1. What day
Title: what day
January 1, 2000 is the first day of that year.
So, May 4, 2000, is the first day of that year?
Note: what needs to be submitted is an integer. Do not fill in any redundant content
Answer: 125
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int s=31+29+31+30+4;
printf("%d",s);
return 0;
}
2. Clear code
Title: clear code
The font of Chinese characters exists in the font, and even today, the 16 dot matrix font is still widely used.
The 16 dot matrix font regards each Chinese character as 16x16 pixel information. And record this information in bytes.
One byte can store 8 bits of information, and 32 bytes can store a font of Chinese characters.
Convert each byte to binary representation, 1 for ink and 0 for background color. 2 bytes per line,
There are 16 lines in total. The layout is:
1st byte, 2nd byte
3rd byte, 4th byte
...
31st byte, 32nd byte
This topic is to give you a piece of information composed of multiple Chinese characters. Each Chinese character is represented by 32 bytes. Here is the value of bytes as signed integers.
The requirements of the topic are hidden in this information. Your task is to restore the glyphs of these Chinese characters, see the requirements of the questions, and fill in the answers according to the requirements.
This message is (10 Chinese characters in total):
4 0 4 0 4 0 4 32 -1 -16 4 32 4 32 4 32 4 32 4 32 8 32 8 32 16 34 16 34 32 30 -64 0
16 64 16 64 34 68 127 126 66 -124 67 4 66 4 66 -124 126 100 66 36 66 4 66 4 66 4 126 4 66 40 0 16
4 0 4 0 4 0 4 32 -1 -16 4 32 4 32 4 32 4 32 4 32 8 32 8 32 16 34 16 34 32 30 -64 0
0 -128 64 -128 48 -128 17 8 1 -4 2 8 8 80 16 64 32 64 -32 64 32 -96 32 -96 33 16 34 8 36 14 40 4
4 0 3 0 1 0 0 4 -1 -2 4 0 4 16 7 -8 4 16 4 16 4 16 8 16 8 16 16 16 32 -96 64 64
16 64 20 72 62 -4 73 32 5 16 1 0 63 -8 1 0 -1 -2 0 64 0 80 63 -8 8 64 4 64 1 64 0 -128
0 16 63 -8 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 4 -1 -2 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 5 0 2 0
2 0 2 0 7 -16 8 32 24 64 37 -128 2 -128 12 -128 113 -4 2 8 12 16 18 32 33 -64 1 0 14 0 112 0
1 0 1 0 1 0 9 32 9 16 17 12 17 4 33 16 65 16 1 32 1 64 0 -128 1 0 2 0 12 0 112 0
0 0 0 0 7 -16 24 24 48 12 56 12 0 56 0 -32 0 -64 0 -128 0 0 0 0 1 -128 3 -64 1 -128 0 0
Note: what needs to be submitted is an integer. Do not fill in any redundant content.
Answer: 387420489
#include"stdio.h"
void ej(int n)
{
int k=1,s[9];
while(k)
{
for(k=1;k<9;k++)
{
s[k]=n%2;
n=n/2;
}
for(k=8;k>0;k--)
{
if(s[k]==0)printf(" ");
else printf(".");
}
}
}
void fej(int n)
{
int k=1,s[9];
n=-n;
while(k)
{
for(k=1;k<9;k++)
{
if(n%2==0)
s[k]=1;
else
s[k]=0;
n=n/2;
}
if(s[1]==0)
{
s[1]=1;
for(k=8;k>0;k--)
if(s[k]==0)printf(" ");
else printf(".");
}
else
{
s[1]+=1;
for(k=1;k<9;k++)
{
if(s[k]==1)
{
break;
}
else if(s[k]==2)
{
s[k]=0;
s[k+1]+=1;
}
}
for(k=8;k>0;k--)
if(s[k]==0)printf(" ");
else printf(".");
}
}
}
int main()
{
freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
int n,i,j;
for(j=0;j<10;j++)
{
for(i=1;i<33;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
if(n>=0)
ej(n);
else
fej(n);
if(i%2==0)
printf("\n");
}
printf("******\n");
}
return 0;
}
3. Product tail zero
Title: product tail zero
The following 10 rows of data have 10 integers in each row. Please find out how many zeros are at the end of their product?
5650 4542 3554 473 946 4114 3871 9073 90 4329
2758 7949 6113 5659 5245 7432 3051 4434 6704 3594
9937 1173 6866 3397 4759 7557 3070 2287 1453 9899
1486 5722 3135 1170 4014 5510 5120 729 2880 9019
2049 698 4582 4346 4427 646 9742 7340 1230 7683
5693 7015 6887 7381 4172 4341 2909 2027 7355 5649
6701 6645 1671 5978 2704 9926 295 3125 3878 6785
2066 4247 4800 1578 6652 4616 1113 6205 3264 2915
3966 5291 2904 1285 2193 1428 2265 8730 9436 7074
689 5510 8243 6114 337 4096 8199 7313 3685 211
Note: what needs to be submitted is an integer, indicating the number of zeros at the end. Do not fill in any superfluous content.
Answer: 31
#include<stdio.h>
int min(int a,int b)
{
return a>b?b:a;
}
int main()
{
freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
int i,a[100]={0},i5=0,i2=0,sm=0;
for(i=0;i<100;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[i]);
for(i=0;i<100;i++)
{
while(1)
{
if(a[i]%5==0)
{
i5++;
a[i]/=5;
}
else if(a[i]%2==0)
{
i2++;
a[i]/=2;
}
else break;
}
}
sm=min(i2,i5);
printf("%d\n",sm);
fclose(stdin);
return 0;
}
4. Number of tests
Title: test times
The residents of Planet x have a bad temper, but fortunately, when they are angry, the only unusual action is to drop their mobile phones.
Major manufacturers have launched a variety of fall resistant mobile phones. The Quality Supervision Bureau of Planet x stipulates that mobile phones must pass the fall resistance test and evaluate a fall resistance index before they are allowed to be listed and circulated.
Planet x has many towering towers, which can be used for fall resistance test. The height of each floor of the tower is the same. Slightly different from the earth, their first floor is not the ground, but equivalent to our second floor.
If the mobile phone is not broken when dropped from the 7th floor, but the 8th floor is broken, the falling resistance index of the mobile phone = 7.
In particular, if the mobile phone is broken when dropped from the first floor, the fall resistance index = 0.
If the n-th floor at the highest level of the tower is not damaged, the falling resistance index = n
In order to reduce the number of tests, 3 mobile phones are sampled from each manufacturer to participate in the test.
The tower height of a test is 1000 floors. If we always adopt the best strategy, how many times do we need to test at most under the worst luck to determine the fall resistance index of the mobile phone?
Please fill in the maximum number of tests.
Note: what needs to be filled in is an integer. Do not fill in any redundant content.
Answer: 19
Idea: there are two solutions: dynamic programming and manual calculation. The latter method is easy to understand and will not be explained. It is mainly to solve dynamic programming
First, understand dp[i][j] i Indicates the number of mobile phones j Indicates the number of floors dp[][]It means yes i Mobile phone j The number of tests required under the worst luck in the case of floors
Let's assume that there is no one without the best strategy j We're all going to fall on the first floor of the building j But when there is only one mobile phone, this is actually the best strategy, so we can gradually expand upward
Suppose we have i-1 The number of mobile phones on all floors has been found. Now let's ask for some i Number of tests with a mobile phone
To do this, we need to traverse the previous floors k(1~j-1)Suppose in k If the floor breaks, we'll choose i-1 Mobile phone for k-1 Worst case scenario for a two storey building dp[i-1][k-1]+1
If in k If the layer is not broken, we can choose i Mobile phones for the rest j-k Worst case of layer dp[i][j-k]+1
In the worst case, we need to take the maximum value between the two, but we are the best strategy, so we need to take the minimum value for the previous non optimal strategy, that is:
dp[i][j]=min(dp[i][j],max(dp[i-1][k-1],dp[i][j-k])+1);
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
#include<stack>
#include<bitset>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cmath>
#include<set>
#include<list>
#include<deque>
#include<map>
#include<queue>
#define ll long long int
using namespace std;
inline ll gcd(ll a,ll b){return b?gcd(b,a%b):a;}
inline ll lcm(ll a,ll b){return a/gcd(a,b)*b;}
int moth[13]={0,31,28,31,30,31,30,31,31,30,31,30,31};
int dir[4][2]={1,0 ,0,1 ,-1,0 ,0,-1};
int dirs[8][2]={1,0 ,0,1 ,-1,0 ,0,-1, -1,-1 ,-1,1 ,1,-1 ,1,1};
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll mod=1e9+7;
int dp[5][1007];
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
for(int i=1;i<=3;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=1000;j++)
dp[i][j]=j;
for(int i=1;i<=1000;i++)
for(int j=2;j<=3;j++){
for(int k=1;k<i;k++)
dp[j][i]=min(dp[j][i],max(dp[j-1][k-1],dp[j][i-k])+1);
}
cout<<dp[3][1000]<<endl;
return 0;
}
5. Quick sort
Title: quick sort.
The following code can find the k-th smallest element from the array a [].
It uses a divide and conquer algorithm similar to that in quick sort, and the expected time complexity is O(N).
Please read the analysis source code carefully and fill in the missing information in the underlined part
#include <stdio.h>
int quick_select(int a[], int l, int r, int k)
{
int p = rand() % (r - l + 1) + l;
int x = a[p];
{
int t = a[p];
a[p] = a[r];
a[r] = t;
}
int i = l, j = r;
while(i < j)
{
while(i < j && a[i] < x)
i++;
if(i < j)
{
a[j] = a[i];
j--;
}
while(i < j && a[j] > x)
j--;
if(i < j)
{
a[i] = a[j];
i++;
}
}
a[i] = x;
p = i;
if(i - l + 1 == k)
return a[i];
if(i - l + 1 < k)
return quick_select( a, i+1, r, k-i-1+l); //Fill in the blanks
else
return quick_select(a, l, i - 1, k);
}
int main()
{
int a[] = {1, 4, 2, 8, 5, 7, 23, 58, 16, 27, 55, 13, 26, 24, 12};
printf("%d\n", quick_select(a, 0, 14, 4));
return 0;
}
6. Incremental triplet
Title: increasing triples
Given three integer arrays
A = [A1, A2, ... AN],
B = [B1, B2, ... BN],
C = [C1, C2, ... CN],
Please count how many triples (i, j, k) satisfy:
1 <= i, j, k <= N
Ai < Bj < Ck
[input format]
The first line contains an integer N.
The second line contains N integers A1, A2,... AN.
The third line contains N integers B1, B2,... BN.
The fourth line contains N integers C1, C2,... CN.
For 30% of data, 1 < = n < = 100
For 60% of the data, 1 < = n < = 1000
For 100% data, 1 < = n < = 100000 0 < = AI, Bi, CI < = 100000
[output format]
An integer represents the answer
[sample input]
3
1 1 1
2 2 2
3 3 3
[sample output]
27
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n,a[4][100005]={0};
int j,i,k,sum=0;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(j=0;j<3;j++)
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
scanf("%d",&a[j][i]);
// pai xu
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
for(j=0;j<n;j++)
if(a[1][j]<a[2][i])
{
for(k=0;k<n;k++)
if(a[0][k]>=a[1][j])
break;
sum+=k;
}
printf("%d",sum);
return 0;
}
7. Spiral polyline
Title: spiral polyline
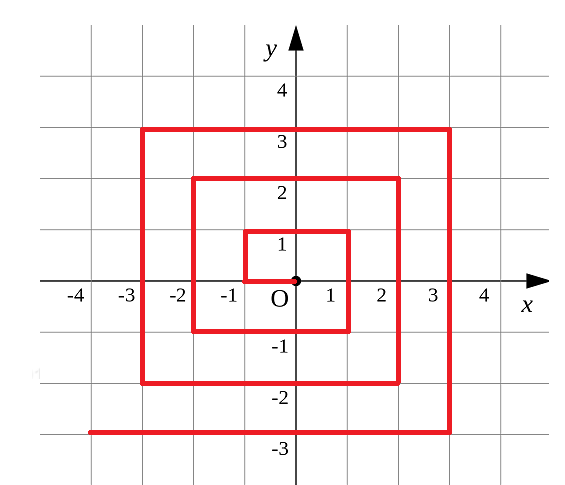
As shown in Figure P1 The spiral polyline shown in PNG passes through all integral points on the plane exactly once.
For the whole point (X, Y), we define its distance from the origin. dis(X, Y) is the length of the spiral line segment from the origin to (X, Y).
For example, dis(0, 1)=3, dis(-2, -1)=9
Given the coordinates of the whole point (X, Y), can you calculate dis(X, Y)?
[input format]
X and Y
For 40% of data, - 1000 < = x, y < = 1000
For 70% of data, - 100000 < = x, y < = 100000
For 100% data, - 1000000000 < = x, y < = 1000000000
[output format]
Output dis(X, Y)
[sample input]
0 1
[sample output]
3
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a,b,x1=0,y1=0,x2=0,y2=0,s=0;
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
while(1)
{
printf("%d %d\n",x1,y1);
x1=y1-1;
if(y1==b&&(a>=x1&&a<=x2))
{
s+=(x2-a);
break;
}
s+=(x2-x1);
x2=x1;
printf("%d %d\n",x1,y1);
y1=-x1;
if(x1==a&&(b>=y2&&b<=y1))
{
s+=(b-y2);
break;
}
s+=(y1-y2);
y2=y1;
printf("%d %d\n",x1,y1);
x1=y1;
if(y1==b&&(a>=x2&&a<=x1))
{
s+=(a-x2);
break;
}
s+=(x1-x2);
x2=x1;
printf("%d %d\n",x1,y1);
y1=-x1;
if(x1==a&&(b>=y1&&b<=y2))
{
s+=(y2-b);
break;
}
s+=(y2-y1);
y2=y1;
//break;
}
printf("%d",s);
return 0;
}
8. Log statistics
Title: log statistics
Xiao Ming maintains a programmer forum. Now he has collected a "like" log with N lines. The format of each line is:
ts id
Indicates that the post with id number at ts time receives a "like".
Now Xiao Ming wants to count which posts used to be "hot posts". If a post has received no less than K likes in any time period of D, Xiaoming thinks that the post was once a "hot post".
Specifically, if there is a time when t satisfies that the post receives no less than K likes during the period of [T, T+D) (note that the left closed and right open interval), the post was once a "hot post".
Given the log, please help Xiao Ming count all the post numbers that were once "hot posts".
[input format]
The first line contains three integers N, D, and K.
Each of the following N lines contains two integers ts and id.
For 50% of the data, 1 < = k < = n < = 1000
For 100% data, 1 < = k < = n < = 100000 0 < = TS < = 100000 0 < = ID < = 100000
[output format]
Output the hot post id from small to large. One line per id.
[input example]
7 10 2
0 1
0 10
10 10
10 1
9 1
100 3
100 3
[output example]
1
3
#include<stdio.h>
void sort(int (*a)[10],int n)
{
int i,j;
for(j=n-1;j>0;j--)
for(i=0;i<j;i++)
{
if(a[i][1]>a[i+1][1])
{
a[i][1]^=a[i+1][1];
a[i+1][1]^=a[i][1];
a[i][1]^=a[i+1][1];
a[i][0]^=a[i+1][0];
a[i+1][0]^=a[i][0];
a[i][0]^=a[i+1][0];
}
}
}
int main()
{
freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
int n,d,k;
int a[10][10]={0},b[20]={0};
int i,j=0;
scanf("%d%d%d",&n,&d,&k);
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&a[i][0],&a[i][1]);
}
sort(a,n);
for(i=0;i<n-1;i++)
printf("%d %d\n",a[i][0],a[i][1]);
for(i=0;i<n-1;i++)
{
if(a[i][1]==a[i+1][1])
{
if(abs(a[i][0]-a[i+1][0])<k)
printf("%d\n",a[i][1]);
}
}
fclose(stdin);
return 0;
}
9. Global warming
Title: global warming
You have a NxN pixel photo of a sea area, "." Indicates sea, "#" indicates land, as follows:
.......
.##....
.##....
....##.
...####.
...###.
.......
Among them, a piece of land connected in the four directions of "up, down, left and right" constitutes an island. For example, there are two islands in the figure above.
As the sea level rises due to global warming, scientists predict that a pixel of the edge of the island will be submerged by the sea in the next few decades. Specifically, if a land pixel is adjacent to the ocean (there is an ocean in the four adjacent pixels above, below, left and right), it will be submerged.
For example, the sea area in the above figure will look like the following in the future:
.......
.......
.......
.......
....#...
.......
.......
Please calculate: according to the prediction of scientists, how many islands in the picture will be completely submerged.
[input format]
The first line contains an integer n. (1 <= N <= 1000)
The following n rows and N columns represent a sea area photo.
The picture ensures that the pixels in row 1, column 1, row N and column n are oceans.
[output format]
An integer represents the answer.
[input example]
7
.......
.##....
.##....
....##.
...####.
...###.
.......
[output example]
1
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
int mp[110][110];
int ans[11000];
bool vis[110][110];
void dfs(int x,int y,int k)
{
if(mp[x][y]=='.')
return;
if(vis[x][y])
return;
vis[x][y]=1;
if(mp[x-1][y]=='#'&&mp[x+1][y]=='#'&&mp[x][y-1]=='#'&&mp[x][y+1]=='#')
ans[k]++;
dfs(x+1,y,k);
dfs(x-1,y,k);
dfs(x,y-1,k);
dfs(x,y+1,k);
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
getchar();
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
scanf("%c",&mp[i][j]);
}
int len=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
if(mp[i][j]=='#'&&!vis[i][j])
{
dfs(i,j,len);
len++;
}
}
}
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
if(ans[i]==0)
sum++;
printf("%d\n",sum);
return 0;
}
10. Maximum product
Title: maximum product
Give N integers A1, A2,... AN. Please choose K numbers from them to maximize their product.
####Please find the maximum product. Since the product may exceed the integer range, you only need to output the remainder of the product divided by 100000009.
####Note that if x < 0, we define that the remainder of X divided by 100000009 is the remainder of negative (- X) divided by 100000009.
####Namely: 0 - ((0-x)% 100000009)
[input format]
The first line contains two integers N and K.
The following N lines each contain an integer Ai.
For 40% of the data, 1 < = k < = n < = 100
For 60% of the data, 1 < = k < = 1000
For 100% data, 1 < = k < = n < = 100000 - 100000 < = AI < = 100000
[output format]
An integer representing the answer.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
[input example]
5 3
-100000
-10000
2
100000
10000
[output example]
999100009
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Another example:
[input example]
5 3
-100000
-100000
-2
-100000
-100000
[output example]
-999999829
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
long long a[100005], dp[2][100005];
int main()
{
int n, k;
cin >> n >> k;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
cin >> a[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++){
int s = (i - 1) % 2, t = i % 2;
if (i == 0){
for (int j = i; j < n;j++)
if (j == 0){
dp[0][j] = a[j];
}
else {
if (dp[0][j - 1] > a[j])
dp[0][j] = dp[0][j - 1];
else dp[0][j] = a[j];
}
}
else {
for (int j = i; j < n; j++){
if (i == j)dp[t][j] = (dp[s][j - 1] * a[j]) % 1000000009;
else {
if (dp[t][j - 1]>a[j] * dp[s][j - 1])
dp[t][j] = dp[t][j - 1];
else dp[t][j] = (a[j] * dp[s][j - 1]) % 1000000009;
}
}
}
}
cout << dp[(k - 1) % 2][n - 1] << endl;
return 0;
}