Function
1. Functional overview
- Use Python to complete a program to add or delete student information about MySQL database, mainly involving knowledge points: cursor use, SQL statements, and the basic knowledge previously learned.
2. Mind Mapping
The idea has been put into practice
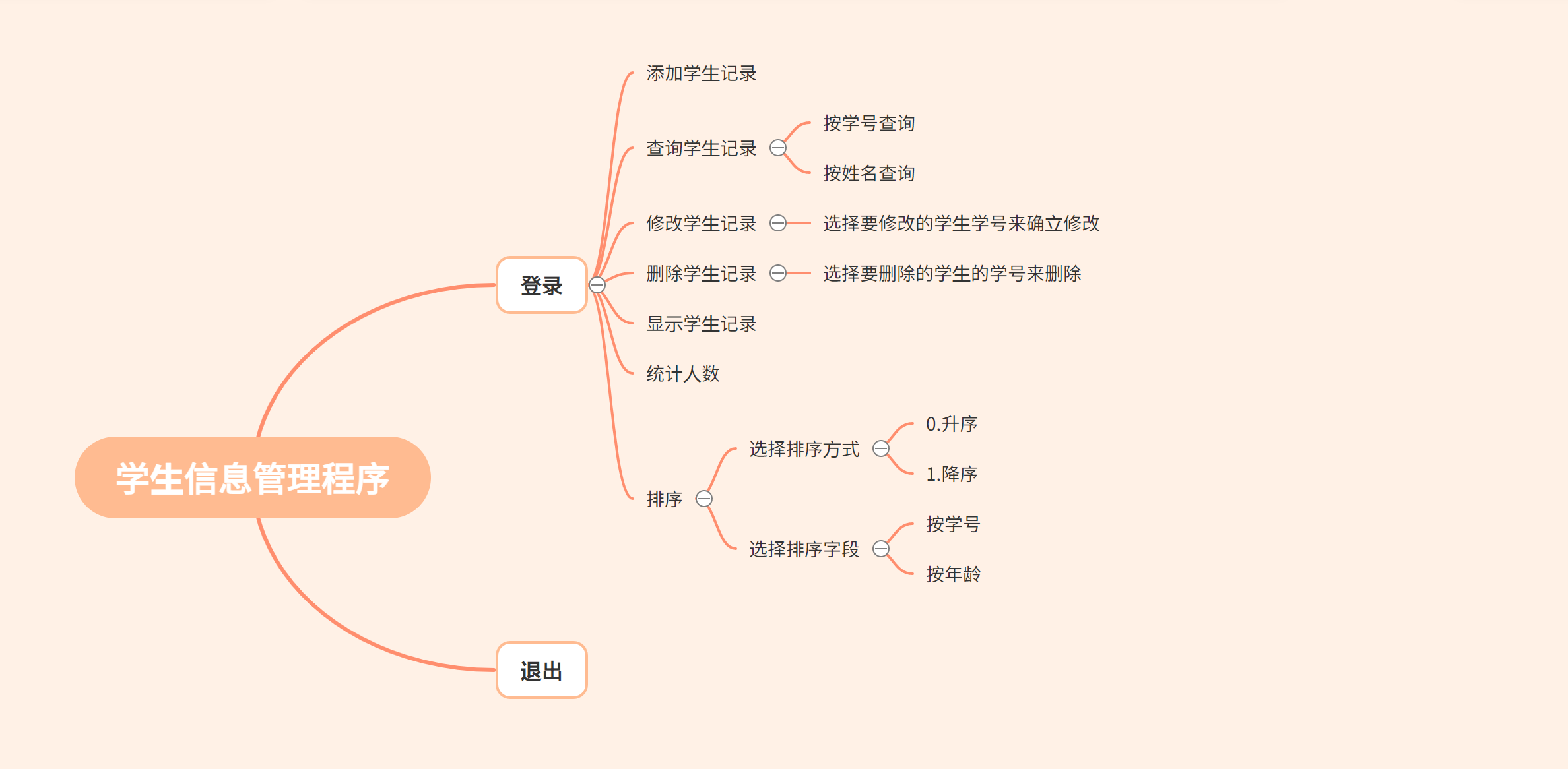
2. Start Practice
Pre-war preparation
You need to first import the sqlite3 module and pymysql database as follows:
import pymysql
import sqlite3
# Define database link parameters
host = '127.0.0.1'
port = 3306
db = 'student'
user = 'root'
password = 'password'
# Get Database Links
conn = pymysql.connect(host=host,
user=user,
password=password,
port=port,
db=db, )
If sqlite3 is not installed
You can execute the pip install sqlite3 command by typing cmd -> from Windows+R -> as follows:
Because the blogger has already downloaded it, do not install it again.
Define the Student Management System Menu
Before we start, we should think in our brains. It's important to think about what this database should do!
def menu():
print('============Student Information Management System=====================')
print('============Function Menu=====================')
print('\t\t1.Enrollment Information')
print('\t\t2.Find Student Information')
print('\t\t3.Delete Student Information')
print('\t\t4.Modify Student Information')
print('\t\t5.sort')
print('\t\t6.Statistics of the number of students')
print('\t\t7.Show all student information')
print('\t\t0.Sign out')
print('==============================================')
Define the main function
Next we define the main functions: add, find, delete, modify, sort, statistics, display all.
# Define the main function
def main():
while True:
menu()
num = int(input('Please select what you want to do:'))
if num in (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7):
if num == 0:
answer = input('Are you sure you want to exit the system? y/n\t') # Judge to 0
if answer == 'y' or answer == 'Y':
print('Thank you for your use!!!')
break
else:
continue
elif num == 1:
insert()
elif num == 2:
search()
elif num == 3:
delete()
elif num == 4:
modify()
elif num == 5:
sort()
elif num == 6:
total()
elif num == 7:
show()
1. Enrollment information
Focus of this section
- The most important thing about database links is that you must create a cursor object. Don't forget that this is equivalent to a record pointer in Access. Remember to write
- Note how the SQL statement is written (if you have questions about your own writing, you can copy it to MySQL to check if the code is incorrect) as follows:
Note that this figure is after borrowing so don't be too (haha)
def insert():
# Create Cursor Object
cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
# cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.SSCursor)
while True:
name = input("Please enter the student name:")
if not name:
print('Please enter a valid name!')
continue
try:
# Execute SQL Query
gender = input("Please enter the student's last name:")
age = input("Please enter the student age:")
sql = "insert into student (name,gender,age) values ('" + name + "','" + gender + "'," + age + ")"
count = cursor.execute(sql)
if count > 0:
# Submit database modifications
conn.commit()
# Prompt User Success
print('Record Inserted Successfully~')
answer = input('Do you want to continue adding? y/n\n')
if answer != 'y':
break
else:
continue
except pymysql.err.IntegrityError:
print('Primary key does not allow duplication')
2. Find student information
Focus of this section
- Create Cursor Object
- Query by ID or name
def search():
# Create Cursor Object
cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.SSCursor)
while True:
mode = input('Press ID Find Please enter 1, Find by name Enter 2:')
if mode == '1':
id = input('Please enter a student ID')
sql = f"select * from student where id={id}"
cursor.execute(sql)
print(cursor.fetchall())
answer = input('Do you want to continue adding? y/n\n')
if answer != 'y':
break
else:
continue
elif mode == '2':
name = input('Please enter the student name:')
sql = f"select * from student where name='{name}'"
cursor.execute(sql)
print(cursor.fetchall())
answer = input('Do you want to continue adding? y/n\n')
if answer != 'y':
break
else:
continue
else:
print('Your input is incorrect, please re-enter')
continue # Return while True
3. Delete student information
Basic content is similar, you can spare time to practice by yourself
def delete():
# Create Cursor Object
cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.SSCursor)
while True:
student_id = input('Please enter the ID: ')
if student_id != '':
sql = f"select * from student where id={student_id}"
cursor.execute(sql)
answer = input('Do you want to continue deleting? y/n\n')
if answer != 'y':
show()
break
else:
continue
else:
print('Error in input! Please re-enter')
continue
4. Modify student information
Focus of this section
- Explicitly modify what,
- Another simple writing format for formart
def modify():
show()
# Create Cursor Object
cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.SSCursor)
while True:
student_id = input('Please enter the student number you want to modify (e.g. 1),2):')
if student_id != '':
name = input('Please enter the name to be modified:')
gender = input('Please enter the gender to be modified:')
age = input('Please enter the age at which you are ready to modify:')
sql = f"update student set name='{name}',gender='{gender}',age={age} where id={student_id}"
d=cursor.execute(sql)
if d:
print("Successfully modified!")
else:
print("Modification failed!")
answer = input('Do you want to continue with the modification? y/n\n')
if answer != 'y':
show()
break
else:
continue
else:
print('Error in input! Please re-enter')
continue
5. Sorting
Focus of this section
- This section of code is error prone. Check SQL statements
- The way to traverse (review) Of course there are other ways to do this, but I'm writing another day
def sort():
show()
# Create Cursor Object
cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.SSCursor)
asc_or_desc = input('Please select (0).Ascending Order, 1.Descending order:')
sor = ""
if asc_or_desc == '0':
sor = "asc"
elif asc_or_desc == '1':
sor = "desc"
else:
print('Your input is incorrect, please re-enter')
sort()
# Replenish when available
# mode = input('Please choose the sort method (1. Sort by English results, 2. Sort by Python results 3. Sort by Java 0. Sort by main program)')
mode = input('Please choose the sorting method (1).Sort by number,2.Sort by age)')
if mode == '1':
sql = f"select * from student order by id " + sor
cursor.execute(sql)
all_records = cursor.fetchall()
for record in all_records:
print(record[0], record[1], record[2], record[3])
elif mode == '2':
sql = f"select * from student order by age " + sor
cursor.execute(sql)
all_records = cursor.fetchall()
for record in all_records:
print(record[0], record[1], record[2], record[3])
6. Total Statistics
Nothing in this section, it's very simple
def total():
# Create Cursor Object
cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.SSCursor)
sql = f"select gender,count(gender) as 'Number of people' from student group by gender"
cursor.execute(sql)
all_records = cursor.fetchall()
for record in all_records:
print(record[0], record[1])
7. Display all information about students
Focus of this section
- Note the placeholder position and consider a different way to write when you have time to practice
def show():
# Create Cursor Object
cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.SSCursor)
sql = f"select * from student"
cursor.execute(sql)
all_records = cursor.fetchall()
format_title = '{:^6}\t{:^12}\t{:^8}\t{:^10}'
print(format_title.format('ID', 'Full name', 'Gender', 'Age'))
format_data = '{:^6}\t{:^12}\t{:^8}\t{:^10}'
for record in all_records:
print(format_data.format(record[0], record[1], record[2], record[3]))