Original link: http://tecdat.cn/?p=24896

Beautiful circle chart. I'm not sure if there is any additional benefit to the data analyst itself, but if it can attract the attention of decision makers, it is additional value to me.
However, with coord\_polar() or coord in ggplot2 found occasionally\_ Radar () can be difficult to build. The two main problems I found are that the change of polar coordinates will bend your path into a circle, and the radar can't communicate with geom_bin is used in combination to fill the background.
That's why I usually use it in Cartesian coordinate system. More like a mathematical solution. Map your data and drawing requirements so that they eventually become a circle. As an added benefit, I also found it to build / load faster. It's important to me because I let them interact in Shiny Apps.
I used mtcars data in my example. The figure shows 12 cars in the collection:
- Cylinder in background. 4. Light, medium and dark colors for cylinders 6 and 8.
- Mark the miles per gallon of each car in blue.
This article is a step-by-step demonstration of how to add the required elements to the circular diagram. Many things may be improved. Please feel free to comment.
I use the first 12 cars and want a column containing row names.
add_rownames\[1:12,\]
Draw data mapping
To map the values of any column I want to draw, I create a function. It basically checks how many variables you want to plot and plots sinusoids for x and y values.
lev <- levels num <- length dir <- rep dir_ <- map_dbl interp data <- mutate_
Store mapping data to map mpg variables for all tags.
#Data point rotate_data
I wanted to show the plot range data, so I forged a series of qsec data. Basically, you generate a data frame with multiple values (rows) for qsec on each vehicle (label).
#Make up some range data bind_rows rotate_data
Use polygon to draw the range and path and point to draw the mpg value.
lim <- max #Use your own data and aesthetics to draw the pattern of each layer ggplot() + geom_polygon+ geom_point+ theme+ coord_equal
Radial line
I guess the desired grid is made up of circled radial outer lines. Create x, xend, y, and yend data points to draw segments between them.
r <- data_frame %>% mutate r$xed <- 0 r$yed <- 0
#Use your own data and aesthetics to draw the pattern of each layer ggplot() + geom_segment + geom_polygon+ geom_point + ylim + xlim + theme+ coord_equal

label
Add a text label to the variable you rotate.
label <- levels
ggplot() + geom_segment + geom_polygon + geom_path + geom_point + geom_text+ theme + coord_equal
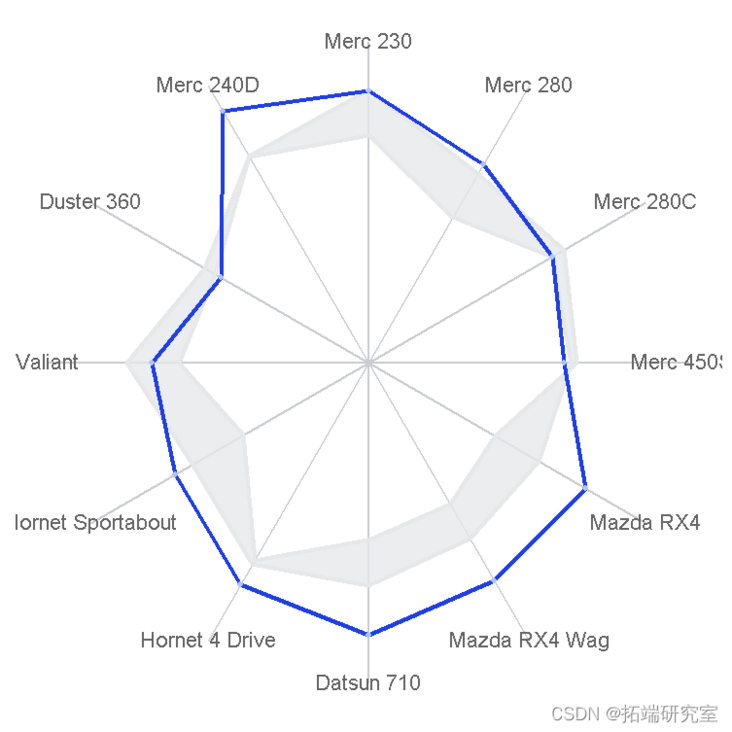
Draw a circle
To draw a circle, I'll use a circle with a fill option.
t <- seq
d <- data.frame
if(fed==TRUE) { # #Add a point in the center so that the whole "cake" is filled
d <- rbind
}
return(d)Grid circles and labels
Circular gridlines are built by calling circle multiple times and storing all points in the data frame.
cregrd <- data_frame crld <- cili %>% mutate poties <- bind_rows loics$lv <- as.factor
Circular labels can be added in a number of ways. But in order to simply set all axis text and axis labels to blank, I built a data box that can be drawn using text.
c <- data_frame cl <- cl\[x <= max,\]
ggplot() + geom_segment + geom_path+ geom_text+ geom_polygon + geom_point + geom_text + xlim + theme+ coord_equal
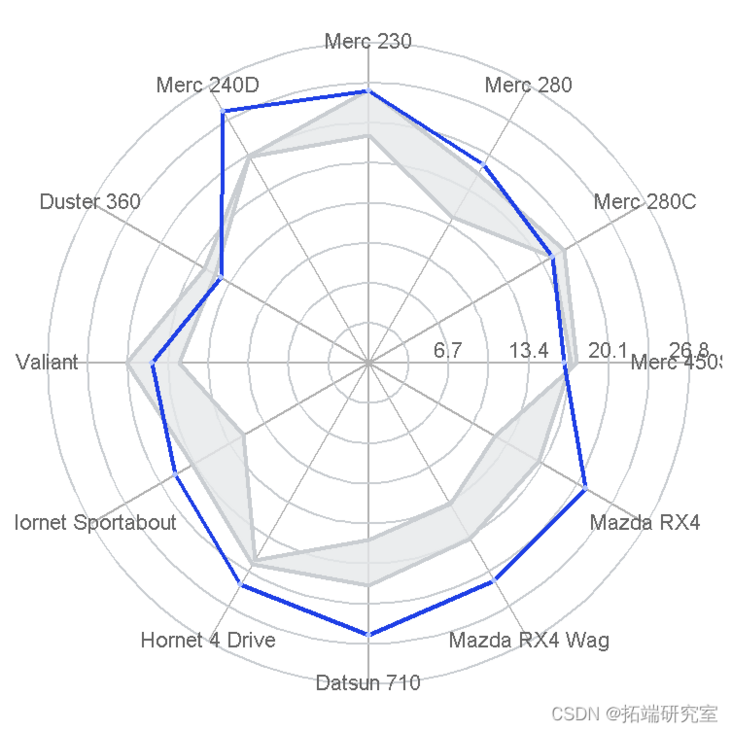
background
With circle, you can also easily build a circular part, which you can fill with the Filled = TRUE parameter. There is a slight - 1/num offset to align the section correctly. Here, you propose the factor variable you want to color. Of course, you can also change the code to change the "height" of each bar according to the variable.
num <- length levels <- rev tart <- seq bg <- data_frame mutate bgdta <- tdf bgdta$lv <- as.factor
Center circle
Not much detail, but you may want to add some center circles.
lm <- max ggplot() + geom_polygon+ geom_segment + geom_path+ geom_text + geom_polygon+ geom_polygon+ geom_path + geom_point + geom_text + ylim + xlim + theme + coord_equal


Most popular insights
1.R language dynamic graph visualization: how to create a graph with exquisite animation
2.Visual analysis of R language survival analysis
3.Python data visualization - seaborn Iris iris data
4.The experiment of Bufeng injection (Pufeng injection) is simulated and dynamic with r language
5.R language survival analysis data analysis visualization case
6.r language data visualization analysis case: exploring brfss data analysis