1, Overview and introduction of Haproxy
(1) Introduction to Haproxy
- Haproxy is an open source high-performance reverse proxy or one of the load balancing service software. It is also a popular cluster scheduling tool at present
- It supports dual machine hot standby, virtual host, TCP and HTTP based application proxy and other functions
- For dual machine hot standby, Haproxy has simple configuration and good health check function for server nodes. When the back-end server of its proxy fails, Haproxy will automatically remove the failed server. After the server recovers, Haproxy will automatically add RS server (similar to the health check of keepalived)
- For high-performance reverse proxy, haproxy is used for services with large traffic but requiring session persistence or seven layer applications. Haproxy runs on ordinary server hardware. It can support tens of thousands of concurrent connections only by simple optimization. Its operation mode makes it easy and safe to integrate into the architecture of various websites, and makes the ip address of the application server not exposed in the network. Haproxy software introduces frontend and backend functions, and frontend acl matching rules allow operation and maintenance managers to match rules according to any HTTP request as the header, and then direct the request to the relevant backend (i.e. the server pool server group waiting for the front end to transfer the request). Through frontend and backup (standby server), we can easily realize the seven layer proxy function of haproxy. Haproxy is a rare excellent proxy service software
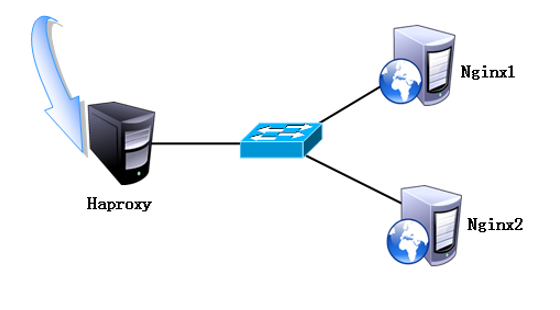
(2) Comparison of Haproxy with LVS and Nginx
- LVS has the best performance, but compared with Haproxy, it is much more complex to build
- The upstream module of Nginx supports the cluster function, but the health check function of cluster nodes is not strong, and the performance is not as good as that of Haproxy
(3) Proxy mode of Haproxy
Two agent modes are supported:
First: four layer TCP proxy
For example, it can be used for mail server, internal protocol communication server, Mysql server, etc
Second: seven layer agent
In the four layer TCP proxy mode, Haproxy only forwards traffic between the client and the server in two directions. However, in the seven layer mode, Haproxy analyzes the application layer protocol and can control the protocol by running, rejecting, exchanging, adding, modifying or deleting the contents specified in the request or reply
2, Building web cluster with Haproxy+nginx
Experimental environment
The systems used in the following experiments are Centos7!
| name | ip address | Play a role |
|---|---|---|
| haproxy | 192.168.100.1 | haproxy proxy server |
| nginx1 | 192.168.100.2 | nginx server |
| nginx2 | 192.168.100.3 | nginx server |
Experimental purpose
Using the cluster built by haproxy+nginx, the internal web server does not need to expose the ip address on the network, and the pages of the two web servers can be switched back and forth to achieve load balancing
Experimental steps
(1) Deploy two nginx servers (the two have the same steps and different web pages)
******(1)First do the basic configuration, nginx1 and nginx2
--nginx1:
[root@Centos7 ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname nginx1
[root@Centos7 ~]# su
[root@nginx1 ~]# mount /dev/cdrom /mnt/
mount: /dev/sr0 Write protected, will mount as read-only
mount: /dev/sr0 Already mounted or /mnt busy
/dev/sr0 Already mounted to /mnt upper
--nginx2:
[root@Centos7 ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname nginx2
[root@Centos7 ~]# su
[root@nginx2 ~]# mount /dev/cdrom /mnt/
mount: /dev/sr0 Write protected, will mount as read-only
mount: /dev/sr0 Already mounted or /mnt busy
/dev/sr0 Already mounted to /mnt upper
******(2)Install the necessary components and upload on the two machines respectively nginx Source package for configuration, compilation, installation, and writing web page
--nginx1:
[root@nginx1 ~]# yum -y install pcre-devel zlib-devel
. . . . . .
complete!
[root@nginx1 ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg nginx-1.12.0.tar.gz
[root@nginx1 ~]# tar xf nginx-1.12.0.tar.gz -C /usr/src/
[root@nginx1 ~]# cd /usr/src/nginx-1.12.0/
[root@nginx1 nginx-1.12.0]# useradd -M -s /sbin/nologin nginx
[root@nginx1 nginx-1.12.0]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx &&make &&make install
[root@nginx1 nginx-1.12.0]# echo "11111111" > /usr/local/nginx/html/index.html
[root@nginx1 nginx-1.12.0]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
[root@nginx1 nginx-1.12.0]# netstat -anpt | grep nginx (check whether the port number has successfully started nginx)
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 6297/nginx: master
[root@nginx1 nginx-1.12.0]# curl 127.0.0.1 (test whether it can be accessed normally)
11111111
--nginx2:
[root@nginx2 ~]# yum -y install pcre-devel zlib-devel
[root@nginx2 ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg nginx-1.12.0.tar.gz
[root@nginx2 ~]# tar xf nginx-1.12.0.tar.gz -C /usr/src/
[root@nginx2 ~]# cd /usr/src/nginx-1.12.0/
[root@nginx2 nginx-1.12.0]# useradd -M -s /sbin/nologin nginx
[root@nginx2 nginx-1.12.0]# ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx && make && make install
[root@nginx2 nginx-1.12.0]# echo "2222222" > /usr/local/nginx/html/index.html
[root@nginx2 nginx-1.12.0]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx
[root@nginx2 nginx-1.12.0]# netstat -anpt | grep nginx
tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:80 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 3923/nginx: master
[root@nginx2 nginx-1.12.0]# curl 127.0.0.1
2222222
(2) Deploy haproxy server
******(1)Basic configuration first
[root@Centos7 ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname haproxy
[root@Centos7 ~]# su
[root@haproxy ~]# mount /dev/cdrom /mnt/
mount: /dev/sr0 Write protected, will mount as read-only
mount: /dev/sr0 Already mounted or /mnt busy
/dev/sr0 Already mounted to /mnt upper
******(2)Install necessary components upload haproxy And install it
[root@haproxy ~]# yum -y install pcre-devel bzip2-devel
. . . . . .
complete!
[root@haproxy ~]# ls
anaconda-ks.cfg haproxy-1.5.19.tar.gz
[root@haproxy ~]# tar xf haproxy-1.5.19.tar.gz -C /usr/src/
[root@haproxy ~]# cd /usr/src/haproxy-1.5.19/
[root@haproxy haproxy-1.5.19]# make TARGET=linux26 (64 bit system installed)
[root@haproxy haproxy-1.5.19]# make install
[root@haproxy haproxy-1.5.19]# cd
******(3)to configure haproxy
[root@haproxy ~]# vim /usr/src/haproxy-1.5.19/examples/haproxy.cfg (template file)
-------------------Gorgeous split line————————————————————————————————————————
Profile resolution:
global Global part
log /dev/log local0 info
log /dev/log local1 notice hold info and notice The logs are stored separately for viewing
maxconn 4096 maximum connection
uid 99 user id
gid 99 group id
# pidfile /var/run/haproxy. PID file path and file name
daemon Background operation
defaults Default configuration
log global Apply log configuration for global section
mode http Mode is http
option httplog
option dontlognull
retries 3 Check the number of failures of the node. If it reaches 3 consecutive times, it is considered that the node is unavailable
maxconn 2000 maximum connection
contimeout 5000 Connection timeout 5000
clitimeout 50000 Client timeout 50000
srvtimeout 50000 Server timeout 50000
# option httpclose close close client request
listen webcluster 0.0.0.0:80 web Cluster (listening address and interface)
option httpchk GET /index.html inspect http file
balance roundrobin Load balancing scheduling algorithm polling roundrobin
server inst1 192.168.100.2:80 check inter 2000 fall 3
server inst2 192.168.100.3:80 check inter 2000 fall 3
##The above two server items are the address, name, port, inspection interval and health inspection times of nginx node service. 3 times are considered as failure
Log storage location in global section/dev/log In the directory log The file is a socket( socket). It is the site of a communication line, and these terminals( sockets)There is a data communication network between.
Its communication process is:
Programs access remote computers by socket Address of the computer being accessed socket The address is the same as that of the remote computer socket A communication line is established between addresses. socket It's like a unique identity
-------------------------------------------—
******(4)Create a new directory and create a new configuration file
[root@haproxy ~]# mkdir /etc/haproxy
[root@haproxy ~]# vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
write in:
global
log /dev/log local0 info
log /dev/log local1 notice
maxconn 4096
uid 99
gid 99
daemon
defaults
log global
mode http
option httplog
option dontlognull
retries 3
maxconn 2000
contimeout 5000
clitimeout 50000
srvtimeout 50000
listen webcluster 0.0.0.0:80
option httpchk GET /index.html
balance roundrobin
server inst1 192.168.100.2:80 check inter 2000 fall 3
server inst2 192.168.100.3:80 check inter 2000 fall 3
Save exit
******(5)optimization haproxy Command execution path so that the system can recognize haproxy Command of
[root@haproxy ~]# cp /usr/src/haproxy-1.5.19/examples/haproxy.init /etc/init.d/haproxy
[root@haproxy ~]# chmod +x /etc/init.d/haproxy
[root@haproxy ~]# ln -s /usr/local/sbin/haproxy /usr/sbin/haproxy
[root@haproxy ~]# /etc/init.d/haproxy restart
Reloading systemd: [ determine ]
Restarting haproxy (via systemctl): [ determine ]
(3) Verify
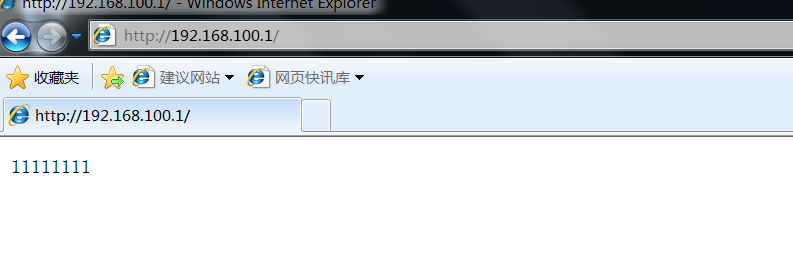
Open a test machine to access the address 192.168 of the haproxy server one hundred point one
First visit
Second visit
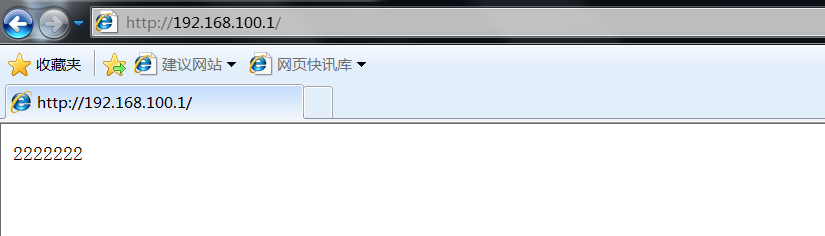
It is found that the page can be switched successfully, and the intranet web server does not expose the ip address. Therefore, the establishment of haproxy+nginx cluster is completed!!
3, Extension -- log management of haproxy
You should know that the log of haproxy is output to the syslog of the system by default, which is very inconvenient to view. In order to facilitate the management and viewing of the log of haproxy, it needs to be defined separately in the production environment
[root@haproxy ~]# cd /etc/rsyslog.d/ [root@haproxy rsyslog.d]# vim haproxy.conf (write a new configuration file) write in: local0.* /var/log/haproxy/ha-info.log local1.* /var/log/haproxy/ha-notice.log Save exit [root@haproxy rsyslog.d]# vim /etc/sysconfig/rsyslog (modify the system log file) Amend to read: # Options for rsyslogd # Syslogd options are deprecated since rsyslog v3. # If you want to use them, switch to compatibility mode 2 by "-c 2" # See rsyslogd(8) for more details SYSLOGD_OPTIONS="-r -m 0 -c 2" Save exit [root@haproxy rsyslog.d]# systemctl restart rsyslog (restart rsyslog service) [root@haproxy rsyslog.d]# /etc/init.d/haproxy restart (restart haproxy service) Restarting haproxy (via systemctl): [ determine ] [root@haproxy rsyslog.d]# tail -5 /var/log/haproxy/ha-info.log (use the tester to access it again and check the log. It is found that it has been successfully recorded) Feb 20 21:30:15 haproxy haproxy[1800]: 192.168.100.10:49159 [20/Feb/2021:21:30:14.911] webcluster webcluster/inst2 185/0/0/0/185 200 242 - - ---- 1/1/0/1/0 0/0 "GET / HTTP/1.1" Feb 20 21:30:15 haproxy haproxy[1800]: 192.168.100.10:49159 [20/Feb/2021:21:30:15.096] webcluster webcluster/inst1 179/0/0/1/180 200 243 - - ---- 1/1/0/1/0 0/0 "GET / HTTP/1.1" Feb 20 21:30:15 haproxy haproxy[1800]: 192.168.100.10:49159 [20/Feb/2021:21:30:15.276] webcluster webcluster/inst2 189/0/0/1/190 200 242 - - ---- 1/1/0/1/0 0/0 "GET / HTTP/1.1" Feb 20 21:30:15 haproxy haproxy[1800]: 192.168.100.10:49159 [20/Feb/2021:21:30:15.466] webcluster webcluster/inst1 187/0/0/1/188 200 243 - - ---- 1/1/0/1/0 0/0 "GET / HTTP/1.1" Feb 20 21:30:15 haproxy haproxy[1800]: 192.168.100.10:49159 [20/Feb/2021:21:30:15.654] webcluster webcluster/inst2 123/0/1/0/124 200 242 - - ---- 1/1/0/1/0 0/0 "GET / HTTP/1.1"