Using IDEA, Myeclipse
Write service interface HelloService 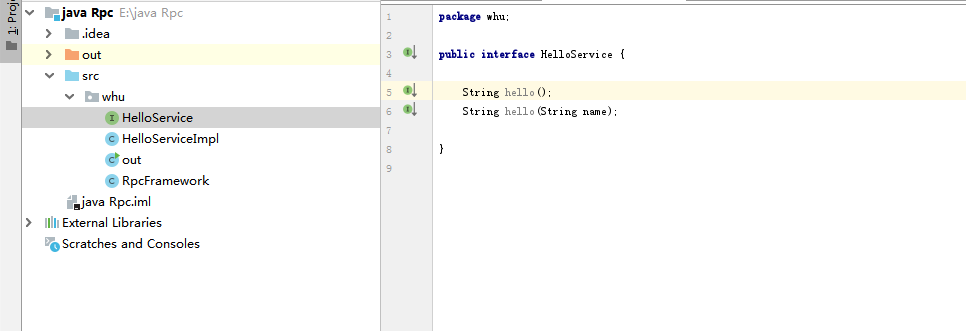
Server implementation class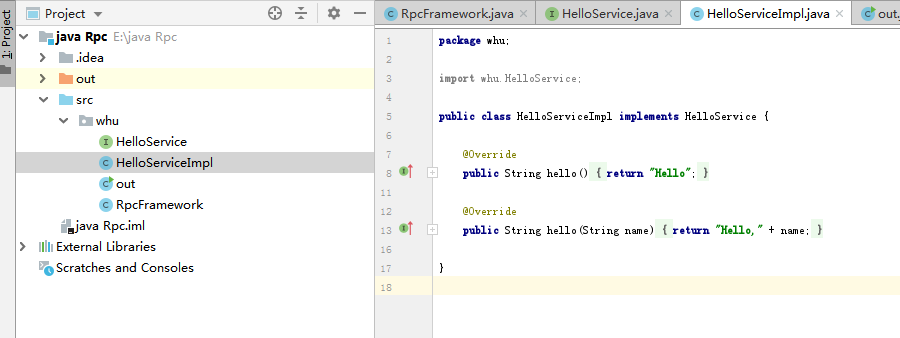
Write the calling class of the server
package whu;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
public class RpcFramework {
//Registration start method
public static void export(Object service, Class interfaceClazz, int port) throws Exception {
if (service == null) {
throw new IllegalAccessException("service instance == null");
}
if (port < 0 || port > 65535) {
throw new IllegalAccessException("Invalid port " + port);
}
System.out.println("Export service " + service.getClass().getName() + " on port " + port);
//Server socket
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(port);
//It's the same with when (true) when the loop reaches constant listening
for (;;) {
final Socket socket = server.accept();//Block waiting for client connection
try {
new Thread(new Runnable() {//Multithreading
@Override
public void run() {
try {
try {
//Get the stream object from the client
ObjectInputStream input = new ObjectInputStream(socket.getInputStream());
try {
String interfaceName = input.readUTF();//Get the name of the interface to be called from the client
String methodName = input.readUTF();//Method to be called from client
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = (Class<?>[]) input.readObject();//Parameter type of the method to be called from the client
Object[] arguments = (Object[]) input.readObject();//Parameters of the calling method
ObjectOutputStream output = new ObjectOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());//Return the reserved stream object of the client
try {
//Judge whether the interface the client needs to call exists in the server
if (!interfaceName.equals(interfaceClazz.getName())) {
throw new IllegalAccessException("Interface wrong, export:" + interfaceClazz
+ " refer:" + interfaceName);
}
Method method = service.getClass().getMethod(methodName, parameterTypes);//The method of obtaining the server by reflection
Object result = method.invoke(service, arguments);//Execute server method
output.writeObject(result);//Return to client
} catch (Throwable t) {
output.writeObject(t);
} finally {
output.close();
}
} finally {
input.close();
}
} finally {
socket.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();//Open thread
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
I'm going to pass in an object directly. You can also write a map to register multiple objects
Server startup class
package whu;
public class out {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
HelloService service = new HelloServiceImpl();
RpcFramework.export(service, HelloService.class, 9000);
}
}
Client call class
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.net.Socket;
public class Rpcfrowd {
/**
* @param args
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")//Shielded yellow line
public static <T> T refer(final Class<T> interfaceClass, final String host, final int port) throws Exception {
//System.out.println("Get remote service " + interfaceClass.getName() + " from server " + host + ":" + port);
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(interfaceClass.getClassLoader(), new Class<?>[] { interfaceClass },
new InvocationHandler() {//jdk dynamic agent
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Socket socket = new Socket(host, port);//Set up the ip and port of the incoming server of the client socket
System.out.println("socket adopt");
try {
ObjectOutputStream output = new ObjectOutputStream(socket.getOutputStream());//Write stream object to server
try {
output.writeUTF(interfaceClass.getName());//Interface name to call
output.writeUTF(method.getName());//Method name to call
output.writeObject(method.getParameterTypes());//Parameter type to call
output.writeObject(args);//Parameters to call
System.out.println("Send successfully");
ObjectInputStream input = new ObjectInputStream(socket.getInputStream());//Receive the return information of the server
try {
Object result = input.readObject();//Receive the return information of the server
System.out.println("Successful reception"+result);
if (result instanceof Throwable) {
throw (Throwable) result;
}
return result;//Return
} finally {
input.close();
}
} finally {
output.close();
}
} finally {
socket.close();
}
}
});
}
}
Note that the first return is to return the generated proxy class object and the second is to return the return value of the calling method
Client startup class
import whu.HelloService;
public class clid {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
HelloService service = (HelloService)Rpcfrowd.refer(Class.forName("whu.HelloService"), "127.0.0.1", 9000);
String result = service.hello("rod---");
System.out.println(result);
}
}
Run server startup class
Run client startup class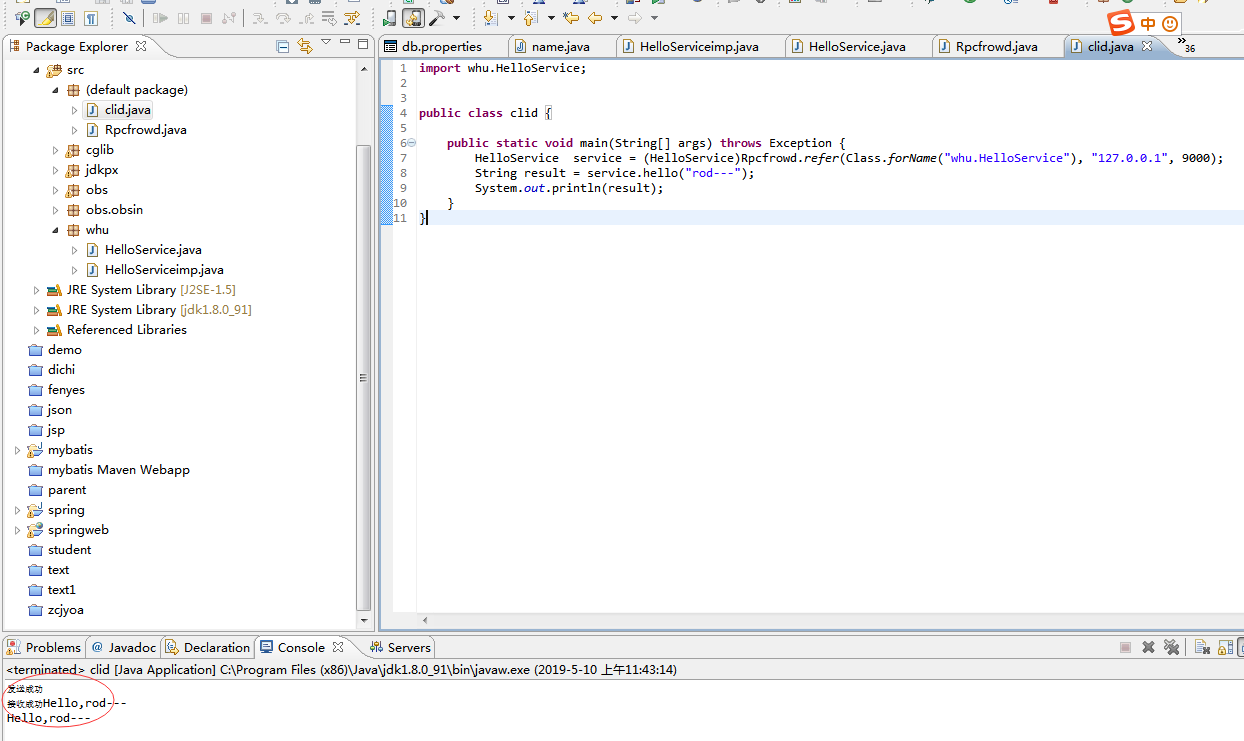
A simple rpc remote call is implemented. Here, I mentioned that the server needs an interface and the implementation class client only needs an interface