1. First Vue example
Resolution: {{meshage}} find the data with the same name as the meshage in data, and convert the value into the value bound by the meshage in data
Note: {{message}} is called difference expression
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>first Vue Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
{{ messeage }}
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
messeage:"hello Vue!"
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
2. el mount point
(1) Scope of Vue instance
The scope is the inside of the el hit element. That is, inside the div (view).
<div id="app">
{{ messeage }}
</div>
(2) Can I use selectors other than id selectors
You can use other selectors, but you usually use id selectors
(3) Can I set other dom elements
Other tags other than div can be supported, such as < p > < / P >, but HTML and BODY cannot be used, but they must be double tags, not single tags. Div tags are usually used.
3. Data: data object
- The data used by Vue is defined in data
- Complex types of data (such as objects, arrays, etc.) can be written in data
- Rendering complex type data can follow js syntax (such as point syntax of objects and index syntax of arrays)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>el Shut in</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
{{ messeage }}
{{school.name}}{{school.address}}
{{arr[0]}}{{arr[2]}}
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
messeage:"hello sdfsdfsd!",
school:{
name:'tsinghua',
address:'Beijing'
},
arr:['Dalian','Shenyang','Dandong']
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
4. Vue instruction
(1)v-show instruction: Show hide
(1) v-show: switch the display status of elements according to true and false
(2) Principle: modify the display of elements to display and hide
(3) The content after the instruction finally resolves to a Boolean value
(4) If the value is true, the element is displayed; if the value is false, the element is hidden
Note: this instruction is used for frequent display and hiding of content
<!-- View view -->
<div id="app">
//true is displayed, false is not displayed
<span v-show="b">Hello</span>
<span v-show="c">Zhang San</span>
<span v-show="age >= 19">Zhang San</span>
</div>
<script>
// Model model
var model = {b:true, c:false,age:16};
// ViewModel view model (a Vue object)
var vm = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:model
});
</script>
Instance of v-show
Knowledge points of this case:
(1) The method event of v-show is written as this.isshow =! This.isshow;
(2) v-show is to modify the display of elements to show and hide
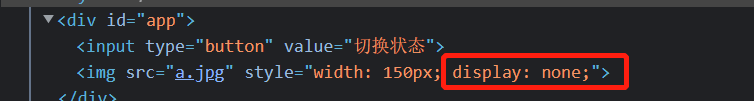
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>el Shut in</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<input type="button" value="Switching state" @click="changeShow" >
<img src="a.jpg" style="width: 150px;" v-show="isShow">
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
isShow:false,
},
methods:{
changeShow(){
this.isShow = !this.isShow;
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
(2)v-if, v-else: Branch (either v-if alone or both)
(1) v-if: switch the display state of elements according to true and false
(2) The essence is to display and hide dom elements by manipulating them (dom elements are those tags, p tags, div tags, etc.)
(3) If the expression is true, the element exists in the dom tree; if it is false, it is removed from the dom tree
<!-- View view -->
<div id="app">
//The content in "" is equivalent to the content in if brackets
//Note: no other labels can be added between v-if and v-else
//The v-else element must follow the element with v-if or v-else-if, otherwise it will not be recognized
<span v-if="name == 'Zhang San'">100</span>
<span v-if="age >= 20">200</span>
<span v-else>300</span>
</div>
<script>
// Model model
var model = {name:'Zhang San', age:10};
// ViewModel view model (a Vue object)
var vm = new Vue({
el:'#app',
data:model
});
</script>
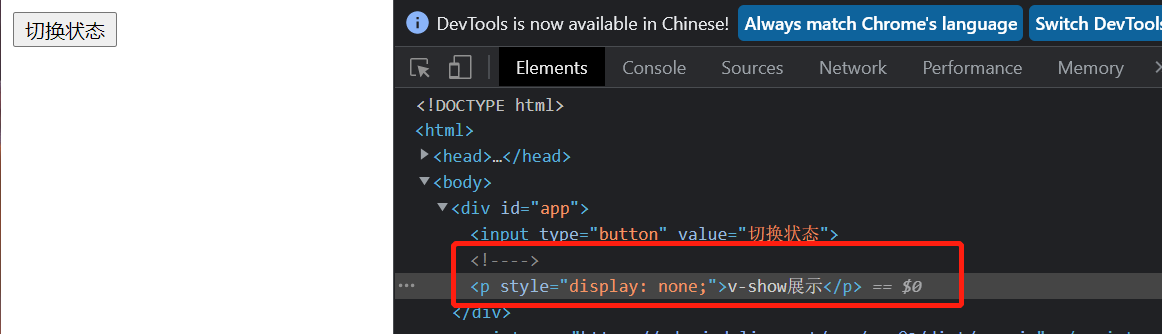
Difference between v-show and v-if
v-show: the essence is to modify the display of elements to show and hide
v-if: the essence is to display and hide by manipulating dom elements (dom elements are those tags, p tags, div tags, etc.)
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
<input type="button" value="Switching state" @click="changeShow" >
<p v-if="isShow">v-if Exhibition</p>
<p v-show="isShow">v-show Exhibition</p>
</div>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script>
var app = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
isShow:false,
},
methods:{
changeShow(){
this.isShow = !this.isShow;
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
As shown in the figure below:
-When both contents are displayed, the browser console is shown in the figure below

- When both contents are hidden, the browser console is shown in the figure below