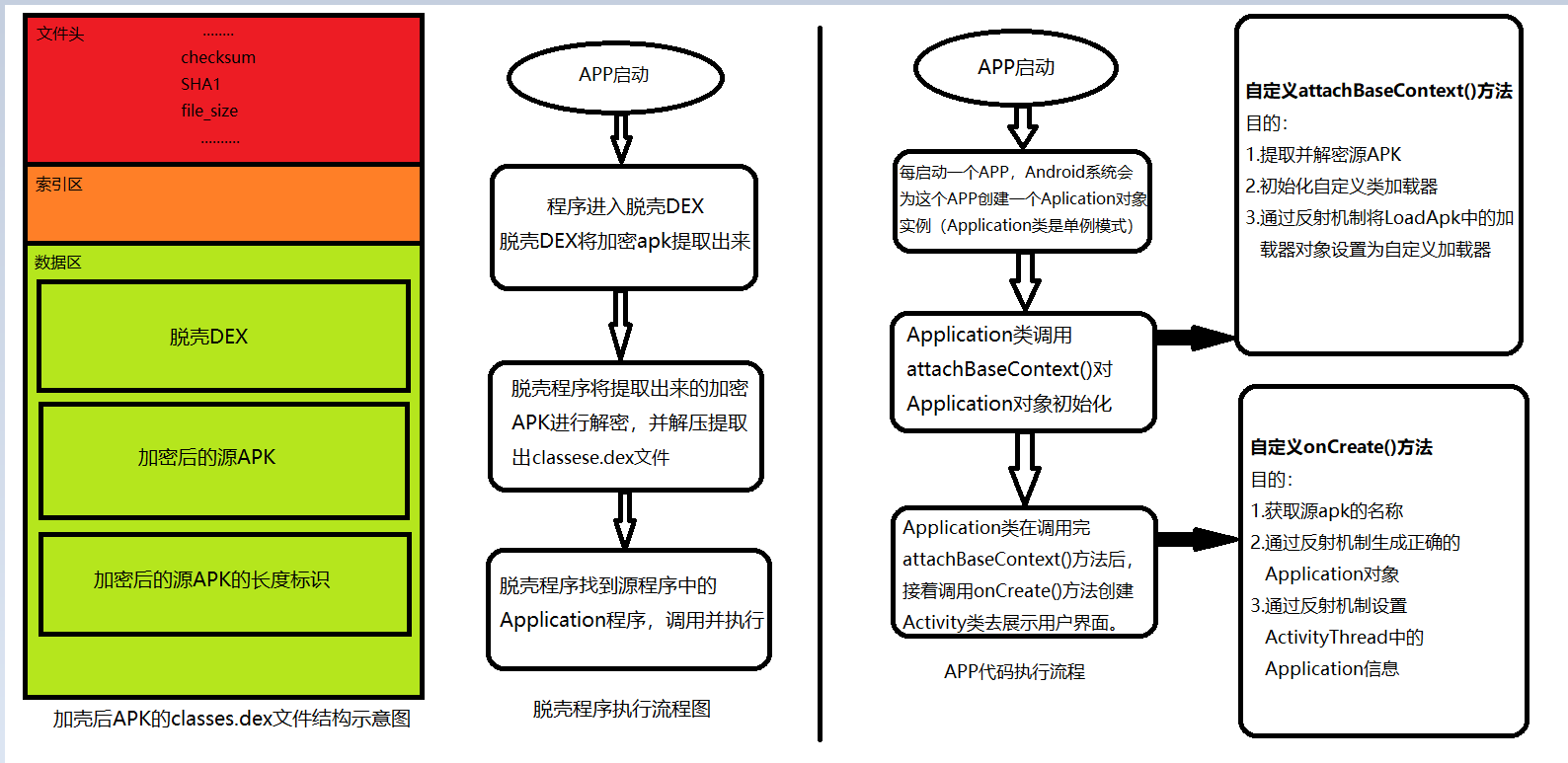
As shown in the figure above,
(1) The best time to extract and decrypt APK is before the Activeness of the shelled APK is pulled up. Activity is pulled up by onCreate() method. Therefore, the source APK should be extracted and decrypted before onCreate() method.
(2) After extracting and decrypting the source APK, we rewrite the onCreate() method of the shelled APK to make it originate from APK.
The main logic code analysis of the shelling program:
1 //********Rewrite attachBaseContext()function*********** 2 protected void attachBaseContext(Context base) 3 { 4 super.attachBaseContext(base); 5 try 6 { 7 //---------Extract Encryption apk--------------------------------------------- 8 //Create two private, writable directories payload_odex and payload_lib 9 File odex = this.getDir("payload_odex",MODE_PRIVATE); //For storage sources APK Of dex file 10 File libs = this.getDir("payload_lib",MODE_PRIVATE); //For storage sources APK Of so file 11 odexPath = odex.getAbsolutePath(); 12 libPath = libs.getAbsolutePath(); 13 apkFileName = odex.getAbsolutePath()+"/abc.apk"; 14 File dexFile = new File(apkFileName); 15 Log.i("demo","apk size:"+dexFile.length()); 16 if (!dexFile.exists()) 17 { 18 //stay payload_odex Under the file directory, create abc.apk Empty files 19 dexFile.createNewFile(); 20 //Read out the whole shell dex file 21 //readDexFileFromApk()The method is attachBaseContext()Method Outside Implementation 22 byte[] dexdata = this.readDexFileFromApk(); 23 //Shelling(Separate encrypted sources apk And decryption),Separation apk Files for dynamic loading 24 //splitPayloadFromDex()The method is attachBaseContext()Method Outside Implementation 25 this.splitPayloadFromDex(dexdata); 26 } 27 28 //---------Load the source after decryption apk program------------------------------------ 29 //Configuring Dynamic Loading Environment 30 //Obtaining the Current through Reflective Mechanisms activity Thread objects 31 Object currentActivityThread = RefInvoke.invokeStaticMethod( 32 "android.app.ActivityThread", 33 "currentActivityThread", 34 new Class[] {}, 35 new Object[] {}); 36 37 //Capturing Shell apk The name of the package 38 String packageName = this.getPackageName(); 39 //Getting and setting the current through reflection APK Various information 40 ArrayMap mPackages = (ArrayMap) RefInvoke.getFieldObject( 41 "android.app.ActivityThread", 42 currentActivityThread, 43 "mPackages"); 44 WeakReference wr = (WeakReference) mPackages.get(packageName); 45 46 //Customize a DexClassLoader Object to load the loaded and decrypted source apk Sum source apk Classes within and C/C++Code 47 DexClassLoader dLoader = new DexClassLoader( 48 apkFileName, 49 odexPath, 50 libPath, 51 (ClassLoader) RefInvoke.getFieldObject( 52 "android.app.LoadedApk", 53 wr.get(), 54 "mClassLoader")); 55 //Put the current process in place DexClassLoader()Set to Shell apk Customized on the previous line DexClassLoader() 56 RefInvoke.setFiedObject( 57 "android.app.LoadedApk", 58 "mClassLoader", 59 wr.get(), 60 dLoader); 61 62 Log.i("demo","classloader:"+dLoader); 63 64 try 65 { 66 Object actObj = dLoader.loadClass("com.example.forceapkobj.MainActivity"); 67 Log.i("demo","actObj:"+actObj); 68 } 69 catch (Exception e) 70 { 71 Log.i("demo","activity:"+Log.getStackTraceString(e)); 72 } 73 }catch (Exception e) 74 { 75 Log.i("demo","error:"+Log.getStackTraceString(e)); 76 e.printStackTrace(); 77 } 78 } 79 80 81 /* 82 *@name :readDexFileFromApk() 83 *@function :Extraction of DEX File Content from Shelling Program 84 *@param :nothing 85 *@throws :IOException 86 *@return :byte[] 87 */ 88 private byte[] readDexFileFromApk() throws IOException 89 { 90 //Define a Byte Type of array object for storage dex Content of the document 91 ByteArrayOutputStream dexByteArrayOutputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); 92 //Define a ZIP Object for decompression APK 93 ZipInputStream localZipInputStream = new ZipInputStream( 94 new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream( 95 this.getApplicationInfo().sourceDir))); 96 97 while (true) 98 { 99 ////Unzip and traverse ZIP file,Read arrays as binary streams arrayOfByte[] 100 ZipEntry localZipEntry = localZipInputStream.getNextEntry(); 101 if (localZipEntry == null) 102 { 103 localZipInputStream.close(); 104 break; 105 } 106 //Find shelling dex file 107 if (localZipEntry.getName().equals("classes.dex")) 108 { 109 110 byte[] arrayOfByte = new byte[1024]; 111 while (true) 112 { 113 int i = localZipInputStream.read(arrayOfByte); 114 if (i == -1) 115 { 116 break; 117 } 118 dexByteArrayOutputStream.write(arrayOfByte,0,i); 119 } 120 } 121 localZipInputStream.closeEntry(); 122 } 123 localZipInputStream.close(); 124 return dexByteArrayOutputStream.toByteArray(); 125 } 126 127 /* 128 *@name :splitPayloadFromDex(byte apkdata[]) 129 *@function :Extract encrypted apk files and so files from dehulled dex files and decrypt them 130 *@param :apkdata -DEX file binary stream to be decrypted 131 *@throws :IOException 132 *@return :nothing 133 */ 134 private void splitPayloadFromDex(byte apkdata[]) throws IOException 135 { 136 //---------Peel off the encryption source APK--------------------------------------------- 137 //Get the whole dex Length of file 138 int ablen = apkdata.length(); 139 //Acquire shelling dex The last four bits of data, i.e. obtaining source encryption APK Length 140 //ablen-4 stay arraycopy()Chinese means from apkdata The penultimate fourth place begins 141 byte[] dexlen = new byte[4]; 142 System.arraycopy(apkdata,ablen-4,dexlen,0,4); 143 144 //Convert the obtained 4-byte length value to a computable binary array type int type 145 ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(dexlen); 146 DataInputStream in = new DataInputStream(bais); 147 int readInt = in.readInt(); 148 System.out.println(Integer.toHexString(readInt)); 149 150 //Define a binary stream array to store the encryption to be extracted apk 151 byte[] newdex = new byte[readInt]; 152 //Encryption apk Save to newdex in 153 /* 154 apkdata Is the data content of the entire dex file 155 ablen Is the length of the entire dex file - 4, that is, the location of the entire dex file from the beginning to the end of the encrypted apk 156 readInt Represents the length of the encrypted apk 157 ablen-4 Re-readInt denotes the position from the beginning of the whole DEX to the end of the shelled dex. 158 */ 159 System.arraycopy(apkdata,ablen-4-readInt,newdex,0,readInt); 160 161 //---------Decrypt Source APK------------------------------------------------------- 162 //decrypt()The function is in splitPayloadFromDex()Extrafunctional Realization 163 newdex = decrypt(newdex); 164 165 //---------Release the decrypted source APK To Disk----------------------------------------- 166 File file = new File(apkFileName); 167 try 168 { 169 FileOutputStream localFileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(file); 170 localFileOutputStream.write(newdex); 171 localFileOutputStream.close(); 172 }catch (IOException e) 173 { 174 throw new RuntimeException(localIOException); 175 } 176 177 //---------Analyse the source of release APK---------------------------------------------- 178 //Define a ZIP object 179 ZipInputStream localZipInputStream = new ZipInputStream( 180 new BufferedInputStream(new FileOutputStream(file))); 181 while (true) 182 { 183 //Unzip and traverse ZIP package 184 ZipEntry localZipEntry = localZipInputStream.getNextEntry(); 185 if (localZipInputStream == null) 186 { 187 localZipInputStream.close(); 188 break; 189 } 190 //Extraction APK Medium so File, and release it to the sheller program that was initially created on disk payload_lib To go in the catalogue 191 String name = localZipEntry.getName(); 192 if (name.startWith("lib/") && name.endwith(".so")) //Verify whether the traversed file is so file 193 { 194 File storeFile = new File(libPath+"/"+name.substring(name.lastIndexOf('/'))); 195 storeFile.createNewFile(); 196 FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(storeFile); 197 byte[] arrayOfByte = new byte[1024]; 198 while (true) 199 { 200 int i = localZipInputStream.read(arrayOfByte); 201 if (i == -1) 202 { 203 break; 204 } 205 fos.write(arrayOfByte,0,i); 206 } 207 fos.flush(); 208 fos.close(); 209 } 210 localZipInputStream.closeEntry(); 211 } 212 localZipInputStream.close(); 213 } 214 215 /* 216 *@name :decrypt(byte srcdata[]) 217 *@function :Decrypt the encrypted apk file 218 *@param :srcdata -Binary stream of apk file to be decrypted 219 *@throws :No byte 220 *@return :srcdata -byte[]type 221 */ 222 private byte[] decrypt(byte[] srcdata) 223 { 224 //Decryption algorithm, according to the encryption algorithm to write the corresponding decryption process 225 return srcdata; 226 } 227 228 229 //**********Rewrite onCreate()Method*********** 230 public void onCreate () 231 { 232 //To be continued 233 }
# 0x02 Second Generation Shell
Updating...
# 3rd Generation Shell 0x03
Updating...