🏇
Small
wood
come
Yes
\textcolor{Orange} {here comes Koki}
Here comes Koki
🍣
no
Tube
Yes
straight
meet
open
punching
,
learn
Just
finish
matter
Yes
\textcolor{green} {no matter, just rush, and learning is over}
No matter what, just drive and learn 🍣
🍣
this
day
of
order
mark
yes
return
Attend to
one
lower
s
e
r
v
l
e
t
with
and
learn
Learn
one
lower
S
p
r
i
n
g
M
V
C
primary
reason
\textcolor{green} {today's goal is to review servlet s and learn the principles of spring MVC}
Today's goal is to review servlet s and learn the principles of spring MVC 🍣
🙏
Bo
main
also
stay
learn
Learn
rank
paragraph
,
as
if
hair
present
ask
topic
,
please
Tell
know
,
wrong
often
sense
thank
\textcolor{Orange} {blogger is also in the learning stage. If you find any problems, please let me know. Thank you very much}
Bloggers are also in the learning stage. If you find any problems, please let us know. Thank you very much 💗
 The code used can be found here
The code used can be found here
First, we need to review what spring (focus: IOC and AOP) and mvc (model view controller) are
🐳 Click to send you to "you can view Spring related"
MVVM: VM: view model bidirectional binding
jsp is essentially a servlet
Spring: it is a hodgepodge. We can register all bean s used in spring MVC into spring
1, Review the servlet
To tell you the truth, if you don't look back, I don't know. I'm almost forgotten.
Create a normal maven project and add web support. Right click add framework support on the project to see it.
step Suddenly \textcolor{red} {step} Steps
- Project framework:
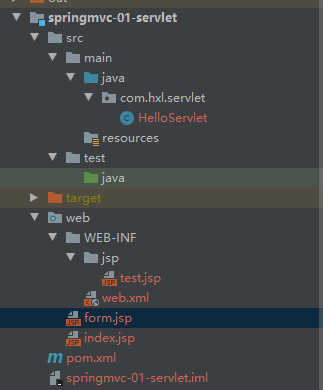
- Import dependency:
<dependencies>
<!--Servlet rely on-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>4.0.1</version>
</dependency>
<!--JSP rely on-->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet.jsp</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet.jsp-api</artifactId>
<version>2.3.3</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
- Write a servlet
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
//1. Get front-end parameters
String method = req.getParameter("method");
if(method.equals("add")){
//Assign a value to the session object
req.getSession().setAttribute("msg","Yes add method");
}
if(method.equals("delete")){
req.getSession().setAttribute("msg","Yes delete method");
}
//2. Call the business layer
//3. View forwarding or redirection (resp.sendRedirect();
req.getRequestDispatcher("/WEB-INF/jsp/test.jsp").forward(req,resp);
}
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
doGet(req, resp);
}
}
- Writing servlet interfaces
The timeout setting is involved in the middle. The default welcome page
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<!--register servlet-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.hxl.servlet.HelloServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<!--servlet Request path for-->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>hello</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/hello</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<!-- <!–Set timeout–>
<session-config>
<session-timeout>15</session-timeout>
</session-config>
<!–Welcome page, the default is index.jsp–>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
-->
</web-app>
- Test page test.jsp
If you don't want users to see the location of the page, it should be placed under the WEB-INF, and the public page should be placed under the web
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
${msg}
</body>
</html>
- Request form form.jsp
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" language="java" %>
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="/hello" method="post">
<input type="text" name="method">
<input type="submit">
</form>
</body>
</html>
Start view
http://localhost:8080/hello A 500 error will be reported because there is no data
http://localhost:8080/hello?method=add : the add method is executed
What the MVC framework does
- Mapping URLs to Java classes or methods of Java classes
- Encapsulate user submitted data
- Processing request – calling related business processing – encapsulating response data
- Render the response data, and represent layer data such as jsp/html
2, Spring MVC principle
Spring MVC is a part of the Spring Framework. It is a lightweight web framework based on java to implement MVC.
🐳 Click send you to Web on Servlet Stack
🐳 Click to send you to Spring MVC 4.2.4.RELEASE Chinese document
🐳 Click to send you to the Spring MVC document directory
I Guys by What Do you want learn Learn S p r i n g M V C ? \textcolor{red} {why should we learn spring MVC?} Why should we learn spring MVC?
Features of spring MVC:
1. Lightweight, easy to learn
2. Efficient MVC framework based on request response
3. Good compatibility with Spring and seamless combination
4. Agreement is greater than configuration
5. Powerful function; Redfull, data validation, formatting, localization, themes, etc
6. Concise and flexible
Central controller
Spring's web framework is designed around dispatcher servlet. The dispatcher servlet is used to distribute requests to different processors. You can use annotation based controller declaration.
Like many other MVC frameworks, the Spring MVC framework is request driven and provides requests and other functions around a central Servlet. The dispatcher Servlet is an actual Servlet (it inherits from the HttpServlet base class)
The principle of Spring MVC is shown in the figure below
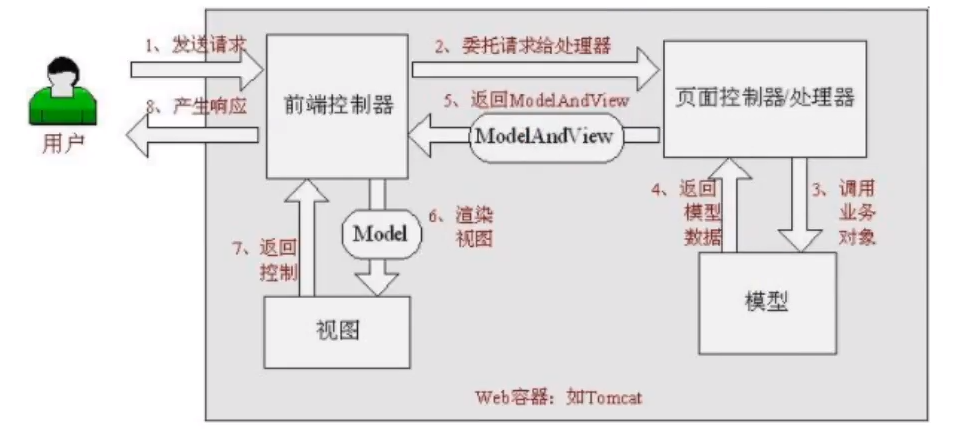
When a request is initiated, the front controller intercepts the request, generates a proxy request according to the request parameters, finds the actual controller corresponding to the request, processes the request, creates a data model, accesses the database, and responds to the model to the central controller. The controller uses the model and view results, returns the results to the central controller, and then returns the results to the requester.
Basic environment
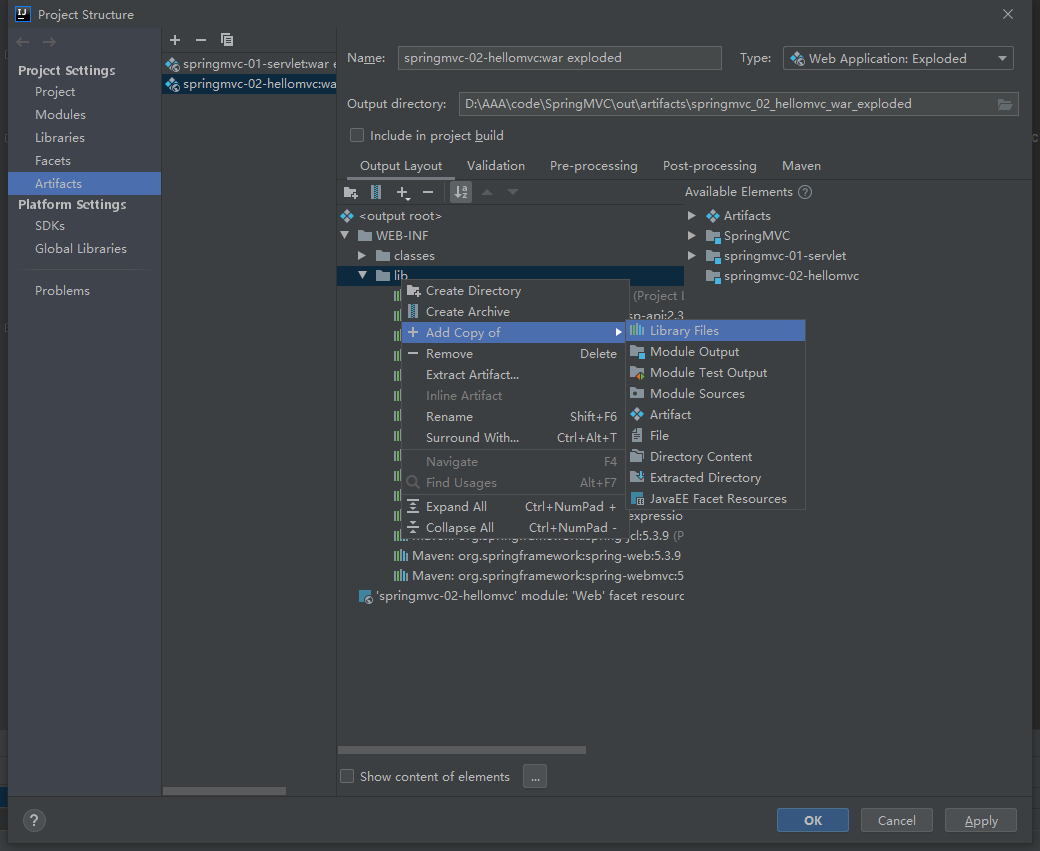
New Module
− − > \textcolor{orange}{-->} − − > Add web support (first, we confirm that maven has spring webmvc dependency, and at the same time, we confirm that the projects published by Artifacts have lib dependency)
− − > \textcolor{orange}{-->} − − > configure web.xml and register DispatcherServlet
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd"
version="4.0">
<!--DispatcherServlet: This is SpringMVC Core of: request distribution-->
<!--org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatchServlet-->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<!--DispatcherServlet To bind Spring Configuration file for-->
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<!--classpath*: Will find the configuration files of all paths, and classpath: Will find the configuration file under the current path-->
<param-value>classpath:springmvc-servlet.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<!--Startup level: 1 means that the server starts as soon as it starts-->
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<!--stay SpringMVC Medium: / /* Differences between
/: Only match all requests, not match jsp page
/*: Match all requests, including jsp page
-->
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springmvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
− − > \textcolor{orange}{-->} − − > write the configuration file for the spring MVC file. Name: springmvc-servlet.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--springmvc Three core elements-->
<!--Processor mapper-->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping"/>
<!--Processor adapter-->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter"/>
<!--View parser: template engine Thymeleaf Freemarker-->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver" id="internalResourceViewResolver">
<!--Prefix, suffix-->
<property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/jsp/"/>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"/>
</bean>
<!--BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping:bean-->
<bean id="/hello" class="com.hxl.controller.HelloController"/>
</beans>
− − > \textcolor{orange}{-->} − − > add process mapper
− − > \textcolor{orange}{-->} − − > Add processor adapter
− − > \textcolor{orange}{-->} − − > Add view parser
− − > \textcolor{orange}{-->} − − > write that we want to operate the business Controller, either implement the Controller interface or add annotations; You need to return a ModelAndView to load data and seal the view
package com.hxl.controller;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.Controller;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class HelloController implements Controller {
public ModelAndView handleRequest(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse) throws Exception {
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
//Business code
String result = "HelloSpringMVC";
modelAndView.addObject("msg", result);
//View jump
modelAndView.setViewName("test");
return modelAndView;
}
}
− − > \textcolor{orange}{-->} − − > give your class to the spring IOC container and register the bean
<!--BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping:bean--> Look at the configuration file above
− − > \textcolor{orange}{-->} − − > write the jsp page to jump to, display the data stored in ModelAndView, and our normal page
− − > \textcolor{orange}{-->} − − > configure Tomcat Startup Test
can can meet reach of ask topic : interview ask Out present 404 , Row check step Suddenly : \textcolor{red} {possible problems: 404 in access, troubleshooting steps:} Possible problems: visit 404, troubleshooting steps:
-
Check the console output to see if there is any missing jar package
-
If the jar package exists and the display cannot be output, add lib dependencies in the project release of IDEA (add a lib folder under this, and then put all dependencies in it)
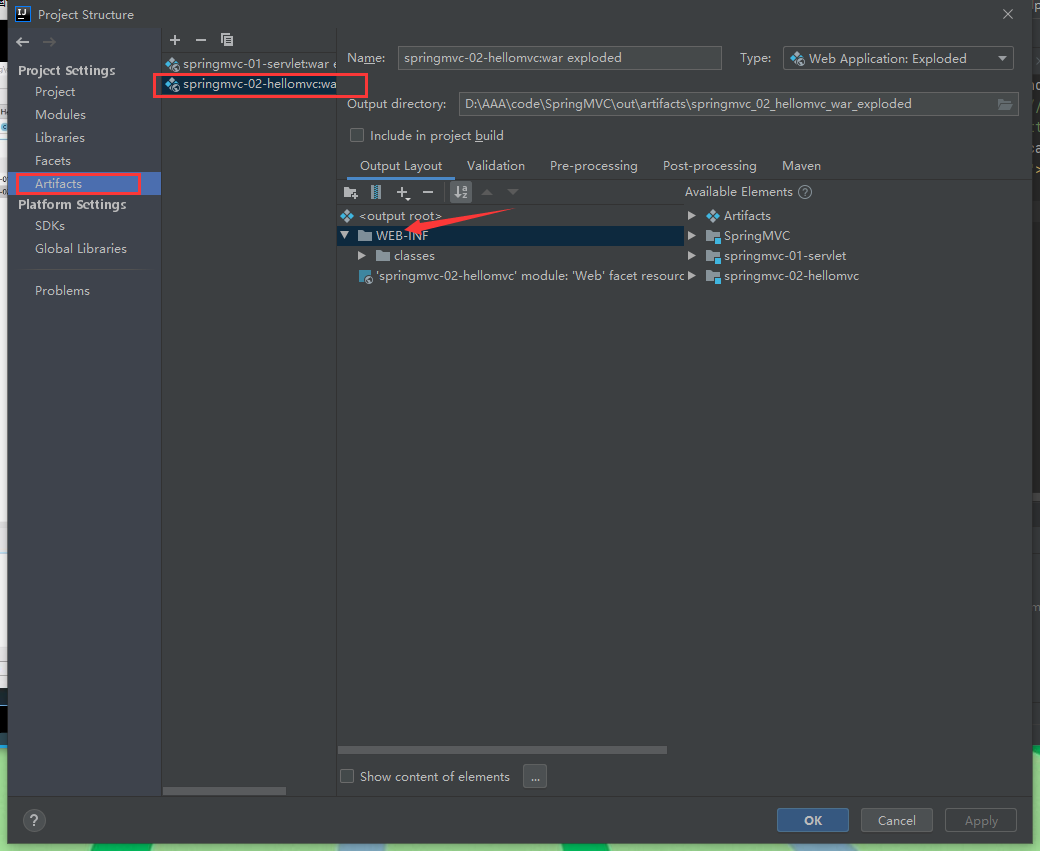
-
Restart Tomcat
Spring MVC execution principle
The following figure is a relatively complete flow chart of spring MVC. The implementation represents the technology provided by the spring MVC framework and does not need to be implemented by developers. The dotted line indicates that it needs to be implemented by developers
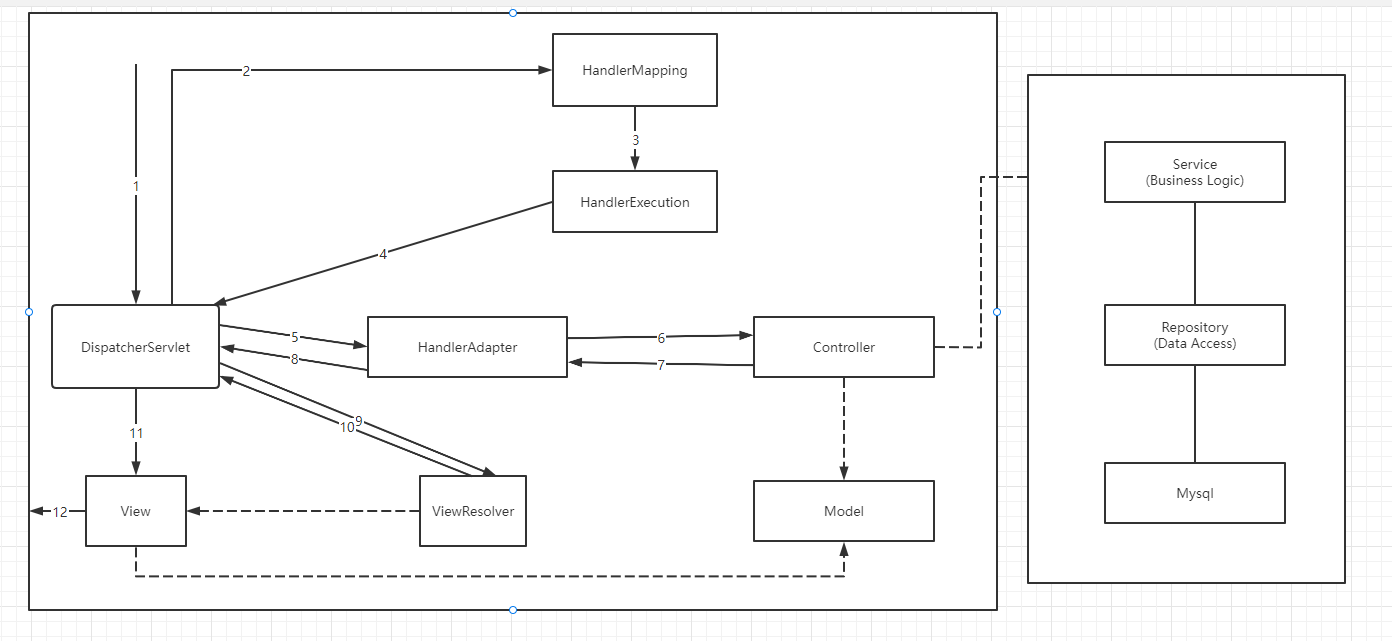
Analysis execution process
- DispatcherServlet represents the front controller and is the control center of the whole spring MVC. The user sends a request, and the DispatcherServlet accepts the request and intercepts the request;
- For example, the url of the request is: http://localhost:8080/SpringMVC/hello
- Split the url into three parts:
- http://localhost:8080 Server domain name
- Spring MVC is a web site deployed on a server
- hello indicates the controller
- Through analysis, the url is expressed as: request the hello controller of the spring MVC site located on the server localhost:8080
- HandlerMapping is processor mapping. DispatcherServlet calls HandlerMapping, which looks up the Handler according to the request url.
- HandlerExecution refers to a specific Handler. Its main function is to find the controller according to the url. The controller found by the url above is: hello
- HandlerExecution is the information passed to the dispatcher servlet after parsing, such as parsing controller mapping
- HandlerAdapter indicates that the processor is configured to execute the Handler according to specific rules
- The Handler lets the specific Controller execute
- The Controller returns the specific execution information to the HandlerAdapter, such as ModelAndView
- The HandlerAdapter passes the view logical name or model to the dispatcher servlet.
- DispatcherServlet calls the view resolver to resolve the logical view name passed by the HandlerAdapter
- The view parser passes the parsed logical view name to the dispatcher servlet
- DispatcherServlet calls the specific view according to the view result parsed by the view parser
- The final view is presented
View parser: ModelAndView given to it by dispatcher Servlet
Got the data of ModelAndView
Resolve the view name of ModelAndView
Splice the view name and find the corresponding view
Render the data to this view