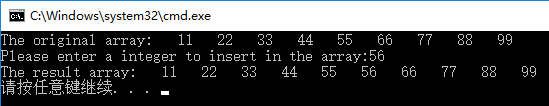
1. Insert a number into an array that has been arranged in ascending order. After inserting, the array elements are still arranged in ascending order
#include<stdio.h>
#define N 10
void fun(int *a)
{
int number,i;
printf("Please enter a integer to insert in the array:");
scanf("%d", &number);
for (i = N - 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
if (number <= *(a + i))
{
*(a + i + 1) = *(a + i);
}
else
{
*(a + i + 1) = number;
break;
}
}
if (number < *a)
{
*a = number;
}
printf("The result array:");
for (i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
printf("%5d", *(a + i));
}
printf("\n");
}
void main()
{
int number;
int i;
int a[N] = { 11,22,33,44,55,66,77,88,99 };
printf("The original array:");
for (i = 0; i < N-1; i++)
{
printf("%5d", *(a+i));
}
printf("\n");
fun(a);
}
2. Function comb(char *a,char *b) reverses string a, and then appends string B at the end
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
void comb(char *a, char *b)
{
int i, j;
int len = strlen(a);
char c;
for (i = 0; i < len / 2; i++)
{
c = *(a + i);
*(a + i) = *(a + len - i - 1);
*(a + len - i - 1) = c;
}
*(a + len++) = ' ';
j = 0;
while (*(a + len + j) = *(b + j++));
}
void main()
{
char a[100] = "margorP C";
char b[] = "Design";
comb(a, b);
printf("%s\n", a);
}
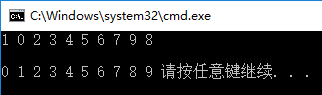
3. Input 10 elements of one-dimensional array, exchange with a[9] the largest, exchange with a[0] the smallest, and output 10 elements of array
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
void input(int number[])
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &number[i]);
}
}
void max_min(int array[])
{
int *max, *min;
int *p, *arr_end;
arr_end = array + 10;
max = min = array;
for (p = array + 1; p < arr_end; p++) //The address p points to array[10] after the for loop ends
{
if(*p>*max)
{
max = p;
}
else if(*p<*min)
{
min = p;
}
}
*p = array[0]; //Exchange with array[10]
array[0] = *min;
*min = *p;
*p = array[9];
array[9] = *max;
*max = *p;
}
void output(int array[])
{
int *p;
for (p = array; p < array + 10; p++)
{
printf("%d ",*p);
}
}
void main()
{
int number[11];
input(number);
printf("\n");
max_min(number);
output(number);
}
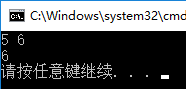
4. Output the larger number of two integers, which are input by keyboard
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
void main()
{
int *p1, *p2;
p1 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int));
p2 = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int));
scanf("%d%d", p1, p2);
if (*p2 > *p1)
{
*p1 = *p2;
}
free(p2);
printf("%d\n", *p1);
free(p1);
}
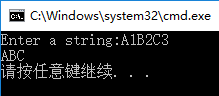
5. Delete the numeric characters in the string
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
void fun(char *s)
{
char *p = s;
while (*p)
{
if ((*p >= '0') && (*p <= '9'))
{
p++;
}
else
{
*(s++) = *(p++);
}
}
*s = '\0';
}
void main()
{
char item[100];
printf("Enter a string:");
gets_s(item);
fun(item);
printf("%s\n", item);
}
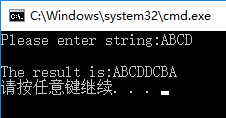
6. Connect the positive and negative order of the string indicated by s to form a new string and put it in the array indicated by t
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
void fun(char *s,char *t)
{
int i, d;
d = strlen(s);
for (int i = 0; i < d; i++)
{
t[i] = s[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < d; i++)
{
t[i + d] = s[d - 1 - i];
}
t[2 * d] = '\0';
}
void main()
{
char s[100], t[100];
printf("Please enter string:");
scanf("%s", s);
fun(s, t);
printf("\nThe result is:%s\n", t);
}
7. Receive a string from the keyboard, and sort it from small to large, and delete the duplicate characters
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
void main()
{
char str[100], *p, *q, *r, c;
printf("Input string:");
gets_s(str);
for (p = str; *p; p++)
{
for (q = r = p; *q; q++)
{
if (*r > *q)
{
r = q;
}
}
if (r != p)
{
c = *r;
*r = *p;
*p = c;
}
}
for (p = str; *p;p++)
{
for (q = p+1 ; *p == *q;)
{
strcpy(p, q); //After using strcpy, q points to the address of the next string element, so the for loop above does not write q++
}
}
printf("Result string:%s\n", str);
}
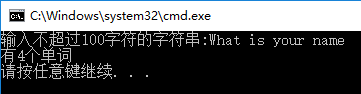
8. Count the number of words in the string
#include<stdio.h>
int wordCount(char *s)
{
int num = 0,i,word=0;
while (*s != '\0')
{
if (*s == ' ')
{
word = 0;
}
else if (word == 0)
{
word = 1;
num++;
}
s++;
}
return(num);
}
void main()
{
char str[101];
int wordnum;
printf("Enter a string of no more than 100 characters:");
gets_s(str);
wordnum = wordCount(str);
printf("Yes%d Word\n", wordnum);
}
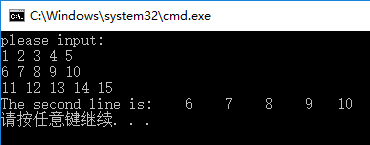
9. Output the second row element of a two-dimensional array with three rows and five columns
#include<stdio.h>
void main()
{
int a[3][5],i,j;
printf("please input:\n");
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
scanf("%d", *(a + i) + j);
}
}
printf("The second line is:");
for (j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
printf("%5d", *(*(a + 1) + j));
}
printf("\n");
}