Getting to know JDBC
1, JDBC concept
jdbc English full name: java database connectivity is a set of specifications for Java to access database, which can be understood as a set of classes and interfaces provided by java to connect database
The relationship between jdbc and database driver:
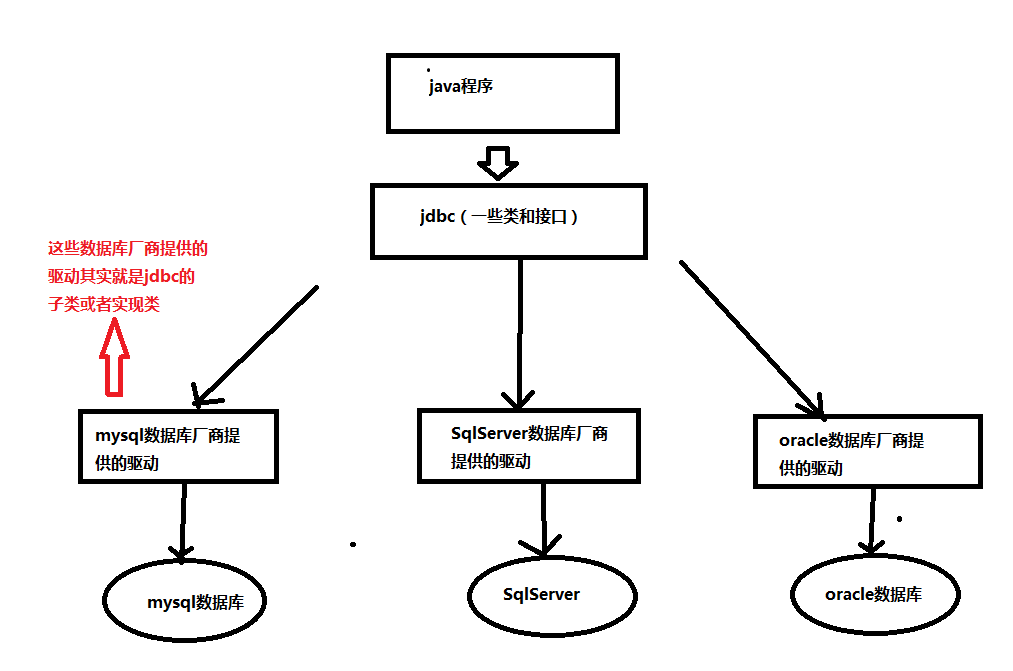
2, jdbc easy to use
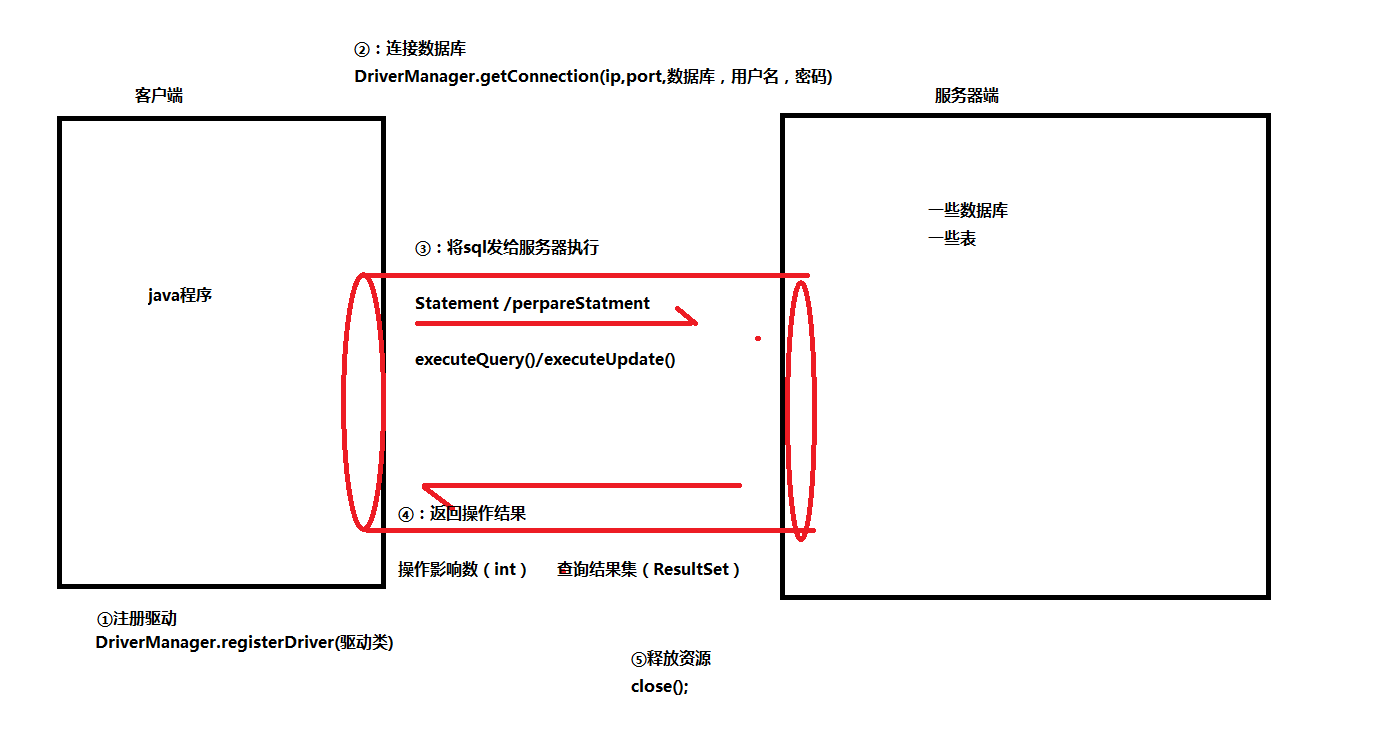
Usage process: (the driver jar needs to be imported before use)
①: Registration driver
②: connect to database
③: obtain the execution platform of sql statements
④: execute sql statement
⑤: treatment results
⑥: release resources
Execution flow chart:
Code implementation (data addition, deletion and modification):
1 public class Demo13 { 2 public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception { 3 //1.Registration driver 4 /* 5 * Because looking at the Driver source code, we found that the Driver has been registered in the static code block of this class, so we don't need to register again 6 * Note: after jdk1.6, you can omit the step of registration driver and do not write the system to automatically register 7 * Paste the source code: 8 * static { 9 * try { 10 * java.sql.DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver()); 11 * } catch (SQLException E) { 12 * throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!"); 13 * } 14 * } 15 * 16 * 17 */ 18 //DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver()); 19 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); 20 21 22 //2.Connect to database 23 /* 24 * Parameter 1: fixed format of connecting ip port database name 25 * Parameter 2: database user name 26 * Parameter 3: database password 27 */ 28 Connection con = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb","root","root"); 29 //3.Get sql Statement execution platform 30 Statement stat= con.createStatement(); 31 //4.implement sql Sentence 32 /* 33 * executeUpdate()Method is used to add, delete and modify statements 34 * Parameters are sql statements 35 * The return value is of type int. several statements were executed successfully 36 */ 37 int result= stat.executeUpdate("insert into car values(null,'BMW')"); 38 //5.Processing results 39 /* 40 * The processing of the result here is actually to see the business logic. Generally, it is to judge whether the statement is executed successfully or not 41 */ 42 if(result>0){ 43 System.out.println("Execution successful"); 44 }else{ 45 System.out.println("Execution failed"); 46 } 47 //6.Release resources 48 stat.close(); 49 con.close(); 50 } 51 52 }
Here is the code for the query operation:
1 public class Demo03JDBC { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException { 3 // 1:Registration driver 4 Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"); 5 // 2:Get connection to server 6 Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/day04db", "root", "123"); 7 // 3:Send to server sql instructions 8 // 3.1 Obtain Statement Implementation class object of interface 9 Statement stat = conn.createStatement(); 10 // 3.2 implement sql (Query data) 11 ResultSet rs = stat.executeQuery("select * from product"); 12 13 // 4:Process the returned result set(Know column name and type) 14 /* 15 while (rs.next()) {// Determine whether there is next line of data 16 int cid = rs.getInt("cid"); // Take out the cid column 17 String cname = rs.getString("cname"); // Take out the came column 18 System.out.println(cid + "\t" + cname); 19 } 20 */ 21 //Process the returned result set(Don't know column name,Know the type of column):Get by column index 22 /* 23 while (rs.next()) {// Determine whether there is next line of data 24 int cid = rs.getInt(1); // Take out the first column 25 String cname = rs.getString(2); // Take out the second column 26 System.out.println(cid + "\t" + cname); 27 } 28 */ 29 //Process the returned result set(Don't know column name,Don't know the type of column):Get by column index 30 /* 31 while (rs.next()) {// Determine whether there is next line of data 32 Object obj1 = rs.getObject(1); 33 Object obj2 = rs.getObject(2); 34 System.out.println(obj1 +"\t" + obj2); 35 } 36 */ 37 //Process the returned result set(Don't know column name,Don't know the type of column,Don't know how many columns):Get by column index 38 ResultSetMetaData metaData = rs.getMetaData(); //Get the raw data of the table 39 //Get number of columns 40 int count = metaData.getColumnCount(); 41 while(rs.next()){ //13 second 42 for (int i = 1; i <=count; i++) { //4 second 43 Object obj = rs.getObject(i); 44 System.out.print(obj+"\t"); 45 } 46 System.out.println(); 47 } 48 49 // 5:Release resources 50 rs.close(); 51 stat.close(); 52 conn.close(); 53 } 54 }
Simple package of jdbc tool class: (mainly to realize the idea)
1 /* 2 * This file is used to encapsulate the common functions of JDBC: 3 * 4 * 1:Package driver registration 5 * 2:Encapsulate the connection to the database 6 * 3:Release of encapsulated resources 7 * 8 * JDK1.6 After that, Java automatically registers the driver 9 */ 10 public class MyJDBCUtils { 11 private static String classDriverName = null; 12 private static String url = null; 13 private static String username = null; 14 private static String password = null; 15 // 1:Package driver registration 16 /* 17 * Since the driver's registration only needs to be executed once, the code can be encapsulated in a static code block 18 * Since Properties only need to be parsed once, the parsed code is still placed in a static code block 19 */ 20 static { 21 try { 22 //1:Establish Properties object 23 Properties prop = new Properties(); 24 //2:Read data from file to collection 25 prop.load(new FileInputStream("jdbc.properties")); 26 //3:Get data for collection 27 classDriverName = prop.getProperty("driverClassName"); 28 url = prop.getProperty("url"); 29 username = prop.getProperty("username"); 30 password = prop.getProperty("password"); 31 32 33 Class.forName(classDriverName); 34 } catch (Exception e) { 35 e.printStackTrace(); 36 } 37 } 38 39 // 2:Encapsulate the connection to the database 40 public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException { 41 Connection conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password); 42 return conn; 43 } 44 45 //Encapsulation method: processing result set 46 public static void printResultSet(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException{ 47 ResultSetMetaData metaData = rs.getMetaData(); 48 int count = metaData.getColumnCount(); 49 50 while(rs.next()){ 51 for (int i = 1; i <= count; i++) { 52 Object obj = rs.getObject(i); 53 System.out.print(obj+"\t"); 54 } 55 System.out.println(); 56 } 57 58 } 59 60 61 // 3:Release of encapsulated resources null stat conn 62 public static void closeAll(ResultSet rs, Statement stat, Connection conn) { 63 if (rs != null) { 64 try { 65 rs.close(); 66 } catch (SQLException e) { 67 e.printStackTrace(); 68 } 69 } 70 if (stat != null) { 71 try { 72 stat.close(); 73 } catch (SQLException e) { 74 e.printStackTrace(); 75 } 76 } 77 if (conn != null) { 78 try { 79 conn.close(); 80 } catch (SQLException e) { 81 e.printStackTrace(); 82 } 83 } 84 } 85 }