For 3.2 Data query - SELECT (single table query, join query, nested query, set query, multi table query) Learning notes;
0. Preface
- This article is a note on the database query SELECT part edited by Mr. Wang Shan in introduction to database system, which adopts SQL Sever database.
- All examples in this article will have screenshots of the results for verification.
- The results in the book may be slightly different from those on the machine. It may be the problem of database version or software display, or the textbook needs to be upgraded.
1. Mind map
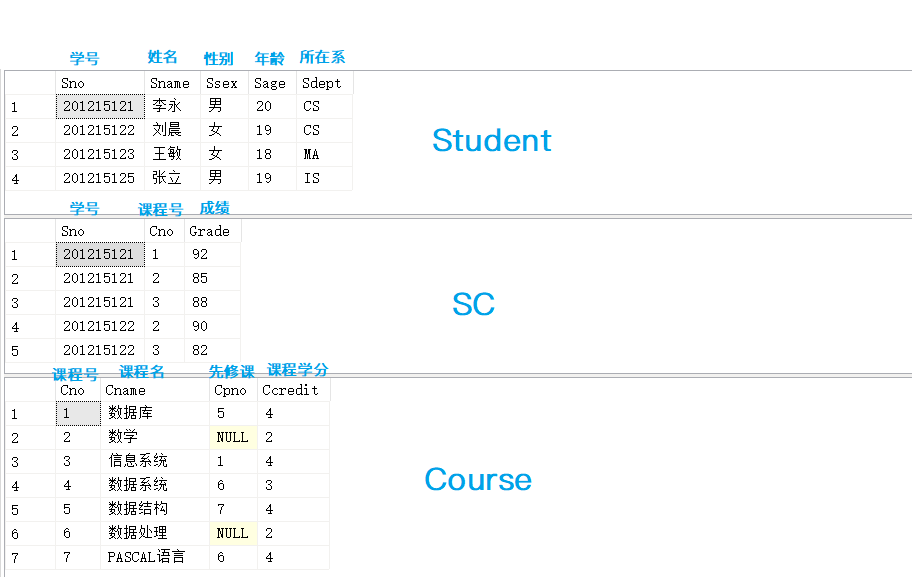
2. Data and structure of student / SC / course table
- This article focuses on these three tables.
3. General format of select statement
Let's first understand the format of SELECT and the location of keywords as a whole.
SELECT [ALL|DISTINCT] <Target list expression> [alias] [ ,<Target list expression> [alias]] ... FROM <Table name or view name> [alias] [ ,<Table name or view name> [alias]] ... [WHERE <Conditional expression>] [GROUP BY<Column name 1> [HAVING <Conditional expression>]] [ORDER BY <Column name 2> [ASC|DESC]
4. Single table query
(1) Select several columns in the table
① Query specified column
- Query specified column
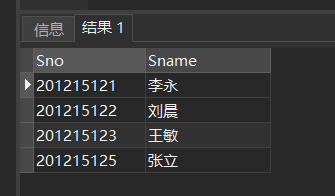
[example 1] query the student number and name of all students.
SELECT Sno,Sname FROM Student;
[example 2] query the name, student number and Department of all students.
SELECT Sname,Sno,Sdept FROM Student;
② Query all columns
- SELECT all attribute columns: list all column names after the SELECT keyword, and specify < target list expression > as*
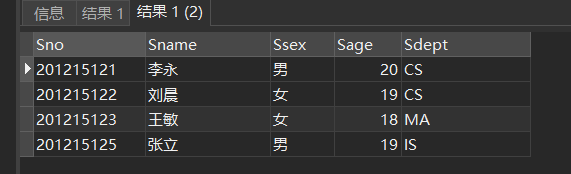
[example 3] query the detailed records of all students.
SELECT Sno,Sname,Ssex,Sage,Sdept FROM Student; //Two ways SELECT *FROM Student;
③ Query calculated values
- The < target list expression > of the SELECT clause can be:
Arithmetic expression
string constant
function
Column alias
❶ arithmetic expression
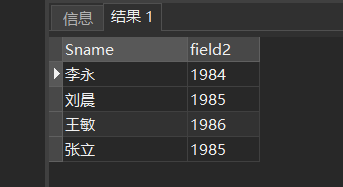
[example 4] check the names of all students and their year of birth. It is assumed that the current year is 2004. (before 2004)
SELECT Sname,2004-Sage FROM Student;
❷ string constants and functions
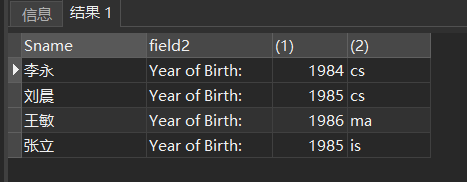
[example 5] query the names, year of birth and all departments of all students. It is required to use lowercase letters to represent all department names. Here, it is assumed that the current year is 2004.
SELECT Sname,'Year of Birth: ', 2004-Sage, LOWER(Sdept) FROM Student;
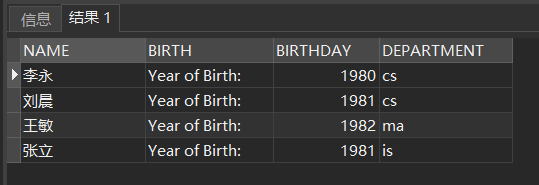
❸ use the column alias to change the column title of the query result
SELECT Sname NAME,'Year of Birth: ' BIRTH, 2000-Sage BIRTHDAY, LOWER(Sdept) DEPARTMENT FROM Student;
(2) Select several tuples (rows) in the table
① Key words DISTINCT Remove duplicate rows from the table
- If the DISTINCT keyword is not specified, it defaults to ALL
SELECT Sno FROM SC; /*Equivalent to:*/ SELECT ALL Sno FROM SC;
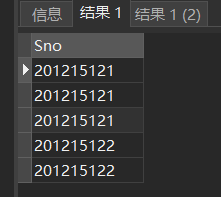
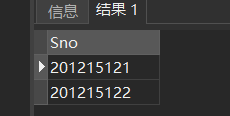
[example 6] query the student number of the elective course. Specify the DISTINCT keyword to remove duplicate rows in the table
SELECT DISTINCT Sno FROM SC;
② Query tuples (rows) that meet the criteria
- Common query criteria
| query criteria | predicate |
| compare | =,>,<,>=,<=,!=,<>,!>,!<; NOT + the above comparison operators |
| Determine scope | BETWEEN AND,NOT BETWEEN AND |
| Determine set | IN,NOT IN |
| Character matching | LIKE,NOT LIKE |
| Null value | IS NULL,IS NOT NULL |
| Multiple conditions (logical operation) | AND,OR,NOT |
❶ compare size
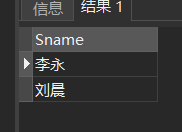
[Example 7] check the list of all students in the computer science department.
SELECT Sname FROM Student WHERE Sdept='CS';
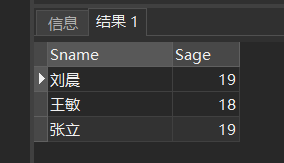
[example 8] query the names and ages of all students under the age of 20.
SELECT Sname,Sage FROM Student WHERE Sage < 20;
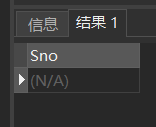
[Example 9] query the student number of students who fail in the examination.
SELECT DISTINCT Sno FROM SC WHERE Grade<60;
❷ determine the scope
Predicate:
- BETWEEN ... AND ...
- NOT BETWEEN ... AND ...
[example 10] query the information of students aged between 20 and 23 (including 20 and 23)
SELECT Sname,Sdept,Sage FROM Student WHERE Sage BETWEEN 20 AND 23;
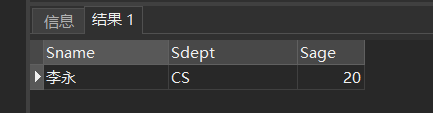
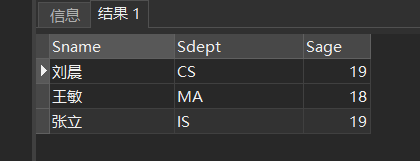
[example 11] query the name, department and age of students who are not between 20 and 23 years old
SELECT Sname,Sdept,Sage FROM Student WHERE Sage NOT BETWEEN 20 AND 23;
❸ determination set
Predicate:
- In < value table >,
- Not in < value table >
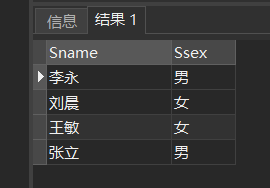
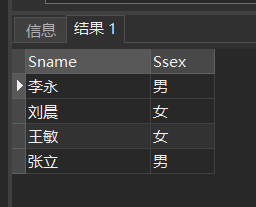
[example 12] query the names and genders of students in the Department of information (IS), the Department of Mathematics (MA) and the Department of Computer Science (CS).
SELECT Sname,Ssex FROM Student WHERE Sdept IN ( 'IS','MA','CS' );
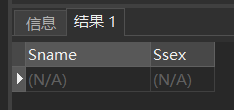
[example 13] query the name and gender of students who are neither information department, mathematics department nor computer science department.
SELECT Sname,Ssex FROM Student WHERE Sdept NOT IN ( 'IS','MA','CS' );
❹ character matching
Predicate:
- [NOT] LIKE '< match string >' [ESCAPE '< ESCAPE character >']
The matching string is a fixed string
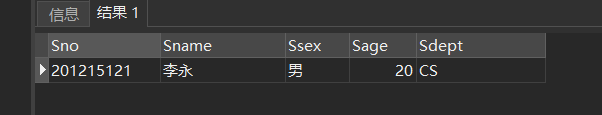
[example 14] query the details of students with student number 201215121.
SELECT * FROM Student WHERE Sno LIKE '201215121'; /*Equivalent to:*/ SELECT * FROM Student WHERE Sno = '201215121';
The matching string is a string with wildcards
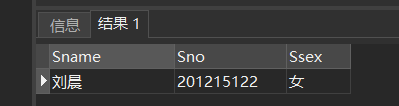
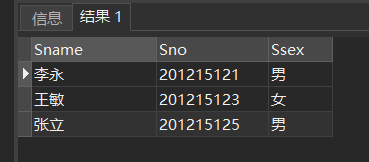
[example 15] query the name, student number and gender of all students surnamed Liu. (% means several digits, and means one digit)
SELECT Sname,Sno,Ssex FROM Student WHERE Sname LIKE 'Liu%';
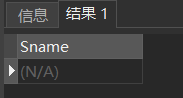
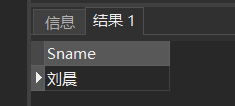
[example 16] query the name of a student whose last name is "Ouyang" and whose full name is three Chinese characters.
SELECT Sname FROM Student WHERE Sname LIKE 'Ouyang_';
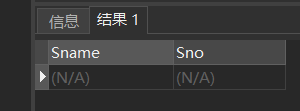
[example 17] query the name and student number of the student whose second word in the name is "Yang".
SELECT Sname,Sno FROM Student WHERE Sname LIKE '_Yang%';
[example 18] query the names of all students not surnamed Liu.
SELECT Sname,Sno,Ssex FROM Student WHERE Sname NOT LIKE 'Liu%';
❺ use escape character '' to escape wildcard characters into ordinary characters
- ESCAPE '\' indicates that "\" is an ESCAPE character
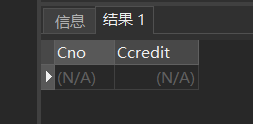
[example 19] query DB_ The course number and credits of the design course.
SELECT Cno,Ccredit FROM Course WHERE Cname LIKE 'DB\_Design' ESCAPE '\';
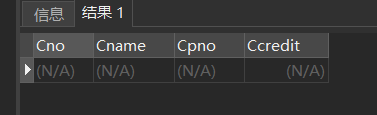
[example 20] query with "DB_" Details of courses with i as the penultimate character at the beginning.
SELECT * FROM Course WHERE Cname LIKE 'DB\_%i_ _' ESCAPE '\';
❻ queries involving null values
Predicate:
- IS NULL
- IS NOT NULL
- "IS" cannot be replaced by "="
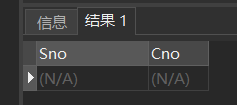
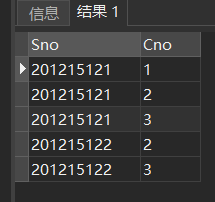
[example 21] some students did not take the exam after taking elective courses, so they had course selection records, but did not get test results. Query the student number and corresponding course number of students with missing grades.
SELECT Sno,Cno FROM SC WHERE Grade IS NULL;
[example 22] check the student number and course number of all students with grades.
SELECT Sno,Cno FROM SC WHERE Grade IS NOT NULL;
❼ multiple criteria query
Logical operators:
- AND and OR to join multiple query criteria
- AND takes precedence over OR
- You can change the priority with parentheses
Can be used to implement a variety of other predicates
- [NOT] IN
- [NOT] BETWEEN ... AND ...
[example 23] query the names of students under the age of 20 in the computer department
SELECT Sname FROM Student WHERE Sdept= 'CS' AND Sage<20;
Rewrite [example 12] to query the names and gender of students in the Department of information (IS), the Department of Mathematics (MA) and the Department of Computer Science (CS).
SELECT Sname,Ssex FROM Student WHERE Sdept IN ( 'IS','MA','CS' ); /*Can be rewritten as:*/ SELECT Sname,Ssex FROM Student WHERE Sdept= 'IS' OR Sdept= 'MA' OR Sdept= 'CS';
(3) ORDER BY clause
ORDER BY clause