Requirements: some time ago, when developing a project, there was a requirement. Because some information of the APP is sensitive, if the user presses the home key to return to the background during the operation of the APP, after the specified time, and then switches to the foreground, it is necessary to verify the fingerprint or gesture set by the user to authenticate the user
Scheme I:
When the APP enters the front desk, it will rootViewController Set as the specified verification interface
But there is a problem: when the user authentication is successful? How to return to the user's previous interface? I don't have a good solution for the time being. If you think of a good idea, we can discuss it together~
Scheme II:
When the APP enters the foreground, it overwrites a UIWindow on the current interface and sets UIWindowLevel. After the user's authentication is successful, it can hide or remove the Window object
The code is as follows:
func applicationDidEnterBackground(_ application: UIApplication) {
leaveTime = Date()
}
func applicationWillEnterForeground(_ application: UIApplication) {
let interval = Int(Date().timeIntervalSince(leaveTime))
//Here, if it takes more than 20 seconds, let the user verify it
if interval > 20
{
let validateVC = ValidationVC()
//After the user authentication is successful, you can reset the next windowslevel;
validateVC.closeCallBack = {
self.gestureWindow?.windowLevel = -1
}
let window = UIWindow(frame: UIScreen.main.bounds)
window.windowLevel = UIWindowLevelAlert + 1
window.rootViewController = validateVC
window.makeKeyAndVisible()
self.gestureWindow = window
}
}
UIWindowLevel
about UIWindowLevel I want to say a few more words, UIWindow It will be displayed according to UIWindowLevel To sort, i.e Level The high one will be at the top. The default is 0
open var windowLevel: UIWindowLevel // default = 0.0
The system defines three window levels for us, namely:
public let UIWindowLevelNormal: UIWindowLevel public let UIWindowLevelAlert: UIWindowLevel public let UIWindowLevelStatusBar: UIWindowLevel
Let's print out the values of these three level s to see the following:
STWLog("UIWindowLevelNormal: \(UIWindowLevelNormal)")
STWLog("UIWindowLevelStatusBar: \(UIWindowLevelStatusBar)")
STWLog("UIWindowLevelAlert: \(UIWindowLevelAlert)")
Print results:
AppDelegate.swift:(43)----------UIWindowLevelNormal: 0.0 AppDelegate.swift:(44)----------UIWindowLevelStatusBar: 1000.0 AppDelegate.swift:(45)----------UIWindowLevelAlert: 2000.0
So we can see their level at a glance;
Let's write a small Demo to test:
@UIApplicationMain
class AppDelegate: UIResponder, UIApplicationDelegate {
var window: UIWindow?
var normalWindow: UIWindow!
var alertLevelWindow: UIWindow!
var statusLevelWindow: UIWindow!
var alertLevelWindow2: UIWindow!
func application(_ application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplicationLaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
window = UIWindow(frame: CGRect(x: 0, y: 0, width: 100, height: 100))
window?.tag = 10
window?.backgroundColor = .red
window?.rootViewController = ViewController()
window?.makeKeyAndVisible()
//Customize the Window and set the windowLevel to UIWindowLevelNormal
normalWindow = UIWindow(frame: CGRect(x: 50, y: 50, width: 100, height: 100))
normalWindow?.tag = 100
normalWindow.backgroundColor = .green
normalWindow.windowLevel = UIWindowLevelNormal
normalWindow.rootViewController = ViewController()
normalWindow.makeKeyAndVisible()
//Customize the Window and set the windowLevel to UIWindowLevelNormal
alertLevelWindow = UIWindow(frame: CGRect(x: 150, y: 150, width: 100, height: 100))
alertLevelWindow?.tag = 10000
alertLevelWindow.backgroundColor = .blue
alertLevelWindow.windowLevel = UIWindowLevelAlert
alertLevelWindow.rootViewController = ViewController()
alertLevelWindow.makeKeyAndVisible()
//Customize the Window and set the windowLevel to UIWindowLevelStatusBar
statusLevelWindow = UIWindow(frame: CGRect(x: 100, y: 100, width: 100, height: 100))
statusLevelWindow?.tag = 1000
statusLevelWindow.backgroundColor = .yellow
statusLevelWindow.windowLevel = UIWindowLevelStatusBar
statusLevelWindow.rootViewController = ViewController()
statusLevelWindow.makeKeyAndVisible()
//Customize the Window and set the windowLevel to UIWindowLevelStatusBar
alertLevelWindow2 = UIWindow(frame: CGRect(x: 200, y: 200, width: 100, height: 100))
alertLevelWindow2?.tag = 100000
alertLevelWindow2.backgroundColor = .white
alertLevelWindow2.windowLevel = UIWindowLevelAlert + 10 //Set a Level at will
alertLevelWindow2.rootViewController = ViewController()
alertLevelWindow2.makeKeyAndVisible()
print("current keyWindow: \(String(describing: UIApplication.shared.keyWindow!.tag))")
return true
}
func applicationWillEnterForeground(_ application: UIApplication) {
DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: DispatchTime.now() + 2.0, execute: {
self.alertLevelWindow2 = nil
})
DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: DispatchTime.now() + 4.0, execute: {
print("here keyWindow: \(String(describing: UIApplication.shared.keyWindow!.tag))")
for window in UIApplication.shared.windows
{
print("current window of tag Value is:\(window.tag)")
}
})
}
}
The operation results are shown in the figure below:
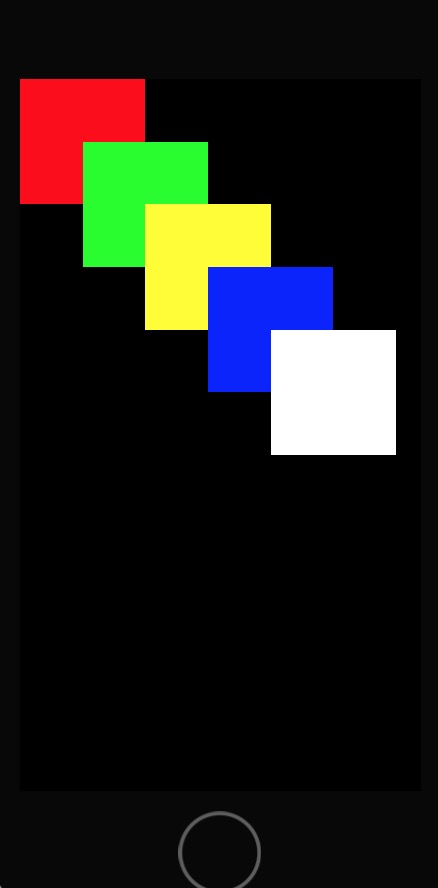
Print result display:
current keyWindow: 100000 here keyWindow: 10000 current window of tag Value is:0 current window of tag Value is:10 current window of tag Value is:100 current window of tag Value is:1000 current window of tag Value is:10000
What is? keWindow ? Let's see how the official documents describe:
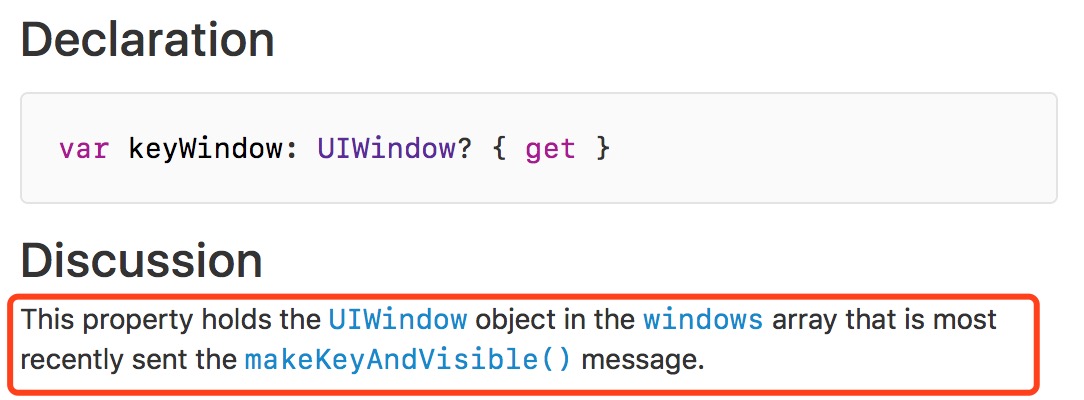
That is to say windows Array, the most recent time called makeKeyAndVisible The way is keyWindow;
Summary:
- UIWindowLevel The value of is not only UIWindowLevelNormal , UIWindowLevelAlert, UIWindowLevelStatusBar These three can be user-defined arbitrary values, even negative numbers
- UIWindow The display of can indeed be passed UIWindowLevel To distinguish priorities, all windows will be added to the interface, but will be listed by priority, uiwindowlevel The large one is displayed above, uiwindowlevel The small ones are shown below.
- UIWindowLevel When the priorities are equal, it depends on who instantiates later, who instantiates later, and who displays first
- If the current Keywindow object set to nil The object is removed from the Removed from the Windows array, and the last instantiated Window object will become KeyWindow , But still follow the description in summary 2, UIWindowLevel The large one is displayed above, UIWindowLevel The small ones are shown below.