UDP-based GUI Simple Chat Room
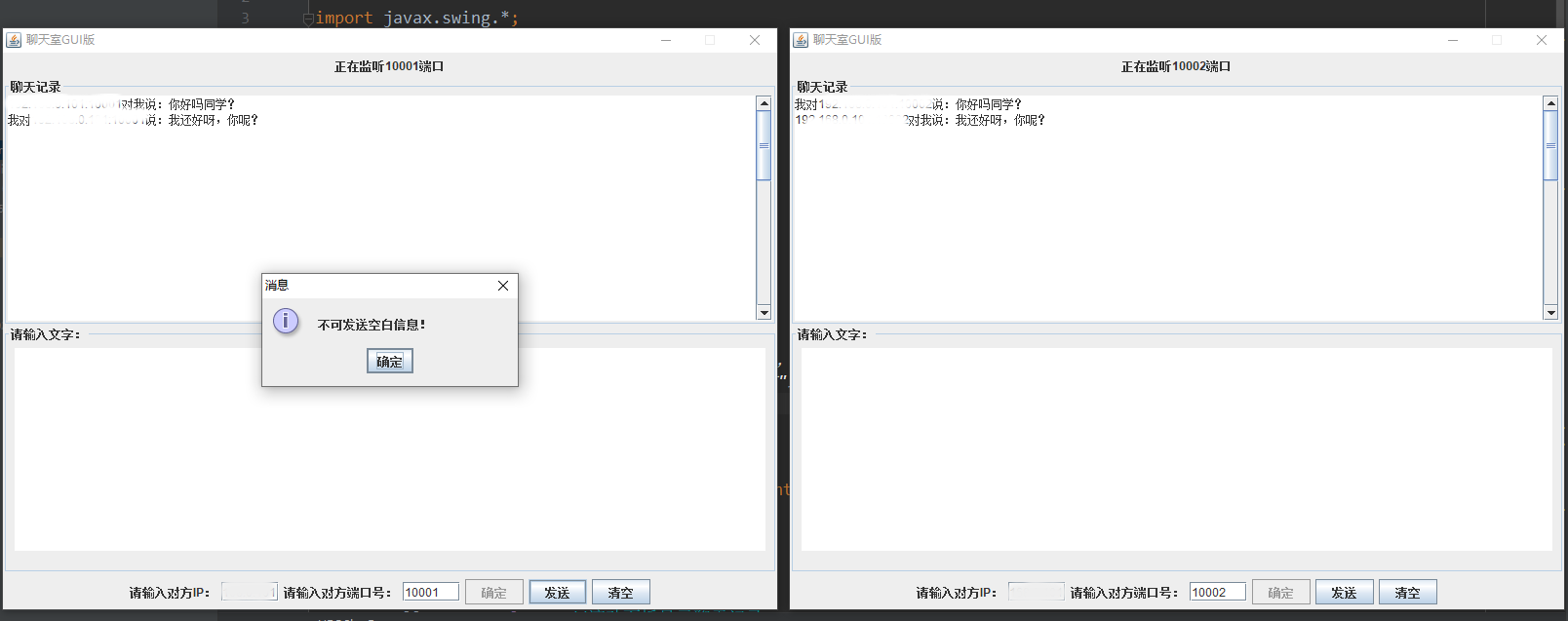
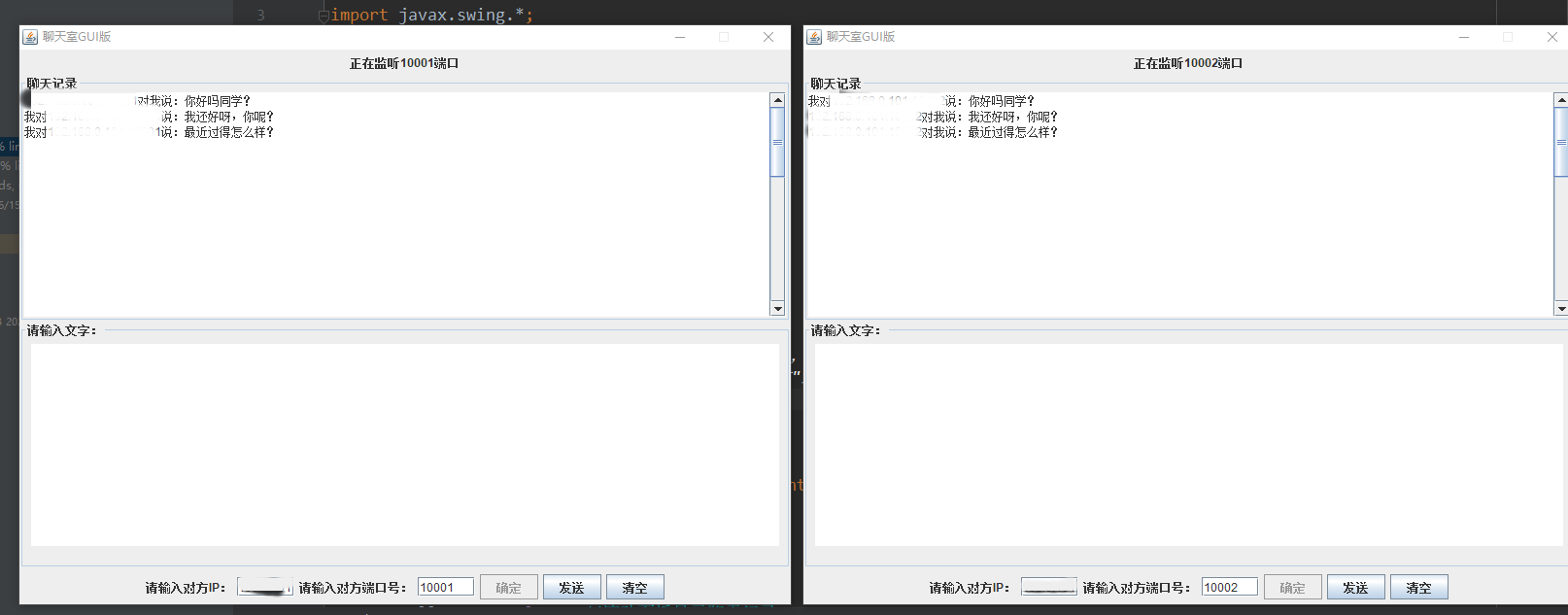
1. Effects
2. Project Development
All classes, methods, and internal classes used in this program:
- public class UDPChat extends JFrame{};
- public class UDPChatFace extends JPanel implements ActionListener{}:
- public void init(){};
- private void sendMessage(byte[] data){};
- private void send(){};
- private class Receive extends Thread{};
- public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {};
2.1. Project Description
Write a simple chat room with GUI interface based on UDP protocol
Develop software: IDEA
2.2. Project ideas
UDP protocol is used to transmit and receive information. Because chat rooms belong to instant messaging, they must receive and send at the same time. Therefore, multi-threading can be considered to accomplish this purpose.
2.3. Project involves knowledge points
- GUI interface knowledge
- UDP Protocol
- Multithreaded
2.4, UDP communication protocol
- Advantages: fast transmission, high security
Reason: Unlike TCP's three-time handshake protocol, UDP is a stateless transport protocol, so data transfer is very fast; because there are no TCP's confirmation mechanism, three-time handshake mechanism and other mechanisms, it is relatively safe, but not absolutely secure. - Disadvantages: unreliable, responsible for sending only, not responsible for "sending" to
- Suitable for high speed and low quality data transmission, such as video, communication, games, etc.
2.5, GUI interface design
Components used: JPanel, JScrollPane, JLabel, JTextField, JTextArea, JButton
public class UDPChatFace extends JPanel implements ActionListener { //Create variable JPanel panel_1; JPanel panel_2; JPanel panel_3; JScrollPane panel_2_1;//Scroll panel to display chat records JPanel panel_2_2; JLabel label1;//Monitor JLabel label2;//ip JLabel label3;//port JTextField textField_ip;//ip input JTextField textField_port;//Port Number Input JTextArea textArea_history;//Chat Log Text Field JTextArea textArea_message;//Input Text Information Text Field JButton button_concern; JButton button_send; JButton button_clear; //port settings //Generally set above 8000, most of the port numbers below 8000 are occupied private int localPort = 10001;//Local Port private int otherPort = 10002;//Opposite port private String ip; String message;//Input Box Information private DatagramSocket socket; public UDPChatFace(){ init(); } public void init(){ //add component panel_1 = new JPanel(); panel_2 = new JPanel(); panel_3 = new JPanel(); textArea_history = new JTextArea(40,68);//Set the size of the chat log box textArea_history.setEditable(false);//Set chat log box not to be entered textArea_message = new JTextArea(13,70); textArea_message.addKeyListener(new KeyAdapter() { @Override public void keyPressed(KeyEvent e) { //Keyboard listens for events and functions of pressing return message after text box input if (e.getKeyCode() == KeyEvent.VK_ENTER){ if (textArea_message.getText().equals("")){ JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(panel_1,"No blank messages can be sent!"); //Popup return; }else { send(); //send message } } } }); panel_2_1 = new JScrollPane(textArea_history); //Add the Chat Log input box to the scrolling panel panel_2_1.setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder("Chat Log"));//Border Settings panel_2_2 = new JPanel(); panel_2_2.setBorder(BorderFactory.createTitledBorder("Please enter text:"));//Border Settings String str = "Is listening****port";//Label label1 = new JLabel(str,JLabel.RIGHT);//Align right label2 = new JLabel("Please enter the other party IP: ",JLabel.RIGHT); label3 = new JLabel("Please enter the port number of the other party:",JLabel.RIGHT); textField_ip = new JTextField(5); textField_port = new JTextField(5); //Binding Events button_send = new JButton("Send out"); button_send.addActionListener(this); button_clear = new JButton("empty"); button_clear.addActionListener(this); button_concern = new JButton("Determine"); button_concern.addActionListener(this); setLayout(new BorderLayout()); add(panel_1,BorderLayout.NORTH); add(panel_2,BorderLayout.CENTER); add(panel_3,BorderLayout.SOUTH); panel_1.setLayout(new FlowLayout()); panel_1.add(label1); panel_2.setLayout(new GridLayout(2,1)); panel_2.add(panel_2_1); panel_2.add(panel_2_2); panel_2_2.add(textArea_message); panel_3.setLayout(new FlowLayout()); panel_3.add(label2); panel_3.add(textField_ip); panel_3.add(label3); panel_3.add(textField_port); panel_3.add(button_concern); panel_3.add(button_send); panel_3.add(button_clear); ...... }
2.6. Functional implementation
2.6.1,'OK'button
Function: Enter the IP and port number of the other party, establish chat, and start the listening thread to receive information at the same time
//Listen for events @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { Object source = e.getSource(); if (button_send.equals(source)){//Send out ...... }else if (button_clear.equals(source)){//empty ...... }else if (button_concern.equals(source)){//Determine if (textField_ip.getText().equals("") || textField_port.getText().equals("")){ JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this,"Incorrect input IP And port number!");//Popup }else { label1.setText("Is listening" + textField_port.getText() + "port"); ip = textField_ip.getText(); otherPort = Integer.parseInt(textField_port.getText()); if (otherPort == 10002){ localPort = 10001; } else { localPort = 10002; } new Receive().start();//Start listening thread System.out.println(localPort); System.out.println(otherPort); button_concern.setEnabled(false);//Settings button can no longer be clicked } } }
2.6.2,'Empty'button
Function: to empty chat records
//Listen for events @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { Object source = e.getSource(); if (button_send.equals(source)){//Send out ...... }else if (button_clear.equals(source)){//empty textArea_history.setText(""); }else if (button_concern.equals(source)){//Determine ...... } }
2.6.3,'Send'button
Function: Implement data sending
- Bind Listen Events
//Listen for events @Override public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) { Object source = e.getSource(); if (button_send.equals(source)){//Send out if (textArea_message.getText().equals("")){ JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this,"No blank messages can be sent!"); }else { send(); } }else if (button_clear.equals(source)){//empty ...... }else if (button_concern.equals(source)){//Determine ...... }
- Sending of data
Transfer data using UDP protocol
public void init(){ ...... //Save space and prevent new objects from being sent each time try { socket = new DatagramSocket(); } catch (SocketException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //For sending messages in text boxes private void sendMessage(byte[] data){ System.out.println("Message sent successfully"); try { DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(data, data.length, InetAddress.getByName(ip), localPort); socket.send(packet); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } //send message private void send(){ message = textArea_message.getText(); byte[] data = message.getBytes(); sendMessage(data); String str = "I am right" + ip + ":" + otherPort + "Say:" + message + '\n'; textArea_history.append(str);//Add to Chat Log Box textArea_message.setText("");//Empty Input Information Box }
2.6.4,'Receive'Threads
Function: Synchronize sending and receiving information
//Programs need to receive and send synchronously when running, so multithreading should be used, with a new thread for receiving messages private class Receive extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { System.out.println("Listening is running"); DatagramPacket packet = null; try { socket = new DatagramSocket(otherPort); System.out.println("Monitor" + otherPort); byte[] data = new byte[1024*4]; packet = new DatagramPacket(data, data.length); while (true){ socket.receive(packet); byte[] bytes = packet.getData(); String message = new String(bytes,0,bytes.length); String str = ip + ":" + localPort + "Tell me:" + message + '\n'; textArea_history.append(str); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
2.7. Start Program
import javax.swing.*; /** * Start Program * @author TT * @create 2020-06-16-0:53 */ public class UDPChat extends JFrame { public static void main(String[] args) { JFrame frame = new JFrame("chat room GUI edition"); frame.add(new UDPChatFace());//Notice the order, and the add method comes first frame.setVisible(true); frame.setSize(800,600); frame.setResizable(false); frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(WindowConstants.EXIT_ON_CLOSE); } }
2.8. Notes
- The program sets two port numbers 10001 and 10002, respectively, so if one client uses 10001, the other client should enter 10002, otherwise an error will occur
- The default IP setting for this program is to get the native IP, i.e. "Chat with yourself". If you need to interact between two computers (same local area network), you can simply set the IP address entered in the text box to the sending and receiving addresses.
3. Tips
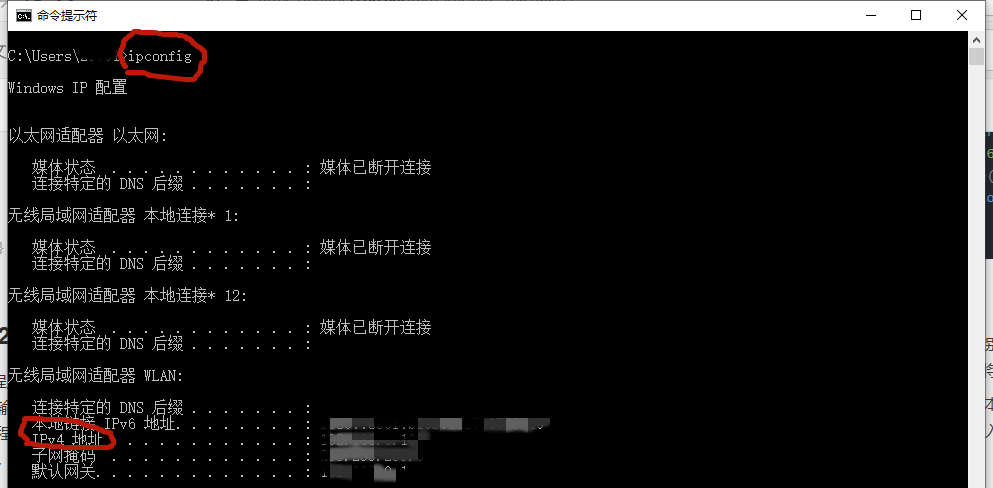
3.1, Get Local IP Address
- "win + R" opens "run"
- Enter cmd, return and open Command Prompt
- Enter ipconfig, return
- Where the "IPV4" address is the local IP address
3.2. Setup method of IDEA running the same program twice
- Click the Run option on the menu bar
- Select Edit Configurations
- Check Allow parallel run in the upper right corner of the window and click OK.
4. Summary (Understanding of UDP)
Say some blogger's little ideas about UDP for whites new to the UDP protocol:
- UDP protocol, whether sent or received, must have a socket, a packet
- A socket can be interpreted as a "courier company". A package can be interpreted as a "package". Whether we are "courier" or "courier", "goods" (data) are stored in a "package".Therefore, if you want to send data, you must first store the data in the package and then use theSocket.sendThe "package" method sends the "package"; similarly, if you want to receive data, you must first create a byte[] type variable, which can be interpreted as a "vehicle carrying the package".The "car" is big enough to pass the "package"Socket.receiveThe (packet) method takes it in and reads the data.
Once you've finished, you can collect some favorites. Praise o()!
Reprint troubles to inform and mark the source!