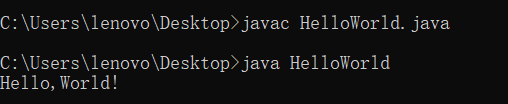
HelloWorld code block
public class HelloWorld{
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("Hello,World!");
}
}
notes
//Single-Line Comments
/*
multiline comment
*/
//Documentation Comments
/**
*
*/
Identifier, keyword
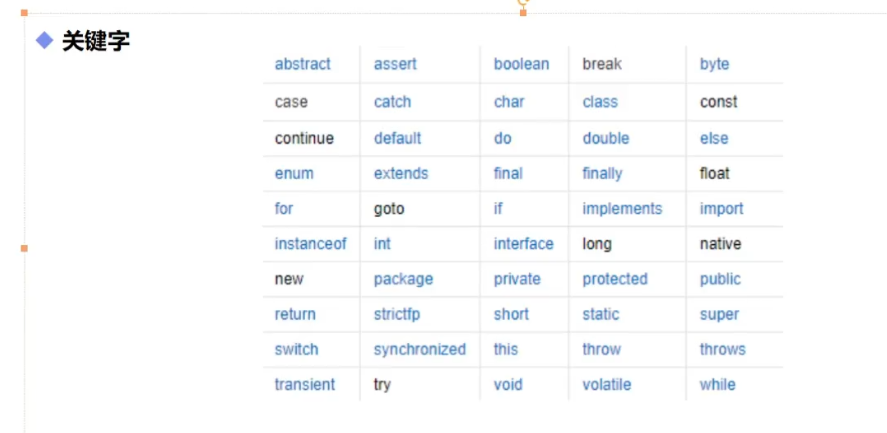
Identifier considerations
1. All identifiers are marked with (a-z) \ (a-z) \ ($) \ () start
2. After the initial letter, the above characters and numbers can be combined
3. Keyword cannot be used as method name and variable name
4. Case sensitive
5. Class name and variable name can be in Chinese
data type
Strongly typed language: it must be used according to strict specifications. All variables must be defined before they can be used. High security
There are two types of data types: basic type and reference type
Basic type
integer
-byte 1 byte
-short 2 bytes
-int 4 bytes
-long 8 bytes 1 byte = 8bit
Floating point type
-float 4-byte definition ends with f
-double 8 bytes
Character char
String - > reference type
boolean has only two values: true and false
reference type
- class
- Interface
- array
Development (interview)
- Integer extended binary 0b octal 0 decimal hexadecimal 0x
int i=10; int i1=0b10; int i2=010; int i3=0x10;
- Floating point extension
//How to show the floating-point expansion of banking business=================================
//BigDecimal math tool class
//====================================
//float finite discrete rounding error is approximately close to but not equal to
//double
//It is best to use floating point numbers for comparison
float d1 =0.1f;
double d2 = 1.0/10;
System.out.println(d1);
System.out.println(d2);
System.out.println(d1==d2); //false
float d3 = 123123123f;
float d4=d3+1;
System.out.println(d3==d4);//true
- Character class expansion
char c = 'a';
char c1='in';
System.out.println((int)c); //Forced conversion
System.out.println((int)c1);//Are all characters coded by nature or numbers
char c2='\u0061';
System.out.println(c2);
- Escape character \ t \n
- Boolean simplification code
Type conversion
- Force type conversion high - > low
int i =128;
byte b = (byte)i;//Memory overflow force conversion high to low
System.out.println(i);// 128
System.out.println(b);// -128
The data in the computer is stored in the form of complement.
-1 + (- 127) 1000 0001 + 1111 1111 = 1000 0000 is the complement of - 128
-128 there is no original code and inverse code. It is artificially specified that 10 million is the complement of - 128 (Indian A3)
- Automatic type conversion low - > High
- Attention
Memory overflow, precision loss, boolean type cannot be forcibly converted
System.out.println((int)45.2);// 45
System.out.println((int)-45.456f);// -45
char i1 = 'a';
int i2 = i1+1;
System.out.println(i2);// 98
System.out.println((char)i2);// b
===============================================================
//When the operands are large, pay attention to the removal problem
int money = 10_0000_0000;// 1 billion
int years =20;
int total = money*years;
System.out.println(total);//overflow
long total2=money*years;//The default is int type. There is a problem before conversion.
long total3=money*(long)years;// 2 billion
System.out.println(total3);
Variable, constant, scope
variable
public class Demo08 {
//Instance variables: subordinate objects
String name;
int age; //Default value
//boolean defaults to false
//Class variable
static double salary = 10000;
//main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Local variables; Variable value must be declared
int i = 10;
// example
Demo08 Demo08 = new Demo08();
System.out.println(Demo08.age);//0
System.out.println(Demo08.name);//null
System.out.println(salary);//2500 direct output
}
//Other methods
public void add(){
}
}
constant
Cannot be changed after initialization
public class Demo09 {
//Modifiers are not front and rear
static final double PI =3.14;
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(PI);
}
}
Scope
- Class variable
- Instance variable
- local variable
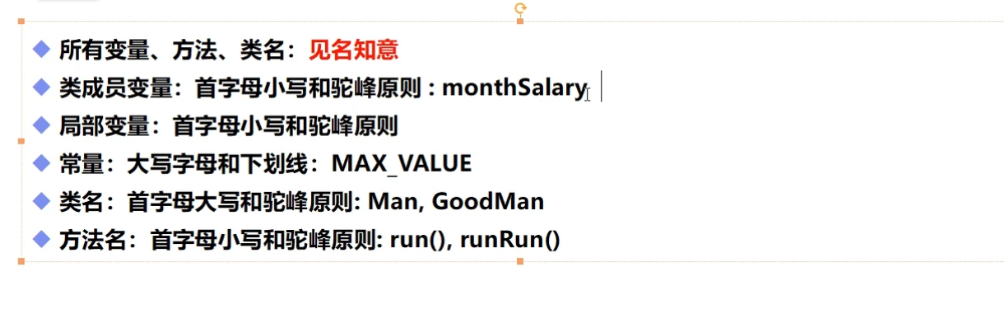
Naming conventions
Basic operator
Operator type
- Arithmetic operators: + - * /% + –
- Assignment operator:=
- Relational operator: > < = > = < ==
- Logical operator: & & |!
- Bit operation: & ^ ~ < > > > > and or_ Non shift left shift right
boolean b = true;
System.out.println("a && b:" + (a&&b));//fasle
System.out.println("a || b:" + (a||b));//true
System.out.println("!(a && b):" + !(a&&b));//true
- Conditional operator:?:
++ –
int a =3;
int b=a++;
int c=++a;
System.out.println(a);//5
System.out.println(b);//3
System.out.println(c);//5
Short circuit operation&&
int c=3;
boolean d = (c<3)&&(c++>2);
System.out.println(b);//false
System.out.println(c);//3
Efficient multiplication and division < < > >
System.out.println(2<<3);//16
System.out.println(15>>1);//7
Ternary operator?:
- String connection
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
System.out.println("s"+a+b);//s1020
System.out.println(a+b+"s");//30s
- ?:
int score = 85;
String type = (score>=85) ? "excellent" : "other";
System.out.println(type);//excellent
#Package mechanism
The essence of a package is a folder
Generally, the inversion of the company's domain name is used to protect life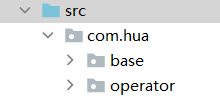

Standard development - > Alibaba Development Manual
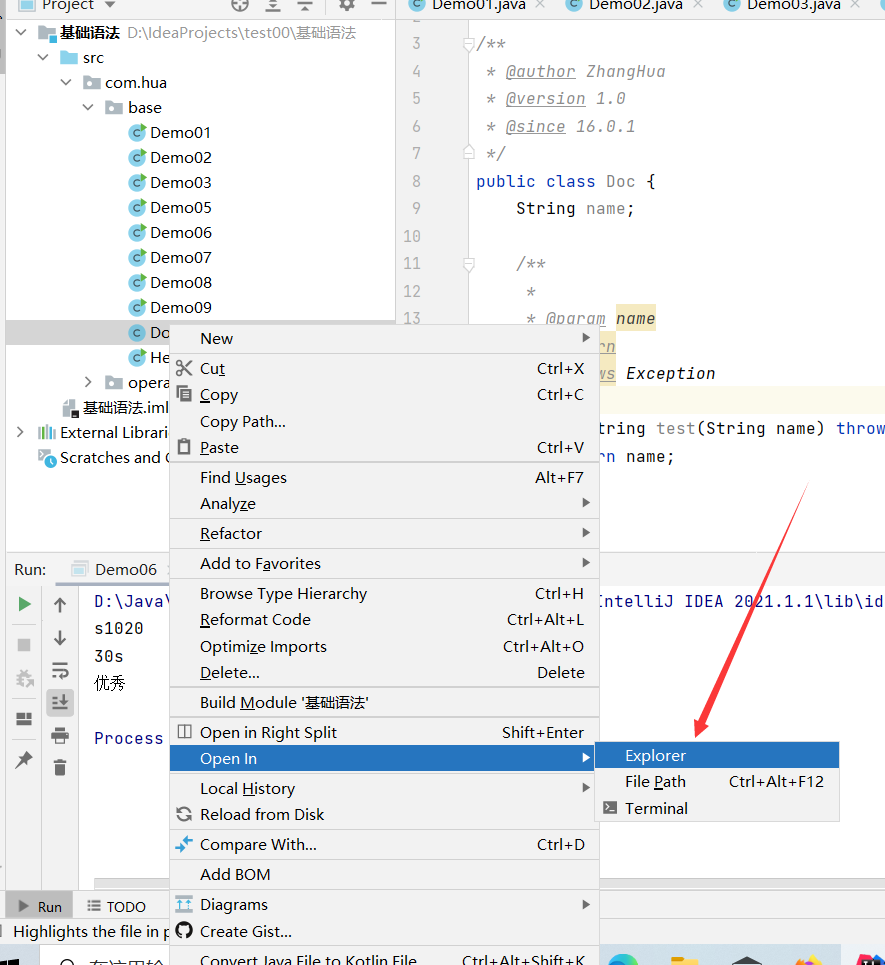
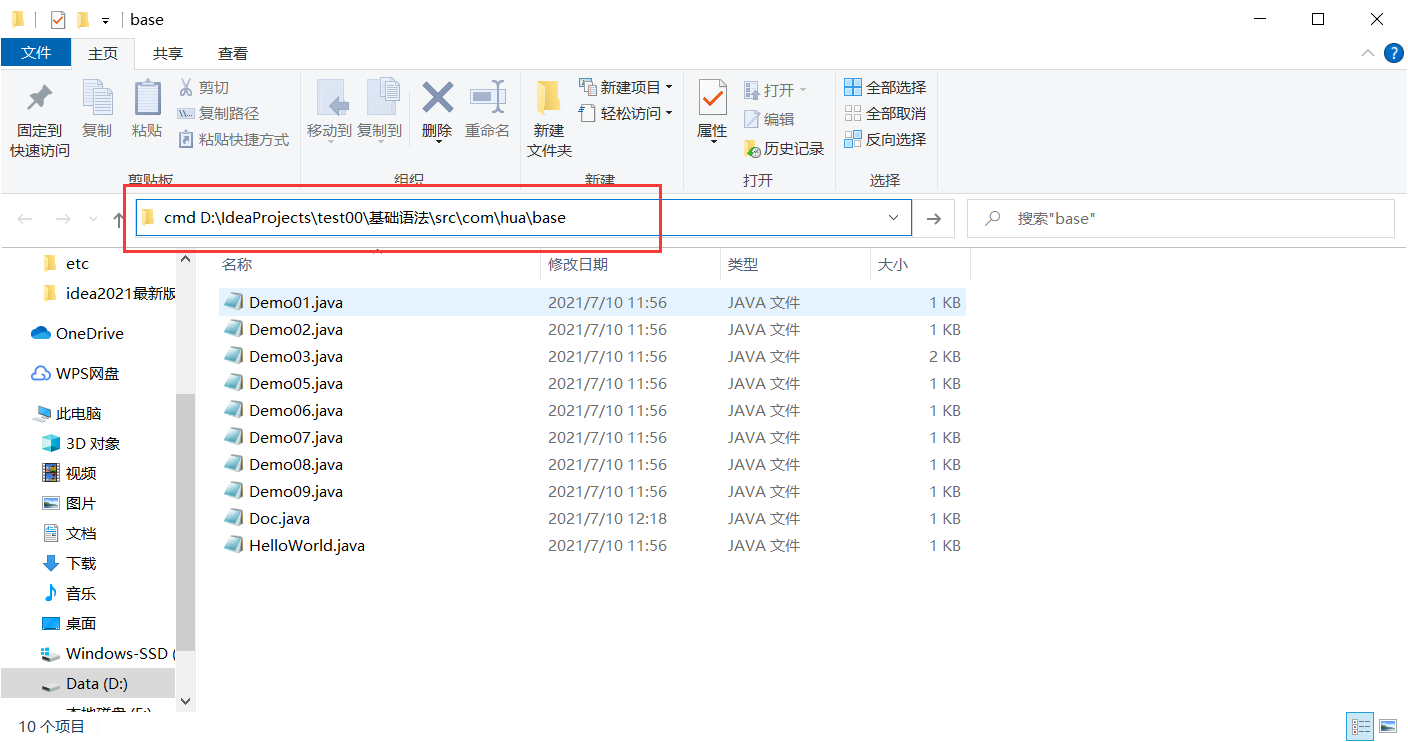
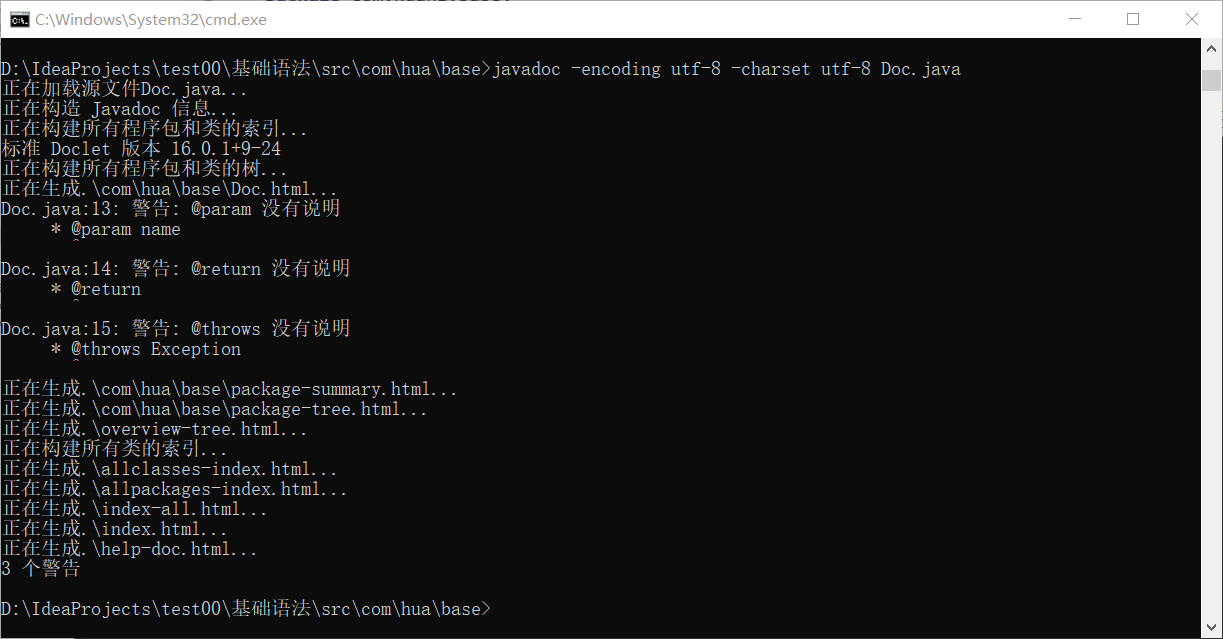
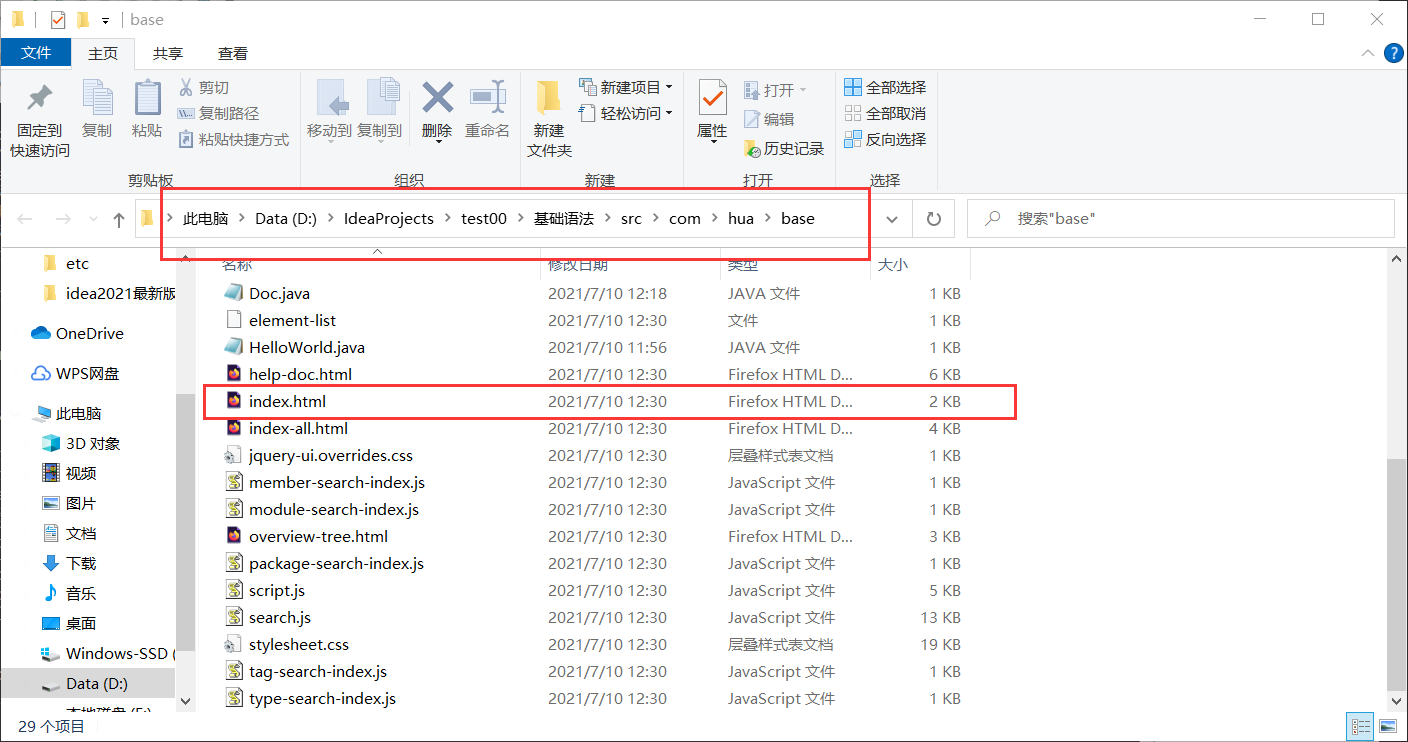
javadoc
jdk help documentation
javadoc is used to generate its own api documents