preface
To serialize and deserialize a class, you only need to implement the java.io.Serializable interface or the java.io.Externalizable interface. Serialization and deserialization can provide support for Java Remote Method Invocation (RMI).
Java serialization
There are three ways to serialize Java:
- Implement the java.io.Serializable interface
- Implement the java.io.Externalizable interface and rewrite the writeExternal() and readExternal() methods
- Implement java.io.Serializable interface, strictly add private void writeobject (objectoutputstream) throws IOException {} and private void readObject (objectinputstream) throws IOException, classnotfoundexception {} methods
Among them, 3 can be regarded as an alternative to 2, unconventional
difference
- All attributes of the class that implements the Serializable interface can be serialized and deserialized; The Externalizable interface can use methods to specify that some attributes are serialized and deserialized.
- The default constructor will not be called during Serializable serialization; Externalizable calls the default constructor.
Serializable and Externalizable interfaces
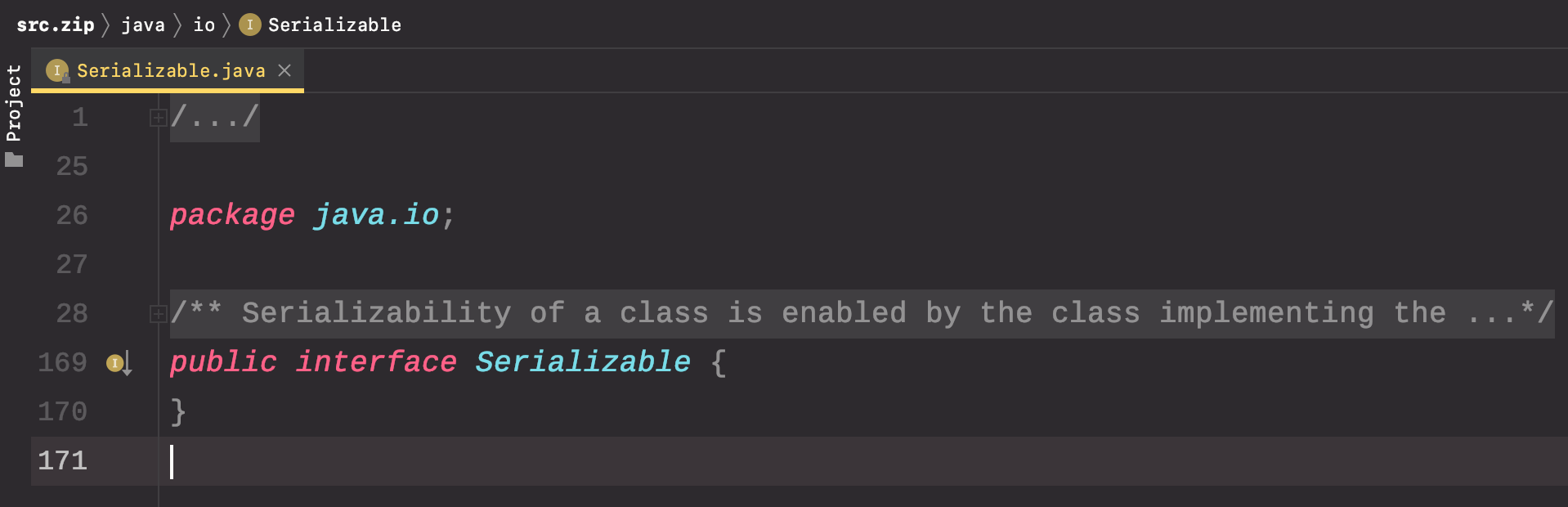
java.io.Serializable
This interface is a sign that the class supports serialization. Classes that need serialization / deserialization should implement it. This interface is an empty interface and is used only as a flag. A class must implement the Serializable interface to serialize!
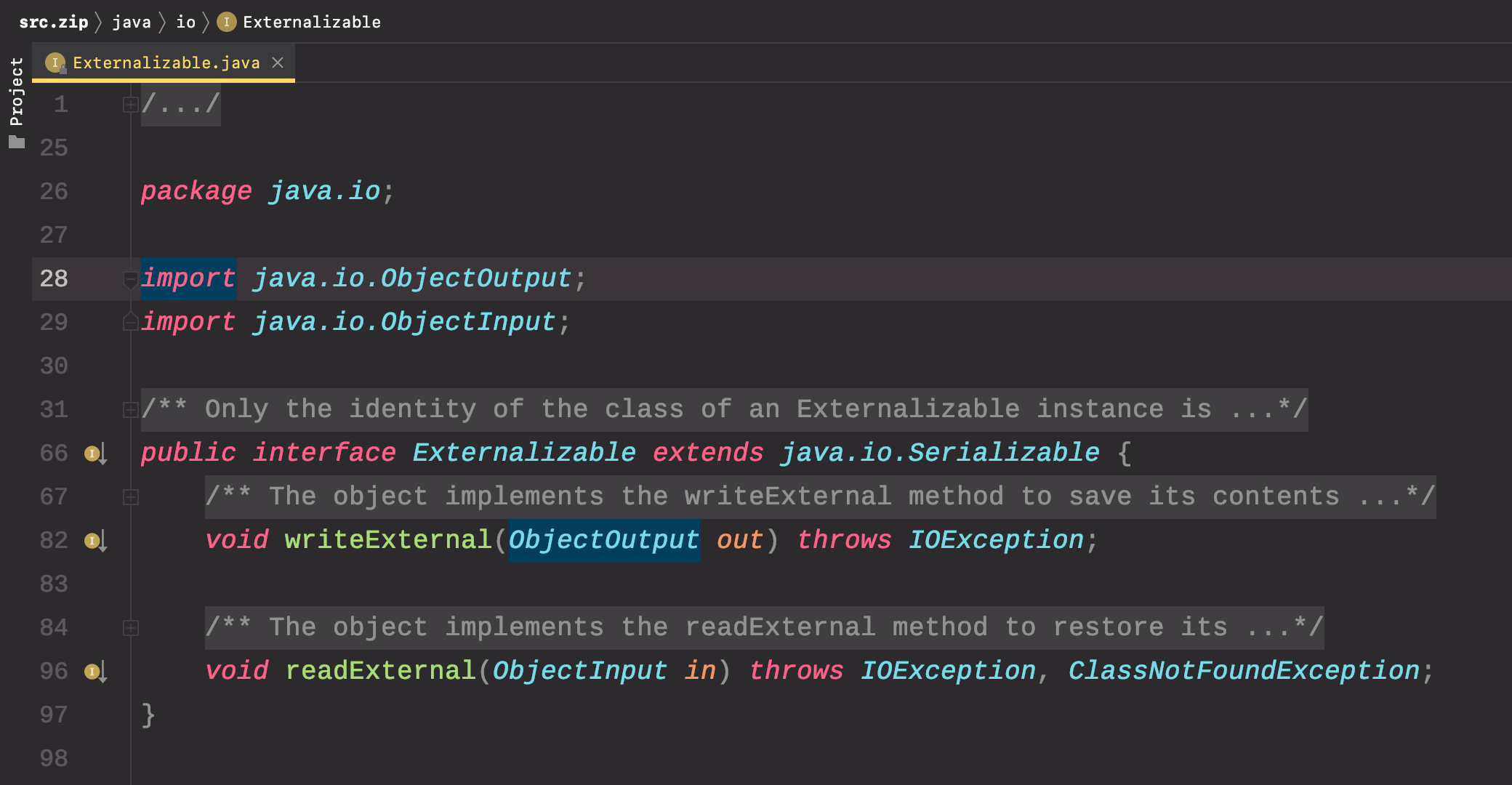
java.io.Externalizable
It inherits from java.io.Serializable and declares two methods writeExternal() and readExternal()
ObjectStream object stream
Serialization and deserialization are a concept. The specific implementation is the exchange of Object instances and ObjectStream streams. The operations are in java.io
import java.io.*;
ObjectOutputStream serialization
Serialization generally uses the ObjectOutputStream class to output objects, generate object streams, and then pass in file streams to write files
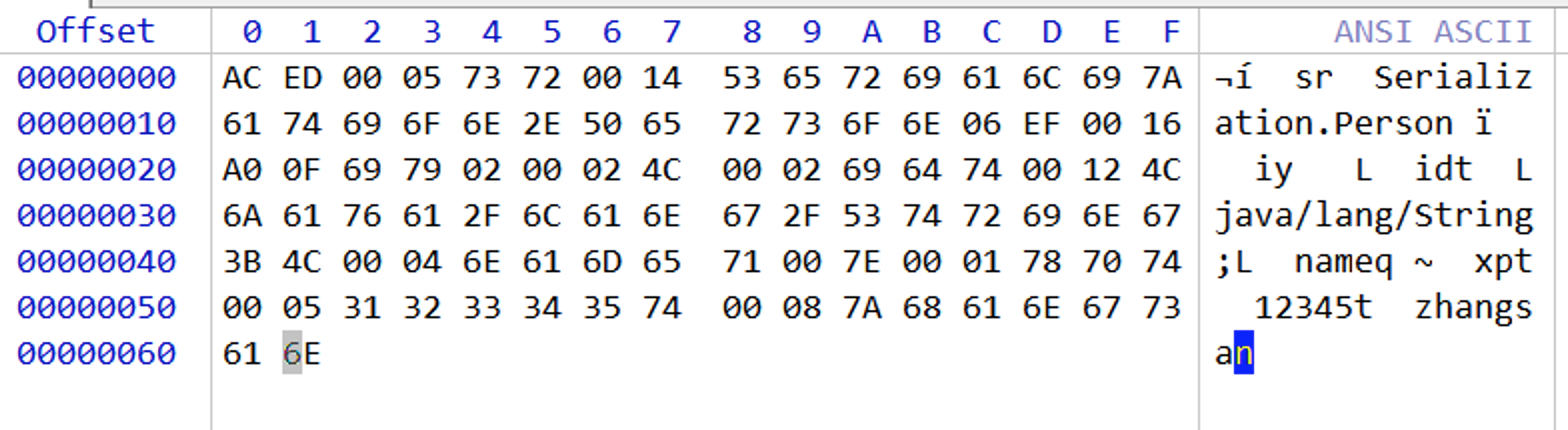
Person p = new Person();
p.setName("zhangsan");
p.setId("12345");
p.setSex("Male");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutStream(new FileOutputStream(new File("tmp.out")))
oos.writeObject(p);
View serialization string
ObjectIntputStream deserialization
Deserialization generally uses the ObjectInputStream class to read the file input file stream, and then pass in the object stream to generate an instance
ObjectInputStream oos = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(new File("tmp.out")))
Person p = (Person) ois.readObject();
The result of deserialization is Object, which requires type conversion
When there are multiple serialized objects in the same object stream: the sequence of deserialization is consistent with that of serialization, just read in order
Person p1 = (Person) ois.readObject(); Person p2 = (Person) ois.readObject(); Person p3 = (Person) ois.readObject();
How to serialize and deserialize?
Serializable interface implementation demo
- Serializable interface is convenient, concise and commonly used
- Serialize all attributes
- Deserialization does not call the (default) constructor
import java.io.*;
public class SerializationTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File f = File.createTempFile("serialize",".out");
System.out.println("[+]create object");
PersonSerialize p = new PersonSerialize("zhangsan",12321);
System.out.println("[.]serialize");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f));
oos.writeObject(p);
System.out.println("[.]Deserialization");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(f));
PersonSerialize pp = (PersonSerialize) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(pp);
f.deleteOnExit();
}
}
class PersonSerialize implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2818606485066001460L;
public String name;
private int id;
public PersonSerialize() {
System.out.println("Parameterless constructor");
}
public PersonSerialize(String name, int id) {
System.out.println("Parametric constructor");
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
}
}
Output:
[+]create object Parametric constructor [.]serialize [.]Deserialization PersonSerialize@6f539caf
Externalizable interface implementation demo
- The Externalizable interface is used to program special requirements
- Specify attribute serialization
- Deserialization calls the parameterless constructor
- The readExternal and readExternal methods need to be overridden
import java.io.*;
public class ExternalSerializationTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File f = File.createTempFile("externalserialize",".out");
System.out.println("[+]create object");
System.out.print("p1 ");
PersonExternalSerialize p1 = new PersonExternalSerialize();
System.out.print("p2 ");
PersonExternalSerialize p2 = new PersonExternalSerialize("zhangsan","Male",12321);
System.out.println("[.]serialize");
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(f));
System.out.print("p1 ");
oos.writeObject(p1);
System.out.print("p2 ");
oos.writeObject(p2);
System.out.println("[.]Deserialization");
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(f));
System.out.print("p1 ");
PersonExternalSerialize pp = (PersonExternalSerialize) ois.readObject();
System.out.print("p2 ");
PersonExternalSerialize ppp = (PersonExternalSerialize) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(pp);
System.out.println(ppp);
System.out.println(ppp.sex);
f.deleteOnExit();
}
}
class PersonExternalSerialize implements Externalizable{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 4184813134939827841L;
public String name;
public String sex;
private int id;
@Override
public void writeExternal(ObjectOutput out) throws IOException {
System.out.println("writeExternal");
out.writeObject(name);
out.writeObject(id);
}
@Override
public void readExternal(ObjectInput in) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
System.out.println("readExternal");
this.name = (String) in.readObject();
this.id = (int) in.readObject();
}
public PersonExternalSerialize() {
System.out.println("Parameterless constructor");
}
public PersonExternalSerialize(String name, String sex,int id) {
System.out.println("Parametric constructor");
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.id = id;
}
}
Output:
[+]create object p1 Parameterless constructor p2 Parametric constructor [.]serialize p1 writeExternal p2 writeExternal [.]Deserialization p1 Parameterless constructor readExternal p2 Parameterless constructor readExternal PersonExternalSerialize@378fd1ac PersonExternalSerialize@49097b5d null
It can be observed that the sex attribute is not serialized, so it is null; Deserialization first called the parameterless constructor
This also demonstrates the deserialization of multiple instances, which can be taken out in turn
finish
Welcome to leave a message in the comment area and follow my CSDN @Ho1aAs