catalogue
4. Arrangement and combination
7. Decimal conversion to arbitrary base
1. Maximum common factor
Title No.: Exp06-Basic04
Title: maximum common factor
Title Description: write a program to solve the maximum common divisor of m and n by recursive method. For positive integers u and v, the Euclidean rolling division algorithm can be used to calculate their maximum common factor. The specific process is as follows:
u% v → r~1~
v % r~1~ → r~2~
r~1~% r~2~ → r~3~
r~2~ % r~3~ → r~4~
... ...
r~n-1~% r~n~ → r~n+1~=0
When the remainder r~n+1~=0, the calculation process ends, and r~n ~ is the maximum common factor of positive integers u and v.
Input: randomly input two positive integers m and n from the keyboard. Output: maximum common factor.
Example 1:
Input: 12 15
Output: 3
Example 2:
Input: 28 49
Output: 7
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int gcd(int x, int y)
{
if (y == 0)return x;
else
return gcd(y, x % y);
}
int main()
{
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
cout << gcd(x, y);
return 0;
}Compare a basic problem, using the rolling division method to find the maximum common divisor
2.Hermite polynomial
Title No.: Exp06-Basic02, GJBook3-10-03
Title: Hermite polynomial
Title Description: write a program to solve the Hermite polynomial value by recursive method. Hermite polynomials are defined as follows.
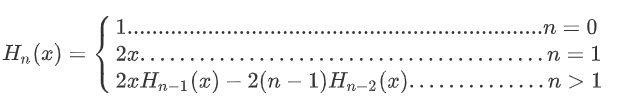
Input: randomly input a non negative integer and a real number from the keyboard as the values of n and x.
Output: the value of H~n~(x), accurate to 2 decimal places.
Example 1:
Input: 0 1.5
Output: 1.00
Example 2:
Input: 2 2.4
Output: 21.04
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
double Hermite(int n,double x)
{
if (n == 0)return 1;
if (n == 1)return 2 * x;
return 2 * x * Hermite(n - 1, x) - 2 * (n - 1) * Hermite(n - 2, x);
}
int main()
{
int n;
double x;
cin >> n >> x;
cout << fixed << setprecision(2) << Hermite(n, x);
return 0;
}Note that the return value type of Hermite function is double, and recursion is written directly according to the given formula
3. Ackerman function
Title No.: Exp06-Basic03, GJBook3-10-04
Title: Ackerman function
Problem Description: write a program to calculate the {Ackerman} function value. The Ackerman} function is defined as follows
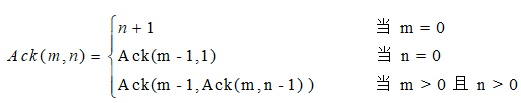
Input: input two non negative integers randomly from the keyboard as the values of m and n.
Output: value of Ack(m, n).
Example 1: input 2} 3} output 9
Example 2: input 3} output 2} 29
Example 3: input {0 3} output} 4
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int Ack(int m, int n)
{
if (m == 0)return n + 1;
if (n == 0)return Ack(m - 1, 1);
return Ack(m - 1, Ack(m, n - 1));
}
int main()
{
int m, n;
cin >> m >> n;
cout << Ack(m, n) << endl;
return 0;
}4. Arrangement and combination
Title No.: Exp06-Basic01, GJBook3-10-02
Title: arrangement and combination
Problem Description: write a program to find the value of function C(m,n).
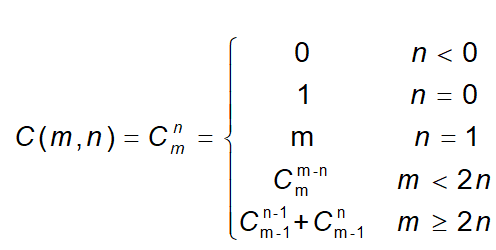
Input: randomly input a natural number and a non negative integer from the keyboard as the values of M and n (m ≥ n).
Output: value of function C(m,n).
Example 1:
Input:
4 1
Output:
4
Example 2:
Input: 6 2 Output: 15
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int C(int m, int n)
{
if (n < 0)return 0;
if (n == 0)return 1;
if (n == 1)return m;
if (m < 2 * n)return C(m, m - n);
if (m >= 2 * n)return C(m - 1, n - 1) + C(m - 1, n);
}
int main()
{
int m, n;
cin >> m >> n;
cout << C(m, n);
return 0;
}Pay attention to the relative positions of m and n in the C function {and don't confuse the two
5. Maximum element
Title No.: Exp06-Enhance01, GJBook3-10-05
Title: maximum element
Title Description: write a program to solve the maximum element value in the integer array with length n by recursive method.
Input: in the first line, enter a positive integer n (0 < n ≤ 100), indicating the number of elements of the array; in the second line, enter n integers in turn as the elements of the array.
Output: the value of the largest element.
Example 1:
Input: 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Output: 9
Example 2:
Input: 10 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Output: 9
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int Max(int* a,int len)
{
if (len == 1)return *a;
if (a[len - 2] < a[len - 1])
a[len - 2] = a[len - 1];
return Max(a, len - 1);
}
int main()
{
int n, * a;
cin >> n;
//a = new int[n];
a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
for (int i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
}
cout << Max(a,n);
return 0;
}Hahaha, since there is no new in C language, malloc function is generally used to dynamically distribute a's memory
6. Array reverse order
Title No.: Exp06-Enhance02
Title: array reverse order
Title Description: write a program to reverse the array with recursive method.
Input: in the first line, enter a positive integer n (0 < n ≤ 100), indicating the number of elements of the array; in the second line, enter n integers in turn as the elements of the array.
Output: sequentially output the elements in the array in reverse order. The elements are separated by a Western space, and there are no characters after the last element.
Example 1:
Input: 8 0 2 3 4 5 9 10 8
Output: 8 10 9 5 4 3 2 0
Example 2:
Input: 5 0 2 3 3 5
Output: 5 3 3 2 0
#include <iostream>
#include <malloc.h>
using namespace std;
void Reverse(int* a,int len)
{
if (len == 1)
cout << a[len - 1];//Do not output spaces at the end of the line to prevent errors
if (len > 1)
{
cout << a[len - 1]<<" ";
Reverse(a, len - 1);
}
}
int main()
{
int n, * a;
cin >> n;
a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * n);
for (int i = 0;i < n;i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
}
Reverse(a, n);
return 0;
}After testing, the Reverse of this question can also be written directly like this
void Reverse(int* a,int len)
{
if (len > 0)
{
cout << a[len - 1]<<" ";
Reverse(a, len - 1);
}
}7. Decimal conversion to arbitrary base
Title No.: Exp06-Enhance05, freshman-1022
Title: decimal conversion to arbitrary base
Title Description: write a program to convert decimal positive integer N into b-ary number (2 ≤ B ≤ 36) by recursive method, in which the corresponding relationship between characters, ASCII code values and values is as follows:
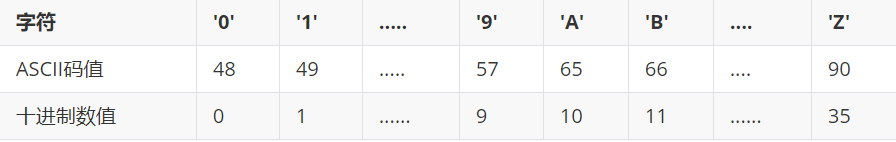
Input: input two non negative integers in one line, respectively decimal N and b, where 0 < = n < = 2 ^ 31, 2 < = b < = 36.
Output: b-ary number of N.
Example 1:
Input: 579 8
Output: 1103
Example 2:
Input: 579 20
Output: 18J
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void trans(long long a, int b)
{
if (0 == a)
return;
trans(a / b, b);
cout<< "0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ"[a % b];
}
int main()
{
long long a;
int b;
cin >> a >> b;
if (a == 0)cout << "0";
else trans(a, b);
return 0;
}
8. Sequential search
Title No.: Exp06-Basic05, GJBook3-10-06
Title: sequential retrieval
Title Description: write a program for sequential retrieval in integer groups by recursive method.
Input:
In the first line, enter a positive integer n (0 < n ≤ 100), indicating the number of elements of the array;
In the second line, input n integers as the elements of the array;
In the third line, enter the keyword to be retrieved.
Output:
If the array contains keywords, the position where they first appear (the position where the subscript value is small) is output; otherwise, NULL is output.
Example 1:
Input: 8 0 2 3 4 5 9 10 8 3
Output: 2
Example 2:
Input: 8 0 2 3 4 5 9 10 8 6
Output: NULL
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int Search(int* a, int key, int len,int num)
{
if (num == len)return -1;
if (*(a + num) == key)return num;
else
return Search(a, key, len, num + 1);
}
int main()
{
int len, * a, key;
cin >> len;
a = new int[len];
for (int i = 0;i < len;i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
}
cin >> key;
int x = Search(a, key, len, 0);
if (x == -1)cout << "NULL" << endl;
else cout << x << endl;
return 0;
}