Reference notes
https://github.com/PariseC/Algorithms_for_solving_VRP
1. Applicable scenarios
- Solving MDCVRP problem
- Single vehicle type
- The vehicle capacity shall not be less than the maximum demand of the demand node
- Multi vehicle base
- The total number of vehicles in each depot meets the actual demand
1. Applicable scenarios
- Solving MDCVRP problem
- Single vehicle type
- The vehicle capacity shall not be less than the maximum demand of the demand node
- Multi vehicle base
- The total number of vehicles in each depot meets the actual demand
2. Code analysis
According to the number of parking lots, the two car path planning problem can be divided into single parking lot path planning problem and multi parking lot path planning problem. For the path planning problem with only vehicle capacity constraints under the condition of a single parking lot, it has been realized in the previous post ACO algorithm solution In this paper, ACO algorithm is used to solve the path planning problem with only vehicle capacity constraints under the condition of multiple depots. In order to maintain the continuity of the code and the consistency of the solution idea, the above ACO algorithm code is mainly modified as follows to solve the MDCVRP problem.
- Demand is used in the Model data structure class_ Dict attribute storage demand node set, depot_dict attribute stores the collection of parking lot nodes, demand_ id_ The list attribute stores the required node ID set, distance_ The matrix attribute stores the Euclidean distance between any nodes;
- Remove Node from the Node data structure class_ Seq attribute, add Depot_ The capacity property records the fleet limits for the depot
- In the splitRoutes function, the nearest parking lot is allocated as its vehicle supply base when dividing the vehicle path (meeting the limit of the number of vehicles in the parking lot)
3. Data format
Store data in csv file, where demand csv file records demand node data, including demand node id, demand node abscissa, demand node ordinate and demand quantity;
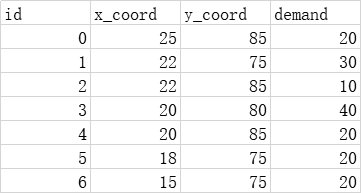
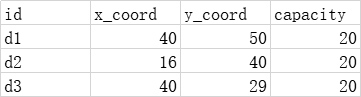
depot.csv file records yard node data, including yard id, yard abscissa, yard ordinate and fleet number. It should be noted that the demand node id should be an integer. The parking lot node id is arbitrary, but it cannot be repeated with the demand node id.
4. Step by step implementation
(1) Data structure
To facilitate data processing, Sol() class, Node() class and Model() class are defined. Their properties are shown in the following table:
- Sol() class, representing a feasible solution
| attribute | describe |
|---|---|
| nodes_seq | Demand node seq_no ordered permutation set, corresponding to the solution of TSP |
| obj | Optimization target value |
| routes | Vehicle path set, corresponding to the solution of CVRP |
- Node() class, representing a network node
| attribute | describe |
|---|---|
| id | Physical node id, optional |
| x_coord | Physical node x coordinate |
| y_coord | Physical node y coordinate |
| demand | Physical node requirements |
| depot_capacity | Fleet size of vehicle base |
- The Model() class stores algorithm parameters
| attribute | describe |
|---|---|
| best_sol | Global optimal solution, value type is Sol() |
| demand_dict | Demand node set (Dictionary), value type is Node() |
| depot_dict | Parking lot node collection (Dictionary), with value type of Node() |
| sol_list | Feasible solution set, value type is Sol() |
| opt_type | Optimization target type, 0: minimum number of vehicles, 1: minimum driving distance |
| vehicle_cap | Vehicle capacity |
| distance_matrix | Network arc distance |
| popsize | Ant colony size |
| alpha | Information heuristic factor |
| beta | Expected heuristic factor |
| Q | Total pheromone |
| rho | Pheromone Volatilization Coefficient |
| tau | Network arc pheromone |
| tau0 | Path initial pheromone |
(2) File reading
def readCsvFile(demand_file,depot_file,model):
with open(demand_file,'r') as f:
demand_reader=csv.DictReader(f)
for row in demand_reader:
node = Node()
node.id = int(row['id'])
node.x_coord = float(row['x_coord'])
node.y_coord = float(row['y_coord'])
node.demand = float(row['demand'])
model.demand_dict[node.id] = node
model.demand_id_list.append(node.id)
with open(depot_file,'r') as f:
depot_reader=csv.DictReader(f)
for row in depot_reader:
node = Node()
node.id = row['id']
node.x_coord=float(row['x_coord'])
node.y_coord=float(row['y_coord'])
node.depot_capacity=float(row['capacity'])
model.depot_dict[node.id] = node
(3) Calculate the distance matrix and initialize the path pheromone
def initDistanceTau(model):
for i in range(len(model.demand_id_list)):
from_node_id = model.demand_id_list[i]
for j in range(i+1,len(model.demand_id_list)):
to_node_id=model.demand_id_list[j]
dist=math.sqrt( (model.demand_dict[from_node_id].x_coord-model.demand_dict[to_node_id].x_coord)**2
+(model.demand_dict[from_node_id].y_coord-model.demand_dict[to_node_id].y_coord)**2)
model.distance_matrix[from_node_id,to_node_id]=dist
model.distance_matrix[to_node_id,from_node_id]=dist
model.tau[from_node_id,to_node_id]=model.tau0
model.tau[to_node_id,from_node_id]=model.tau0
for _,depot in model.depot_dict.items():
dist = math.sqrt((model.demand_dict[from_node_id].x_coord - depot.x_coord) ** 2
+ (model.demand_dict[from_node_id].y_coord -depot.y_coord)**2)
model.distance_matrix[from_node_id, depot.id] = dist
model.distance_matrix[depot.id, from_node_id] = dist
(4) Target value calculation
The fitness calculation relies on the "splitRoutes" function to separate the vehicle route and the number of vehicles required by the TSP feasible solution. After obtaining the vehicle route, the "selectDepot" function is called to calculate the driving distance according to the distribution of the nearest yard and the "calDistance" number under the condition of meeting the fleet size.
def selectDepot(route,depot_dict,model):
min_in_out_distance=float('inf')
index=None
for _,depot in depot_dict.items():
if depot.depot_capacity>0:
in_out_distance=model.distance_matrix[depot.id,route[0]]+model.distance_matrix[route[-1],depot.id]
if in_out_distance<min_in_out_distance:
index=depot.id
min_in_out_distance=in_out_distance
if index is None:
print("there is no vehicle to dispatch")
route.insert(0,index)
route.append(index)
depot_dict[index].depot_capacity=depot_dict[index].depot_capacity-1
return route,depot_dict
def splitRoutes(node_id_list,model):
num_vehicle = 0
vehicle_routes = []
route = []
remained_cap = model.vehicle_cap
depot_dict=copy.deepcopy(model.depot_dict)
for node_id in node_id_list:
if remained_cap - model.demand_dict[node_id].demand >= 0:
route.append(node_id)
remained_cap = remained_cap - model.demand_dict[node_id].demand
else:
route,depot_dict=selectDepot(route,depot_dict,model)
vehicle_routes.append(route)
route = [node_id]
num_vehicle = num_vehicle + 1
remained_cap =model.vehicle_cap - model.demand_dict[node_id].demand
route, depot_dict = selectDepot(route, depot_dict, model)
vehicle_routes.append(route)
return num_vehicle,vehicle_routes
def calRouteDistance(route,model):
distance=0
for i in range(len(route)-1):
from_node=route[i]
to_node=route[i+1]
distance +=model.distance_matrix[from_node,to_node]
return distance
def calObj(node_id_list,model):
num_vehicle, vehicle_routes = splitRoutes(node_id_list, model)
if model.opt_type==0:
return num_vehicle,vehicle_routes
else:
distance = 0
for route in vehicle_routes:
distance += calRouteDistance(route, model)
return distance,vehicle_routes
(5) Location update
When updating the ant location, call the "searchNextNode" function to search the next node that the ant may visit according to the network arc pheromone concentration and heuristic information.
def movePosition(model):
sol_list=[]
local_sol=Sol()
local_sol.obj=float('inf')
for k in range(model.popsize):
#Random initialization of ants
nodes_id=[int(random.randint(0,len(model.demand_id_list)-1))]
all_nodes_id=copy.deepcopy(model.demand_id_list)
all_nodes_id.remove(nodes_id[-1])
#Determine the next access node
while len(all_nodes_id)>0:
next_node_no=searchNextNode(model,nodes_id[-1],all_nodes_id)
nodes_id.append(next_node_no)
all_nodes_id.remove(next_node_no)
sol=Sol()
sol.node_id_list=nodes_id
sol.obj,sol.routes=calObj(nodes_id,model)
sol_list.append(sol)
if sol.obj<local_sol.obj:
local_sol=copy.deepcopy(sol)
model.sol_list=copy.deepcopy(sol_list)
if local_sol.obj<model.best_sol.obj:
model.best_sol=copy.deepcopy(local_sol)
def searchNextNode(model,current_node_id,SE_List):
prob=np.zeros(len(SE_List))
for i,node_id in enumerate(SE_List):
eta=1/model.distance_matrix[current_node_id,node_id]
tau=model.tau[current_node_id,node_id]
prob[i]=((eta**model.alpha)*(tau**model.beta))
#The roulette method is used to select the next access node
cumsumprob=(prob/sum(prob)).cumsum()
cumsumprob -= np.random.rand()
next_node_id= SE_List[list(cumsumprob > 0).index(True)]
return next_node_id
(6) Pheromone update
Here, the ant week model is used to update the network arc pheromone, which can be updated according to the node of the feasible solution_ id_ The list attribute (the solution of TSP problem) updates the network arc pheromone.
def upateTau(model):
rho=model.rho
for k in model.tau.keys():
model.tau[k]=(1-rho)*model.tau[k]
#According to the node of the solution_ id_ List attribute updates path pheromone (solution of TSP problem)
for sol in model.sol_list:
nodes_id=sol.node_id_list
for i in range(len(nodes_id)-1):
from_node_id=nodes_id[i]
to_node_id=nodes_id[i+1]
model.tau[from_node_id,to_node_id]+=model.Q/sol.obj
(7) Draw convergence curve
def plotObj(obj_list):
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] #show chinese
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # Show minus sign
plt.plot(np.arange(1,len(obj_list)+1),obj_list)
plt.xlabel('Iterations')
plt.ylabel('Obj Value')
plt.grid()
plt.xlim(1,len(obj_list)+1)
plt.show()
(8) Draw vehicle route
def outPut(model):
work=xlsxwriter.Workbook('result.xlsx')
worksheet=work.add_worksheet()
worksheet.write(0,0,'opt_type')
worksheet.write(1,0,'obj')
if model.opt_type==0:
worksheet.write(0,1,'number of vehicles')
else:
worksheet.write(0, 1, 'drive distance of vehicles')
worksheet.write(1,1,model.best_sol.obj)
for row,route in enumerate(model.best_sol.routes):
worksheet.write(row+2,0,'v'+str(row+1))
r=[str(i)for i in route]
worksheet.write(row+2,1, '-'.join(r))
work.close()
(9) Output results
def plotRoutes(model):
for route in model.best_sol.routes:
x_coord=[model.depot_dict[route[0]].x_coord]
y_coord=[model.depot_dict[route[0]].y_coord]
for node_id in route[1:-1]:
x_coord.append(model.demand_dict[node_id].x_coord)
y_coord.append(model.demand_dict[node_id].y_coord)
x_coord.append(model.depot_dict[route[-1]].x_coord)
y_coord.append(model.depot_dict[route[-1]].y_coord)
plt.grid()
if route[0]=='d1':
plt.plot(x_coord,y_coord,marker='o',color='black',linewidth=0.5,markersize=5)
elif route[0]=='d2':
plt.plot(x_coord,y_coord,marker='o',color='orange',linewidth=0.5,markersize=5)
else:
plt.plot(x_coord,y_coord,marker='o',color='b',linewidth=0.5,markersize=5)
plt.xlabel('x_coord')
plt.ylabel('y_coord')
plt.show()
(10) Main function
def run(demand_file,depot_file,Q,tau0,alpha,beta,rho,epochs,v_cap,opt_type,popsize):
"""
:param demand_file: demand file path
:param depot_file: depot file path
:param Q:Total pheromone
:param tau0: Initial value of path pheromone
:param alpha:Information heuristic factor
:param beta:Expected heuristic factor
:param rho:Information volatilization factor
:param epochs:Number of iterations
:param v_cap:Vehicle capacity
:param opt_type:Optimization type:0:Minimize the number of vehicles,1:Minimize travel distance
:param popsize:Ant colony size
:return:
"""
model=Model()
model.vehicle_cap=v_cap
model.opt_type=opt_type
model.alpha=alpha
model.beta=beta
model.Q=Q
model.tau0=tau0
model.rho=rho
model.popsize=popsize
sol=Sol()
sol.obj=float('inf')
model.best_sol=sol
history_best_obj = []
readCsvFile(demand_file,depot_file,model)
initDistanceTau(model)
for ep in range(epochs):
movePosition(model)
upateTau(model)
history_best_obj.append(model.best_sol.obj)
print("%s/%s, best obj: %s" % (ep,epochs, model.best_sol.obj))
plotObj(history_best_obj)
plotRoutes(model)
outPut(model)