The following is an example of parsing a string, which you can refer to:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//Parses the given String text into an XML document and returns the newly created document
org.dom4j.Document document = DocumentHelper.parseText(xmlString);
//Get the root node, in this example, the responsedata node
Element rootElement = document.getRootElement();
//Gets an element under the root node
Element resultcode = rootElement.element("resultcode");
Element resultdesc = rootElement.element("resultdesc");
//getData returns the data of the element
String resultcodeData = (String) resultcode.getData();
String data = (String) resultdesc.getData();
//Traverse all child nodes
for (Iterator i = rootElement.elementIterator(); i.hasNext(); ){
Element next = (Element) i.next();
System.out.println(next.getName()+": "+next.getData());
}
//Traverse a child node, such as resultcode
for (Iterator i = rootElement.elementIterator("resultcode"); i.hasNext(); ){
Element next = (Element) i.next();
System.out.println(next.getName()+": "+next.getData());
}
}
DOM4J parsing xml string process:
1,use parseText Method will xml Convert string to Document object 2,obtain Root Node, XML Parsing is from Root Element start 3,use element Method to obtain a child node directly or use elementIterator Iterator traversal
In addition to using strings, we can also use xml files to generate document objects
//Read the XML file and get the document object
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
org.dom4j.Document document = reader.read(new File("input.xml"));
DOM4J generates strings in xml format
In addition to using Dom4j to parse XML format strings, we can also use Domj to generate XML format strings, which is very useful when we construct XML format request parameters.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <requestData> <username>xxx</username> <password>yyy</password> </requestData>
For example, if we want to generate the above xml string, we can use the following method
/**
* Generate a string in xml format
* @return
*/
public static String createXmlString(){
//Create document object
org.dom4j.Document document = DocumentHelper.createDocument();
//Set encoding
document.setXMLEncoding("UTF-8");
//Create root node
Element requestData = document.addElement("requestData");
//Add the username child node to the root node
Element username = requestData.addElement("username");
//Add content to child nodes
username.setText("xxx");
//Add the password child node
Element password = requestData.addElement("password");
//Add content
password.setText("yyy");
//Convert document object to string
String xml = document.asXML();
System.out.println(xml);
return xml;
}
Output:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <requestData><username>xxx</username><password>yyy</password></requestData>
explain:
//Define an XML document object through this sentence Document document = DocumentHelper.createDocument();
//An XML element is defined by this sentence, and the root node is added here
Element requestData = document.addElement("requestData ");
Element There are several important ways:
addComment: add a comment
addAttribute: add attribute
addElement: add child element
setText: set the content of the node
Note: setText and addAttribute Is a different effect Example:
username.addAttribute("username","xxx");
The generated format is as follows:
addAttribute You should pay attention to adding an attribute to a node instead of adding node content [](https://codechina.csdn.net/m0_60958482/java-p7) II. Org. Using JDK w3c. dom. Document parsing xml string --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Method 1 requires us to add dependencies. If we don't want to add dependencies, we can use it directly JDK of org.w3c.dom.Document Analyze Now I'll use it org.w3c.dom.Document To parse the beginning xml character string Examples are as follows:
/**
* use org.w3c.dom.Document To analyze xml character string
*/
public static void parseXmlString() throws ParserConfigurationException, IOException, SAXException {
//Create a factory instance of the DOM parser
DocumentBuilderFactory documentBuilderFactory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
//Get parser from DOM factory
DocumentBuilder documentBuilder = documentBuilderFactory.newDocumentBuilder();
//Generate Document instance using parser
Document document = documentBuilder.parse(new InputSource(new StringReader(xmlString)));
//Gets the node list of the responsedata element
NodeList responsedata = document.getElementsByTagName("responsedata");
//Traverse the node list
for (int i=0; i< responsedata.getLength();i++){
//Get specific elements
org.w3c.dom.Element node = (org.w3c.dom.Element) responsedata.item(i);
//Output value
System.out.println("resultcode:"+node.getElementsByTagName("resultcode").item(0).getFirstChild().getNodeValue());
System.out.println("resultdesc:"+node.getElementsByTagName("resultdesc").item(0).getFirstChild().getNodeValue());
}
}
be careful: DOM The parsed data is kept in memory, which is convenient for us to modify, but at the same time, if xml When the file is large, the memory occupied will be large, which may cause memory overflow [](https://codechina.csdn.net/m0_60958482/java-p7)org.w3c.dom.Document generates an xml string ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- example:
/**
* use org.w3c.dom.Document To generate xml character string
*/
public static String createXmlStr(){
String xmlString = "";
DocumentBuilderFactory documentBuilderFactory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
try {
DocumentBuilder documentBuilder = documentBuilderFactory.newDocumentBuilder();
//Generate Document instance using parser
Document document = documentBuilder.newDocument();
//Set version number
document.setXmlVersion("1.0");
//Create parent element
org.w3c.dom.Element requesData = document.createElement("requesData");
//Create child element
org.w3c.dom.Element username = document.createElement("username");
//Add element content
username.setTextContent("xxx");
org.w3c.dom.Element password = document.createElement("password");
password.setTextContent("yyy");
//Add child element to parent element
requesData.appendChild(username);
requesData.appendChild(password);
//Add parent element to Document
document.appendChild(requesData);
//Create converter instance
TransformerFactory transFactory = TransformerFactory.newInstance();
Transformer transformer = transFactory.newTransformer();
//Sets the encoding of the output
last
Having talked about spring cloud alibaba, what core skills should I master if I want to further improve myself for the whole microservice architecture?
Personally, for the whole microservice architecture, such as RPC, Dubbo, Spring Boot, Spring Cloud Alibaba, Docker, kubernetes, Spring Cloud Netflix, Service Mesh, etc., these are the most core knowledge and the only way for architects! The following figure is the self drawn outline of the micro service architecture route system. If you have friends who don't know what technology you should master, you can make a reference according to the outline drawn by Xiaobian.
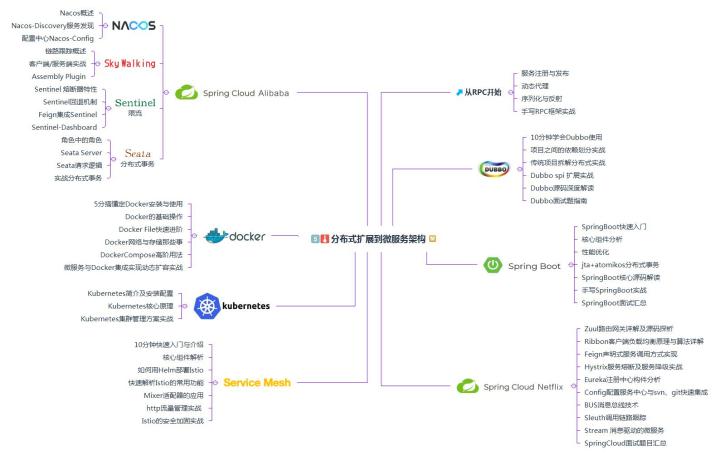
If you think the picture is not clear enough, you can also come to Xiaobian to share the original xmind document!
In addition to this micro service system outline, I also sorted out the strongest learning notes corresponding to the core knowledge points of each topic:
-
Amazing - spring cloud Alibaba pdf
-
SpringCloud microservice architecture notes (I). pdf
-
SpringCloud microservice architecture notes (II). pdf
-
SpringCloud microservice architecture notes (III). pdf
-
SpringCloud microservice architecture notes (IV). pdf
-
Dubbo framework RPC implementation principle pdf
-
Dubbo's latest comprehensive and in-depth interpretation pdf
-
Spring Boot tutorial pdf
-
SpringBoo core collection pdf
-
First Docker book - full version pdf
-
Use spring cloud and Docker to practice microservices pdf
-
K8S(kubernetes) study guide pdf
Please download** Click the portal: amazing - spring cloud Alibaba**

In addition, if you don't know where to start learning, Xiaobian also has a hand drawn outline of the corresponding knowledge architecture system for the core knowledge points of each micro service, but it is all the exported xmind files, and all the source files are here, so you can share them for free!
ud microservice architecture notes (IV). pdf
-
Dubbo framework RPC implementation principle pdf
-
Dubbo's latest comprehensive and in-depth interpretation pdf
-
Spring Boot tutorial pdf
-
SpringBoo core collection pdf
-
First Docker book - full version pdf
-
Use spring cloud and Docker to practice microservices pdf
-
K8S(kubernetes) study guide pdf
Please download** Click the portal: amazing - spring cloud Alibaba**
[external chain picture transferring... (IMG inruagxu-1629232066289)]
In addition, if you don't know where to start learning, Xiaobian also has a hand drawn outline of the corresponding knowledge architecture system for the core knowledge points of each micro service, but it is all the exported xmind files, and all the source files are here, so you can share them for free!
