"Do you know ThreadLocal?"
"Tell me about your understanding of ThreadLocal"
Of course, some interviewers will slowly lead to this topic, such as asking "how to prevent their variables from being tampered with by other threads in a multi-threaded environment", giving the initiative to yourself, and the rest depends on yourself.
What can ThreadLocal do? Before understanding its application scenario, let's first look at its implementation principle. Only after knowing the implementation principle can we judge whether it conforms to its own business scenario.
##What is ThreadLocal
First, it is a data structure, a bit like HashMap. It can save "key: value" key value pairs, but only one ThreadLocal can be saved, and the data of each thread does not interfere with each other.
ThreadLocal<String> localName = new ThreadLocal();
localName.set("Zhan Xiaolang");
String name = localName.get();
A ThreadLocal object localName is initialized in thread 1, and a value accounting for Xiaolang is saved through the set method. At the same time, it is initialized in thread 1 through localName Get () can get the value set before, but if it is in thread 2, it will get a null.
Why and how? However, as mentioned earlier, ThreadLocal ensures that the data of each thread does not interfere with each other.
Look at the source code of the set(T value) and get() methods
public void set(T value) {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null)
map.set(this, value);
else
createMap(t, value);
}
public T get() {
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t);
if (map != null) {
ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this);
if (e != null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
T result = (T)e.value;
return result;
}
}
return setInitialValue();
}
ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) {
return t.threadLocals;
}
It can be found that each thread has a ThreadLocalMap data structure. When the set method is executed, its value is saved in the threadLocals variable of the current thread. When the set method is executed, it is obtained from the threadLocals variable of the current thread.
Therefore, the value of set in thread 1 cannot be touched by thread 2, and if it is reset in thread 2, it will not affect the value in thread 1, ensuring that threads will not interfere with each other.
What is the threadloadmap in each thread?
##ThreadLoalMap
This paper analyzes the source code of 1.7.
From the name, you can guess that it is also a data structure similar to HashMap, but the Map interface is not implemented in ThreadLocal.
In threadloadmap, an Entry array with a size of 16 is also initialized. The Entry object is used to save each key value pair, but the key here is always ThreadLocal object. Isn't it amazing? Through the set method of ThreadLocal object, the ThreadLocal object itself is regarded as a key and put into threadloadmap.
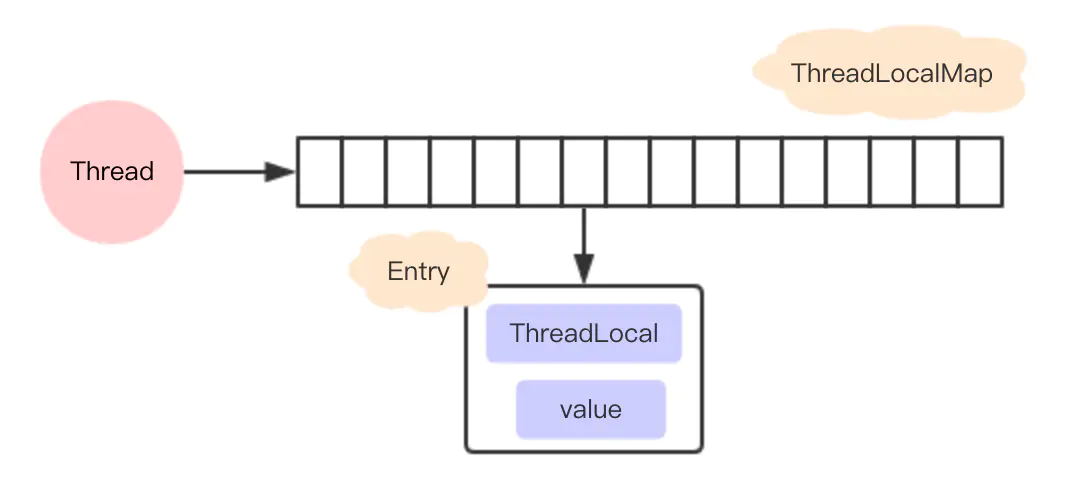
It should be noted that the Entry of threadloadmap inherits the WeakReference. The big difference between threadloadmap and HashMap is that there is no next field in the Entry, so there is no linked list.
##hash conflict
If there is no linked list structure, what if there is a hash conflict?
Let's first look at the implementation of inserting a key value into threadloadmap
private void set(ThreadLocal<?> key, Object value) {
Entry[] tab = table;
int len = tab.length;
int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1);
for (Entry e = tab[i];
e != null;
e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) {
ThreadLocal<?> k = e.get();
if (k == key) {
e.value = value;
return;
}
if (k == null) {
replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i);
return;
}
}
tab[i] = new Entry(key, value);
int sz = ++size;
### last
Because the copy is too long, I won't introduce it one by one here,**This Java Back end architecture advanced notes include: Java Gather, JVM,Java Concurrency, microservices SpringNetty And RPC ,Network, log Zookeeper ,Kafka ,RabbitMQ ,Hbase ,MongoDB,Cassandra ,Java Foundation, load balancing, database, consistency algorithm Java Algorithm, data structure, distributed cache**And so on.

This knowledge system is suitable for all Java Programmers learn that there are detailed explanations and introductions about the knowledge points in the above directory. Mastering all the contents of this knowledge point will improve your quality,**It also summarizes many questions encountered during the interview and the corresponding video analysis summary.**
**[CodeChina Open source project: [first tier big factory] Java Analysis of interview questions+Core summary learning notes+Latest explanation Video]](https://codechina.csdn.net/m0_60958482/java-p7)**
ttps://codechina.csdn.net/m0_60958482/java-p7)**
[External chain picture transfer...(img-O1Av8YyP-1630558501793)]