react source code analysis 10 Commit phase
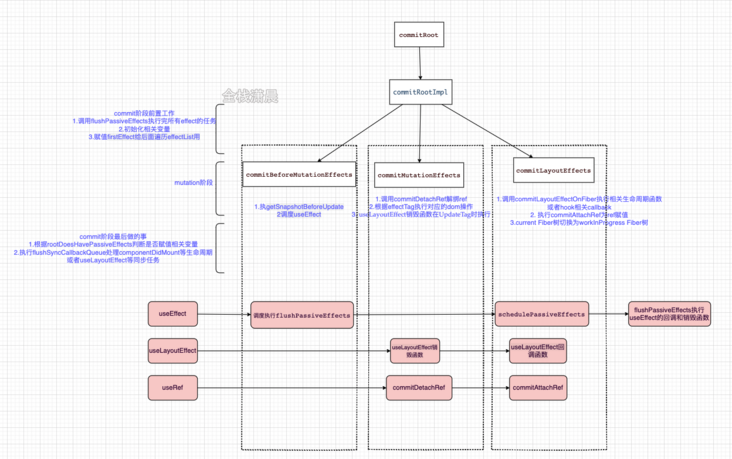
commitRoot(root) will be called at the end of the render phase; Enter the commit phase, where root refers to fiberRoot, and then traverse the effectList generated in the render phase. The Fiber node on the effectList saves the corresponding props changes. After that, it will traverse the effectList to perform the corresponding dom operations and life cycle, hooks callback or destroy functions. What each function does is as follows
The commitRootImpl function is actually scheduled in the commitRoot function
//ReactFiberWorkLoop.old.js
function commitRoot(root) {
var renderPriorityLevel = getCurrentPriorityLevel();
runWithPriority$1(ImmediatePriority$1, commitRootImpl.bind(null, root, renderPriorityLevel));
return null;
}The commitRootImpl function is mainly divided into three parts:
Pre work in commit phase
- Call flushpassive effects to complete the task of all effects
- Initialize related variables
Assign firstEffect to the following traversal of the effectList
//ReactFiberWorkLoop.old.js do { // Call flushpassive effects to complete the task of all effects flushPassiveEffects(); } while (rootWithPendingPassiveEffects !== null); //... // The reset variable finishedWork refers to rooFiber root.finishedWork = null; //Reset priority root.finishedLanes = NoLanes; // Scheduler callback function reset root.callbackNode = null; root.callbackId = NoLanes; // Reset global variables if (root === workInProgressRoot) { workInProgressRoot = null; workInProgress = null; workInProgressRootRenderLanes = NoLanes; } else { } //rootFiber may have new side effects and add it to effectLis let firstEffect; if (finishedWork.effectTag > PerformedWork) { if (finishedWork.lastEffect !== null) { finishedWork.lastEffect.nextEffect = finishedWork; firstEffect = finishedWork.firstEffect; } else { firstEffect = finishedWork; } } else { firstEffect = finishedWork.firstEffect; }
mutation stage
Traverse the effectList and execute three methods, commitBeforeMutationEffects, commitMutationEffects and commitLayoutEffects, respectively, to execute the corresponding dom operation and life cycle
When introducing the dual cache Fiber tree, after building the workInProgress Fiber tree, we will point the current of the fiberRoot to the workInProgress Fiber to make the workInProgress Fiber current. This step occurs after the commitMutationEffects function is executed and before commitLayoutEffects, because componentWillUnmount occurs in the commitMutationEffects function, At this time, you can also get the previous Update, and componentDidMount and componentDidUpdate will be executed in commitLayoutEffects. At this time, you can get the updated real dom
function commitRootImpl(root, renderPriorityLevel) { //... do { //... commitBeforeMutationEffects(); } while (nextEffect !== null); do { //... commitMutationEffects(root, renderPriorityLevel);//commitMutationEffects } while (nextEffect !== null); root.current = finishedWork;//Switch current Fiber tree do { //... commitLayoutEffects(root, lanes);//commitLayoutEffects } while (nextEffect !== null); //... }
After mutation
- Assign relevant variables according to rootdoeshavepassive effects
Execute flushSyncCallbackQueue to handle life cycles such as componentDidMount or synchronization tasks such as uselayouteeffect
const rootDidHavePassiveEffects = rootDoesHavePassiveEffects; // Assign relevant variables according to rootdoeshavepassive effects if (rootDoesHavePassiveEffects) { rootDoesHavePassiveEffects = false; rootWithPendingPassiveEffects = root; pendingPassiveEffectsLanes = lanes; pendingPassiveEffectsRenderPriority = renderPriorityLevel; } else {} //... // Ensure scheduled ensureRootIsScheduled(root, now()); // ... // Execute flushSyncCallbackQueue to handle life cycles such as componentDidMount or synchronization tasks such as uselayouteeffect flushSyncCallbackQueue(); return null;
Now let's look at what the three functions in the mutation phase do respectively
commitBeforeMutationEffects
This function mainly does the following two thingsExecute getSnapshotBeforeUpdate
In the source code commitBeforeMutationEffectOnFiber The corresponding function is commitBeforeMutationLifeCycles Called in this function getSnapshotBeforeUpdate,Now we know getSnapshotBeforeUpdate Yes mutation In phase commitBeforeMutationEffect Function, and commit The phases are synchronized, so getSnapshotBeforeUpdate Also execute synchronously
function commitBeforeMutationLifeCycles( current: Fiber | null, finishedWork: Fiber, ): void { switch (finishedWork.tag) { //... case ClassComponent: { if const instance = finishedWork.stateNode; const snapshot = instance.getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(//getSnapshotBeforeUpdate finishedWork.elementType === finishedWork.type ? prevProps : resolveDefaultProps(finishedWork.type, prevProps), prevState, ); } }
Scheduling useEffect
In the flushPassiveEffects function, flushPassiveEffectsImpl is called to traverse pendingPassiveHookEffectsUnmount and pendingPassiveHookEffectsMount, and the corresponding effect callbacks and destruct functions are executed. These two arrays are assigned in commitLayoutEffects function (which will be mentioned later). effectList is assigned to rootWithPendingPassiveEffects after mutation. Then scheduleCallback schedules the execution of flushpassive effects
function flushPassiveEffectsImpl() { if (rootWithPendingPassiveEffects === null) {//After mutation, it becomes root return false; } const unmountEffects = pendingPassiveHookEffectsUnmount; pendingPassiveHookEffectsUnmount = [];//Callback function of useEffect for (let i = 0; i < unmountEffects.length; i += 2) { const effect = ((unmountEffects[i]: any): HookEffect); //... const destroy = effect.destroy; destroy(); } const mountEffects = pendingPassiveHookEffectsMount;//Destruction function of useEffect pendingPassiveHookEffectsMount = []; for (let i = 0; i < mountEffects.length; i += 2) { const effect = ((unmountEffects[i]: any): HookEffect); //... const create = effect.create; effect.destroy = create(); } }
componentDidUpdate or componentDidMount Will be commit Phase synchronous execution(This will be discussed later),and useEffect Will be commit Stage asynchronous scheduling, so it is suitable for the processing of side effects such as data requests
> Attention, and in render Phasic fiber node I'll call Placement Like the label, useEffect or useLayoutEffect There are also corresponding effect Tag,Corresponding in the source code export const Passive = /* */ 0b0000000001000000000;
```js
function commitBeforeMutationEffects() {
while (nextEffect !== null) {
const current = nextEffect.alternate;
const effectTag = nextEffect.effectTag;
// getSnapshotBeforeUpdate is executed in the commitBeforeMutationEffectOnFiber function
if ((effectTag & Snapshot) !== NoEffect) {
commitBeforeMutationEffectOnFiber(current, nextEffect);
}
// scheduleCallback scheduleuseeffect
if ((effectTag & Passive) !== NoEffect) {
if (!rootDoesHavePassiveEffects) {
rootDoesHavePassiveEffects = true;
scheduleCallback(NormalSchedulerPriority, () => {
flushPassiveEffects();
return null;
});
}
}
nextEffect = nextEffect.nextEffect;//Traverse the effectList
}
}
```
commitMutationEffects
commitMutationEffects mainly does the following things- Call commitDetachRef to unbind ref (explained in hook in Chapter 11)
- Perform the corresponding dom operation according to the effectTag
The uselayouteeffect destroy function is executed at UpdateTag
function commitMutationEffects(root: FiberRoot, renderPriorityLevel) { //Traverse the effectList while (nextEffect !== null) { const effectTag = nextEffect.effectTag; // Call commitDetachRef to unbind ref if (effectTag & Ref) { const current = nextEffect.alternate; if (current !== null) { commitDetachRef(current); } } // Perform the corresponding dom operation according to the effectTag const primaryEffectTag = effectTag & (Placement | Update | Deletion | Hydrating); switch (primaryEffectTag) { // Insert dom case Placement: { commitPlacement(nextEffect); nextEffect.effectTag &= ~Placement; break; } // Insert update dom case PlacementAndUpdate: { // insert commitPlacement(nextEffect); nextEffect.effectTag &= ~Placement; // to update const current = nextEffect.alternate; commitWork(current, nextEffect); break; } //... // Update dom case Update: { const current = nextEffect.alternate; commitWork(current, nextEffect); break; } // Delete dom case Deletion: { commitDeletion(root, nextEffect, renderPriorityLevel); break; } } nextEffect = nextEffect.nextEffect; } }
Now let's look at the operation dom These functions
**commitPlacement Insert node:**
The simplified code is very clear. Find the nearest node parent Node and sibling node, and then according to isContainer To determine whether it is inserted before or after the sibling node append reach parent After node
```js
unction commitPlacement(finishedWork: Fiber): void {
//...
const parentFiber = getHostParentFiber(finishedWork);//Find the nearest parent
let parent;
let isContainer;
const parentStateNode = parentFiber.stateNode;
switch (parentFiber.tag) {
case HostComponent:
parent = parentStateNode;
isContainer = false;
break;
//...
}
const before = getHostSibling(finishedWork);//Find sibling node
if (isContainer) {
insertOrAppendPlacementNodeIntoContainer(finishedWork, before, parent);
} else {
insertOrAppendPlacementNode(finishedWork, before, parent);
}
}
```
**commitWork Update node:**
You can see in the simplified source code
If fiber of tag yes SimpleMemoComponent Will call commitHookEffectListUnmount Execute the corresponding hook You can see that the parameters passed in are HookLayout | HookHasEffect,That is, execution useLayoutEffect Destroy function for.
If it is HostComponent,Then call commitUpdate,commitUpdate Finally, it will call updateDOMProperties Processing correspondence Update of dom operation
```js
function commitWork(current: Fiber | null, finishedWork: Fiber): void {
if (!supportsMutation) {
switch (finishedWork.tag) {
//...
case SimpleMemoComponent: {
commitHookEffectListUnmount(HookLayout | HookHasEffect, finishedWork);
}
//...
}
}
switch (finishedWork.tag) {
//...
case HostComponent: {
//...
commitUpdate(
instance,
updatePayload,
type,
oldProps,
newProps,
finishedWork,
);
}
return;
}
}
```
```js
function updateDOMProperties(
domElement: Element,
updatePayload: Array<any>,
wasCustomComponentTag: boolean,
isCustomComponentTag: boolean,
): void {
// TODO: Handle wasCustomComponentTag
for (let i = 0; i < updatePayload.length; i += 2) {
const propKey = updatePayload[i];
const propValue = updatePayload[i + 1];
if (propKey === STYLE) {
setValueForStyles(domElement, propValue);
} else if (propKey === DANGEROUSLY_SET_INNER_HTML) {
setInnerHTML(domElement, propValue);
} else if (propKey === CHILDREN) {
setTextContent(domElement, propValue);
} else {
setValueForProperty(domElement, propKey, propValue, isCustomComponentTag);
}
}
}
```
**commitDeletion Delete node:**
If it is ClassComponent Will execute componentWillUnmount,delete fiber,If it is FunctionComponent Will delete ref,And execute useEffect The specific destruction function can be viewed in the source code unmountHostComponents,commitNestedUnmounts,detachFiberMutation These functions
```js
function commitDeletion(
finishedRoot: FiberRoot,
current: Fiber,
renderPriorityLevel: ReactPriorityLevel,
): void {
if (supportsMutation) {
// Recursively delete all host nodes from the parent.
// Detach refs and call componentWillUnmount() on the whole subtree.
unmountHostComponents(finishedRoot, current, renderPriorityLevel);
} else {
// Detach refs and call componentWillUnmount() on the whole subtree.
commitNestedUnmounts(finishedRoot, current, renderPriorityLevel);
}
const alternate = current.alternate;
detachFiberMutation(current);
if (alternate !== null) {
detachFiberMutation(alternate);
}
}
```
commitLayoutEffects
After commitMutationEffects, all dom operations have been completed and the dom can be accessed. commitLayoutEffects mainly does- Call commitLayoutEffectOnFiber to execute related life cycle functions or hook related callback
- Execute committatchref to assign a value to ref
```js
function commitLayoutEffects(root: FiberRoot, committedLanes: Lanes) {
while (nextEffect !== null) {
const effectTag = nextEffect.effectTag;
// Call commitLayoutEffectOnFiber to execute lifecycle and hook
if (effectTag & (Update | Callback)) {
const current = nextEffect.alternate;
commitLayoutEffectOnFiber(root, current, nextEffect, committedLanes);
}
// ref assignment
if (effectTag & Ref) {
commitAttachRef(nextEffect);
}
nextEffect = nextEffect.nextEffect;
}
}
```
**commitLayoutEffectOnFiber:**
In the source code commitLayoutEffectOnFiber The alias for the function is commitLifeCycles,As you can see in the simplified code, commitLifeCycles Can judge fiber Type of, SimpleMemoComponent Will execute useLayoutEffect Callbacks, then scheduling useEffect,ClassComponent Will execute componentDidMount perhaps componentDidUpdate,this.setState The second parameter will also be executed, HostRoot Will execute ReactDOM.render The third parameter of the function, for example
```js
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.querySelector("#root"), function() {
console.log("root mount");
});
```
Now you know useLayoutEffect Yes commit Phase synchronization, useEffect Will be commit Phase asynchronous scheduling
```js
function commitLifeCycles(
finishedRoot: FiberRoot,
current: Fiber | null,
finishedWork: Fiber,
committedLanes: Lanes,
): void {
switch (finishedWork.tag) {
case SimpleMemoComponent: {
// This function calls the callback of useLayoutEffect
commitHookEffectListMount(HookLayout | HookHasEffect, finishedWork);
// push effect / / into pendingPassiveHookEffectsUnmount and pendingPassiveHookEffectsMount and schedule them
schedulePassiveEffects(finishedWork);
}
case ClassComponent: {
//Conditional judgment
instance.componentDidMount();
//Conditional judgment
instance.componentDidUpdate(//update is executed synchronously during layout
prevProps,
prevState,
instance.__reactInternalSnapshotBeforeUpdate,
);
}
case HostRoot: {
commitUpdateQueue(finishedWork, updateQueue, instance);//render third parameter
}
}
}
```
stay schedulePassiveEffects Zhonghuijiang useEffect Destruction and callback functions push reach pendingPassiveHookEffectsUnmount and pendingPassiveHookEffectsMount in
```js
function schedulePassiveEffects(finishedWork: Fiber) {
const updateQueue: FunctionComponentUpdateQueue | null = (finishedWork.updateQueue: any);
const lastEffect = updateQueue !== null ? updateQueue.lastEffect : null;
if (lastEffect !== null) {
const firstEffect = lastEffect.next;
let effect = firstEffect;
do {
const {next, tag} = effect;
if (
(tag & HookPassive) !== NoHookEffect &&
(tag & HookHasEffect) !== NoHookEffect
) {
//Push the destruction function of useeffect and add scheduling
enqueuePendingPassiveHookEffectUnmount(finishedWork, effect);
//Push the callback function of useeffect and add it to the schedule
enqueuePendingPassiveHookEffectMount(finishedWork, effect);
}
effect = next;
} while (effect !== firstEffect);
}
}
```
**commitAttachRef:**
commitAttacRef Will judge ref Type of, execution ref Or give ref.current assignment
```js
function commitAttachRef(finishedWork: Fiber) {
const ref = finishedWork.ref;
if (ref !== null) {
const instance = finishedWork.stateNode;
let instanceToUse;
switch (finishedWork.tag) {
case HostComponent:
instanceToUse = getPublicInstance(instance);
break;
default:
instanceToUse = instance;
}
if (typeof ref === "function") {
// Execute ref callback
ref(instanceToUse);
} else {
// If it is the type of value, it is assigned to ref.current
ref.current = instanceToUse;
}
}
}
```
Video Explanation (efficient learning): Enter learning
Previous articles:
1. Introduction and interview questions
3.react source code architecture
4. Source directory structure and debugging
6.legacy and concurrent mode entry functions