1, Publish message to redis
1. Create a new springboot project
Create a new redis queue for the springboot project.
2. Introduce dependency
The introduction of related dependencies, in which lombok is used, requires the installation of lombok plug-ins.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.3.0.RELEASE</version> <relativePath/> </parent> <groupId>com.lpl</groupId> <artifactId>redis-queue</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>redis-queue</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <properties> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId> </dependency> <!--springboot web Scenario dependency--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <!--Property configuration support, using traditional xml or properties Support for this annotation is required for configuration--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <!--springboot redis Scenario dependency--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> <!--Default inheritance lettuce,Switch to jedis Need to exclude dependency--> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>io.lettuce</groupId> <artifactId>lettuce-core</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> <!--join jedis--> <dependency> <groupId>redis.clients</groupId> <artifactId>jedis</artifactId> </dependency> <!--lombok rely on--> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <optional>true</optional> </dependency> <!--alibaba json--> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>fastjson</artifactId> <version>1.2.28</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId> <artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> </dependencies> <!--springboot maven Plug in to maven How to provide springboot , will springboot Project packaged as traditional jar live war function--> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project>
3. Write configuration file
to write application.properties Configuration file to configure redis connection information.
server.port=8000 #redis stand alone configuration spring.redis.database=0 spring.redis.host=192.168.2.75 spring.redis.port=6379 #spring.redis.password=Connection password (empty by default) #Minimum free connections in connection pool spring.redis.jedis.pool.min-idle=0 #Maximum free connections in connection pool spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-idle=8 #Maximum connections in the connection pool (negative indicates no limit) spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-active=8 #Maximum block wait time in connection pool (in milliseconds, negative indicates no limit) spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-wait=-1 #The server name that redis listens to #spring.redis.sentinel.master=myMaster #Sentinel configuration list #spring.redis.sentinel.nodes=192.168.2.76:26379,192.168.2.77:26379 #Connection timeout in milliseconds0No limit) spring.redis.timeout=0 #Do not use ssl encryption spring.redis.ssl=false #redis cluster configuration #Primary and secondary nodes in the cluster #spring.redis.cluster.nodes=192.168.2.75:7001,192.168.2.75:7002,192.168.2.75:7003,192.168.2.75:7004,192.168.2.75:7005,192.168.2.75:7006 #Maximum number of redirections (since the data in the cluster is stored in multiple nodes, it is necessary to locate the data by forwarding when accessing the data) #spring.redis.cluster.max-redirects=2
4. Write entity class
Message entity Message.java
package com.lpl.bean; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Data; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.Date; /** * Sent message entity */ @Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor public class Message implements Serializable { private String id; //Message id private String personNo; //Sender's work number (multiple can be specified, separated by commas, no more than 1000) private String title; //Message title private String content; //Message content private String type; //Message type, system, sms private Date createTime; //Creation time private Date updateTime; //Update time private String statusCode; //Message sending result status code (4000 for success, 4001 for failure) }
Result constant class ConstantResult.java
package com.lpl.common; /** * Some variable definitions in the system */ public class ConstantResult { public static final String SUCCESS_CODE = "200"; //Success status code public static final String FAIL_CODE = "500"; //Failure status code }
Public return result class CommonResult.java
package com.lpl.common; import lombok.AllArgsConstructor; import lombok.Data; import lombok.NoArgsConstructor; /** * Specified public result returned */ @Data @NoArgsConstructor @AllArgsConstructor public class CommonResult<T> { private String code; //Return status code private String msg; //Return to prompt private T data; //Return data public CommonResult(String code, String msg){ this.code = code; this.msg = msg; } }
5. Write redis configuration class
We need to use RedisTemplate to operate redis and write redis configuration class RedisConfig.java . Multiple message listening adapters are configured here to listen to and subscribe to different redis channel messages in different ways.
package com.lpl.config; import com.lpl.listener.Receiver; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; import org.springframework.data.redis.listener.PatternTopic; import org.springframework.data.redis.listener.RedisMessageListenerContainer; import org.springframework.data.redis.listener.adapter.MessageListenerAdapter; import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer; import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer; /** * redis Custom configuration class */ @Configuration public class RedisConfig { /** * Return a RedisTemplate Bean * @param redisConnectionFactory If the cluster version is configured, the cluster version will be used; otherwise, the stand-alone version will be used * @return */ @Bean(name = "redisTemplate") public RedisTemplate<?, ?> getRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory){ RedisTemplate<?, ?> template = new RedisTemplate<>(); //Set key and value serialization mechanism template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()); template.setValueSerializer(new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer<Object>(Object.class)); template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory); //Set up the connection factory of stand-alone or cluster version return template; } /** * System message adapter * @param receiver * @return */ @Bean(name = "systemAdapter") public MessageListenerAdapter systemAdapter(Receiver receiver){ //Specifies the method of callback receiving message in the class MessageListenerAdapter adapter = new MessageListenerAdapter(receiver, "systemMessage"); //adapter.afterPropertiesSet(); return adapter; } /** * SMS adapter * @param receiver * @return */ @Bean(name = "smsAdapter") public MessageListenerAdapter smsAdapter(Receiver receiver){ //Specifies the method of callback receiving message in the class MessageListenerAdapter adapter = new MessageListenerAdapter(receiver, "smsMessage"); //adapter.afterPropertiesSet(); return adapter; } /** * Building redis message listener container * @param connectionFactory * @param systemAdapter * @param smsAdapter * @return */ @Bean public RedisMessageListenerContainer container(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory, MessageListenerAdapter systemAdapter, MessageListenerAdapter smsAdapter){ RedisMessageListenerContainer container = new RedisMessageListenerContainer(); container.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory); //Specify different ways to listen to different channels container.addMessageListener(systemAdapter, new PatternTopic("system")); container.addMessageListener(smsAdapter, new PatternTopic("sms")); return container; } }
To use the redis cluster version, you need to add the following configuration classes:
Read cluster configuration property class RedisClusterProperty.java
package com.lpl.config; import lombok.Data; import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import org.springframework.validation.annotation.Validated; import java.util.List; /** * redis The cluster configuration attribute provides parameter configuration in the redis instance factory */ @Component @Validated @Data @ConfigurationProperties(value = "spring.redis.cluster") public class RedisClusterProperty { private List<String> nodes; //ip and port of each node in the cluster }
redis cluster configuration class RedisClusterConfig.java When we configure the connection factory of class cluster version, this factory will be used to create the RedisTemplate. At this time, the cluster version is used.
package com.lpl.config; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary; import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisClusterConfiguration; import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory; import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * redis Cluster configuration */ @Configuration @Component public class RedisClusterConfig { @Autowired private RedisClusterProperty redisClusterProperty; /** * Configuration return to RedisConnectionFactory connection factory * @return */ @Bean @Primary //If there is a Bean of the same type, the Bean annotated with this annotation takes precedence public RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory(){ RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory = new JedisConnectionFactory( new RedisClusterConfiguration(redisClusterProperty.getNodes())); return redisConnectionFactory; } }
6. Write Service layer
Message publishing business layer interface PublisherService.java
package com.lpl.service; import com.lpl.bean.Message; import com.lpl.common.CommonResult; /** * Message publisher interface */ public interface PublisherService { /** * Publish message to redis * @param message Message object * @return */ CommonResult pubMsg(Message message); }
Message publishing business layer interface implementation class PublisherServiceImpl.java
package com.lpl.service.impl; import com.lpl.bean.Message; import com.lpl.common.CommonResult; import com.lpl.common.ConstantResult; import com.lpl.service.PublisherService; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; import java.util.Date; import java.util.UUID; /** * Message publisher service implementation class */ @Service public class PublisherServiceImpl implements PublisherService { @Autowired private RedisTemplate<String, Message> redisTemplate; /** * Send a message to the redis channel for subscription. Note: use redis cli to login and subscribe to view the Chinese content in hexadecimal form * To view Chinese characters, you need to force the original output redis cli - H localhost - P 6379 -- raw when connecting * Then use the command to subscribe to the channel subscribe system * @param message Message object * @return */ @Override public CommonResult pubMsg(Message message) { //Return results CommonResult result = null; if (null != message){ //Complete message entity if (StringUtils.isEmpty(message.getId())){ //If it is a pass id, it is generated and returned message.setId(UUID.randomUUID().toString()); } message.setCreateTime(new Date()); message.setUpdateTime(new Date()); try{ redisTemplate.convertAndSend(message.getType(), message); //Publish message to specified channel //redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush(message.getType(), message); / / publish to redis in the form of queue System.out.println("Message to redis Queue channel:" + message.getType() + "success!"); result = new CommonResult<Message>(ConstantResult.SUCCESS_CODE, "Message to" + message.getType() + "Channel success!", message); }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); result = new CommonResult<Message>(ConstantResult.FAIL_CODE, "Message to" + message.getType() + "Channel failed!", message); } } return result; } }
7. Write Controller layer
Message publisher controller interface, PublisherController.java
package com.lpl.controller; import com.lpl.bean.Message; import com.lpl.common.CommonResult; import com.lpl.service.PublisherService; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PostMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestBody; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; /** * Message publisher controller */ @RestController public class PublisherController { private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(PublisherController.class); @Autowired private PublisherService publisherService; /** * Publish messages to the specified redis channel * @param message * @return */ @PostMapping("/pubMsg") public CommonResult pubMsg(@RequestBody Message message){ CommonResult commonResult = publisherService.pubMsg(message); return commonResult; } }
8. Message release test
Start the project, we can use the postman tool call to send messages to redis. Call as follows: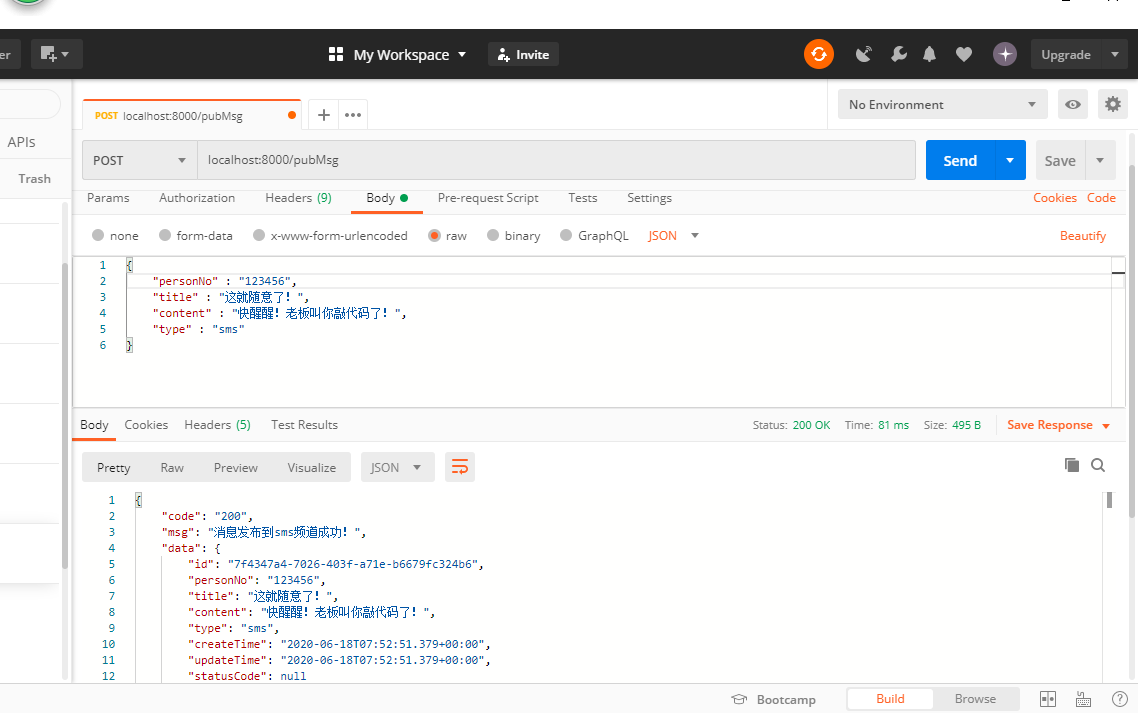
Use the redis cli client to log in to redis and use – raw to force the original output (otherwise, the Chinese content viewed by the subscription is displayed in hexadecimal).
./redis-cli -h localhost -p 6379 --raw
Then use the command to subscribe to the corresponding channel message.
subscribe sms
Here, we see that the message has been published to the specified channel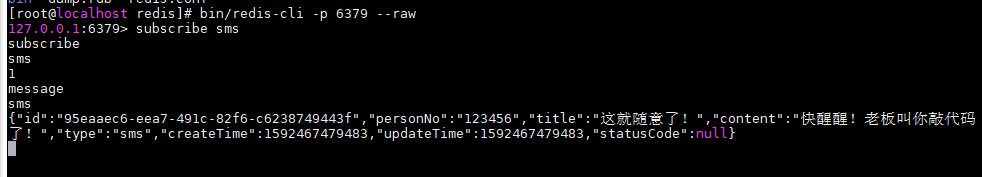
2, Asynchronous receiving, multithreading consumption message
1. Write message listening class
Message listening class Receiver.java , we are RedisConfig.java Class has specified the redis channel to listen to for each method in this class. When messages are published to the channel, the corresponding method in this class will listen to these messages.
package com.lpl.listener; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject; import com.lpl.bean.Message; import com.lpl.service.SendAndStorageProcess; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Async; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger; /** * Message receiving listener */ @Component public class Receiver{ @Autowired private SendAndStorageProcess sendAndStorageProcess; private AtomicInteger counter = new AtomicInteger(); //Message counter /** * Receive system messages and enable asynchronous monitoring * @param message */ @Async public void systemMessage(String message){ int counter = this.counter.incrementAndGet(); System.out.println("Received the" + counter + "Messages!! The channel is: system,The message content is======: "); //Convert message content string to object Message messageObject = JSONObject.parseObject(message, Message.class); System.out.println(messageObject.getContent()); //TODO enables multithreading to send and process messages JSONObject result = sendAndStorageProcess.sendAndStorageMsg(messageObject); } /** * Receive SMS messages and enable asynchronous monitoring * @param message */ @Async public void smsMessage(String message){ int counter = this.counter.incrementAndGet(); System.out.println("Received the" + counter + "Messages!! The channel is: sms,The message content is======: "); //Convert message content string to object Message messageObject = JSONObject.parseObject(message, Message.class); System.out.println(messageObject.getContent()); //TODO enable multi thread call sending JSONObject result = sendAndStorageProcess.sendAndStorageMsg(messageObject); } }
2. Enable asynchronous reception
Enable asynchronous support in the main class (Note: the method that needs to enable asynchronous cannot be private decorated). In the Receiver.java The listening method in class has been turned on asynchrony.
package com.lpl; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync; import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor; import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskScheduler; import java.util.concurrent.Executor; /** * About redis single machine switch to cluster, open application.properties Redis cluster configuration and RedisClusterConfig file of the file * RedisConnectionFactory Bean registration configuration for. */ @SpringBootApplication @EnableAsync public class RedisQueueCacheApplication { public static void main(String[] args) { SpringApplication.run(RedisQueueCacheApplication.class, args); } }
3. Write thread pool configuration class
Thread pool configuration class TaskExecutorConfig.java
package com.lpl.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor; import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService; import java.util.concurrent.Executors; import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor; /** * Thread pool configuration class */ @Configuration public class TaskExecutorConfig { /** * Create a thread pool * @return */ @Bean(name = "threadTaskExecutor") public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor getThreadPoolTaskExecutor(){ ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor(); executor.setCorePoolSize(10); //Core thread pool size executor.setMaxPoolSize(50); //Maximum thread pool size executor.setQueueCapacity(1000); //Task queue size executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(300); //Timeout in seconds for idle threads in the thread pool to wait for work executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy()); //Thread rejection strategy, which provides a simple feedback control mechanism, can slow down the submission of new tasks return executor; } /** * Create a fixed size thread pool * @return */ @Bean(name = "fixedThreadPool") public ExecutorService executorService(){ ExecutorService fixedThreadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10); return fixedThreadPool; } }
4. Write message processing class
Message processing class (multithreading) s endAndStorageProcess.java , the method of sending messages in the class causes the thread to sleep for two seconds, simulating the relatively time-consuming operation of sending messages, which is used to verify multithreading.
package com.lpl.service; import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject; import com.lpl.bean.Message; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.Date; import java.util.concurrent.Callable; import java.util.concurrent.Future; /** * Send and store message tasks */ @Component public class SendAndStorageProcess{ @Autowired private ThreadPoolTaskExecutor threadTaskExecutor; //Inject thread pool /** * Multithreaded call to send message * @param message * @return */ public JSONObject sendAndStorageMsg(Message message) { Future<JSONObject> future = threadTaskExecutor.submit(new Callable<JSONObject>() { //With return value @Override public JSONObject call() throws Exception { //1. Call a relatively time-consuming message sending method String code = sendMessage(message); message.setUpdateTime(new Date()); if ("200".equals(code)){ //Sent successfully message.setStatusCode("4000"); }else{ //fail in send message.setStatusCode("4001"); } //2. Store messages storageMessage(message); JSONObject result = new JSONObject(); result.put("code", "200"); result.put("msg", "Message sent successfully!"); return result; } }); JSONObject jsonResult = new JSONObject(); //Return results try{ if (future.isDone()){ //When the thread scheduling ends, the result will be obtained jsonResult = future.get(); } }catch (Exception e){ e.printStackTrace(); } return jsonResult; //Message sending and storing results } /** * Call interface to send message * @param message * @return */ private String sendMessage(Message message) { try{ //TODO here writes some business logic for sending messages Thread.sleep(2000); //Increase time-consuming operation and view multi-threaded effect System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "Thread successfully sent message, message content:" + message.getContent()); return "200"; //Send message result status code }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "Thread failed to send message, message content:" + message.getContent()); e.printStackTrace(); } return "500"; //Send message result status code } /** * Save message to database * @param message * @return */ private void storageMessage(Message message) { try{ //TODO performs the insert message to data operation here System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "Thread successfully inserted message into database, message content:" + message.getContent()); }catch (Exception e){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "Thread insert message to database failed, message content:" + message.getContent()); e.printStackTrace(); } } }
5. Message consumption test
Call the interface quickly and see the following print, which has achieved the asynchronous and multi-threaded sending effect.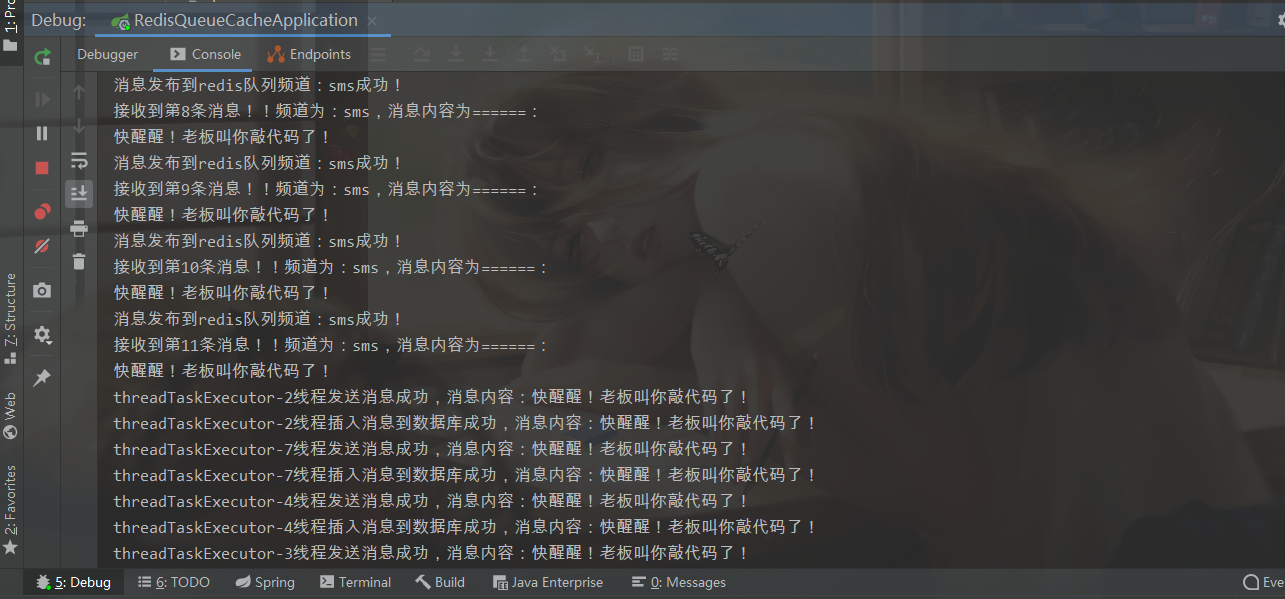
OVER, if there is an error! Thank you for your correction!