1: Introduction
If the reliability of the message is guaranteed? The following problems need to be solved
Question 1: the producer can send 100% messages to the message queue!
Two unexpected situations:
First, the consumer fails to send a message to MQ, and the message is lost;
Second, the switch fails to route to the queue, and the routing key is written incorrectly;
Question 2: consumers can receive 100% requests, and there can be no errors in the process of business execution!
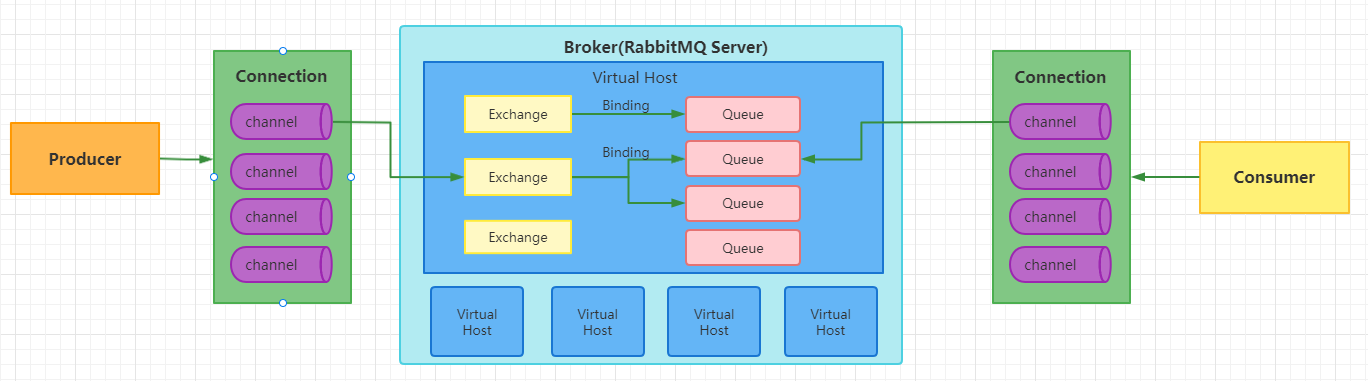
2: Producer confirmation
When using RabbitMQ, the message sender wants to eliminate any message loss or delivery failure scenarios. RabbitMQ provides us with two ways to control the delivery reliability mode of messages.
confirm confirmation mode
Return return mode
rabbitmq the delivery path of the whole message is:
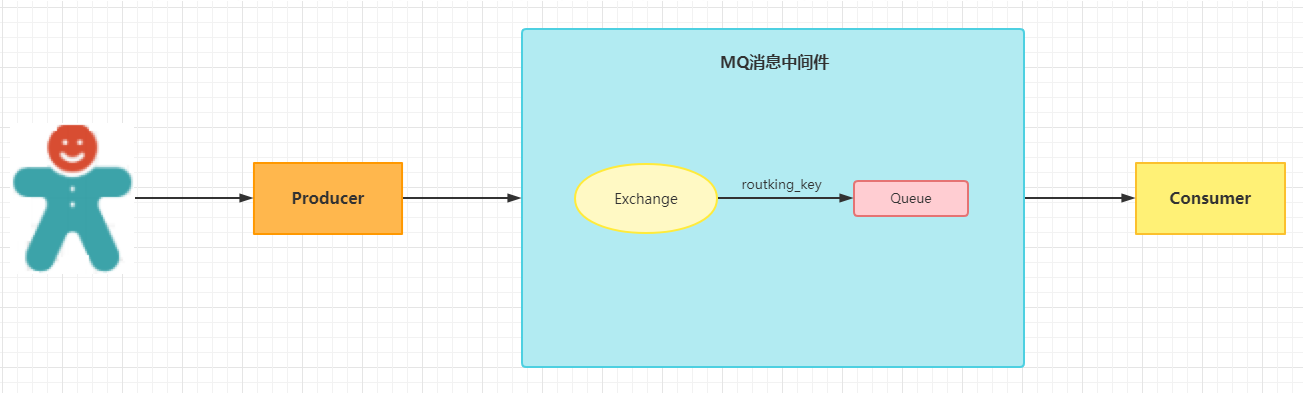
The message sends a message from the producer to the exchange. Whether it is successful or not, a confirmation callback method confirmCallback will be executed.
If the delivery of a message from the exchange to the message queue fails, a return callback method returnCallback will be executed.
We will use these two callback s to control the reliable delivery of messages
1: confirm confirmation mode
target
Demonstrate the effect of message confirmation mode
The producer releases the message confirmation mode. The callback method is executed whether the message enters the switch or not
Implementation steps
1. In the configuration file, turn on the producer publishing message confirmation mode
2. Write producer confirmation callback method
3. In the RabbitTemplate, set the message publishing confirmation callback method
4. Request test:
Test successful callback:
Test failure callback:
Implementation process
1. In the configuration file, turn on the producer publishing message confirmation mode
# Turn on the producer confirmation mode: (confirm), deliver to the switch, and call back whether it fails or succeeds spring.rabbitmq.publisher-confirms=true
2. Write producer confirmation callback method
//Send a message callback confirmation class, implement the callback interface ConfirmCallback, and override the confirm() method
@Component
public class MessageConfirmCallback implements
RabbitTemplate.ConfirmCallback {
/**
* After delivery to the switch, the method will be called back no matter whether the delivery is successful or failed
* @param correlationData Delivery of relevant data
* @param ack Post to switch
* @param cause Reason for delivery failure
*/
@Override
public void confirm(CorrelationData correlationData, boolean ack,
String cause) {
if (ack){
System.out.println("The message entered the switch successfully{}");
} else {
System.out.println("Message failed to enter switch{} , Failure reason:" + cause);
}
}
}3. In the RabbitTemplate, set the message publishing confirmation callback method
@Component
public class MessageConfirmCallback implements
RabbitTemplate.ConfirmCallback{
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
/**
* After creating the RabbitTemplate object, execute the current method and set the callback confirmation method for the template object
* Set message confirmation callback method
* Set message fallback callback method
*/
@PostConstruct
public void initRabbitTemplate(){
//Set message confirmation callback method
rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback(this::confirm);
}
/**
* After delivery to the switch, the method will be called back no matter whether the delivery is successful or failed
* @param correlationData Delivery of relevant data
* @param ack Post to switch
* @param cause Reason for delivery failure
*/
@Override
public void confirm(CorrelationData correlationData, boolean ack,
String cause) {
if (ack){
System.out.println("The message entered the switch successfully{}");
} else {
System.out.println("Message failed to enter switch{} , Failure reason:" + cause);
}
}
}4. Request test:
Test successful callback: http://localhost:8080/direct/sendMsg? exchange=order_ Exchange & routingkey = order. A & MSG = buy Apple phone
Test failure callback: http://localhost:8080/direct/sendMsg?
exchange=order_ XXXXXXXX & routingkey = order. A & MSG = buy Apple phone
2: Return return mode
target
Demonstrate the effect of message fallback mode
Characteristics of message fallback mode: when a message enters the switch and is routed to the queue, a callback method is executed if an exception occurs
Implementation steps
1. In the configuration file, turn on the producer publishing message fallback mode
2. In the MessageConfirmCallback class, implement the interface RabbitTemplate.ReturnCallback
3. And override the returnedMessage() method in the RabbitTemplate.ReturnCallback interface
4. In the RabbitTemplate, set the message publishing fallback callback method
5. Request test:
Test successful callback:
Test failure callback:
Implementation process
1. In the configuration file, turn on the producer publishing message fallback mode
# Turn on the producer fallback mode: (returns), the switch routes messages to the queue, and calls back in case of exceptions spring.rabbitmq.publisher-returns=true
2. In the MessageConfirmCallback class, implement the interface RabbitTemplate.ReturnCallback
@Component
public class RabbitConfirm implements RabbitTemplate.ConfirmCallback
,RabbitTemplate.ReturnCallback {
//.. Omitted
}3. And override the returnedMessage() method in the RabbitTemplate.ReturnCallback interface
/**
* When a message is delivered to the switch, the switch routes to the message queue. If an exception occurs, execute the returnedMessaged party
method
* @param message Post message content
* @param replyCode Return error status code
* @param replyText Return error content
* @param exchange Switch name
* @param routingKey Routing key
*/
@Override
public void returnedMessage(Message message, int replyCode, String
replyText, String exchange, String routingKey) {
System.out.println("Error routing switch to message queue:>>>>>>>");
System.out.println("Switch:"+exchange);
System.out.println("Routing key:"+routingKey);
System.out.println("Error status code:"+replyCode);
System.out.println("Error reason:"+replyText);
System.out.println("Send message content:"+message.toString());
System.out.println("<<<<<<<<");
}4. In the RabbitTemplate, set the message publishing fallback callback method
@PostConstruct
public void initRabbitTemplate(){
//Set message confirmation callback method
rabbitTemplate.setConfirmCallback(this::confirm);
//Set message fallback callback method
rabbitTemplate.setReturnCallback(this::returnedMessage);
}5. Request test failed. Execute returnedMessage method: http://localhost:8080/direct/sendMsg?
exchange=order_ Exchange & routingkey = xxxxx & MSG = buy Apple phone
3: Summary
Confirmation mode
Set publisher confirms = "true" to enable confirmation mode.
Implement the RabbitTemplate.ConfirmCallback interface and override the confirm method
Features: no matter whether the message is successfully delivered to the switch, the confirm method is called back. Only when the sending fails, the business code needs to be written for processing.
Return mode
Set publisher returns = "true" to enable the return mode.
Implement the RabbitTemplate.ReturnCallback interface and override the returnedMessage method
Features: after a message enters the switch, the returnedMessage method is called back only when the route from exchange to queue fails;
3: Consumer confirmation (ACK)
ack refers to an Acknowledge, which has the meaning of confirmation. It is a confirmation mechanism for the consumer to receive a message;
1: Three types of message acknowledgement
Automatic confirmation: acknowledge="none"
Manual confirmation: acknowledge="manual"
Confirm according to the abnormal conditions: acknowledge="auto", (this method is troublesome and will not be explained)
Automatic confirmation means that once a message is received by the Consumer, it will automatically confirm receipt and send the corresponding message from the
RabbitMQ is removed from the message cache. However, in the actual business processing, it is likely that the message will be lost if an exception occurs in the business processing after the message is received.
If a manual confirmation is set, you need to call channel.basicAck() manually after the transaction is successful. If there is an exception, call the channel.basicNack() method to send the message automatically.
 Implement the consumer sign in code yourself: the custom listener involves three objects: the three objects must be injected into the Spring container
Implement the consumer sign in code yourself: the custom listener involves three objects: the three objects must be injected into the Spring container
1. Custom listener object
2. Adapter object of custom listener
3. Listener's container object
You can use the sign in method provided in RabbitTemplate:
2: Code implementation
target
Demonstrate consumer manual validation
Customize the consumer to receive the message listener, listen to the content of the received message, and sign in manually; When the business system throws an exception, it refuses to sign in and returns to the queue
Implementation steps
1. Build a new case project, consumer received ack, to demonstrate the sign in of ack consumers
2. In consumer engineering, create a custom listener class CustomAckConsumerListener to implement
ChannelAwareMessageListener interface
3. Write listener configuration class ListenerConfiguration and configure custom listener binding message queue order.A
Inject the message queue listener adapter object into the ioc container
Inject the message queue listener container object into the ioc container:
Configure connection factory
Configure custom listener adapter object
Configure message queuing
Enable manual sign in
4. Start the consumer service and observe whether the console and consumer listener establish a Connection with RabbitMQ
5. Test sending message and sign in manually
6. Simulation business logic is abnormal
7. Test the exception, demonstrate that the message is rejected and returned to the queue
Implementation process
1. Build a new case project consumer received ACK, and the construction process is similar to the manufacturer's confirmation
2. In consumer engineering, create a custom listener class CustomAckConsumerListener to implement
ChannelAwareMessageListener interface
/**
* Customize the listener. After listening to the message, execute the onMessage method immediately
*/
@Component
public class CustomAckConsumerListener implements
ChannelAwareMessageListener {
/**
* Method executed after listening to the message
* @param message Message content
* @param channel Message channel
*/
@Override
public void onMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws
Exception {
//Get message content
byte[] messageBody = message.getBody();
String msg = new String(messageBody, "utf-8");
System.out.println("After receiving the message, execute the specific business logic{} Message content:"+msg);
//Get delivery label
MessageProperties messageProperties =
message.getMessageProperties();
long deliveryTag = messageProperties.getDeliveryTag();
/**
* The precondition for signing in messages is to enable the manual signing in mode in the listener configuration
* Parameter 1: message delivery label
* Parameter 2: batch sign in: true sign in all at once, false, sign in only the current message
*/
channel.basicAck(deliveryTag,false);
System.out.println("Manual sign in completed:{}");
}
}3. Write listener configuration class ListenerConfiguration and configure custom listener binding message queue order.A
Inject the message queue listener adapter object into the ioc container
Inject the message queue listener container object into the ioc container:
Configure connection factory
Configure custom listeners
Configure message queuing
Enable manual sign in
/**
* Consumer listener configuration, binding listener to message queue
*/
@Configuration
public class ListenerConfiguration {
/**
* Injection message listener adapter
* @param customAckConsumerListener Custom listener object
*/
@Bean
public MessageListenerAdapter
messageListenerAdapter(CustomAckConsumerListener
customAckConsumerListener){
//Create a custom listener adapter object
return new
MessageListenerAdapter(customAckConsumerListener);
}
/**
* Inject message listener container
* @param connectionFactory Connection factory
* @param messageListenerAdapter Custom message listener adapter
*/
@Bean
public SimpleMessageListenerContainer
simpleMessageListenerContainer(
ConnectionFactory connectionFactory,
MessageListenerAdapter messageListenerAdapter){
//Simple message listener container object
SimpleMessageListenerContainer container = new
SimpleMessageListenerContainer();
//Bind message queue
container.setQueueNames("order.A");
//Set connection factory object
container.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
//Setting up the message listener adapter
container.setMessageListener(messageListenerAdapter);
//Set manual confirmation messages: none, manual, auto
Automatic confirmation message)
container.setAcknowledgeMode(AcknowledgeMode.MANUAL);
return container;
}
}4. Start consumer control and observe whether the console and consumer listener establish a Connection with RabbitMQ
5. Test sending message, sign in manually and request address http://localhost:8080/direct/sendMsg?exchange=order_exch Ange & routingkey = order. A & MSG = buy Apple phone
6. Modify the user-defined listener when an exception occurs in the simulation business logic
@Override
public void onMessage(Message message, Channel channel) throws Exception
{
//Get message content
byte[] messageBody = message.getBody();
String msg = new String(messageBody, "utf-8");
System.out.println("After receiving the message, execute the specific business logic{} Message content:"+msg);
//Get delivery label
MessageProperties messageProperties =
message.getMessageProperties();
long deliveryTag = messageProperties.getDeliveryTag();
try {
if (msg.contains("Apple")){
throw new RuntimeException("Apple phones are not allowed!!!");
}
/**
* Manually sign in messages
* Parameter 1: message delivery label
* Parameter 2: batch sign in: true sign in all at once, false, sign in only the current message
*/
channel.basicAck(deliveryTag,false);
System.out.println("Manual sign in completed:{}");
} catch (Exception ex){
/**
* Manually reject sign in
* Parameter 1: delivery label of current message
* Parameter 2: batch sign in: true sign in all at once, false, sign in only the current message
* Parameter 3: whether to return to the queue. true means to return to the queue, and false means not to return
*/
channel.basicNack(deliveryTag,false,true);
System.out.println("Reject sign in and return to the queue:{}"+ex);
}
}7. Test the exception, demonstrate that the message is rejected and returned to the queue
The request address contains an apple. An exception is thrown: http://localhost:8080/direct/sendMsg?exchange=order_ex
Change & routingkey = order. A & MSG = buy an Apple phone
Console print results
2: Summary
If you want to sign in messages manually, you need to customize the implementation of the message receiving listener
ChannelAwareMessageListener interface
Set the AcknowledgeMode mode
none: automatic
auto: exception mode
manual: manual
Call the channel.basicAck method to sign the message
Call the channel.basicNAck method to reject the message