Docker learning notes
The difference between Docker and virtual machine technology
The traditional virtual machine virtualizes a series of hardware, runs a complete operating system, and then installs and runs software in this system
2. The application in the container is the kernel running directly in the host computer. The container does not have its own kernel or hardware, so it is lightweight
3. Each container is separated from each other. Each container has its own file system, which does not affect each other
Installation of Docker
Basic composition of Docker
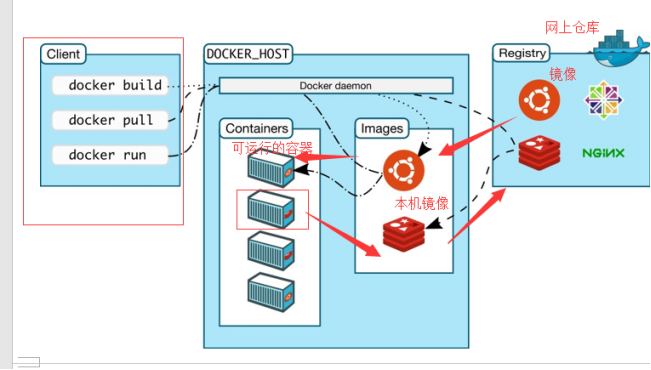
image:
The docker scene is like a template through which container services can be created, and multiple containers can be created through this image
container
Docker uses container technology to run independently or a group of applications, which are created through image
Basic commands: start, stop, delete, etc
The container can be understood as a suggested linux system
repository
A warehouse is a place where images are stored. It is divided into a shared warehouse and a private warehouse
install
Environmental preparation
1. A little bit of common linux commands
2. linux system
Environment view
# The system kernel is 5.4 0 zhangbangyan@zhangbangyan-Lenovo-ideapad-Y700-15ISK:~$ uname -r 5.4.0-80-generic
# System version zhangbangyan@zhangbangyan-Lenovo-ideapad-Y700-15ISK:~$ cat /etc/os-release NAME="Ubuntu" VERSION="18.04.5 LTS (Bionic Beaver)" ID=ubuntu ID_LIKE=debian PRETTY_NAME="Ubuntu 18.04.5 LTS" VERSION_ID="18.04" HOME_URL="https://www.ubuntu.com/" SUPPORT_URL="https://help.ubuntu.com/" BUG_REPORT_URL="https://bugs.launchpad.net/ubuntu/" PRIVACY_POLICY_URL="https://www.ubuntu.com/legal/terms-and-policies/privacy-policy" VERSION_CODENAME=bionic UBUNTU_CODENAME=bionic
install
Help documentation: https://docs.docker.com/
# Uninstall older version of docker sudo apt-get remove docker docker-engine docker.io containerd runc # There are three installation methods: installing from the image warehouse (recommended), installing from the DEB package (purely manual, which is very useful for installing docker on systems that do not need a network), and using convenient script installation (used in some test and development environments)
Install from mirror:
#Set up warehouse
#1. Update apt package
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install \
apt-transport-https \
ca-certificates \
curl \
gnupg \
lsb-release
#2. Add the official GPG key of Docker
curl -fsSL https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu/gpg | sudo gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg
#3. Set stability Library
echo \
"deb [arch=amd64 signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/docker-archive-keyring.gpg] https://download.docker.com/linux/ubuntu \
$(lsb_release -cs) stable" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list > /dev/null
#Install docker engine #1. Update apt index and install the latest docker engine sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io #2. Start docker systemctl start docker #3. Check whether docker is successfully installed docker version #4. Start the image by run ning docker run "Image name#docker run hello-world #5. View mirror zhangbangyan@zhangbangyan-Lenovo-ideapad-Y700-15ISK:~$ docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE hello-world latest d1165f221234 4 months ago 13.3kB
Understanding: uninstalling docker
#Uninstall the docker engine and included packages sudo apt-get purge docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io #The image and container will not be deleted automatically. You need to execute the following instructions sudo rm -rf /var/lib/docker sudo rm -rf /var/lib/containerd
Run process and Docker principle
What does Docker do?
Docker is a client sever system. The daemon of docker runs on the host. Access from the client through Socket!
DockerSever will execute the docker client instruction after receiving it!
Why is Docker faster than virtual machines?
1. Docker has fewer abstraction layers than virtual machines
2. docker uses the kernel of the host, and the VM needs to build a new operating system
Therefore, when creating a new container, you do not need to reload a new operation kernel like the virtual machine to avoid booting. The virtual machine is loaded with the operating system at the minute level. docker uses the host's operating system, omitting this complex process, second level.
Common commands of Docker
Help command
docker version #Display Docker version information docker info #Displays the Docker system information, including the number of images and containers docker command --help #For help commands, you can see the related commands of docker
Help documentation: https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/
Mirror command
docker images view images that exist locally
zhangbangyan@zhangbangyan-Lenovo-ideapad-Y700-15ISK:~$ docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
hello-world latest d1165f221234 4 months ago 13.3kB
#explain
REPOSITORY Mirrored warehouse source
TAG Mirrored label
IMAGE ID mirrored id
CREATED Creation time of scene
SIZE Mirror size
#Optional
Options:
-a, --all Show all images (default hides intermediate images)
--digests Show digests # display summary
-f, --filter filter Filter output based on conditions provided
--format string Pretty-print images using a Go template
--no-trunc Don't truncate output #Do not truncate the output
-q, --quiet Only show image IDs
docker search search image
zhangbangyan@zhangbangyan-Lenovo-ideapad-Y700-15ISK:~$ docker search mysql
NAME DESCRIPTION STARS OFFICIAL AUTOMATED
mysql MySQL is a widely used, open-source relation... 11188 [OK]
mariadb MariaDB Server is a high performing open sou... 4251 [OK]
mysql/mysql-server Optimized MySQL Server Docker images. Create... 833 [OK]
#Optional
Options:
-f, --filter filter Filter output based on conditions provided
--format string Pretty-print search using a Go template
--limit int Max number of search results (default 25)
--no-trunc Don't truncate output
#for example
zhangbangyan@zhangbangyan-Lenovo-ideapad-Y700-15ISK:~$ docker search mysql --filter=STARS=3000
NAME DESCRIPTION STARS OFFICIAL AUTOMATED
mysql MySQL is a widely used, open-source relation... 11188 [OK]
mariadb MariaDB Server is a high performing open sou... 4251 [OK]
docker pull Download Image
zhangbangyan@zhangbangyan-Lenovo-ideapad-Y700-15ISK:~$ docker pull mysql Using default tag: latest #If you do not write tag, the default is latest latest: Pulling from library/mysql 33847f680f63: Pull complete #Layered download, the core federated file system of docker image 5cb67864e624: Pull complete 1a2b594783f5: Pull complete b30e406dd925: Pull complete 48901e306e4c: Pull complete 603d2b7147fd: Pull complete 802aa684c1c4: Pull complete 715d3c143a06: Pull complete 6978e1b7a511: Pull complete f0d78b0ac1be: Pull complete 35a94d251ed1: Pull complete 36f75719b1a9: Pull complete Digest: sha256:8b928a5117cf5c2238c7a09cd28c2e801ac98f91c3f8203a8938ae51f14700fd #autograph Status: Downloaded newer image for mysql:latest docker.io/library/mysql:latest #Real address #Equivalent to docker pull mysql docker pull docker.io/library/mysql:latest #Specified version download docker pull mysql:5.7
docker rmi delete image
docker rmi -f container id #Delete a single mirror docker rmi -f container id container id container id ... #Delete multiple mirrors docker rmi -f $(docker images -aq) #Delete all containers
Container command
Note: you can create a container only with an image. For linux, download a centOS image to test
docker pull centos
Create a new container and start
docker run [Optional parameters] image # Parameter description --name="Name" Container name tomcat01 tomcat02 , Used to distinguish containers -d Run in background mode -it Run in interactive mode and enter the container to view the content -p Specifies the port of the container #Test, start and enter the container zhangbangyan@zhangbangyan-Lenovo-ideapad-Y700-15ISK:~$ docker run -it centos [root@7fcd4fd44d09 /]# ls #View the files in the container, the basic version, and many commands are imperfect bin dev etc home lib lib64 lost+found media mnt opt proc root run sbin srv sys tmp usr var #Exit from container [root@7fcd4fd44d09 /]# exit exit zhangbangyan@zhangbangyan-Lenovo-ideapad-Y700-15ISK:~$ ls Ascend build Docker Study notes.md examples.desktop java_error_in_MINDSTUDIO_3273.log Python-3.7.5 Python-3.7.5.tgz snap tmp var Public template video picture document download music desktop
Lists all running containers
#docker ps command
#Lists currently running containers
-a #List currently running containers + historically running containers
-n=? #Displays recently run containers
-q #Displays only the number of the container
zhangbangyan@zhangbangyan-Lenovo-ideapad-Y700-15ISK:~$ docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
zhangbangyan@zhangbangyan-Lenovo-ideapad-Y700-15ISK:~$ docker ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
7fcd4fd44d09 centos "/bin/bash" 4 minutes ago Exited (0) About a minute ago pensive_feynman
c88bc2806ce6 centos "/bin/bash" 8 minutes ago Exited (0) 5 minutes ago festive_brahmagupta
ee8e88ad5a29 d1165f221234 "/hello" 2 hours ago Exited (0) 2 hours ago keen_edison
5fd01b67ed44 d1165f221234 "/hello" 2 hours ago Exited (0) 2 hours ago recursing_hamilton
Exit container
exit #The container stops and exits directly ctrl + P + Q #The container does not stop and exits
Delete container
docker rm container id #Delete the specified container. You cannot delete the running container. If you want to forcibly delete rm -f docker rm -f $(docker ps -aq) #Delete all containers docker ps -a -q|xargs docker rm #Delete all containers
Start and stop container operation
docker start container id #Start container docker restart container id #Restart container docker stop container id #Stop the currently running container docker kill container id #Force stop of current container
Other commonly used commands
Background startup container
#Command docker run -d image name zhangbangyan@zhangbangyan-Lenovo-ideapad-Y700-15ISK:~$ docker run -d centos f8a821f314e10ba93f984ad45a85003540024b9f57dc7e6a4ad039fa98f07d3a #Problem: docker ps found centos stopped #Common pitfalls: when docker container runs in the background, there must be a foreground process. Once docker finds that there is no application, it will automatically stop #When the container starts and finds that it does not provide services, it will stop immediately
view log
docker logs --help # Docker logs - F - t -- after tracking the container id, it is found that there is nothing in the calendar because the container has no operation #Write your own shell script "while true;do echo zby;sleep 1;done" zhangbangyan@zhangbangyan-Lenovo-ideapad-Y700-15ISK:~$ # docker run -d centos /bin/sh -c "while true;do echo zby;sleep 1;done" 41223283762e4f7e7ea3a8c351458a0eaa85cc591904eff1599fef8769274e59 # zhangbangyan@zhangbangyan-Lenovo-ideapad-Y700-15ISK:~$ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 41223283762e centos "/bin/sh -c 'while t..." 22 seconds ago Up 21 seconds fervent_noether # Show log -tf #Show log --tail number #Displays the number of logs -f #Trace log output #docker logs -f -t --tail 10 41223283762e 2021-07-31T00:42:36.110432088Z zby 2021-07-31T00:42:37.114711623Z zby 2021-07-31T00:42:38.119040224Z zby 2021-07-31T00:42:39.123426760Z zby 2021-07-31T00:42:40.127736602Z zby 2021-07-31T00:42:41.131593133Z zby 2021-07-31T00:42:42.134010682Z zby 2021-07-31T00:42:43.138386661Z zby 2021-07-31T00:42:44.142655565Z zby 2021-07-31T00:42:45.147044534Z zby 2021-07-31T00:42:46.151376580Z zby 2021-07-31T00:42:47.153788476Z zby 2021-07-31T00:42:48.158548960Z zby 2021-07-31T00:42:49.162656416Z zby
View process information in the container
# docker top container id zhangbangyan@zhangbangyan-Lenovo-ideapad-Y700-15ISK:~$ #docker top 41223283762e UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD root 5244 5226 0 08:38 ? 00:00:00 /bin/sh -c while true;do echo zby;sleep 1;done root 5876 5244 0 08:46 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/coreutils --coreutils-prog-shebang=sleep /usr/bin/sleep 1
View the metadata of the image
# docker inspect container id
zhangbangyan@zhangbangyan-Lenovo-ideapad-Y700-15ISK:~$ docker inspect 27f3809f1d88
[
{
"Id": "27f3809f1d8858088f2e8a7897926276577c12458b1f906a8dd781e1e007a25c",
"Created": "2021-07-31T00:10:33.199391228Z",
"Path": "/bin/bash",
"Args": [],
"State": {
"Status": "exited",
"Running": false,
"Paused": false,
"Restarting": false,
"OOMKilled": false,
"Dead": false,
"Pid": 0,
"ExitCode": 127,
"Error": "",
"StartedAt": "2021-07-31T00:10:33.482537506Z",
"FinishedAt": "2021-07-31T00:10:50.218862098Z"
}
Enter the currently running container
# The container is usually run in the background mode. Sometimes it is necessary to enter the container and modify some configurations docke #Command 1 docker exec -it container id /bin/bash zhangbangyan@zhangbangyan-Lenovo-ideapad-Y700-15ISK:~$ #docker exec -it 41223283762e /bin/bash [root@41223283762e /]# #Command 2 docker attach container id Executing current code... # docker exec #After entering the container, open a new terminal, which can be operated inside # docker attach #Entering the terminal where the container is executing will not start a new process
Copy the files in the container to the host
#docker cp container id =: the host address in the container docker cp 41223283762e :/home/test.java /home #View the documents in the host / home directory zhangbangyan@zhangbangyan-Lenovo-ideapad-Y700-15ISK:~$ ls Ascend java_error_in_MINDSTUDIO_3273.log tmp Video Music build Python-3.7.5 var Picture desktop Docker Study notes.md Python-3.7.5.tgz Public documents examples.desktop snap Template download #Show running containers zhangbangyan@zhangbangyan-Lenovo-ideapad-Y700-15ISK:~$ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES d37f9b78eb36 centos "/bin/bash" About a minute ago Up About a minute lucid_chandrasekhar #Enter a running container zhangbangyan@zhangbangyan-Lenovo-ideapad-Y700-15ISK:~$ docker attach d37f9b78eb36 [root@d37f9b78eb36 /]# cd /home [root@d37f9b78eb36 home]# ls [root@d37f9b78eb36 home]# touch test.java #Create an empty document [root@d37f9b78eb36 home]# ls test.java [root@d37f9b78eb36 home]# exit exit zhangbangyan@zhangbangyan-Lenovo-ideapad-Y700-15ISK:~$ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES #Copy the files in the container to the host zhangbangyan@zhangbangyan-Lenovo-ideapad-Y700-15ISK:~$ docker cp d37f9b78eb36:/home/test.java /home #Copying is a manual process. In the future, automatic copying will be realized by using -v data volume technology
Learning method: type all commands by yourself
Summary
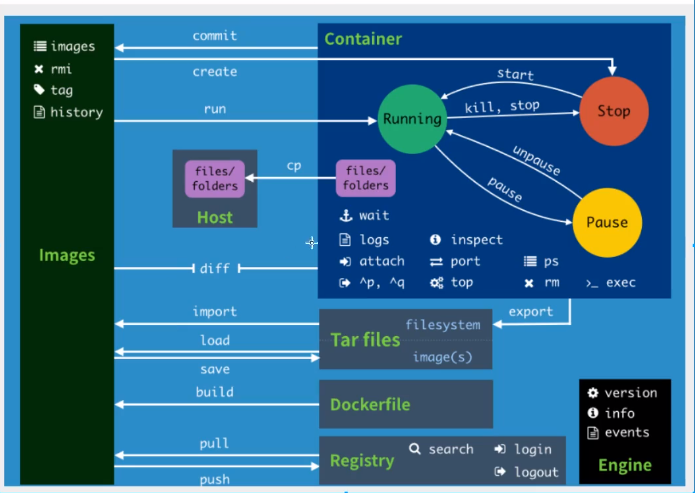
attach #Under the current shell, attach the specified running image build #Customized image through dockerfile commit #Commit the current container as a new image cp #Copy files or directories from the container to the host create #Create a new container, the same as run, but do not start the container diff #View the file changes of the container through docker events #Get the real-time events of the container from the docker service exec #Run the command on a container that has already been run export #The content stream of the container is used as a tar archive file "corresponding to import" history #Show the formation history of a mirror image images #Lists the current image of the system import #Create a new file image from the tar package info #Display system related information inspect #View container details kill #Stop the specified container load #Load an image from a tar package login #Register or log in to a docker server logout #Exit from the current docker registry service logs #Output log information of the current container port #View the internal source port of the container corresponding to the mapped port pause #Pause container ps #List containers pull #Pull the specified image from the image source site push #Push image to docker source server restart #Restart the running container rm #Remove one or more containers rmi #Remove mirror run #Create a new container and run it save #Save an image as a tar package search #Search for images on docker hub start #Start container stop #Stop container tag #Label images in source top #View the process information running in the container unpause #Unsuspend container version #View docker version number wait #Intercepts the exit state when the container stops
The above commands are the most commonly used commands.
docker image explanation
What is mirroring
Image is a medium lightweight and executable independent software package, which is used to package the software running environment and the software developed based on the running environment. It contains all the contents required to run a software, including code, runtime library, environment variables and configuration files.
All applications can run directly by directly packaging the docker image
How to get the image:
- Remote warehouse get
- Copy
- Make an image dockerfile yourself
Docker image loading principle
UnionFS (Federated file system)
Union file system is a layered, lightweight and high-performance file system. It supports the superposition of file system modifications from one submission to another. At the same time, different directories can be mounted into a single virtual file system. The union file system is the foundation of Docker image. Images can be inherited through layering. Based on the basic image (without parent image), various specific application images can be made
Features: multiple file systems can be loaded at the same time, but from the outside, only one file system can be seen. Joint loading will overlay all layers of file systems, so that the final file system will contain all underlying files and directories
Docker image loading principle
The image of docker is actually composed of a layer by layer file system, which is called UnionFS.
boots(boot file system) mainly includes bootloader and kernel. Bootloader is mainly boot plus kernel. Bootfs file system will be loaded when Linux starts up, and bootfs is at the bottom of Docker image. This layer is the same as our typical Linux/Unix system, including boot loader and kernel. When boot loading is completed, the whole kernel will be in memory, and the memory will be exhausted The usage rights have been transferred from bootfs to the kernel. At this time, the system will also uninstall bootfs.
rootfs (root file system), above bootfs. It contains standard directories and files such as / dev,/proc,/bin,/etc in a typical Linux system. rootfs is a variety of operating system distributions, such as Ubuntu, Centos and so on.
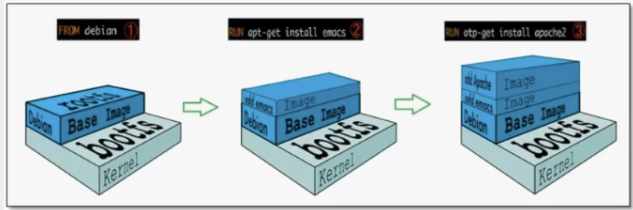
Usually, the CentOS installed into the virtual machine is several G, why is Docker only 200M?

For a thin OS,rootfs can be very small. You only need to package the most basic commands, tools and program libraries. Because the underlying layer directly uses the Host kernel, you only need to provide rootfs.
It can be seen that for different Linux distributions, boots are basically the same, and rootfs will be different, so different distributions can share bootfs
The virtual machine is at the minute level and the container is at the second level!
Hierarchical understanding
You can download an image and pay attention to the log output of the download. You can see that it is downloading layer by layer
reflection:
Why does the Docker image adopt this hierarchical structure?
The biggest benefit, I think, is resource sharing! For example, if multiple images are built from the same base image, the host only needs to keep one base image on the disk, and only one base image needs to be loaded in memory, so that it can serve all containers, and each layer of the image can be shared.
You can view the image hierarchy through the docker image inspect name command
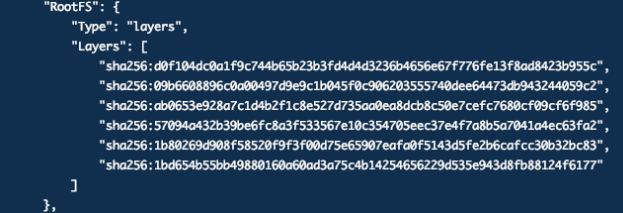
understand:
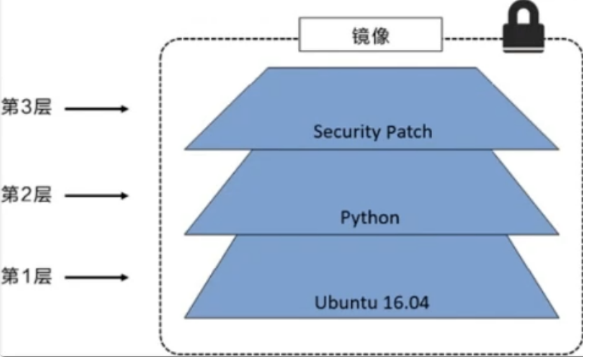
All Docker images start from a basic image layer. When modifying or adding new content, a new image layer will be created on top of the current image layer.
For a simple example, if it is based on Ubuntu Linux 16 04 create a new image, which is the first layer of the new image; If you add a Python package to the image,
A second mirror layer is created above the base mirror layer; If you continue to add a security patch, the third mirror layer will be created. The image currently contains three mirror layers, as shown in the following figure (this is only a simple example for demonstration).
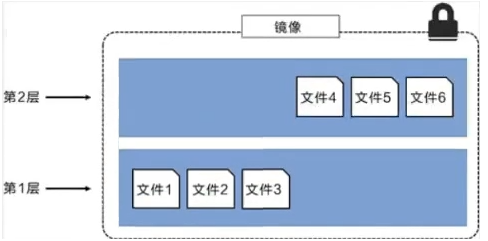
It is important to understand that while adding additional mirror layers, the mirror always remains the combination of all current mirrors. The following figure shows a simple example. Each mirror layer contains 3 files, while the mirror contains 6 files from two mirror layers.
The image layer in the above figure is slightly different from that in the previous figure. The main purpose is to facilitate the display of files
The following figure shows a slightly complex three-tier image. Externally, there are only 6 files in the entire image, because file 7 in the top layer is a newer version of file 5
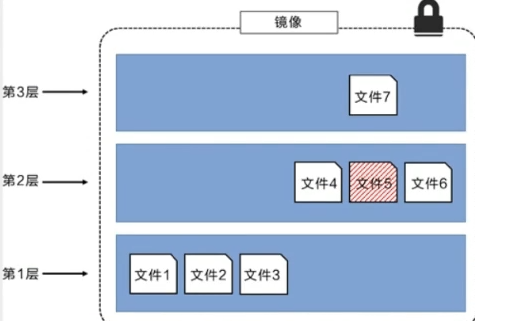
In this case, the files in the upper mirror layer overwrite the files in the lower mirror layer. This allows the updated version of the file to be added to the image as a new image layer
Docker implements the image layer stack through the storage engine (the new version adopts the snapshot mechanism), and ensures that multiple image layers are displayed as a unified file system
AUFS, Overlay2, Device Mapper, Btrfs and ZFS are available for storage on Linux. As the name suggests, each storage engine is based on the corresponding piece system or block device technology in Linux, and each storage engine has its unique performance characteristics.
Docker only supports a Windows filter storage engine on windows, which implements layering and cow based on NTFS file system [1].
The following figure shows the same three-tier image as the system display. All mirror layers are stacked and combined to provide a unified view
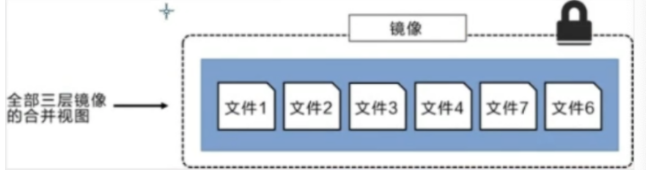
characteristic
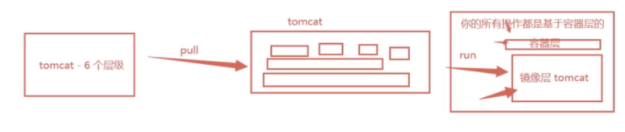
Docker images are read-only. When the container is started, a new writable layer is loaded on the top of the image!
This layer is what we usually call the container layer. What is under the container is called the mirror layer!
commit image
docker commit Submit the container as a new copy # The command works similarly to git docker commit -m="Description information" -a="author" container id Target image name:[TAG]
Actual test
# 1. Start a default tomcat docker run -d -p 8080:8080 tomcat # 2. It is found that the default tomcat does not have a webapps application, and there are no files under the official image default webapps! docker exec -it container id # 3. Copy the file in # 4. Submit the operated container as an image through commit! We can use our modified image later. This is our own modified image. docker commit -m="Description information" -a="author" container id Target image name:[TAG] docker commit -a="kuangshen" -m="add webapps app" container id tomcat02:1.0
Container data volume
What is a container data volume
Review of docker's concept
Package the application and environment into one image
data If the data is in the container, the data will be lost after the container is deleted! Requirement: data can be persisted
There can be a data sharing technology between containers! The data generated in the docker container is synchronized to the local
This is volume technology! To mount the directory, mount the directory in our container to linux.
Summary: container persistence and synchronization! Data can also be shared between containers!
Using data volumes
Method 1: directly use the command to mount - v
docker run -it -v Host Directory: in container directory /bin/bash
Named and anonymous mount
# Anonymous mount -v Path in container! docker run -d -p --name nginx01 -v /etc/nginx nginx #Specify only the container directory docker volume ls #View all volume s # Named mount docker run -d -p --name nginx02 -v juming-nginx:/etc/nginx nginx # Via -v volume name: path within container # Take a look at this volume docker volume inspect juming-nginx
All volumes in the docker container are in / var / lib / docker / volumes / xxx without a specified directory/_ In data
We can easily find our volumes through named mount, which is used in most cases
# How to determine whether a named mount or an anonymous mount or a specified path mount -v In container path #Anonymous mount -v Volume name: path within container #Named mount -v /Host path: path within container #Specified path mount
Extension:
# Change read and write permissions through - v path in container: ro rw ro read only #read-only rw readwrite #Readable and writable # Once the permission of the container is set, the container will limit the content we mount! docker run -d -p --name nginx02 -v juming-nginx:/etc/nginx:ro nginx docker run -d -p --name nginx02 -v juming-nginx:/etc/nginx:rw nginx # As long as ro sees ro, it means that this path can only be operated through the host, and cannot be operated inside the container!
Data volume container
Mount between containers and synchronize data
Command: - volumes from
docker run -it --name docker02 --volumes-from docker01 zby:1.0
Conclusion:
For the transfer of configuration information between containers, the life cycle of data volume containers continues until no containers are used
However, once it is mounted locally, the local data will not be deleted at this time
DockerFile
DckerFile is the build file used to build the docker image! Command script!
Construction steps:
1. Write a dockerfile file
2. docker build builds an image
3. docker run run image
4. docker push publishing images (dockerhub, Alibaba cloud image warehouse)
Through this script, you can generate an image
Mode 2:
#Write a dockerfile file with any name, but dockerfile is recommended #Contents in the file: instruction (in uppercase), parameter vim dockerfile #Contents inside the dockerfile file FROM ubuntu VOLUME ["volume01","volume02"] CMD echo "...end..." CMD /bin/bash #Each command here is a layer of mirroring #View contents in dockerfile zhangbangyan@zhangbangyan-Lenovo-ideapad-Y700-15ISK:~$ #cat dockerfile FROM ubuntu VOLUME ["volume01","volume02"] CMD echo "...end..." CMD /bin/bash #create mirror docker build -f /home/zhangbangyan/dockerfile -t zby:1.0 . # View self created images root@zhangbangyan-Lenovo-ideapad-Y700-15ISK:/home/zhangbangyan# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE zby 1.0 daf7a229f307 7 minutes ago 72.8MB ubuntu latest 1318b700e415 4 days ago 72.8MB centos latest 300e315adb2f 7 months ago 209MB # Start the self written image docker run -it zby:1.0 root@954a4ce3e8cb:/# ls -l total 56 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 7 Jul 23 17:35 bin -> usr/bin drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Apr 15 2020 boot drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 360 Jul 31 08:04 dev drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4096 Jul 31 08:04 etc drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Apr 15 2020 home lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 7 Jul 23 17:35 lib -> usr/lib lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Jul 23 17:35 lib32 -> usr/lib32 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 Jul 23 17:35 lib64 -> usr/lib64 lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 10 Jul 23 17:35 libx32 -> usr/libx32 drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jul 23 17:35 media drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jul 23 17:35 mnt drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jul 23 17:35 opt dr-xr-xr-x 316 root root 0 Jul 31 08:04 proc drwx------ 2 root root 4096 Jul 23 17:38 root drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 4096 Jul 23 17:38 run lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 8 Jul 23 17:35 sbin -> usr/sbin drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jul 23 17:35 srv dr-xr-xr-x 13 root root 0 Jul 31 08:04 sys drwxrwxrwt 2 root root 4096 Jul 23 17:38 tmp drwxr-xr-x 13 root root 4096 Jul 23 17:35 usr drwxr-xr-x 11 root root 4096 Jul 23 17:38 var drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jul 31 08:04 volume01 drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Jul 31 08:04 volume02
This volume must have a synchronized directory with the outside! This volume is mounted anonymously
Many official images are basic packages without many functions. We usually need to build our own images
DockerFile construction process
Basic knowledge
1. Each reserved keyword (instruction) must be uppercase
2. Execution is performed from top to bottom
3. # indicates a comment
4. Each instruction creates and commits a new mirror layer
Dockerfile is development oriented. If we want to publish projects and make images in the future, we need to write a dockerfile file. This file is very simple!
docker image has gradually become the standard of enterprise delivery, which must be mastered!
Steps: development, deployment, operation and maintenance. not a single one can be omitted!
DockerFile: build the file, define all the steps and source code
Dockerimages: build the generated image through dockerfile, and finally release and run the product
docker container: a container is an image that runs to provide a server
Docker instruction

FROM #base image MAINTAINER #Who is the image, name + email RUN # Commands to run during image construction ADD #Step, tomcat image, this tomcat compressed package! Add content WORKDIR #Mirrored working directory VOLUME # Mount directory EXPOSE #Reserved port configuration CMD #Specify the command to run when the container runs. Only the last one can take effect and can be replaced ENTRYPOINT #Specify the commands to run when the container runs. You can append commands ONBUILD #When an inherited DockerFile is built, the ONBUILD instruction will be run to trigger the instruction COPY #Similar to ADD, copy our files to the image ENV #Setting environment variables during construction
Actual test
Most of the images in docker hub are loaded from the basic image, and the software and environment are configured to build them as needed
Create your own centos
# 1. Prepare Dockerfile file [root@iZ2zeg4ytp0whqtmxbsqiiZ dockerfile]# cat mydockerfile-centos FROM centos MAINTAINER xiaofan<594042358@qq.com> ENV MYPATH /usr/local WORKDIR $MYPATH # Mirrored working directory RUN yum -y install vim RUN yum -y install net-tools EXPOSE 80 CMD echo $MYPATH CMD echo "---end---" CMD /bin/bash # 2. Build an image from this file # Command docker build -f dockerfile file path - t image name: [tag] [root@iZ2zeg4ytp0whqtmxbsqiiZ dockerfile]# docker build -f mydockerfile-centos -t mycentos:0.1 . Successfully built d2d9f0ea8cb2 Successfully tagged mycentos:0.1
Difference between CMD and ENTRYPOINT
CMD # Specify the command to run when the container starts. Only the last one will take effect and can be replaced ENTRYPOINT # Specify the command to run when the container starts, and you can append the command
Test CMD
# 1. Prepare dockerfile file [root@iZ2zeg4ytp0whqtmxbsqiiZ dockerfile]# vim dockerfile-cmd-test FROM centos CMD ["ls", "-a"] # 2. Build image [root@iZ2zeg4ytp0whqtmxbsqiiZ dockerfile]# docker build -f dockerfile-cmd-test -t cmdtest . # 3. run and find that our ls -a command takes effect [root@iZ2zeg4ytp0whqtmxbsqiiZ dockerfile]# docker run ebe6a52bb125 . .. .dockerenv bin dev etc home lib lib64 # Want to append a command - l to ls -al [root@iZ2zeg4ytp0whqtmxbsqiiZ dockerfile]# docker run ebe6a52bb125 -l docker: Error response from daemon: OCI runtime create failed: container_linux.go:349: starting container process caused "exec: \"-l\": executable file not found in $PATH": unknown. [root@iZ2zeg4ytp0whqtmxbsqiiZ dockerfile]# docker run ebe6a52bb125 ls -l # cmd, - l replaces CMD["ls", "-a"] command, - l is not a command, so an error is reported
Test ENTRYPOINT
# 1. Prepare dockerfile file [root@iZ2zeg4ytp0whqtmxbsqiiZ dockerfile]# vim dockerfile-entrypoint-test FROM centos ENTRYPOINT ["ls", "-a"] # 2. Build documents [root@iZ2zeg4ytp0whqtmxbsqiiZ dockerfile]# docker build -f dockerfile-entrypoint-test -t entrypoint-test . # 3. run and find that our ls -a command is also effective [root@iZ2zeg4ytp0whqtmxbsqiiZ dockerfile]# docker run entrypoint-test . .. .dockerenv bin dev etc home lib # 4. Our additional command is directly spliced behind the ENTRYPOINT command! [root@iZ2zeg4ytp0whqtmxbsqiiZ dockerfile]# docker run entrypoint-test -l total 56 drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4096 Aug 13 07:52 . drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4096 Aug 13 07:52 .. -rwxr-xr-x 1 root root 0 Aug 13 07:52 .dockerenv lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 7 May 11 2019 bin -> usr/bin drwxr-xr-x 5 root root 340 Aug 13 07:52 dev drwxr-xr-x 1 root root 4096 Aug 13 07:52 etc drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 May 11 2019 home lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 7 May 11 2019 lib -> usr/lib lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 9 May 11 2019 lib64 -> usr/lib64 drwx------ 2 root root 4096 Aug 9 21:40 lost+found