public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext( "C:/work/IOC Containers/springframework.applicationcontext/src/main/resources/bean-factory- config.xml");
HelloApplicationContext obj = (HelloApplicationContext) context.getBean("helloApplicationContext");
obj.getMsg();
}
}
# 3, Singleton design pattern
In our system, there are some objects. In fact, we only need one, such as thread pool, cache, dialog box, registry, log object, object serving as device driver for printer, graphics card and so on. In fact, this kind of object can only have one instance. If multiple instances are created, it may lead to some problems, such as abnormal program behavior, excessive resource use, or inconsistent results.
**Benefits of using singleton mode:**
- For frequently used objects, the time spent creating objects can be omitted, which is a very considerable system overhead for those heavyweight objects;
- because new The number of operations is reduced, so the frequency of use of system memory is reduced, which will reduce GC Pressure, shortening GC Pause time.
**Spring in bean The default scope is singleton(Single case)of** except singleton Scope, Spring in bean There are also the following scopes:
- `prototype` : Each request creates a new one bean example.
- `request` : every time HTTP Every request generates a new bean,Should bean Only in the current HTTP request Valid within.
- `session` : every time HTTP Every request generates a new bean,Should bean Only in the current HTTP session Valid within.
- `global-session`: overall situation session Scope, only based on portlet of web It makes sense in application, Spring5 It's gone. Portlet It can generate semantic code(For example: HTML)Fragment miniaturization Java Web plug-in unit. They are based on portlet Container, can be like servlet Same treatment HTTP Request. However, with servlet Different, each portlet Have different sessions
**Spring How to implement a singleton:**
- xml :` <bean id="userService" class="top.snailclimb.UserService" scope="singleton"/>`
- Notes: `@Scope(value = "singleton")`
**Spring adopt `ConcurrentHashMap` A special way to implement the singleton registry is to implement the singleton mode. Spring The core code to implement the singleton is as follows**
```java
// The singleton registry is implemented through ConcurrentHashMap (thread safety)
private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>(64);
public Object getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(beanName, "'beanName' must not be null");
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// Check whether there are instances in the cache
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
//... A lot of code is omitted
try {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
}
//... A lot of code is omitted
// If the instance object does not exist, we register it in the singleton registry.
addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject);
}
return (singletonObject != NULL_OBJECT ? singletonObject : null);
}
}
//Add object to singleton registry
protected void addSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
this.singletonObjects.put(beanName, (singletonObject != null ? singletonObject : NULL_OBJECT));
}
}
}
4, Agent design pattern
1. Application of agent mode in AOP
AOP (aspect oriented programming) can encapsulate the logic or responsibilities (such as transaction processing, log management, permission control, etc.) that have nothing to do with the business but are jointly invoked by the business modules, so as to reduce the repeated code of the system, reduce the coupling between modules, and facilitate the scalability and maintainability in the future.
Spring AOP is based on dynamic proxy. If the object to be proxy implements an interface, spring AOP will use JDK Proxy to create proxy objects. For objects that do not implement interfaces, JDK Proxy cannot be used for proxy. At this time, spring AOP will use Cglib, At this time, spring AOP will use Cglib to generate a subclass of the proxied object as the proxy, as shown in the following figure:
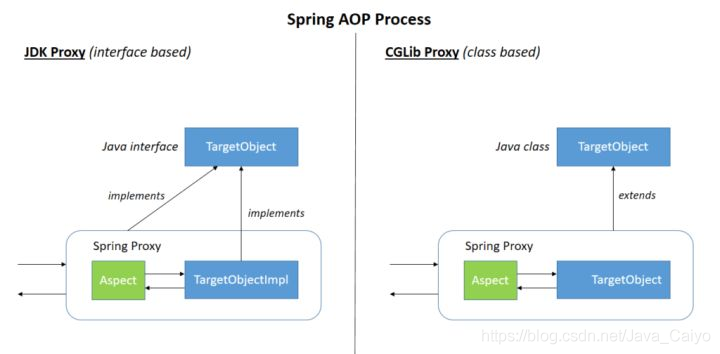
Of course, you can also use AspectJ. Spring AOP has integrated AspectJ. AspectJ should be the most complete AOP framework in the Java ecosystem.
After using AOP, we can abstract some general functions and use them directly where needed, which greatly simplifies the amount of code. It is also convenient when we need to add new functions, which also improves the scalability of the system. AOP is used in logging function, transaction management and other scenarios.
2. What is the difference between spring AOP and AspectJ AOP?
Spring AOP is a runtime enhancement, while AspectJ is a compile time enhancement. Spring AOP is based on proxying, while AspectJ is based on bytecode manipulation.
Spring AOP has integrated AspectJ, which should be regarded as the most complete AOP framework in the Java ecosystem. AspectJ is more powerful than spring AOP, but spring AOP is relatively simpler,
If we have fewer sections, there is little difference in performance between the two. However, when there are too many facets, it is best to choose AspectJ, which is much faster than Spring AOP.
5, Template method
Template method pattern is a behavior design pattern, which defines the skeleton of an algorithm in operation and delays some steps to subclasses. Template method allows subclasses to redefine the implementation of some specific steps of an algorithm without changing the structure of the algorithm.
public abstract class Template {
//This is our template method
public final void TemplateMethod(){
PrimitiveOperation1();
PrimitiveOperation2();
PrimitiveOperation3();
}
protected void PrimitiveOperation1(){
//Current class implementation
}
//Implementation method of quilt subclass
protected abstract void PrimitiveOperation2();
protected abstract void PrimitiveOperation3();
}
public class TemplateImpl extends Template {
@Override
public void PrimitiveOperation2() {
//Current class implementation
}
@Override
public void PrimitiveOperation3() {
//Current class implementation
}
}
In Spring, JDBC Template, hibernate Template and other classes that end with Template for database operations use the Template pattern. In general, we use inheritance to implement the Template mode, but Spring does not use this method, but uses the Callback mode to cooperate with the Template method mode, which not only achieves the effect of code reuse, but also increases flexibility.
6, Observer mode
Observer mode is an object behavior mode. It represents a dependency relationship between objects. When an object changes, the object on which the object depends will also react. Spring event driven model is a classic application of observer pattern. The spring event driven model is very useful and can decouple our code in many scenarios. For example, we need to update the commodity index every time we add commodities. At this time, we can use the observer mode to solve this problem.
1. Three roles in spring event driven model
1) Event role
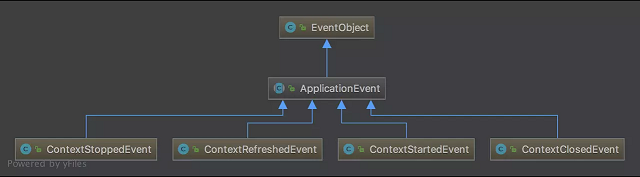
Applicationevent (under the org. Springframework. Context package) plays the role of event. It is an abstract class that inherits Java util. Eventobject and implements Java io. Serializable interface.
The following events exist in Spring by default. They are all implementations of ApplicationContextEvent (inherited from ApplicationContextEvent):
- ContextStartedEvent: the event triggered after the ApplicationContext is started;
- ContextStoppedEvent: the event triggered after the ApplicationContext stops;
- ContextRefreshedEvent: the event triggered after ApplicationContext initialization or refresh is completed;
- ContextClosedEvent: the event triggered after the ApplicationContext is closed.
2) Event listener role
ApplicationListener acts as an event listener, which is an interface, There is only one onApplicationEvent() method defined to handle ApplicationEvent. The source code of the applicationlister interface class is as follows. It can be seen that the events in the interface only need to implement ApplicationEvent. Therefore, in Spring, we just need to implement the applicationlister interface to implement onApplicationEvent() Method to complete the event listening
package org.springframework.context;
import java.util.EventListener;
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ApplicationListener<E extends ApplicationEvent> extends EventListener {
void onApplicationEvent(E var1);
}
3) Event publisher role
ApplicationEventPublisher acts as the publisher of events and is also an interface.
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ApplicationEventPublisher {
default void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
this.publishEvent((Object)event);
}
void publishEvent(Object var1);
}
The publishEvent () method of the ApplicationEventPublisher interface is implemented in the AbstractApplicationContext class. After reading the implementation of this method, you will find that events are actually broadcast through applicationeventmulticast. There are too many specific contents, so we won't analyze them here. We may write a separate article later.
2. Event flow summary of spring
- Define an event: implement an event inherited from ApplicationEvent and write the corresponding constructor;
- Define an event listener: implement the ApplicationListener interface and override the onApplicationEvent() method;
- Publish messages using event publishers: you can publish messages through the publishEvent() method of ApplicationEventPublisher.
Example:
// Define an event, inherit from ApplicationEvent and write the corresponding constructor
public class DemoEvent extends ApplicationEvent{
EventPublisher` of `publishEvent() `Method to publish a message.
Example:
```java
// Define an event, inherit from ApplicationEvent and write the corresponding constructor
public class DemoEvent extends ApplicationEvent{