Article catalog
preface
Initialization after installing Linux
- Turn off selinux function
- Thin boot entry
a) Start self starting service
b) Delete special users and user groups - User and password security
- Generally, the user password is required to be greater than 8 digits. Try to use a strong password, which is composed of numbers, case and special symbols.
- Try not to use the root user to log in, and change the ordinary user into the root user
- Try to log in with a secret key
- Lock important files
- Checking and scanning of file permissions
- Hide Linux version information
- Prohibit Linux from being ping ed
Other operations
summary
preface
Today, a student asked what initialization or optimization should be done after installing the operating system. In fact, after the system is installed in the company, it is directly run through the script. Many people don't like to read the script, which leads to not knowing what kind of operation the script has done. Let's talk about the simple optimization after installing the system today.
Initialization after installing Linux
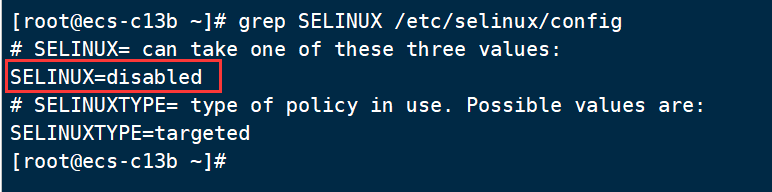
1. Turn off selinux function
[root@ecs-c13b ~]# sed -i 's/SELINUX=enforcing/SELINUX=disabled/' /etc/selinux/config
Check whether the modification of the configuration file is completed
2. Streamline startup items
a) Start self starting service
After general services are installed, several very important services must be started
sshd,rsyslog,network, crond,sysstat
b) Delete special users and user groups
- There are many default users in Linux that can be deleted
[root@ecs-c13b ~]# head -n 13 /etc/passwd |tail -n 10 adm:x:3:4:adm:/var/adm:/sbin/nologin lp:x:4:7:lp:/var/spool/lpd:/sbin/nologin sync:x:5:0:sync:/sbin:/bin/sync shutdown:x:6:0:shutdown:/sbin:/sbin/shutdown halt:x:7:0:halt:/sbin:/sbin/halt mail:x:8:12:mail:/var/spool/mail:/sbin/nologin uucp:x:10:14:uucp:/var/spool/uucp:/sbin/nologin operator:x:11:0:operator:/root:/sbin/nologin games:x:12:100:games:/usr/games:/sbin/nologin gopher:x:13:30:gopher:/var/gopher:/sbin/nologin
- User groups that can be deleted in linux:
adm.lp,news, uucp,games,dip, etc
3. User and password security
1. Generally, the user password shall be greater than 8 digits. Try to use a strong password, which is composed of numbers, case and special symbols.
2. Try not to use the root user to log in, and change the ordinary user into the root user
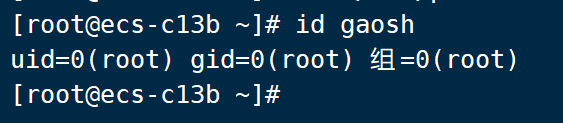
[root@ecs-c13b ~]# useradd gaosh
Modify / etc/passwd
root User restricted login: root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash Replace with: root:x:0:0:root:/root:/sbin/nologin Ordinary users changed to root User: gaosh:x:500:500::/home/gaosh:/bin/bash Change to gaosh:x:0:0::/home/gaosh:/bin/bash
At this point, gaosh becomes root
3. Try to use the secret key to log in
4. Lock important documents
Lock important files so that even if you have root permission, you still cannot delete files. For specific operation steps, refer to the setting method in the following article:
If you learn this operation, you will no longer be afraid to delete the library and run away
5. Check and scan file permissions
Files with suid and sgid permissions and some files with 777 permissions are very dangerous. Operation and maintenance needs time to check, find and modify permissions. In addition, there are some orphan files without owners, which are also dangerous and often become tools used by hackers. Find these files and delete or modify permissions in time.
About suid and sgid permission introduction and use reference:
[linux] step by step operation and maintenance - Fundamentals - file special permission management
How to find files with special permissions, refer to:
[linux] step by step operation and maintenance - basic commands - Search Commands
6. Hide Linux version information
Save location of system version information
[root@ecs-c13b ~]# cat /etc/issue CentOS release 6.9 (Final) Kernel \r on an \m [root@ecs-c13b ~]# cat /etc/issue.net CentOS release 6.9 (Final) Kernel \r on an \m [root@ecs-c13b ~]#
Execute the following command to clear the system version information
[root@gaosh ~]# > /etc/issue [root@gaosh ~]# > /etc/issue.net
7. Prohibit Linux from being ping ed
You can ping the intranet IP through iptables, and the extranet users cannot Ping except the specific IP
Other operations
- configure network
- Sets the number of file descriptors
- Modify character set
- Kernel parameter tuning
- Password gurb
summary
The script of the step-by-step operation and maintenance series will be explained later. In the initialization script, there may be some security operations in addition to the above, such as vulnerability scanning.
This article is from ID: Internet old Xin more content is concerned about the official account of the "geek operation and maintenance home".
