catalogue
redis compilation and installation
1. redis configuration of server1
2. redis installation of server2
3. Configuring redis for server3
3, redis master-slave replication
4, Sentine master-slave automatic switching
2. Automatic switching between master and slave nodes
6, Redis+Mysql read / write separation
7, redis and mysql keep the data consistent
2. Install the database development kit in server3
4. Download and unzip gearman from server3, solve the dependency, and compile
5. Edit the mysql trigger and re import the database
6. Start the service and worker task in server1
Introduction to Redis
Redis is completely open source and complies with BSD protocol. It is a high-performance key value database.
characteristic
1.Redis supports data persistence. It can save the data in memory on disk and can be loaded again for use when restarting.
2.Redis not only supports simple key value data, but also provides storage of list, set, zset, hash and other data structures.
3.Redis supports data backup, that is, data backup in master slave mode.

redis compilation and installation
https://redis.io/download tar zxf redis-5.0.8.tar.gz make && make install utils/install_server.sh
1. redis configuration of server1
server1 host, install and compile redis.
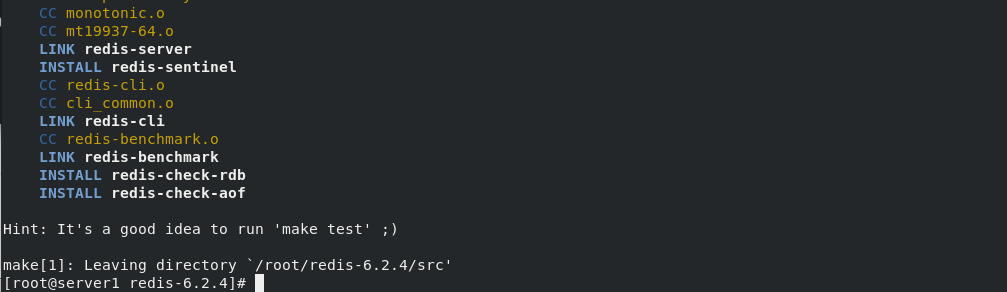
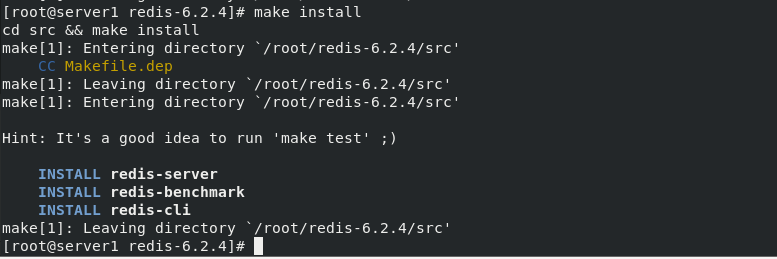 Run the built-in installer. The installation fails. The judgment of the operating system in the file will lead to the failure. Modify the file and reinstall
Run the built-in installer. The installation fails. The judgment of the operating system in the file will lead to the failure. Modify the file and reinstall
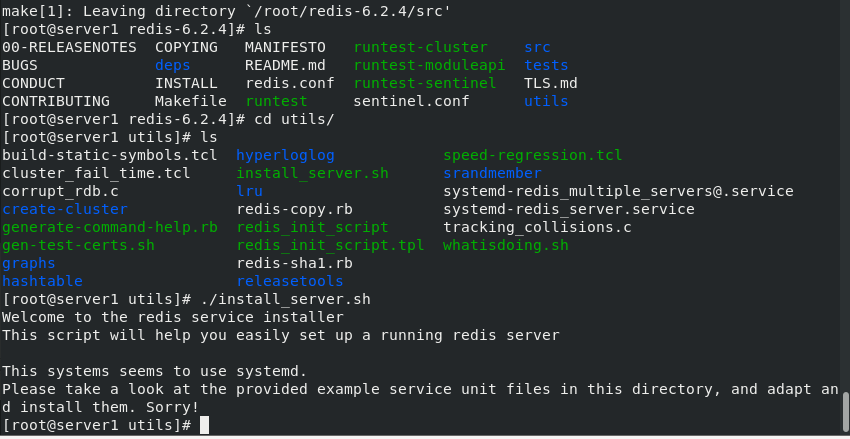
cd utils/ ls ./install_server.sh ##Failed to run the built-in installer vim install_server.sh ##Note the following sections and rerun the built-in installer Press enter when prompted

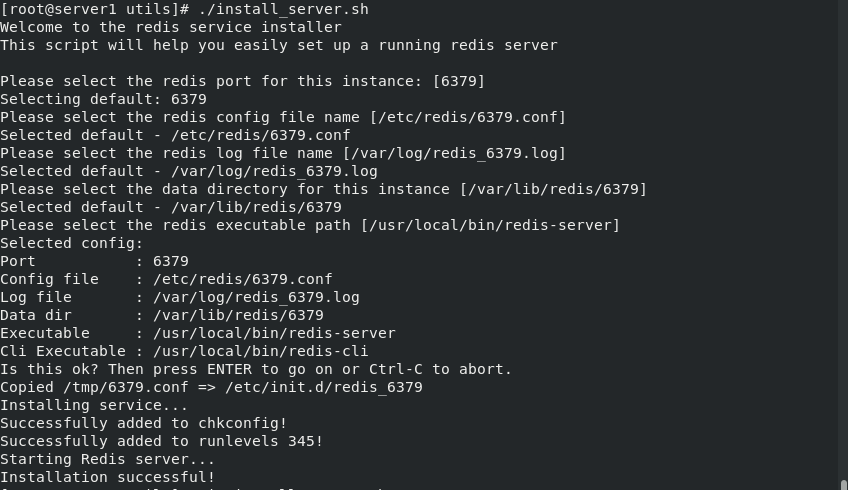
If you want to install again, enter 6380 after 6379 at the prompt:
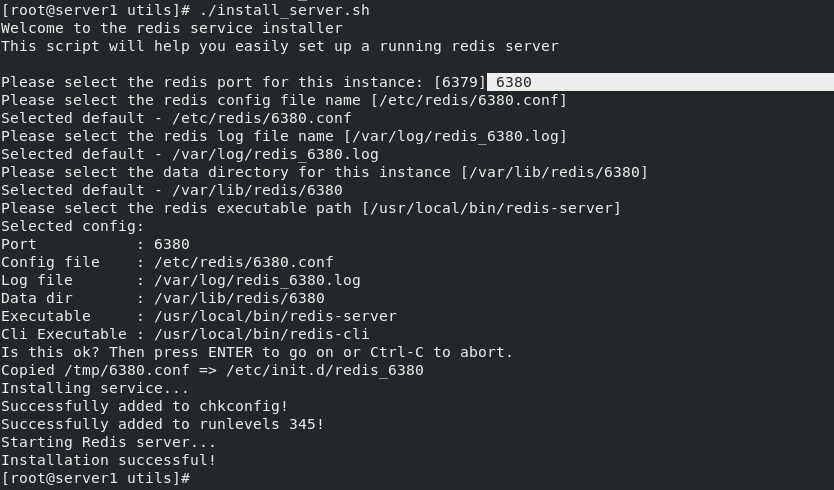
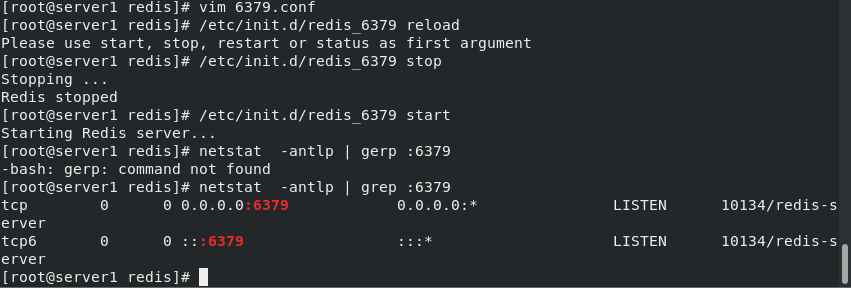
At this time, switch to the configuration directory, you can see that the configuration file is automatically generated, view the port, and open the port. Modify the configuration file and restart the service.
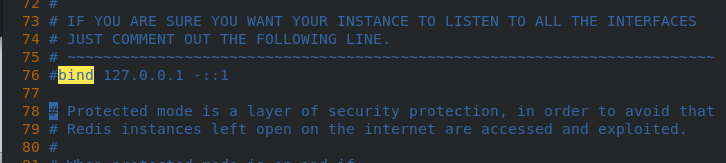
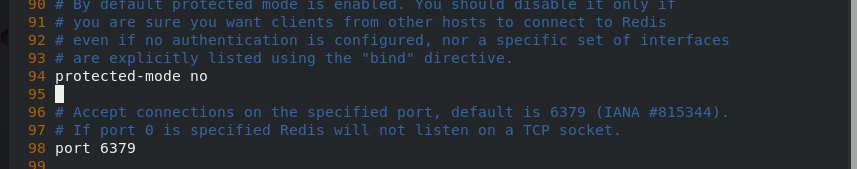
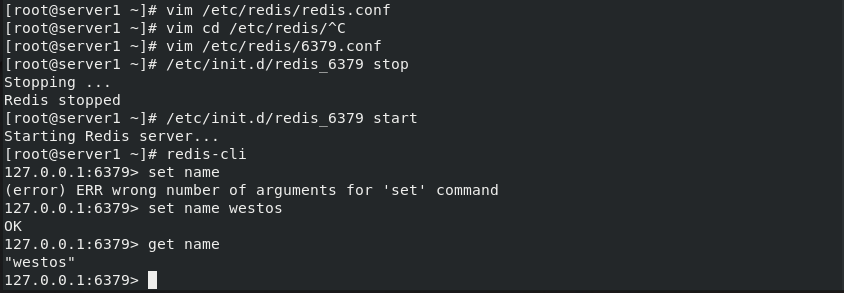
cd /etc/redis ls ##6379.conf netstat -antlp ##6379 vim 6379.conf /// 75 #bind 127.0.0.1 -::1 ##When linking redis, you can only link through the local localhost (127.0.0.1), not the network ip(192.168..). Because it is in the protection mode, you can only link locally, so set this comment 94 protected-mode no ##Set off protection mode /// /etc/init.d/redis_6379 stop /etc/init.d/redis_6379 start netstat -antlp | grep :6379
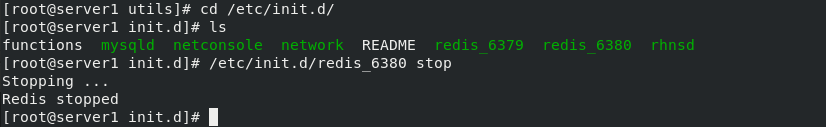

2. redis installation of server2
On the server2 host, use another method to configure redis.
First, unzip the file first, and then build it with systemd support, but the dependency gcc is missing. Install the dependency and make again, but it still fails. Remind jemalloc that the dependency is missing. At this time, delete the redis directory, delete the cache generated in c environment, unzip and make again, remind the lack of systemd, and continue to make after installation. Success, make install
scp -r redis-6.2.4.tar.gz server2: #server1 directly transfers the decompressed mulu to server2 because redis yes c Language development, so you need to download it gcc Install and compile yum install -y gcc #Download gcc yum install -y systemd-devel vim README.md #After checking the user manual, you can find that if the service needs to use knife SYSTEMd, you need to add the parameter USE_SYSTEMD=yes when making make USE_SYSTEMD=yes #redis uses the systemd daemon make install #install
Switch to the utils directory, run the built-in installer, copy the service file to the configuration location where the startup file is automatically stored in the directory, reload the configuration file and restart the service.
cd utils/ ./install_server.sh cp systemd-redis_server.service /usr/lib/systemd/system/redis.service ##Directory is the configuration location where startup files are stored automatically systemctl daemon-reload ##Reload profile systemctl start redis.service
3. Configuring redis for server3
The redis configuration of server3 is the same as that of server1
3, redis master-slave replication
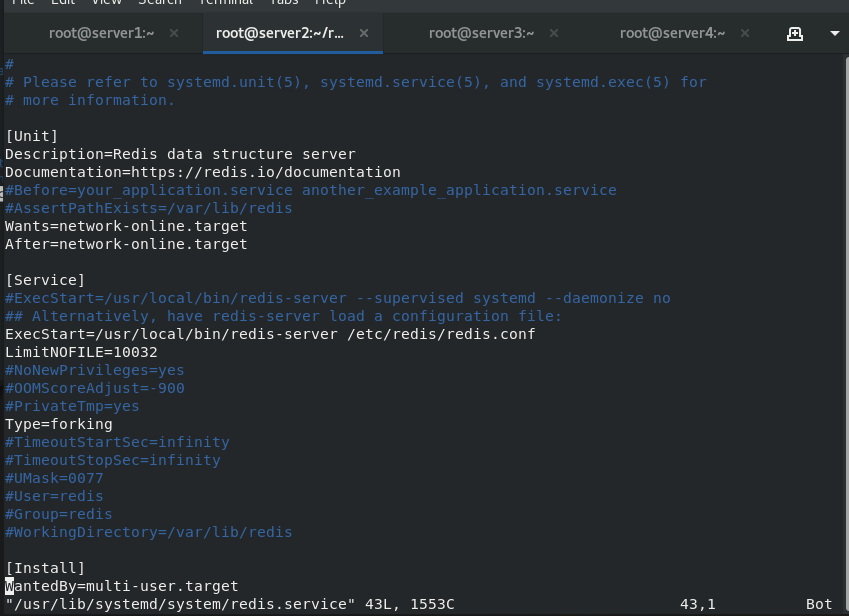
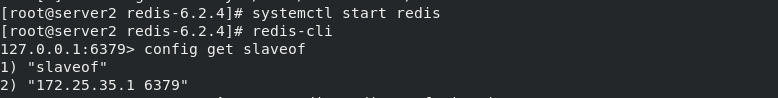
1. Modify the redis.service file in server2, establish the directory where the configuration file and data file are stored, edit the configuration file, and set server2 host as the slave end of server1 host, that is, master-slave copy settings, reload the configuration file and restart the service.
cd /usr/lib/systemd/system/ vim redis.service
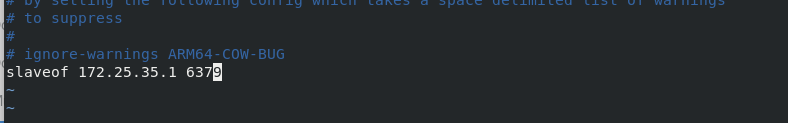
mkdir /etc/redis mkdir /var/lib/redis cd cd redis-6.2.4/ cp redis.conf /etc/redis/ vim /etc/redis/redis.conf /// 94 protected-mode no ##Turn off protection mode 75 #bind 127.0.0.1 -::1 ##Note: allow network ip link redis 257 daemonize yes ##Run as a daemon 302 logfile "/var/log/redis.log" ##Log storage directory 454 dir /var/lib/redis ##Directory where data files are placed 2052 slaveof 172.25.35.16379 ##Master slave replication /// systemctl daemon-reload systemctl restart redis
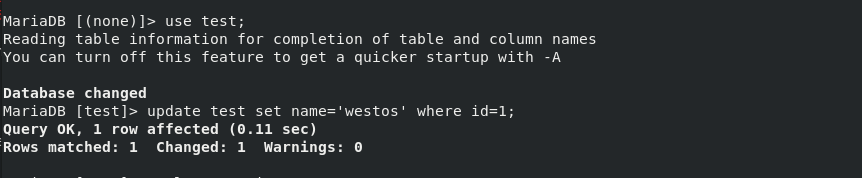
 2. At this time, insert the data on the server1 host, which can be seen on the server2 and server3 hosts, that is, the master-slave replication is set successfully.
2. At this time, insert the data on the server1 host, which can be seen on the server2 and server3 hosts, that is, the master-slave replication is set successfully.
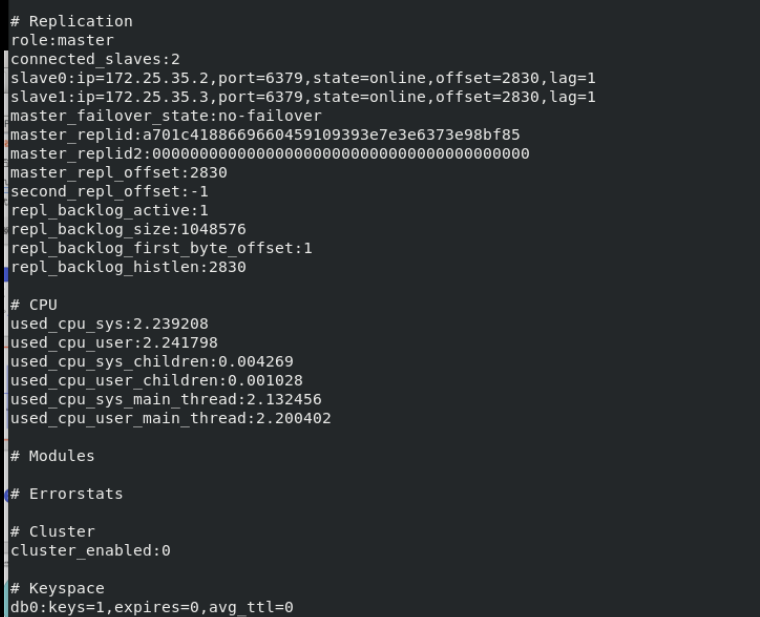
3. After entering redis info, you can see the affiliation of redis

4, Sentine master-slave automatic switching
Use the sentinel mode to automatically monitor the Master node. After hanging up, the slave node will be automatically changed into a Master node
Environment: Currently, server1 is master and server2 and 3 are slave
Configure sentinel mode, i.e. high availability ###server1 cd redis-6.2.4/ cp sentinel.conf /etc/redis/ cd /etc/redis/ vim sentinel.conf /// sentinel monitor mymaster 172.25.35.1 6379 2 ##If the master is server1 and 2, it means that two votes are required to pass, and the host is deemed to be down sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 10000 ##The connection timeout is 10s /// scp sentinel.conf server2:/etc/redis/ scp sentinel.conf server3:/etc/redis/ redis-sentinel /etc/redis/sentinel.conf ##You can see two slave ends
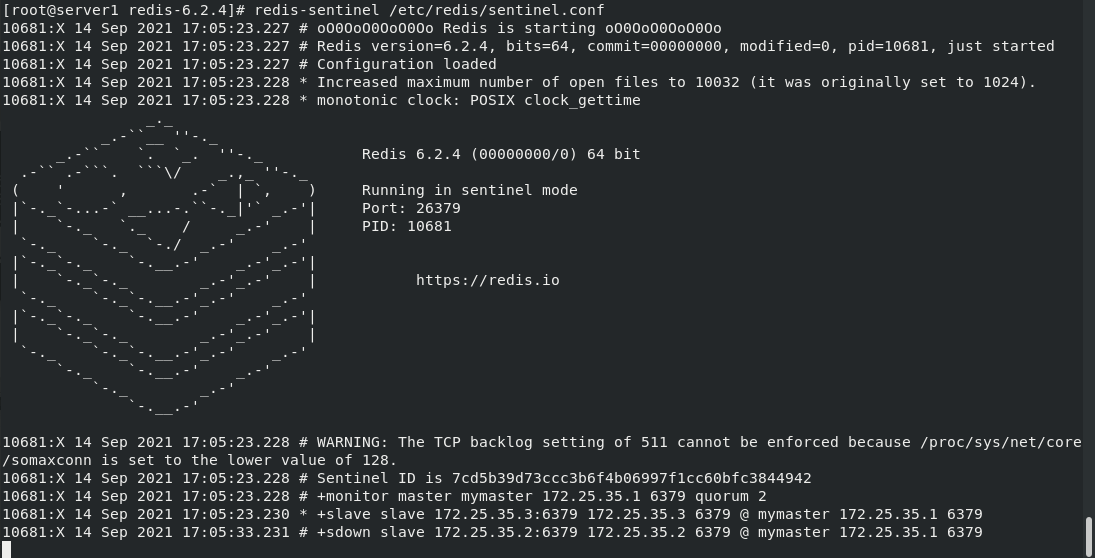
Turn off redis in server1 , Viewing the changes will display the process of closing and running for master of server2 and server3
redis-cli --> info --> SHUTDDOWN
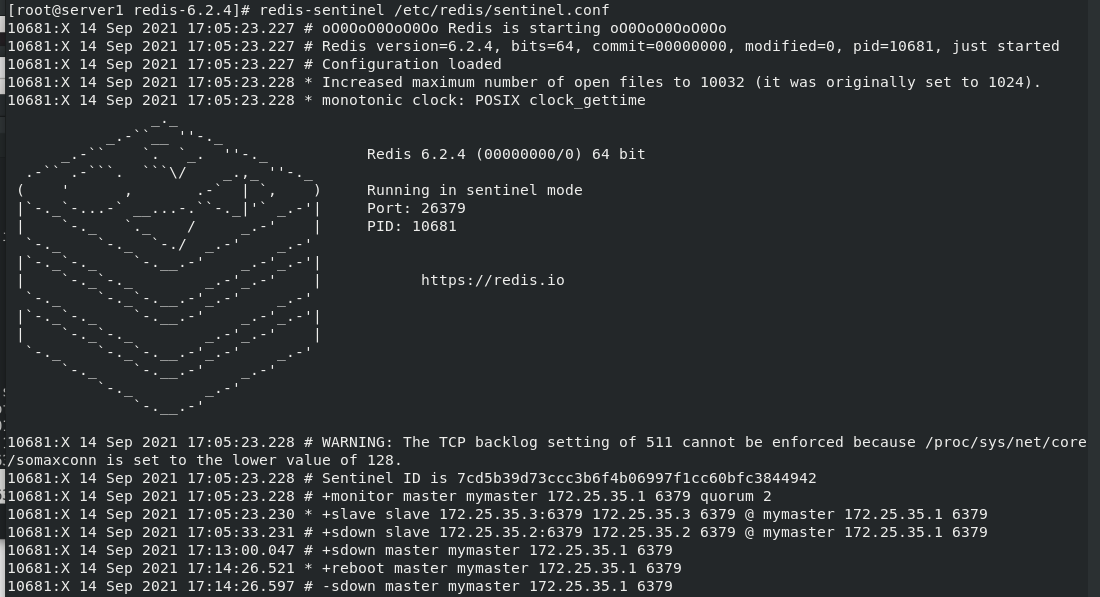
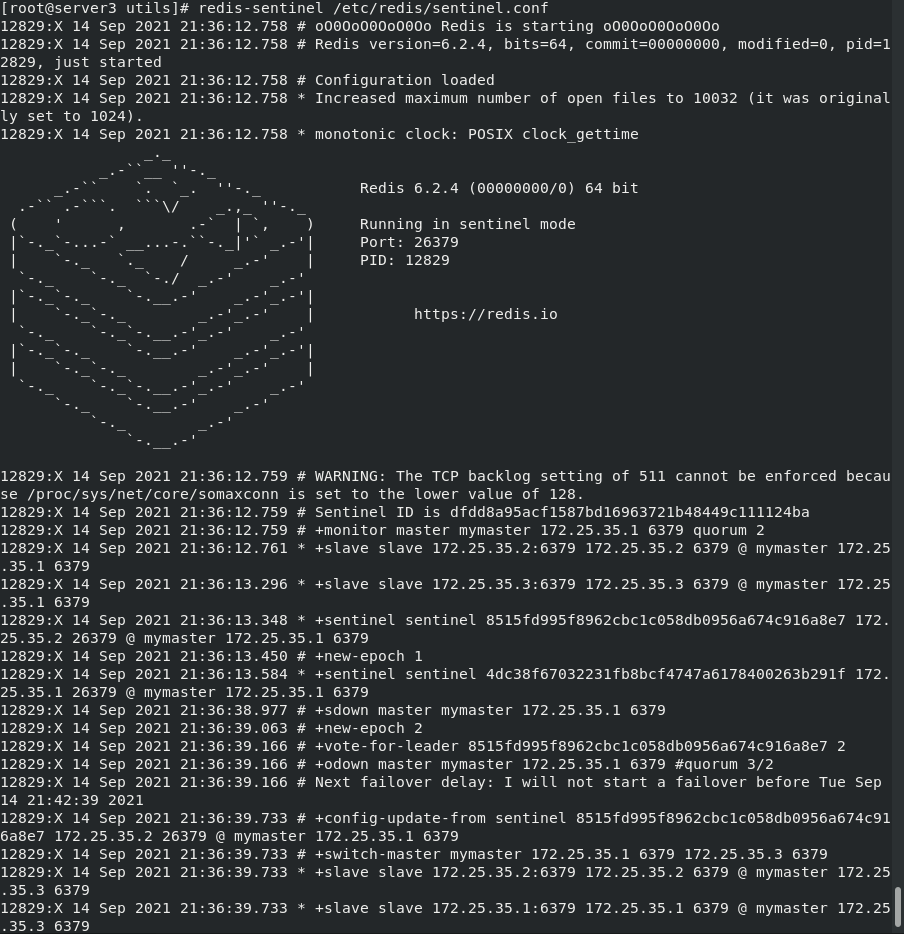
At this time, server3 becomes a master (or server2, because it is the master selected by two slave, so different environments may select different Masters)
Check the status of redis connected to server3. server3 is master, server2 is slave, and server1 is off

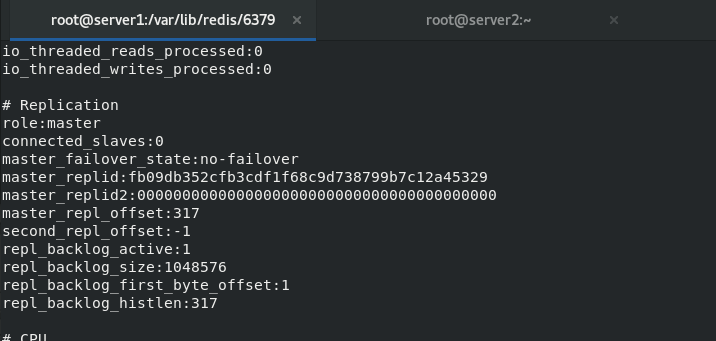
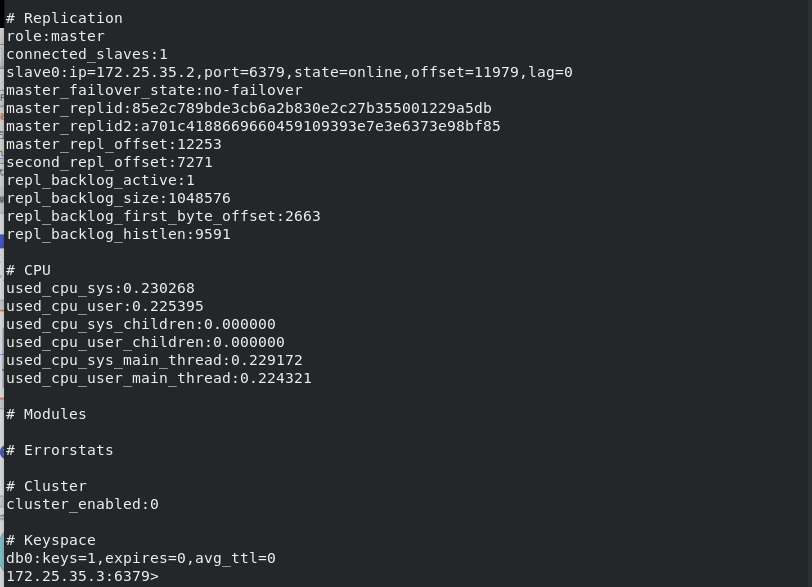 Now server1 is turned off. After redis of server1 is turned on, server1 will automatically switch to slave and clear all previous data
Now server1 is turned off. After redis of server1 is turned on, server1 will automatically switch to slave and clear all previous data
5, redis cluster
Redis cluster summary
1.Redis cluster is a distributed service cluster composed of multiple nodes. It has the characteristics of replication, high availability and fragmentation
2. The redis cluster has no central node and has replication and failover features, which can avoid a single node becoming a performance bottleneck or the whole cluster going offline because a node goes offline
3. The master node in the cluster is responsible for processing the slot (storing data), while the slave node is a replica of the master node
4. The redis cluster divides the entire database into 16384 slots, and each key in the database belongs to one of the 16384 slots
5. Each primary node in the cluster can be responsible for 0 to 16384 slots. When there are nodes in charge of 16384 slots, the cluster enters the online state and can execute the data commands sent by the client
6. The master node will only execute commands related to the slot it is responsible for. When the node receives a command that does not belong to the slot it is processing, it will process the address of the node of the specified slot and return it to the client, and the client will resend it to the correct node
7. If you need complete fragmentation, replication and high availability features, and you want to avoid performance bottlenecks and resource consumption caused by using agents, you can choose to use Redis cluster;
If only some features are required (for example, only sharding is required, but replication and high availability are not required), select one or more of twoproxy, Redis replication and Redis Sentinel separately
1. Cluster construction
Build the cluster manually
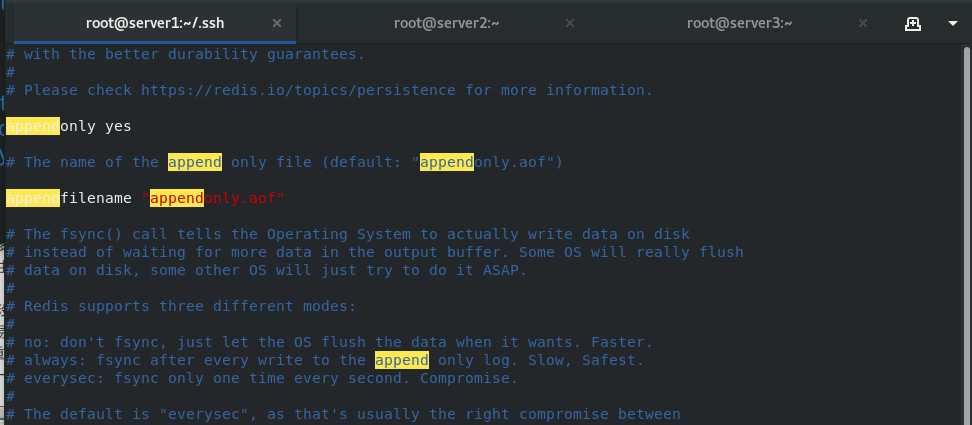
The host of server1 is the master. Restart redis, start AOF mode, establish the media directory and cluster 7001 ~ 7006 directories, configure the configuration files under the directory respectively, and start the service
/etc/init.d/redis_6379 restart
vim /etc/redis/6379.conf
\\\
appendonly yes ##Turn on AOF mode
\\\
cd /usr/local
mkdir redis #Create directory
cd redis/
mkdir 700{1..6} #Create a directory of six nodes
cd 7001
vim redis.conf #Edit profile
///
port 7001
cluster-enabled yes ##Start cluster
cluster-config-file nodes.conf ##Cluster profile
cluster-node-timeout 5000 ##Node timeout
appendonly yes ##Turn on AOF mode
daemonize yes ##Start as a daemon thread
///
redis-server redis.conf ##Start service
ps ax ##redis-server *:7001 [cluster]
cp redis.conf ../7002/ ##Copy profile to 7002-7006
cp redis.conf ../7003/
cp redis.conf ../7004/
cp redis.conf ../7005/
cp redis.conf ../7006/
Then enter the directory of each node to modify the configuration file—— port 7001
For example:
cd 7002/
vim redis.conf
///
port 7002
cluster-enabled yes
cluster-config-file nodes.conf
cluster-node-timeout 5000
appendonly yes
daemonize yes
///
redis-server redis.conf #Start service server1 is master
##Turn on AOF mode
After creating the redis directory, edit the configuration file redis.conf (file in 7001 directory) in each node directory
Finally, you can use ps to view. At this time, the services of all nodes have been started
Create a cluster master-slave node. The – cluster replica parameter is a number. 1 means that each master node needs 1 slave node. Then check the cluster and view the cluster information.
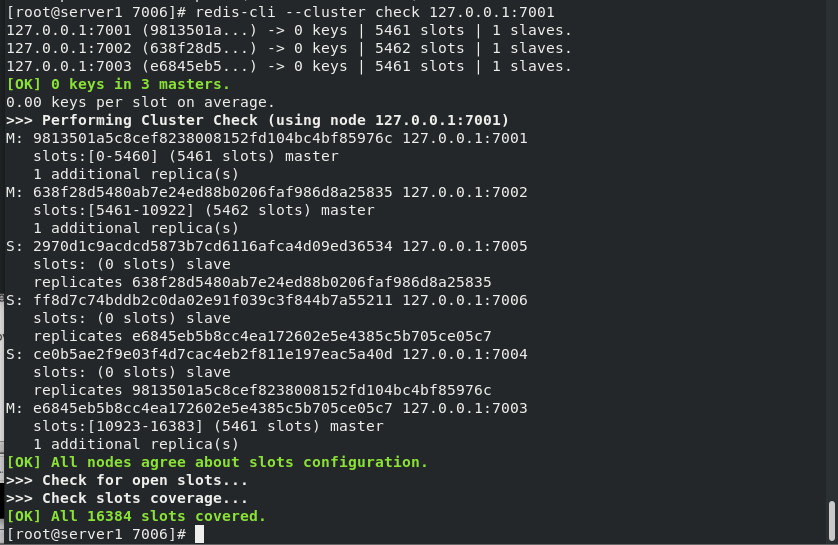
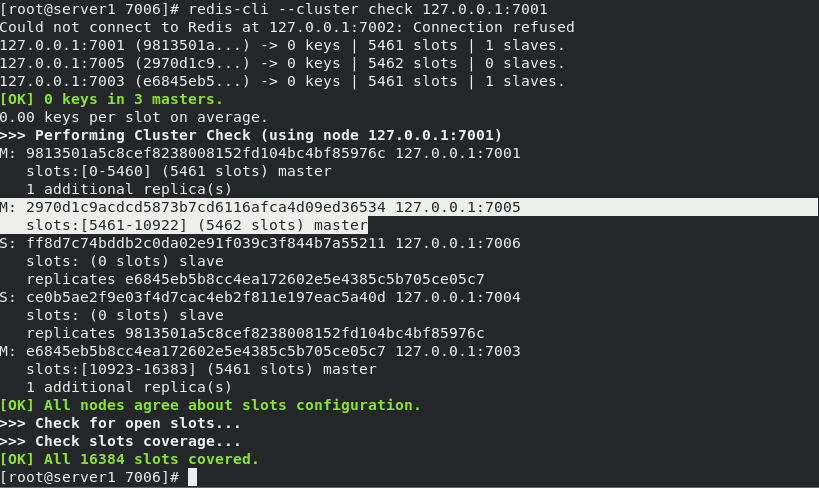
redis-cli --cluster create 127.0.0.1:7001 127.0.0.1:7002 127.0.0.1:7003 127.0.0.1:7004 127.0.0.1:7005 127.0.0.1:7006 --cluster-replicas 1 #Create cluster redis-cli --cluster check 127.0.0.1:7001 ##Check cluster redis-cli --cluster info 127.0.0.1:7001 ##View cluster information
Create six nodes, 1, 2 and 3 as master, one master and one slave
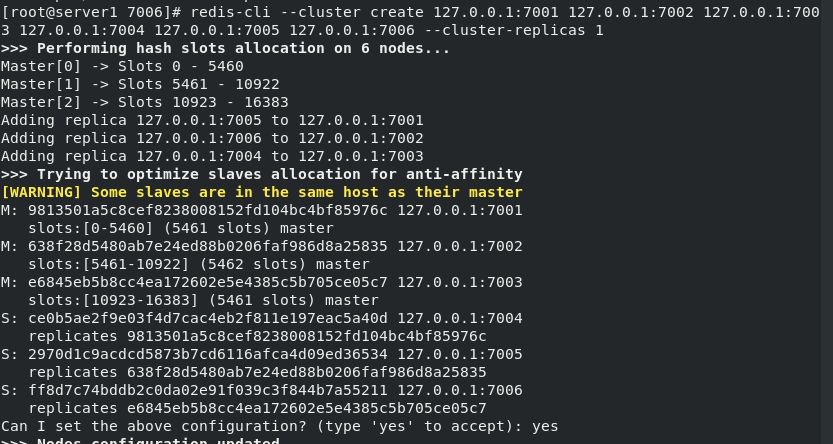
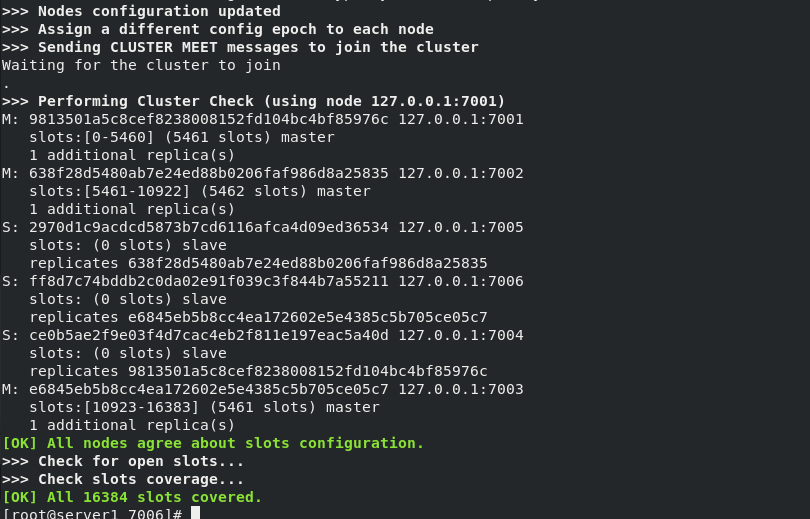
View cluster information (by observing the key here, you can see that the master and slave correspond one by one)
Script build cluster
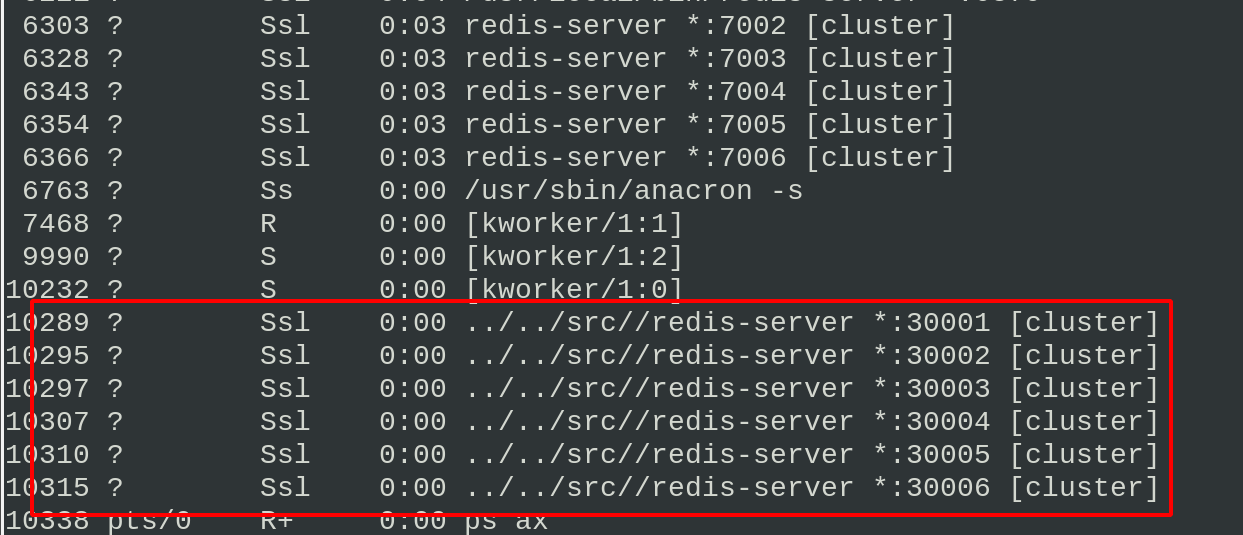
cd cd redis-6.2.4/ cd utils/create-cluster/ ./create-cluster start ##Start instance Starting 30001~30006 ps ax ./create-cluster stop ##Stop all instances and use the manually built cluster to do the next experiment to prevent confusion ps ax #see
2. Automatic switching between master and slave nodes
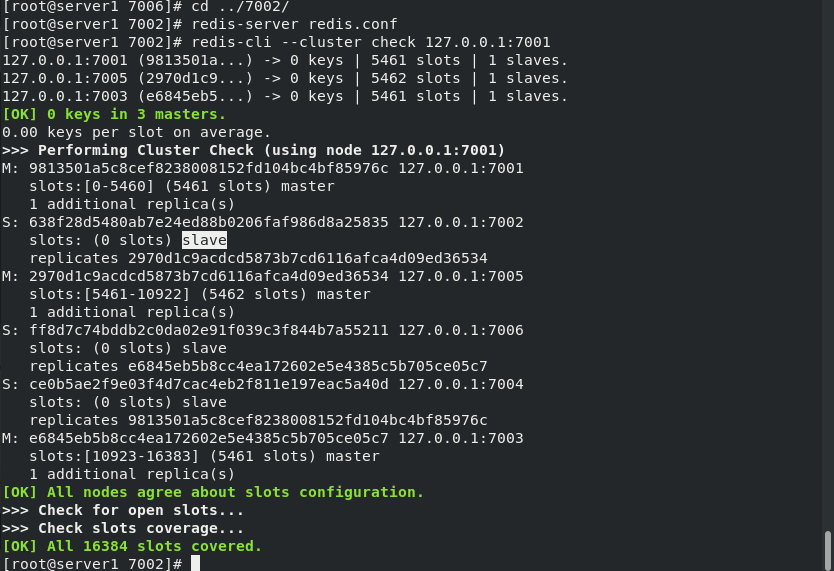
Before viewing the node information, let's go to the node master-slave information, as follows: Master 2 corresponds to slave 5
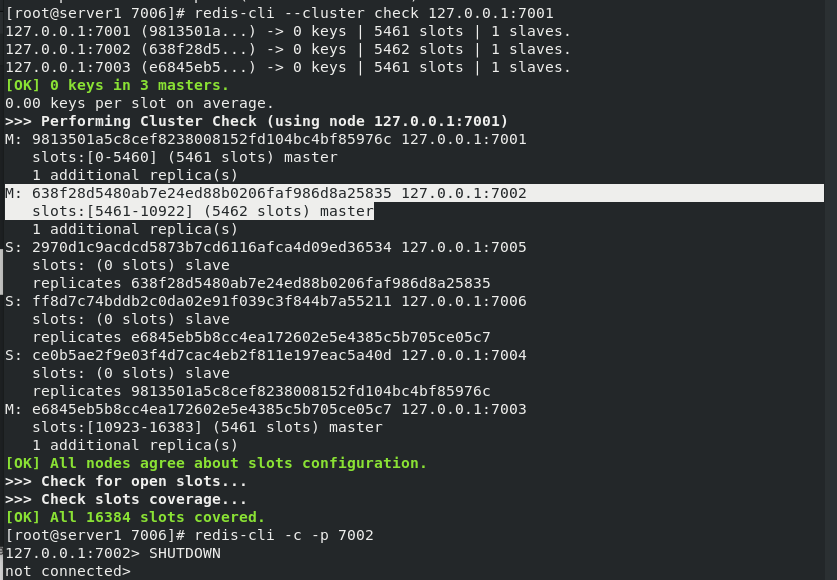
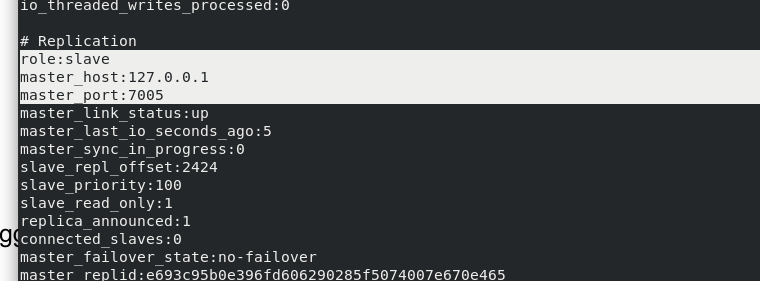
When master 2:7002 is turned off, 7005 will automatically switch to the master node , At this time, there is no slave node. Reopen 7002 and find that 7002 becomes a slave node of 7005


3. Add nodes and shards
Create directories and configuration files for 7007 and 7008 nodes
mkdir 700{7,8}
cd 7007
cp ../7001/redis.conf .
vim redis.conf
///
port 7007
cluster-enabled yes
cluster-config-file nodes.conf
cluster-node-timeout 5000
appendonly yes
daemonize yes
///
redis-server redis.conf
7008 identical
ps ax
Open 7007, The 7007 node is added to the cluster, but no slot is allocated, so this node does not really start to share the cluster work, so it needs to be fragmented. Re fragmentation basically means moving the Hashi slot from one group of nodes to another group of nodes, and it is like creating a cluster.
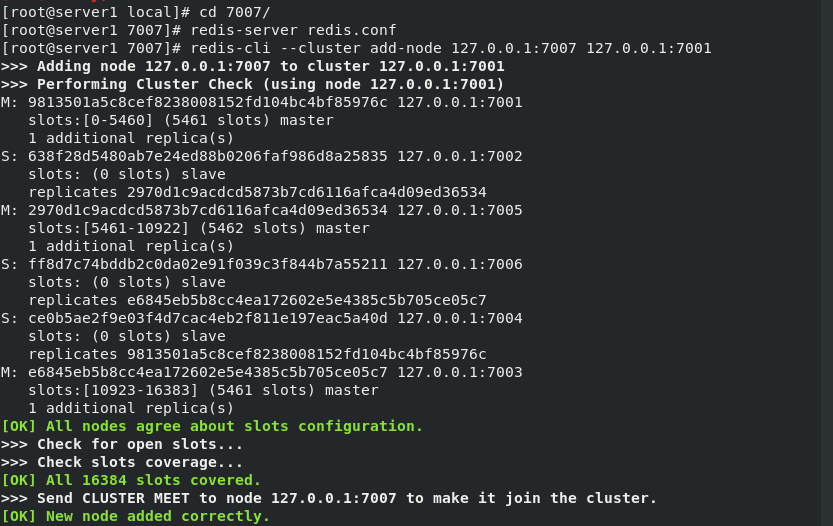
7007 node is master
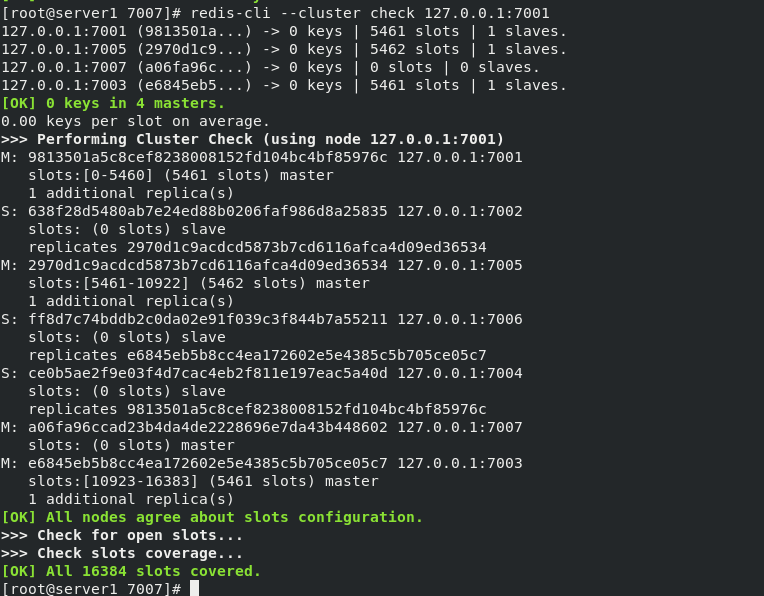
Assign slot
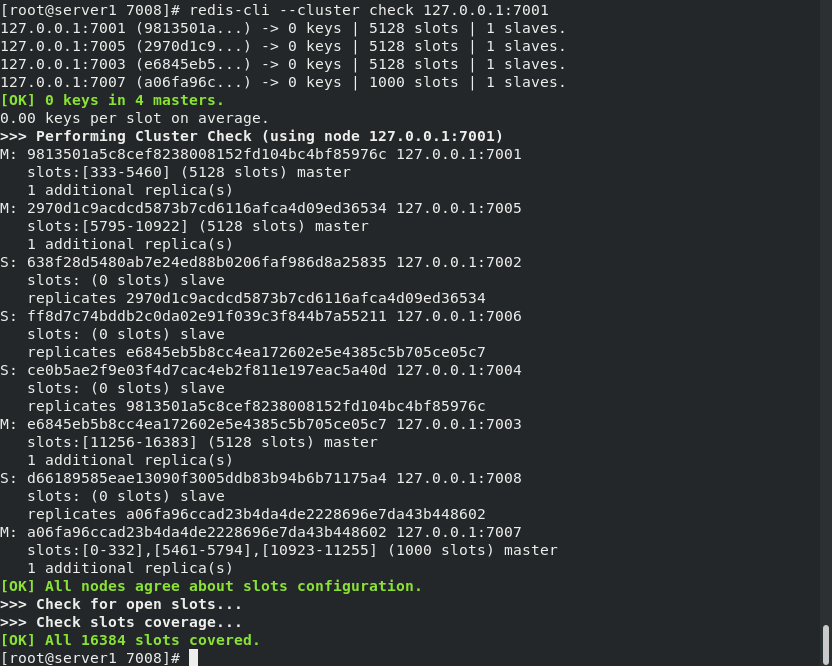
redis-cli --cluster reshard 127.0.0.1:7001 #Repartition Slice operation How many slots do you want to move (from 1 to 16384)? 1000 #Number of slots moved What is the receiving node ##7007 node ID (receiving node ID) Source node #1: all #From which nodes to obtain these keys, enter all to obtain these hash slots from all other master nodes Do you want to proceed with the proposed reshard plan (yes/no)? yes #To determine whether to continue re slicing, enter yes redis-cli --cluster check 127.0.0.1:7001 #Check cluster information
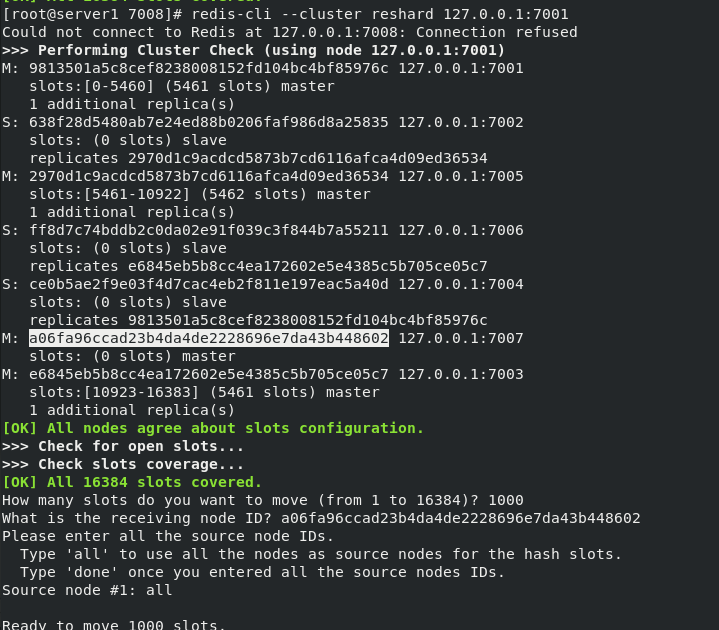
At this time, the 7007 node has 1000 hash slots, and there is no slave node
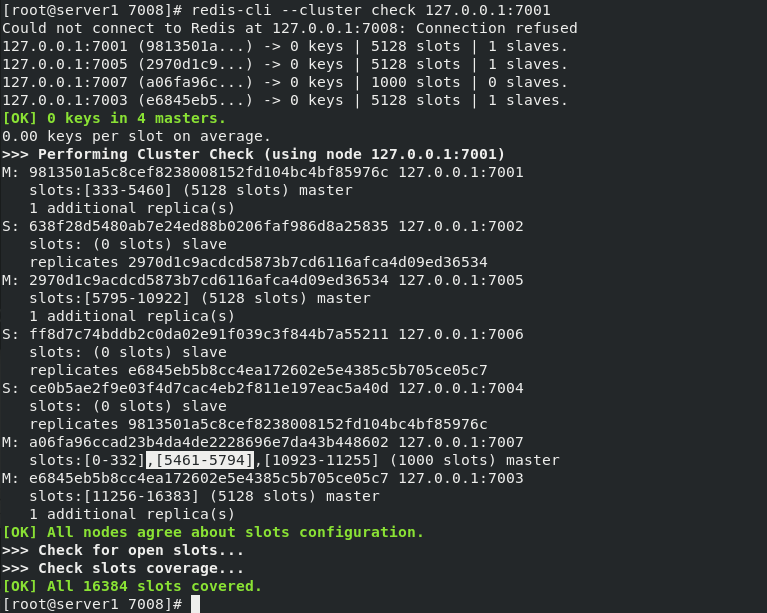
Start 7008 and add 7008 nodes to the cluster of 7001 nodes , As the slave node of 7007. If -- cluster master ID is not specified, it will be randomly assigned to any master node.
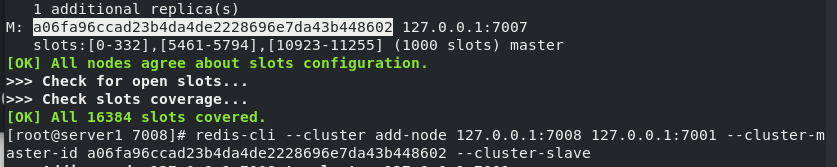
View the cluster. At this time, 7007 has a slave node
6, Redis+Mysql read / write separation
In the actual production environment, the client reads the database directly from redis
If there is no data in the redis cache, you will go to mysql to get the data and cache a copy in redis
There are two situations in which the data in redis cannot be used: the data is expired or the data in mysql is updated. Users access redis when reading and mysql when writing
In fact, the demand for reading is very large. redis just caches the data in memory, and the response speed is fast. It can also reduce the pressure on our background mysql database
Generally, for highly concurrent systems, it is inevitable to build a robust cache system.
The QPS of stand-alone reids may only be tens of thousands. If there is a high concurrency scenario, the stand-alone cannot be solved, and there will be its system bottleneck.
Generally speaking, cache is used to support highly concurrent reads. At this time, we may think of read-write separation. Read-write separation is used to deal with scenarios with large read concurrency and small write concurrency.
In server1 host (nginx+php)
Next, in the last experiment, we need to kill all redis processes. For convenience, we need to install a process management tool to use the kill command to shut down all previous redis processes
yum install -y psmisc ##Easy to use Kill Command killall redis-server ps ax ##No redis and nginx and php are normal
Install the packages php, gearland, libevent devel, libgearman and other related packages
Get package from local host lftp 172.25.254.250 cd /pub/docs/redis mirror rhel7/ exit cd rhel7/ yum install -y *.rpm #Install all systemctl daemon-reload systemctl start php-fpm #Open php
Modify the content of test.php on the test page and modify the master-slave ip
mv test.php /usr/local/nginx/html/
vim test.php
///
3 $redis->connect('172.25.35.2',6379)
10 $connect = mysql_connect('172.25.35.3','redis','westos');
///
In server2 host (redis)
Enable redis info to view the information. Currently, it is the slave of server1. Modify the configuration file / etc/redis/redis.conf, delete the master-slave settings, and restart redis. Info view that server2 is the master at this time
In server3 host (mariadb database)
Stop redis and cancel startup. Delete the redis environment variable and take effect
/etc/init.d/redis_6379 stop chkconfig redis_6379 off ##Cancel startup vim .bash_profile /// PATH=$PATH:$HOME/bin /// source .bash_profile
In server3 host (mariadb database)
Stop rdis and cancel startup. Delete redis environment variables and take effect. Install mariadb, restore mysql configuration files, delete all mysql data files, and start mariadb
/etc/init.d/redis_6379 stop chkconfig redis_6379 off ##Cancel startup vim .bash_profile /// PATH=$PATH:$HOME/bin /// source .bash_profile yum install -y mariadb-server.x86_64 vim /etc/my.cnf /// [mysqld] datadir=/var/lib/mysql socket=/var/lib/mysql/mysql.sock [mysqld_safe] log-error=/var/lib/mysql/mysqld.log pid-file=/var/lib/mysql/mysqld.pid /// systemctl start mariadb
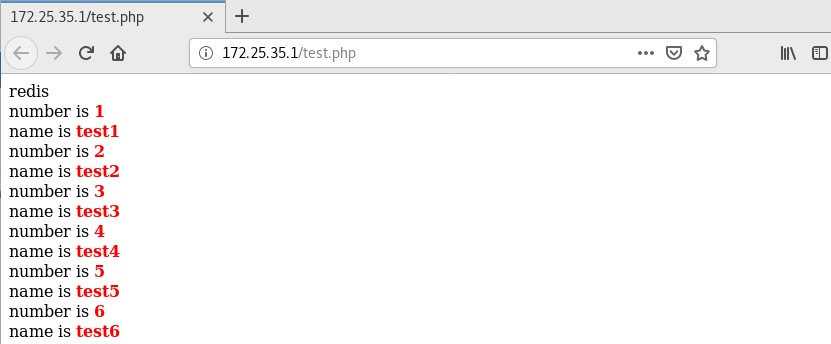
When you enter the database, you can see the test database, import the local file test.sql, enter the database, you can see the imported data, and authorize the redis user
mysql show databases; mysql < test.sql #Import test library contents into mysql > use test > show tables; > select * from test; ##test1~test9 > grant all on test.* to redis@'%' identified by 'westos'; #to grant authorization systemctl restart mariadb.service
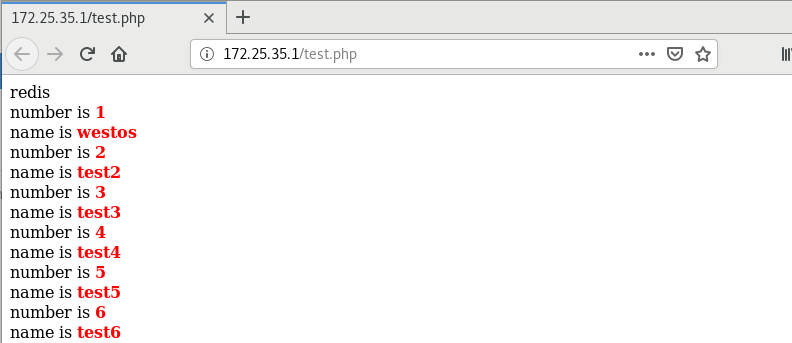
Visit 172.25.173.5/test.php in the browser
This data can only be copied synchronously, not asynchronously. It can only be rewritten and read on redis. The changes on mysql side do not take effect, that is, the data is inconsistent, because the client looks for redis cache when reading and mysql when writing
In server2
redis-cli --> get 1 "test1" --> SET 1 westos ok ...
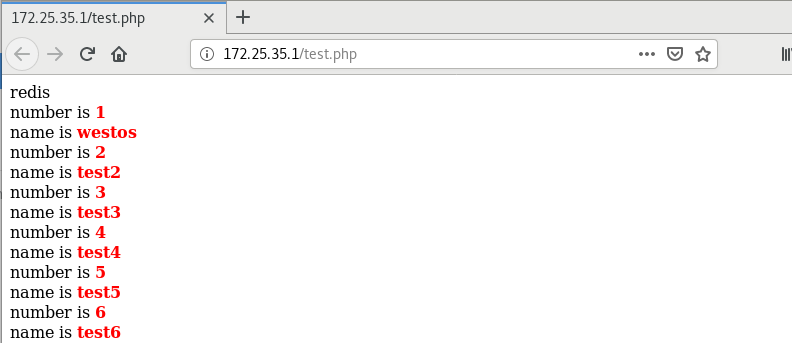
7, redis and mysql keep the data consistent
1. Introduction to Gearman
Gearman provides a general application framework for transferring work to other machines or processes more suitable for work. It allows you to work in parallel, load balance processing, and call functions between languages. It can be used in a variety of applications, from high availability websites to transmitting database replication events
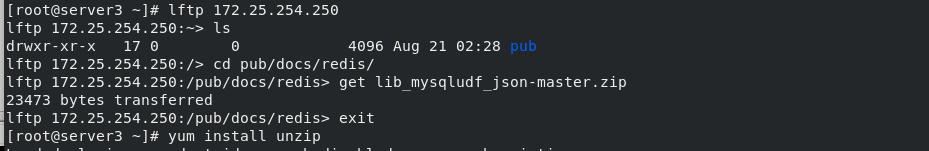
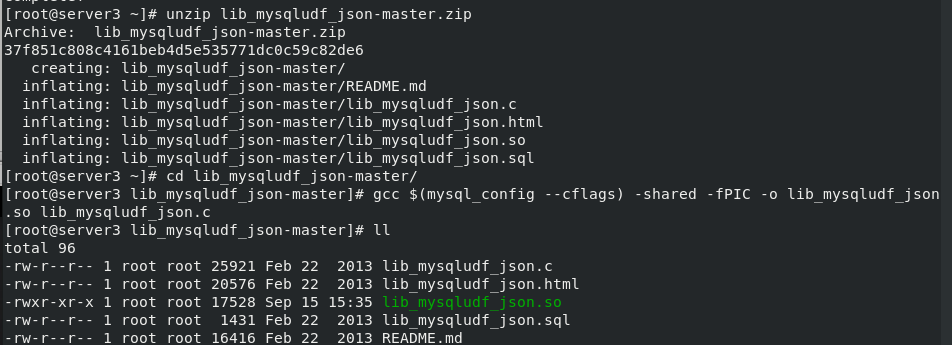
2. Install the database development kit in server3
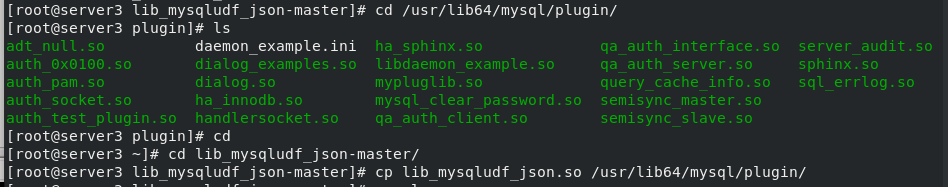
Install the development package of the database, map the relational data to JSON format through the lib_mysqludf_json UDF library function, and copy the lib_mysqludf_json.so module. Enter the database, view the mysql module directory, register the UDF function, and view the function
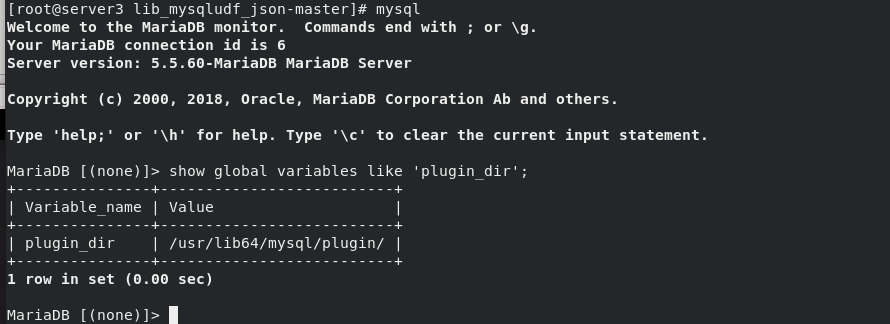
yum install -y unzip unzip lib_mysqludf_json-master.zip cd lib_mysqludf_json-master/ yum install -y gcc gcc $(mysql_config --cflags) -shared -fPIC -o lib_mysqludf_json.so lib_mysqludf_json.c cp lib_mysqludf_json.so /usr/lib64/mysql/plugin/ get into mysql see mysql mysql> show global variables like 'plugin_dir';
3. Register UDF functions
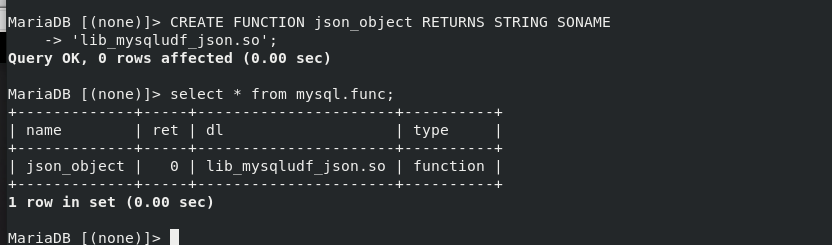
mysql> CREATE FUNCTION json_object RETURNS STRING SONAME 'lib_mysqludf_json.so'; mysql> select * from mysql.func;
4. Download and unzip gearman from server3, solve the dependency, and compile
tar zxf gearman-mysql-udf-0.6.tar.gz
cd gearman-mysql-udf-0.6/
./configure --libdir=/usr/lib64/mysql/plugin/
server1 On the host rhel7 The package contains the following rpm Installation package
yum install -y libgearman* libevent*
#libevent-devel-2.0.21-4.el7.x86_64.rpm
#libgearman-1.1.12-18.el7.x86_64.rpm
#libgearman-devel-1.1.12-18.el7.x86_64.rpm
./configure --libdir=/usr/lib64/mysql/plugin/ Retest
make compile
make install install
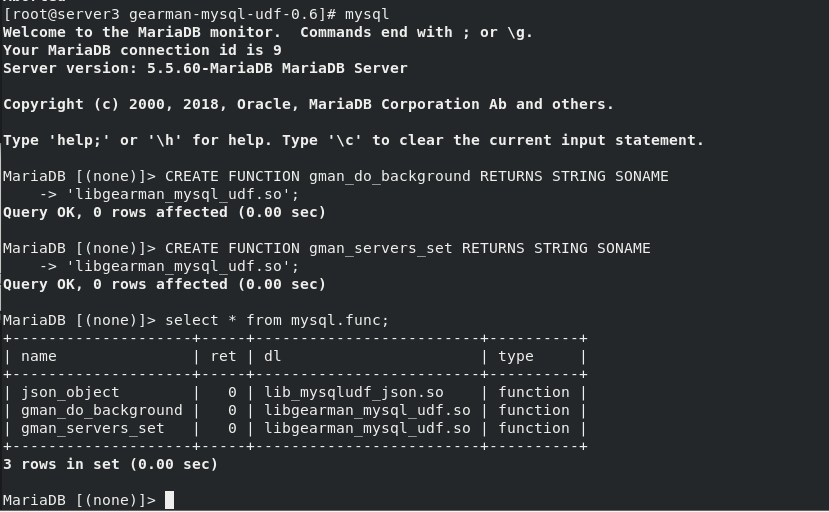
register UDF Function and view
mysql
mysql> CREATE FUNCTION gman_do_background RETURNS STRING SONAME 'libgearman_mysql_udf.so';
mysql> CREATE FUNCTION gman_servers_set RETURNS STRING SONAME 'libgearman_mysql_udf.so';
mysql> select * from mysql.func;
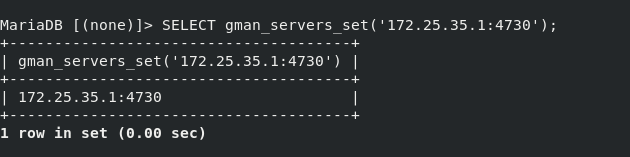
SELECT gman_servers_set('172.25.173.5:4730'); appoint gearman Service information for

5. Edit the mysql trigger and re import the database
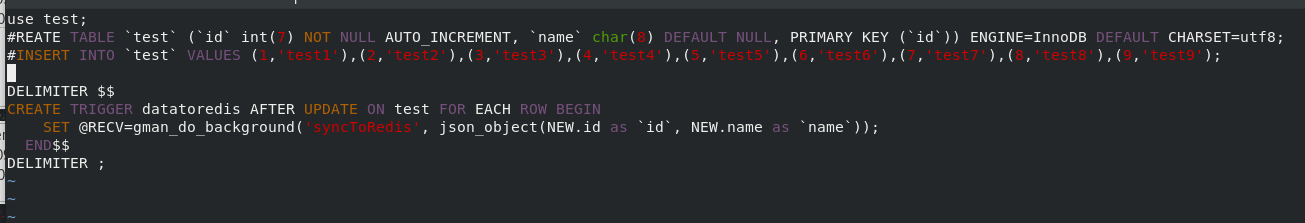
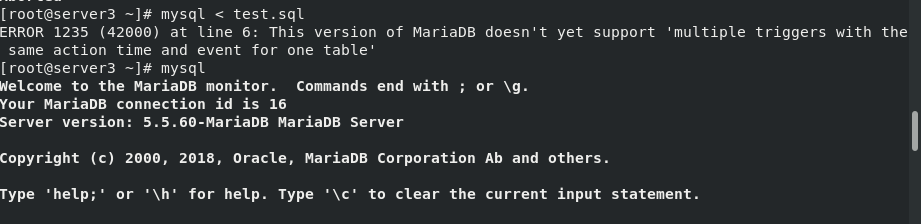
vim test.sql ##Writing mysql triggers mysql -pwestos < test.sql mysql > SHOW TRIGGERS FROM test; ##View triggers
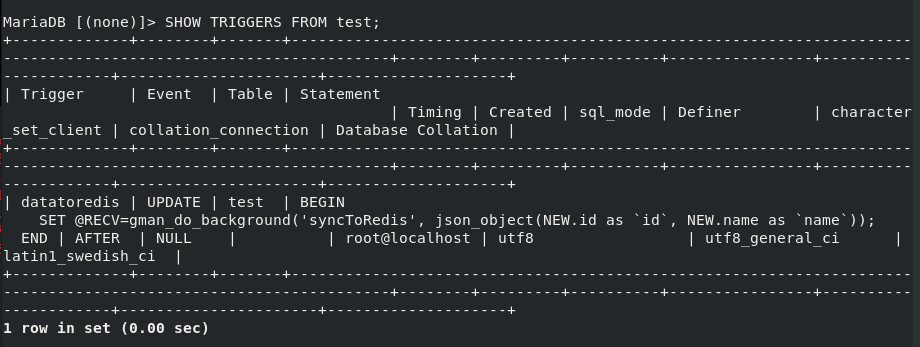
6. Start the service and worker task in server1
systemctl start gearmand ##Start gearman service
php -m | grep gearman #View services
php -m | grep redis
netstat -antlp #Check whether the 4370 port is turned on
cd /root/rhel7/ #Switch the environment to the worker.php directory
vim worker.php #Write the worker side of gearman
///
7 $redis->connect('172.25.35.2', 6379);
///
cp worker.php /usr/local
cd /usr/local
nohup php worker.php & #Run worker.php and enter the background
ps ax #Check whether to open worker.php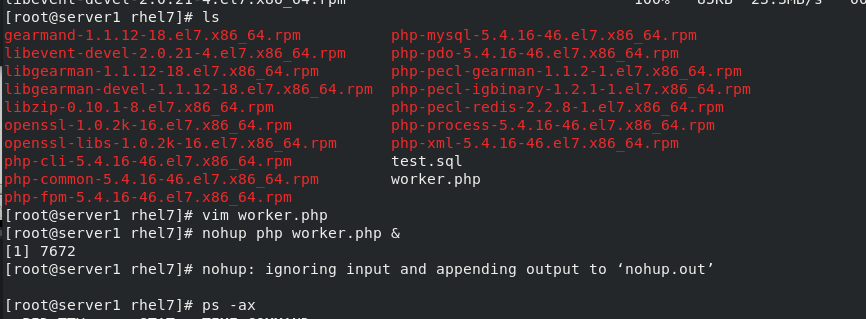

After the service in server1 is started, go to mariadb to change the data. redis in server2 checks whether it is synchronized and the browser checks it.