- Desktop development on Windows platform
- C++: MFC,Qt
- C#: WinForm,WPF
1. Printing method of debugging information:
MFC dialog based program, not dialog based program, can not print;
- Print to the output end;
- TRACE function: similar to printf in C language, you can only see the print information in DEBUG mode (F5 startup)
TRACE("age is %d\n", age); // age is 20
- AfxMessageBox function
int age = 10;
CString str;
str.Format(CString("age is %d"), age);
AfxMessageBox(str);
AfxMessageBox(CString("something wrong"));
- MessageBox function: it is only used in subclasses of CWnd and has more functions than AfxMessageBox
- WIN32 has MessageBox; AfxMessageBox is MFC encapsulated;
- DLG is inherited from CDialogEx; Inherited from CDialog; Inherited from CWnd;
- MB_ Yesnocell enables three keys; MB_ICONWARNING icon changed to warning
int age = 10;
CString str;
str.Format(CString("age is %d"), age);
MessageBox(str, CString("warning"), MB_YESNOCANCEL | MB_ICONWARNING);
- Customize log macro to simplify printing
- \Used to tell the macro that the next line also belongs to the macro;
- __ VA_ARGS__ As a multi parameter replacement;
#define log(fmt, ...) \ CString str; \ str.Format(CString(fmt), __VA_ARGS__); \ AfxMessageBox(str);
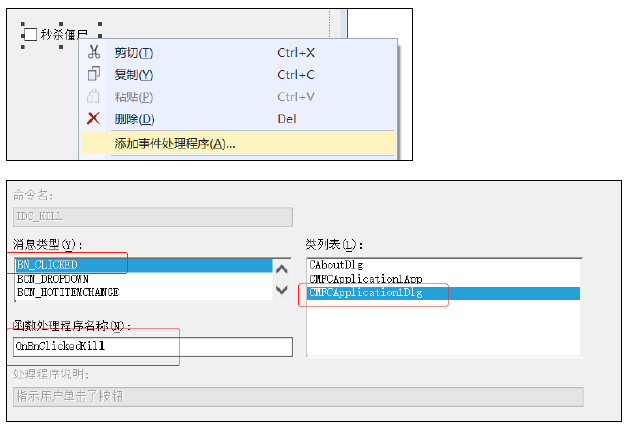
2. Event declaration and registration
- Binding event
- ON_ BN_ Click the clicked key to bind to the member function;
- The first parameter is the control ID; The macro is defined in the resource Defined in H
- The second parameter is: member function address; (the function name is the address, and the address character is the same)
BEGIN_MESSAGE_MAP(CPVZCheaterDlg, CDialogEx) ON_WM_SYSCOMMAND() ON_WM_PAINT() ON_WM_QUERYDRAGICON() ON_BN_CLICKED(IDC_COURSE, &CPVZCheaterDlg::OnBnClickedCourse) ON_BN_CLICKED(IDC_KILL, &CPVZCheaterDlg::OnBnClickedKill) ON_BN_CLICKED(IDC_SUN, &CPVZCheaterDlg::OnBnClickedSun) END_MESSAGE_MAP()
- Event handler function needs declaration + definition
- afx_ The MSG macro is used to identify that the function is used for event handling
- Automatic event registration – (you can also double-click the control directly)
- For keys and checkbox es; Or other controls can be used
3. Control use
- Binding member variables – manual
- Declare key member variable CButton m_bnKill;
- Via DDX_Control(pDX, IDC_KILL, m_bnKill); Bind the variable to the control ID;
- Bind member variables – automatic
- Right click on the control to add a variable;
- Modify the type and name of the member variable bound to the control;

- Status reading and modification of radio boxes
- Method 1
- IsDlgButtonChecked is used to judge whether the control is selected; CheckDlgButton is used to modify;
bool checked = IsDlgButtonChecked(IDC_KILL);
if (m_bnSun.GetCheck()) {
log("Tick");
CheckDlgButton(IDC_KILL,true);
} else {
log("Not checked");
}
- Method 2
- GetDlgItem(IDC_KILL); Returns the cwnd type. Use the subclass CButton to get it;
- Then call int CButton::GetCheck() const.
- void CButton::SetCheck(int nCheck) is used to modify
CButton* button = (CButton*)GetDlgItem(IDC_KILL); bool state = button->GetCheck(); button->SetCheck(true);
- Method 3
- CButton m_bnKill; Member variables through DDX_Control(pDX, IDC_KILL, m_bnKill); Bind to the control ID;
- Then call int CButton::GetCheck() const.
- void CButton::SetCheck(int nCheck) is used to modify
if (m_bnSun.GetCheck()) {
log("Tick");
m_bnSun.SetCheck(true);
} else {
log("Not checked");
}
4. Open URL
- (Uniform Resource Locator), which is the Uniform Resource Locator of WWW, refers to the network address.
- ShellExecute is a global function
ShellExecute(NULL,
CString("open"),
CString("https://ke.qq.com/course/336509"),
NULL, NULL,
SW_SHOWNORMAL);
//ShellExecuteW(
// _In_opt_ HWND hwnd,
// _In_opt_ LPCWSTR lpOperation,
// _In_ LPCWSTR lpFile,
// _In_opt_ LPCWSTR lpParameters,
// _In_opt_ LPCWSTR lpDirectory,
// _In_ INT nShowCmd)
5. Multithreading
- windows multithreading:
- Enable API CreateThread for multithreading; Return handle (ID, void * type); Threads are controlled by handles;
//HANDLE //WINAPI //CreateThread( // _In_opt_ LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpThreadAttributes, // _In_ SIZE_T dwStackSize, // _In_ LPTHREAD_START_ROUTINE lpStartAddress, // _In_opt_ __drv_aliasesMem LPVOID lpParameter, // _In_ DWORD dwCreationFlags, // _Out_opt_ LPDWORD lpThreadId //); m_monitorThread = CreateThread(NULL, NULL, monitorThreadFunc, NULL, NULL, NULL);
The type of function pointer passed is: return DWORD parameter LPVOID lpThreadParameter
typedef DWORD (WINAPI *PTHREAD_START_ROUTINE)(
LPVOID lpThreadParameter
);
- MFC multithreading:
- Enable API CreateThread for multithreading; Return handle (ID, void * type); Threads are controlled by handles;
//CWinThread* AFXAPI AfxBeginThread(AFX_THREADPROC pfnThreadProc, LPVOID pParam, // int nPriority = THREAD_PRIORITY_NORMAL, UINT nStackSize = 0, // DWORD dwCreateFlags = 0, LPSECURITY_ATTRIBUTES lpSecurityAttrs = NULL); AfxBeginThread(MyTimerProc, this);
The type of function pointer passed is: return DWORD parameter LPVOID lpThreadParameter
typedef DWORD (WINAPI *PTHREAD_START_ROUTINE)(
LPVOID lpThreadParameter
);
6. Necessary knowledge of Windows platform software cracking
- File format: PE file
- Assembly language: x86, x64 assembly
- Tool: Ollydbg / / machine code can be disassembled
- Windows API
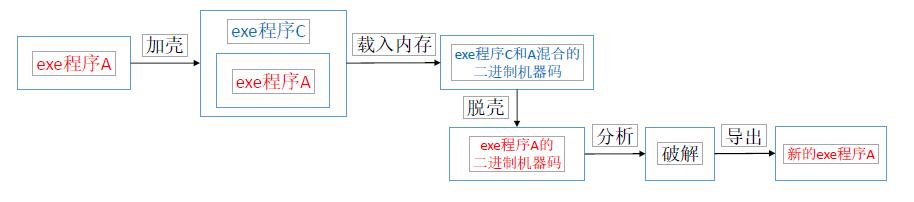
- The executable file under windows is in PE format
- Convert the exe format machine code into assembly; (tool: Ollydbg)
- Modify some instructions in the assembly or directly fill in nop; To meet their own requirements;
- Generate the modified code into exe, which becomes the broken code;
- Shelling and shelling
General software cracking ideas

Shelling and shelling
- The essence of plug-in
- There are two common plug-in functions; In fact, there is no essential difference between data and code. Both data and code are 0 and 1 in memory
- Modify the data in memory (Cheat Engine, which can be used to observe the memory occupation of the process)
- Modify code in memory
- In fact, they all modify a part of the memory space corresponding to the process;
- The memory address of the code segment is unchanged and relatively simple; Global variables and code side are unchanged in process memory
- The space in memory data will change unless it is a global variable; Difficult to realize;
- To change the memory:
Write a program to check the memory occupation, find the memory address to be changed, and fill it in;
- Modify code in memory:
- Find out which code modified the corresponding memory space, and then analyze this code to modify it;
- In fact, you can only change the memory by changing the code; The binary code to be loaded into memory can be changed. Instead of changing the binary code in exe
void CPVZCheaterDlg::OnBnClickedKill() {
if (m_bnKill.GetCheck()) { // need
BYTE data[] = {0xFF, 0x90, 0x90};
WriteMemory(data, sizeof(data), 0x00531310);
} else { // unwanted
BYTE data[] = {0x7c, 0x24, 0x20};
WriteMemory(data, sizeof(data), 0x00531310);
}
}
- Monitoring Games:
- Multi thread monitoring game// The multithreading section above explains;
- Monitoring window function: FindWindowW
//WINUSERAPI //HWND //WINAPI //FindWindowW( // _In_opt_ LPCWSTR lpClassName, // _In_opt_ LPCWSTR lpWindowName);
- Find the window name and class name (using spy + +)
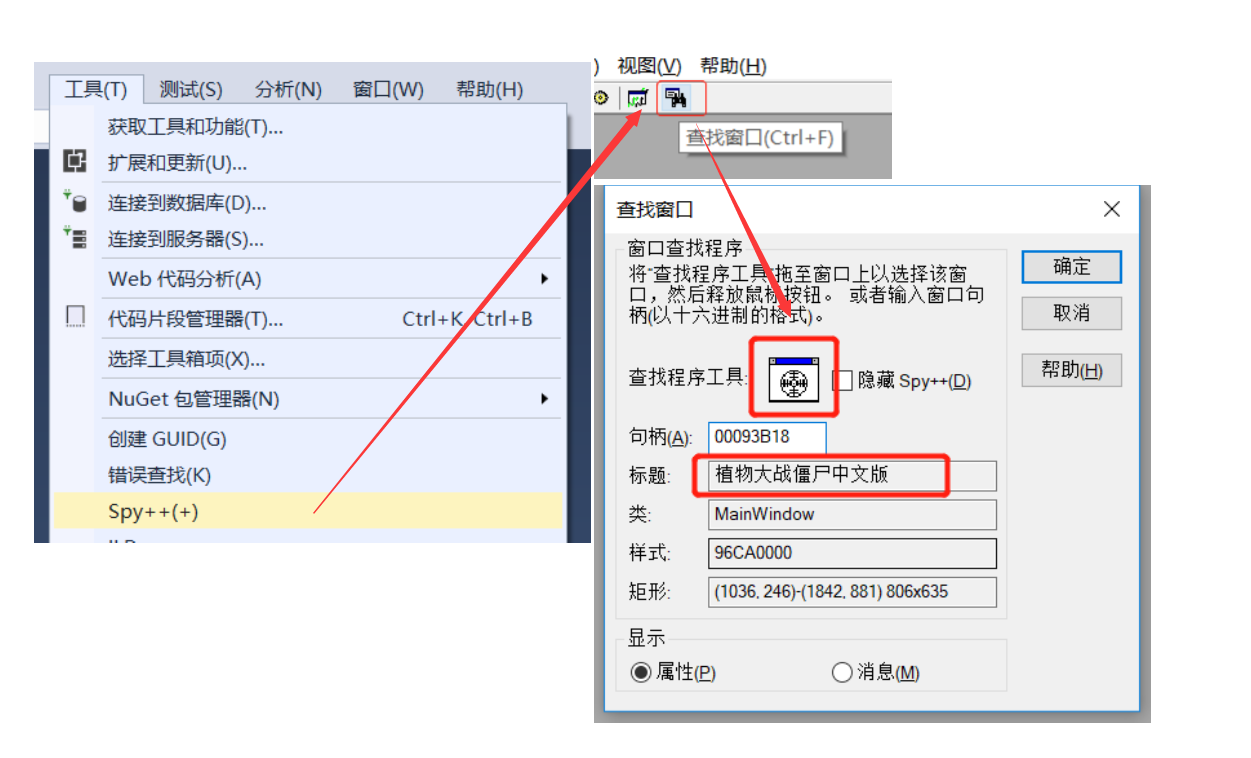
- g_dlg is a class pointer to which this is assigned during initialization;
- FindWindowW obtains the window handle HWND of the corresponding window through the window name and window class name
- SetCheck cancels the selection;
- EnableWindow enable space;
- GetWindowThreadProcessId finds the corresponding process ID through the window handle;
- OpenProcess obtains the handle of the process through the process ID; PROCESS_ALL_ACCESS is permission;
- WriteProcessMemory modifies the memory at the corresponding address through the process handle;
- ReadProcessMemory modifies the memory at the corresponding address through the process handle;
// TODO: add additional initialization code here // Create a sub thread to monitor the opening or closing of the game m_monitorThread = CreateThread(NULL, NULL, monitorThreadFunc, NULL, NULL, NULL);
// Thread used to monitor the game
DWORD monitorThreadFunc(LPVOID lpThreadParameter) {
while (1) {
// Get a handle to the plant vs zombie window
HWND windowHandle = FindWindow(CString("MainWindow"), CString("Plants vs zombies Chinese version"));
if (windowHandle == NULL) {
g_dlg->m_bnKill.SetCheck(FALSE);
g_dlg->m_bnSun.SetCheck(FALSE);
g_dlg->m_bnKill.EnableWindow(FALSE);
g_dlg->m_bnSun.EnableWindow(FALSE);
g_processHandle = NULL;
} else if (g_processHandle == NULL) {
g_dlg->m_bnKill.EnableWindow(TRUE);
g_dlg->m_bnSun.EnableWindow(TRUE);
// Get the process ID of plants vs Zombies
DWORD processPid;
GetWindowThreadProcessId(windowHandle, &processPid);
// Get the process handle of plant vs zombie
g_processHandle = OpenProcess(PROCESS_ALL_ACCESS, FALSE, processPid);
}
if (g_dlg->m_bnSun.GetCheck()) { // Need unlimited sunshine
DWORD value = 9990;
WriteMemory(&value, sizeof(value), 0x6A9EC0, 0x320, 0x8, 0x0, 0x8, 0x144, 0x2c, 0x5560, -1);
}
// Rest and sleep
Sleep(1000);
}
return NULL;
}
- Modify memory based on offset address
- ... As a variable parameter, the parameter passed ends with - 1;
// Memory modification (the following variable parameter is the address chain, which should end with - 1)
void WriteMemory(void *value, DWORD valueSize, ...) {
if (value == NULL || valueSize == 0 || g_processHandle == NULL) return;
DWORD tempValue = 0;
va_list addresses;
va_start(addresses, valueSize);
DWORD offset = 0;
DWORD lastAddress = 0;
while ((offset = va_arg(addresses, DWORD)) != -1) {
lastAddress = tempValue + offset;
::ReadProcessMemory(g_processHandle, (LPCVOID) lastAddress, &tempValue, sizeof(DWORD), NULL);
}
va_end(addresses);
::WriteProcessMemory(g_processHandle, (LPVOID) lastAddress, value, valueSize, NULL);
}