The solution to the unstable data reading of ESP8266 module by Arduino using soft serial port
In this article, I found that Arduino received unstable data when ESP8266 sent data to Arduino when I was doing serial communication between ESP8266 and Arduino, which puzzled me for a long time. Later, I found out the reason after reading an article. When Arduino used soft serial port to receive data, if the baud rate was high, the data reception would be unstable. I summarized the following two aspects I hope you can solve your doubts.
There will be a lot of garbled code when the valid data is not received, as shown in the figure: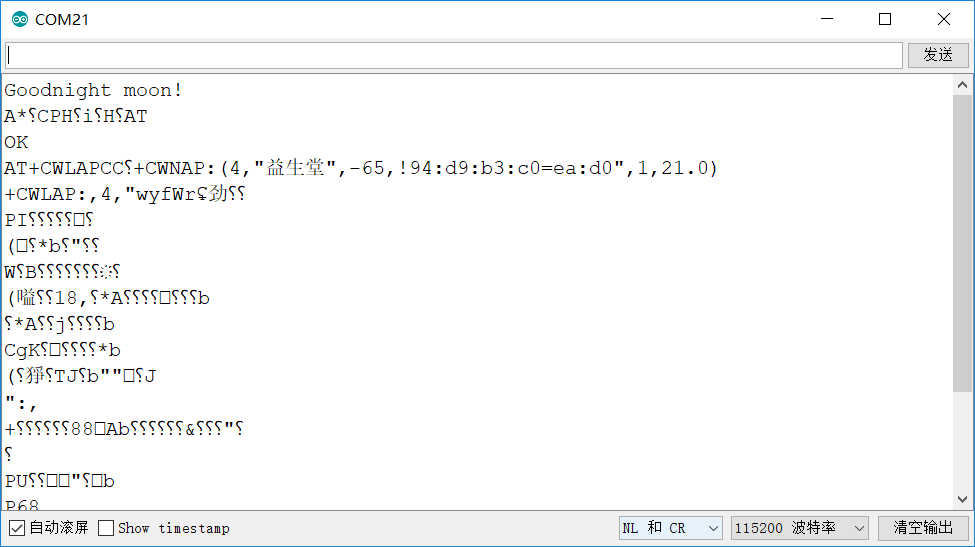
Method 1: replace Arduino board model
This is the simplest and most brainless solution to replace Arduino UNO with ArduinoMega 2560
Because the arduinoMega 2560 has four hard serial ports, the TX1 and RX1 serial ports can perfectly solve the problem that the soft serial port cannot stably receive data
| Arduino | ESP8266 |
|---|---|
| TX1 | RX |
| RX1 | TX |
| 3.3V | VCC |
| 3.3V | CH_PD |
| GND | GND |
Here's the procedure
void setup() {
// Open serial communications and wait for port to open:
Serial.begin(115200);
while (!Serial)
{
; // wait for serial port to connect. Needed for native USB port only
}
while(Serial.read()>=0){} //Clear serial cache
Serial.println("Goodnight moon!"); // set the data rate for the SoftwareSerial port
Serial1.begin(115200);
Serial1.println("AT");
}
void loop() { // run over and over
if (Serial1.available()) //Judge whether serial port 1 receives data (here serial port 1 refers to TX1 and RX1)
{
Serial.write(Serial1.read()); //Send the data read by serial port 1 to serial port 0 (serial port 0 refers to RX0)
}
if (Serial.available()) //Judge whether serial port 0 receives data
{
Serial1.write(Serial.read()); //Send the data read by serial port 0 to serial port 1
}
}
After sending AT+CWJAP?, you can receive the current hotspot information completely
Method two: reduce the baud rate of ESP8266
This method is to reduce the baud rate of ESP8266 through USB-TTL, so that the soft serial port can receive stable information
I'm not going to go over how to reduce baud rate. Please refer to the link Detection of WIFI signal strength with Arduino and esp8266
Just change the sending mode in the serial port monitor to at + ciobaud < 9600 > and then click send
The Arduino program is as follows
void setup() {
// Open serial communications and wait for port to open:
Serial.begin(9600);
while (!Serial)
{
; // wait for serial port to connect. Needed for native USB port only
}
while(Serial.read()>=0){} //Clear serial cache
Serial.println("Goodnight moon!"); // set the data rate for the SoftwareSerial port
Serial1.begin(9600);
Serial1.println("AT");
}
void loop() { // run over and over
if (Serial1.available()) //Judge whether serial port 1 receives data (here serial port 1 refers to TX1 and RX1)
{
Serial.write(Serial1.read()); //Send the data read by serial port 1 to serial port 0 (serial port 0 refers to RX0)
}
if (Serial.available()) //Judge whether serial port 0 receives data
{
Serial1.write(Serial.read()); //Send the data read by serial port 0 to serial port 1
}
}
Open the serial port monitor, change the baud rate to 9600, and the format to NL and CR
Then input AT in the serial monitor and see that the serial interface returns OK
The above is my foolish opinion. If there is something wrong, please correct it
If you don't understand, you can chat with me in person. QQ: 1149484183

