Preliminary preparation (Linux system is installed by default)
Demo system:
- Ubuntu standalone system
Linux The-Land-Like-as-A-Picture 5.8.0-59-generic #66~20.04.1-Ubuntu SMP Thu Jun 17 11:14:10 UTC 2021 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux - Virtual machine Vmware 15
CentOS 7
1. Network configuration:
Independent system
Configuration is complete when installation is complete
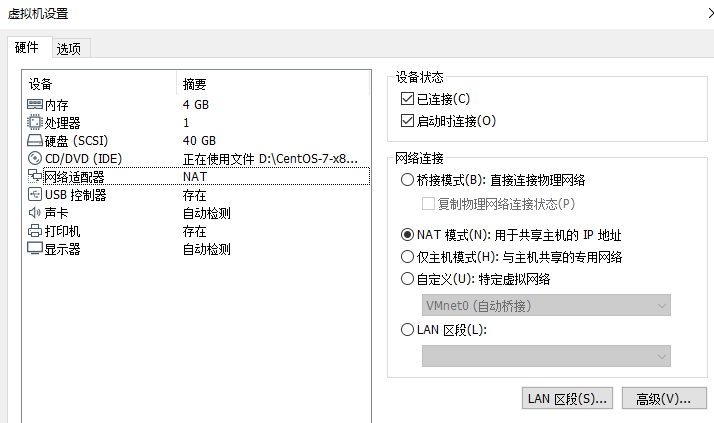
Virtual machine environment vmware:
network configuration
- Right click the network adapter, select VMware Network 8, and turn it on
- Select Configure IPv4, the corresponding IP is 192.168.1.1, and the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0
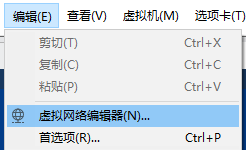
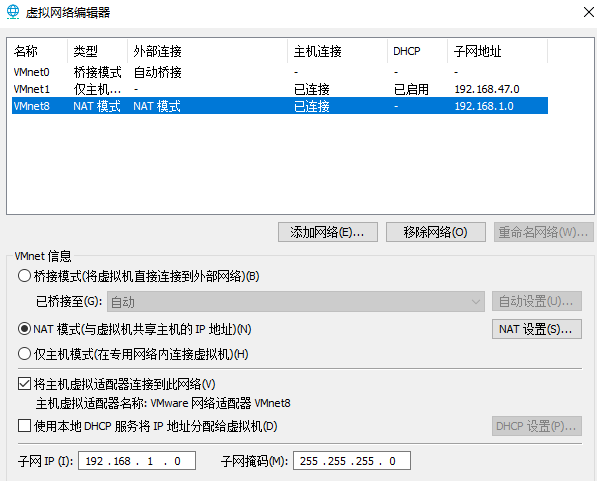
- Open vmware, modify the virtual network editor, set Vmnet8 to NAT mode (default), and enable or disable DHCP service
- Modify the corresponding settings of the virtual machine. The network adapter is NAT and connected
- Enter the system to modify the network:
Connect to the external network: set the virtual network adapter VM8 of the virtual machine to enable DHCP; The system network is set to DHCP automatic acquisition
Do not connect to external network: the system network is set to static, such as 192.168.1.200. Its 200 can be modified by itself, and the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0
2. Early stage Software Acquisition: take typora as an example
Premise: the network can be connected to the external network
Official website link
Installation tutorial
wget -qO - https://typora.io/linux/public-key.asc | sudo apt-key add - sudo add-apt-repository 'deb https://typora.io/linux ./' sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install typora
3. Use of shortcut keys (Ubuntu)
Visual interface shortcut keys
- Ctrl+ALT+T: open a terminal (CentOS needs to open a terminal first)
- Tab: completion command
- Ctrl+C: interrupt command
Common command learning of linux initial
Partial reference: Linux common commands
1. What is an order
Command name [option] [parameter] [object] // Notice that there are spaces between the command name, options, parameters, and objects
2. Directory command of basic command
pwd(print working directory)
pwd is used to display the current working directory of the user
cd(change directory)
cd is used to switch the working path. The format is "cd [directory name]"
.
In the catalog Indicates in the current directory
..
In the directory Represents the previous directory of the current directory
ls(list files )
ls is used to display the file information in the directory in the format of "ls [options] [file]"
ls -al // Used to view all files in the current directory and output corresponding attribute information
mkdir(make directory )
mkdir is used to create folders in the format of "mkdir [name of directory to be created]“
mkdir -p test1/test2 // mkdir -p is used to continue creating folders in folders
rmdir(remove directory )
rmdir is used for folder deletion (not commonly used)
3. File operation commands of common commands
touch
touch is used to create files (can be multiple), such as:
touch file1 file2 . . .
mv(move file )
mv is used to move (generally rename) an existing file or folder
The following command: rename the created file1 file to file3:
mv file1 file3
rm(remove file )
rm (most commonly used), as a delete command, can be used to delete files or folders
rm file2 // No error will be reported at this time - reason: delete a single file mkdir -p test\123\ rm test\ // An error is reported: the directory is deleted rm -rf test // Delete succeeded
cp(copy file)
cp is used to copy files or folders. It is recommended that cp be used as a backup of the original file when modifying files in linux.
Common commands:
cp file2 [path] / [filename]
cp -R test1 ../ // Copy the newly created test1 folder between to the upper directory // - p is required for folder replication cp -a file3 ../ // Copy the newly created file3 file to the upper directory // -a is used not to modify file attributes, including file owner, permission, creation time, etc
ln (link files) soft connection
ln -s file2 [route]/[Link name]
cat (concatenate) view
less file advanced view command (recommended)
less [file name]
Use of related keys
f: Page down
b: Page up
/: find characters
n: Continue down to find results
q: Exit the file view interface
tar (tape archive) compression
tar -xvf xxx.tar -C [route] tar -zxvf xxx.tar.gz tar -cvf xxx.tar [Files to compress] tar -czvf xxx.tar.gz [Files to compress]
4. Authority modification commands of common commands
linux permissions: rwx
- r stands for read
- w stands for writable write
- x means that the file is an executable file
If rwx any location becomes - it represents an unreadable or writable or executable file
Permission Description:
- The first one: - represents the file, and d represents the folder
- The first paragraph (3 digits): represents the authority of the owner
- The second paragraph (3 digits): represents the group of the owner and the authority of the group members
- The third paragraph (the last three digits): represents the permissions of other users
chown(change owner )
chown is used to modify the owner of a file or folder. Only the owner of the file (folder) and root can modify the file permissions
chgrp(change group )
chgrp is used to modify the group of files or folders
chmod(change mode )
chmod is used to modify the corresponding permissions of a file or folder
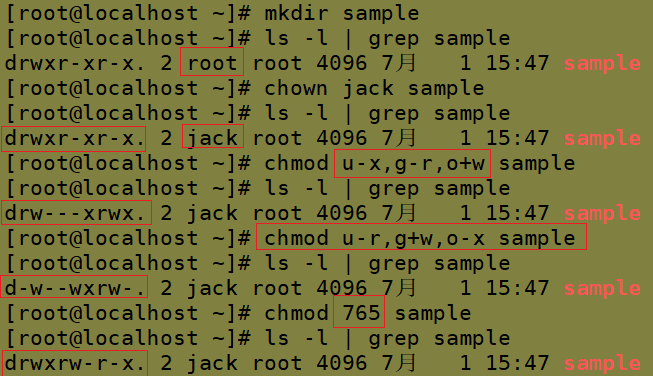
mkdir sample ls -l | grep sample chown jsj sample // Change the owner of the sample in the root home directory to jsj ls -l | grep sample chmod u-x,g-r,o+w sample // Modify the corresponding permission of the owner of the sample folder to no execution permission x, members of the group have no read permission r, and other users have write permission r ls -l | grep sample chmod 765 sample // Modify the permission to rwx rw- r-x (111 110 101)
5. User login commands of common commands
su(swith user)
su is used for switching between users. However, the user before switching remains logged in. If root switches to ordinary or virtual users, no password is required. On the contrary, password verification is required for ordinary users to switch to any other users.
su test:Switch to test User, but the path is still/root catalogue su - test : Switch to test User, the path becomes/home/test
passwd
Perform password modification for the corresponding user under root user
Usage:
passwd [corresponding user]
who
Who is used to view the user terminal information of the currently logged in host. The format is "who [parameter]".
last
Last is used to view the login records of all systems in the format of "last [parameter]"
history
history is used to display 1000 commands executed by the current user
history -c // Clear the history of linux commands executed by the current user
6. System work orders of common commands
echo
echo is used to output a string or corresponding variable (starting with $) at the terminal
echo -e "tab:\t enter:\n" // echo -e is a parsing regular expression, such as \ t and \ n echo -n "echo -n Indicates no carriage return output"
echo classic case: Countdown:
for i in 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 do echo -ne "$i\b" # -n means no carriage return display, \ b in the regular expression is to delete the previous character \ b # The display effect is that the number flashes and disappears every time without entering sleep 1 # Wait for 1s done echo "Launch!"
date
date is used to display the current time
Display the current time by year month day hour: minute: second
date "+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"
The setting time is April 5, 2030, 6:7:8
date -s "20300405 6:07:08"
Classic case of date: take this time as the folder name
getDate=`date +"%Y%m%d-%H.%M"` # The current time is expressed in mm / DD / yyyy - hour Get and pass in the form of minutes to the variable getDate # Note that the mechanism that can be realized is the use of ` # The following commands are also available: GetDATE=$(date +"%Y-%m-%d %H.%M") mkdir $getDate mkdir $GetDATE # Create corresponding folder
reboot
reboot is used to restart the system
Just reboot
shutdown
Shutdown is used to specify the corresponding time for shutdown or restart
shutdown -h now // Shut down immediately shutdown -h 5 // Shutdown in 5 minutes shutdown -r now // Restart now
ps(process status)
ps is used to view the process status in the system. The format is "ps [parameter]"
View the processes running in the current system
ps aux ps -ef
top
Top (Task Manager equivalent to win) is used to dynamically monitor process activity, system load and other information. It is refreshed every 10 seconds by default
pidof
Pidof is used to query the PID value of a specified service process. The format is "pidof [parameter] [service name]"
kill
Kill is used to terminate a service process with a specified PID. The format is "kill [parameter] [process PID]"
killall
Kill is used to batch terminate all processes corresponding to a service, such as closing the sshd service program (i.e. xshell service)
pidof sshd killall sshd pidof sshd
7. Other commands of common commands
Find find
find . -name "*.log" -ls // Find in the current directory to log and displays details. find /root/ -perm 600 // Find the file with permission of 600 in the / root / directory find . -type f -name "*.log" // Find the current directory to Normal file at the end of log find . -type d | sort // Find and sort all current directories find . -size +100M // Find files larger than 100M in the current directory
grep
ps -ef | grep sshd //Find the specified ssh service process ps -ef | grep sshd | grep -v grep // Find the specified service process and exclude gerp ps -ef | grep sshd -c // Find the specified number of processes
cal(calendar )
cal [month] [year]
Show calendar
dd(disk dump)
dd is used to create a file of a specified size
dd if=/dev/zero of=file count=3 bs=100M # Create a file with the size of 3*100M=300M in the current directory ls -l file
man manual
man [corresponding to valid instruction]
vim (with reference)
vim three states
Basically, vim can be divided into three states: command mode, Insert mode and last line mode. The functions of each mode are as follows:
- command mode
Control the movement of the screen cursor, the deletion of characters, words or lines, search, move, copy a section and enter Insert mode, or go to last line mode.
- Common commands in command line mode:
- Control cursor movement: ↑, ↓, j
- Delete current row: dd
- Find: / character
- Enter edit mode: i o a
- Enter bottom line mode:
- Insert mode
Text input can only be made in Insert mode. Press "ESC" to return to command line mode.
- Common commands in edit mode:
ESC exits editing mode to command line mode
- last line mode
Save the file or exit vim, or set the editing environment, such as finding string, listing line number, etc.
- Common commands in bottom line mode:
- Exit editing:: q
- Forced exit:: q!
- Save and exit:: wq
Open file
Commands: vim file names
Example: open AA. In the current directory Txt file VIM AA Txt or VIM AA txt
Note: after opening the file with vim editor, it cannot be edited because it is in command mode. Click i/a/o on the keyboard to enter editing mode.
Edit file
After opening the file with vim editor, click the key: i, a or o to enter the editing mode.
i: Start insertion before the character of the cursor (I: after)
a: Insert after the character of the cursor (A: before)
O: Insert a new line below the line where the cursor is located (O: above)
Save or cancel editing
- Save file:
- ESC enters command line mode
- : enter bottom line mode
- wq save and exit editing
- Cancel editing:
- ESC enters command line mode
- : enter bottom line mode
- q! Undo this modification and exit editing
linux high-level shell script learning
1. What is a script (short for shell script)
shell script is a script program written for the shell.
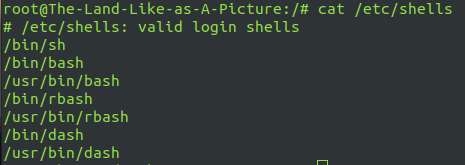
shell editing available in linux
The corresponding location is / etc/shells, including sh, bash, etc. Bash, Bourne Again Shell, is widely used in daily work due to its ease of use and free of charge. Bash is also the default Shell for most Linux systems. To Israel SH ending file, bash XX SH to execute the script.
2. Write corresponding scripts
For the preparation of scripts, specifications are required, including
- The first line shows which compiler to compile with
- The following describes the creation time, corresponding author and corresponding purpose of the script
xshell connection
Xshell creates a new connection. The host fills in the virtual machine system IP, such as 192.168.1.200. The user name is set to root and the password is the login password.
Reasons for using xshell
Usually, linux systems are servers, and most servers can't contact entities, that is, they can only connect and control remotely through the network Among the common remote connection software, X shell is the most commonly used
Vim, as a built-in editor of linux, can realize the editing process of file content faster without the use of mouse
vim scripting
vim configuration file vimrc
vim ~/.vimrc
Fill in the following:
set nu
# Set the line number and cancel the line number as: set nonu
syntax on
# Set auto patch
map <F1> :call AddInfo() <CR>
# For a sh file, press F1
function AddInfo()
if &filetype == 'sh'
call append(0,"#!/bin/bash")
endif
call append(1,"clear")
call append(2,"#############################")
call append(3,"### Author: Author name here ###")
call append(4,"#############################")
call append(5,"#time :".strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M"))
call append(6,"#############################")
call append(7,"#### Descrption ############")
echo
endfunction
ESC: WQ save and exit
Create a utility shell script file
Related resources: linux_shell.tar.gz
How to use: download or ftp to linux system and decompress:
tar -zxvf linux_shell.tar.gz
It includes the script file corresponding to the blog and md tutorial. You can use it according to the tutorial corresponding to the blog
test1. Comparison of the size of SH two numbers
vim test1.sh create test1 SH script file
Press F1 to write script information first:
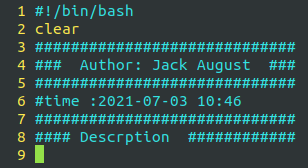
i press the i key to enter the input mode and start script writing:
clear
read -p "Please enter two numbers to judge its size. The first number:" num1
read -p "Second number:" num2
echo "The first number is: $num1, The second number is: $num2"
echo "Start judgment:"
if [ $num1 = $num2 ];then
echo "$num1 be equal to $num2"
elif (($num1 > $num2));then
echo "$num1 greater than $num2"
else
echo "$num1 less than $num2"
fi
Press ZZ to save the file and exit
The final content is as follows:
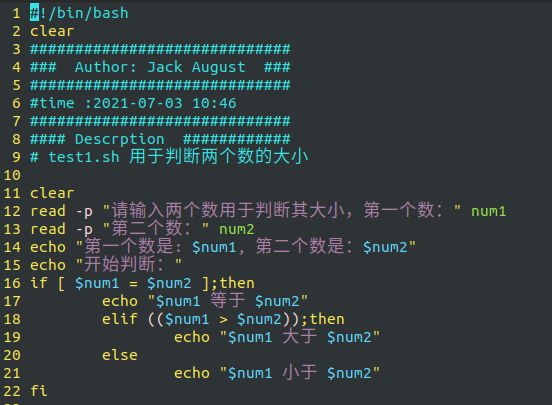
Script execution:
bash test1.sh enter two numbers to judge:

test2.sh calculate whether the input year is a profit year
vim test2.sh create test2 SH script
Press F1 to add information and i to edit:
clear
read -p "Please enter a four digit year greater than 1000: " year
count=`echo $year | awk '{print length($0)}'`
if [ $count -eq 4 ];then
echo "year yes $year"
if (( $year % 100 != 0 ));then
if (( $year %4 != 0 ));then
echo "$yaer Not a leap year"
else
echo "$year It's a leap year"
fi
elif (( $year % 400 != 0 ));then
echo "$year Not a leap year"
else
echo "$year It's a leap year"
fi
else
echo "Wrong number of input digits"
fi
Press ZZ to save the file and exit
The final content is as follows:
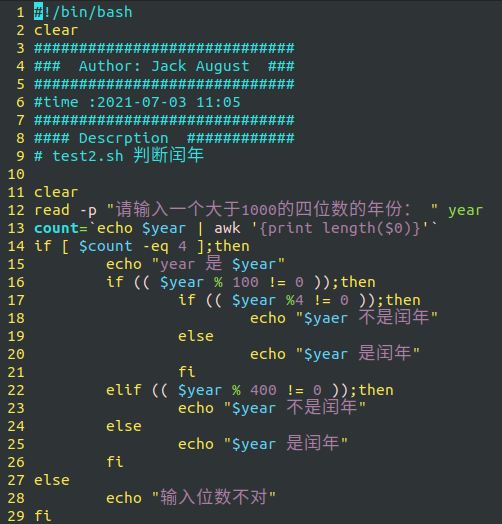
Script execution:
bash test2.sh enter four digits to judge:
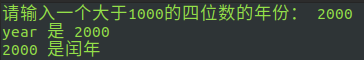
test3.sh games - guess numbers
vim test3.sh create test3 SH script
Press F1 to add information and i to edit:
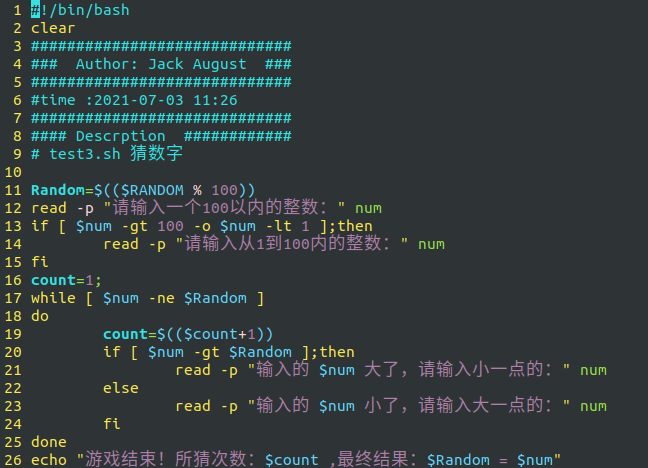
Random=$(($RANDOM % 100))
read -p "Please enter an integer within 100:" num
if [ $num -gt 100 -o $num -lt 1 ];then
read -p "Please enter an integer from 1 to 100:" num
fi
count=1;
while [ $num -ne $Random ]
do
count=$(($count+1))
if [ $num -gt $Random ];then
read -p "Entered $num Large, please enter a smaller one:" num
else
read -p "Entered $num Small, please enter a larger one:" num
fi
done
echo "game over! Number of guesses: $count ,Final result: $Random = $num"
Press ZZ to save the file and exit
The final content is as follows:
Script execution:
bash test3.sh enter a number within 100 to start:

test4.sh calculates how long your birthday will be (a little complicated)
vim test4.sh create test4 SH script
Press F1 to add information and i to edit:
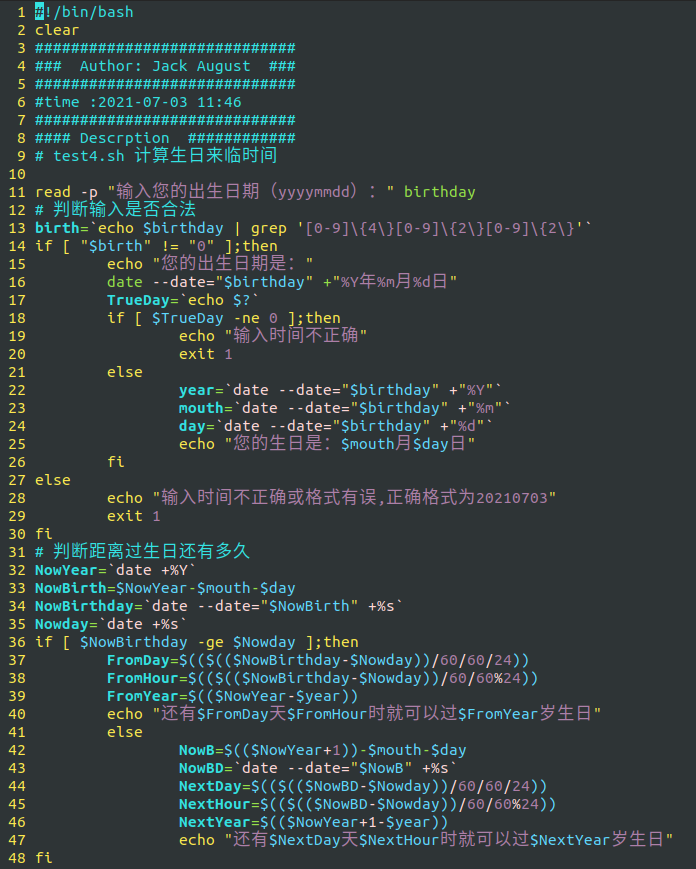
read -p "Enter your date of birth( yyyymmdd): " birthday
# Judge whether the input is legal
birth=`echo $birthday | grep '[0-9]\{4\}[0-9]\{2\}[0-9]\{2\}'`
if [ "$birth" != "0" ];then
echo "Your date of birth is:"
date --date="$birthday" +"%Y year%m month%d day"
TrueDay=`echo $?`
if [ $TrueDay -ne 0 ];then
echo "Incorrect input time"
exit 1
else
year=`date --date="$birthday" +"%Y"`
mouth=`date --date="$birthday" +"%m"`
day=`date --date="$birthday" +"%d"`
echo "Your birthday is: $mouth month $day day"
fi
else
echo "Incorrect input time or format,The correct format is 20210703"
exit 1
fi
# How long is it before your birthday
NowYear=`date +%Y`
NowBirth=$NowYear-$mouth-$day
NowBirthday=`date --date="$NowBirth" +%s`
Nowday=`date +%s`
if [ $NowBirthday -ge $Nowday ];then
FromDay=$(($(($NowBirthday-$Nowday))/60/60/24))
FromHour=$(($(($NowBirthday-$Nowday))/60/60%24))
FromYear=$(($NowYear-$year))
echo "also $FromDay day $FromHour You can live when you are young $FromYear Birthday"
else
NowB=$(($NowYear+1))-$mouth-$day
NowBD=`date --date="$NowB" +%s`
NextDay=$(($(($NowBD-$Nowday))/60/60/24))
NextHour=$(($(($NowBD-$Nowday))/60/60%24))
NextYear=$(($NowYear+1-$year))
echo "also $NextDay day $NextHour You can live when you are young $NextYear Birthday"
fi
Press ZZ to save the file and exit
The final content is as follows:
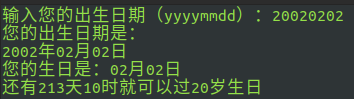
Script execution:
bash test4.sh enter the corresponding format of yyyymmdd to judge:
test5.sh enter numbers and add from 1
vim test5.sh create test5 SH script
Press F1 to add information and i to edit:
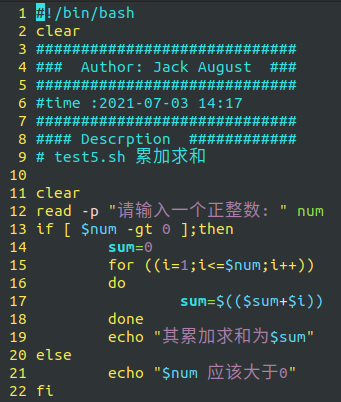
clear
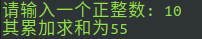
read -p "Please enter a positive integer: " num
if [ $num -gt 0 ];then
sum=0
for ((i=1;i<=$num;i++))
do
sum=$(($sum+$i))
done
echo "Its cumulative sum is $sum"
else
echo "$num Should be greater than 0"
fi
Press ZZ to save the file and exit
The final content is as follows:
Script execution:
bash test5.sh enter a positive integer to calculate:
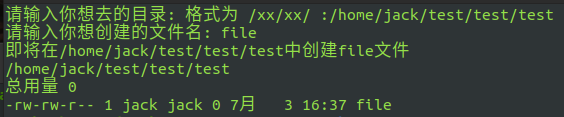
test6.sh basic operations such as judging the existence of files and folders
vim test6.sh create TEST6 SH script
Press F1 to add information and i to edit:
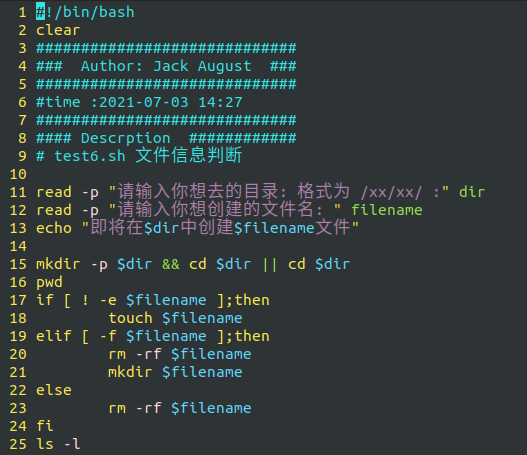
read -p "Please enter the directory you want to go to: Format is /xx/xx/ :" dir
read -p "Please enter the file name you want to create: " filename
echo "About to $dir Create in $filename file"
mkdir -p $dir && cd $dir || cd $dir
pwd
# File does not exist, create
if [ ! -e $filename ];then
touch $filename
# If the file exists, delete it and create a new folder
elif [ -f $filename ];then
rm -rf $filename
mkdir $filename
# If it exists, it will be deleted if it is a folder or other type
else
rm -rf $filename
fi
ls -l
Press ZZ to save the file and exit
The final content is as follows:
Script execution:
bash test6.sh enter the corresponding path and file name to create:
test7.sh get the information of the surviving hosts under the current network segment
vim test7.sh create Test7 SH script
Press F1 to add information and i to edit:
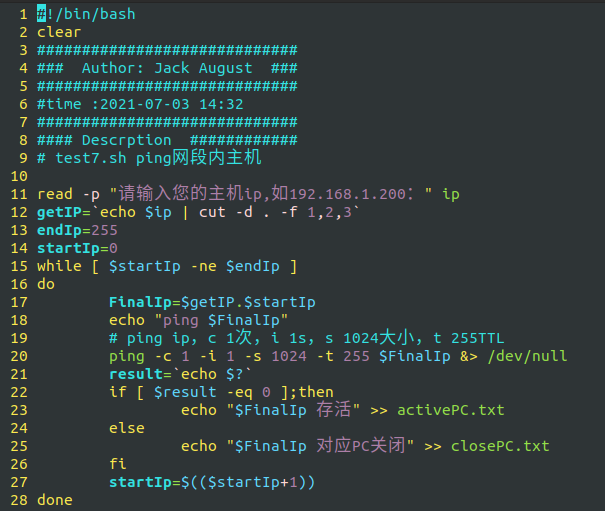
read -p "Please enter your host ip,Such as 192.168.1.200: " ip
# Get the corresponding network segment
getIP=`echo $ip | cut -d . -f 1,2,3`
endIp=255
startIp=0
while [ $startIp -ne $endIp ]
do
FinalIp=$getIP.$startIp
echo "ping $FinalIp"
# ping ip, C once, i 1s, s 1024 size, t 255TTL
ping -c 1 -i 1 -s 1024 -t 255 $FinalIp &> /dev/null
result=`echo $?`
if [ $result -eq 0 ];then
echo "$FinalIp survival" >> activePC.txt
else
echo "$FinalIp corresponding PC close" >> closePC.txt
fi
startIp=$(($startIp+1))
done
Press ZZ to save the file and exit
The final content is as follows:
Script execution:
bash test7.sh enter the host IP to judge:
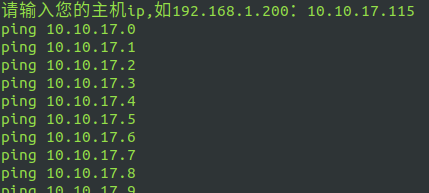
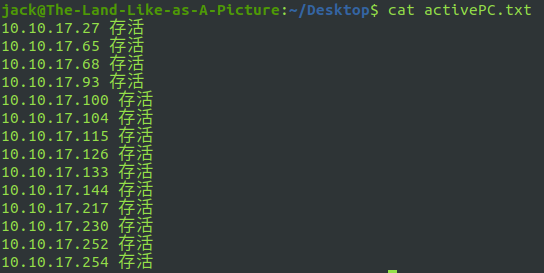
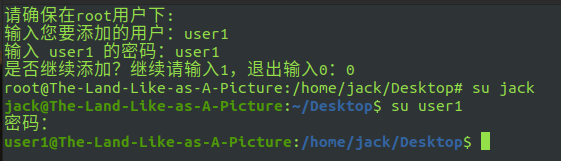
test8.sh add a user and configure the corresponding login password (root permission)
vim test8.sh create test8 SH script
Press F1 to add information and i to edit:
# Must be under root
echo "Please make sure that root User under:"
quit=1
while [ $quit -ne 0 ]
do
read -p "Enter the user you want to add:" username
useradd -d /home/$username -m $username -s /bin/bash
read -p "input $username Password for:" passwd
echo "$username:$passwd" | chpasswd
read -p "Continue adding? To continue, enter 1, to exit, enter 0:" quit
done
Press ZZ to save the file and exit
The final content is as follows:
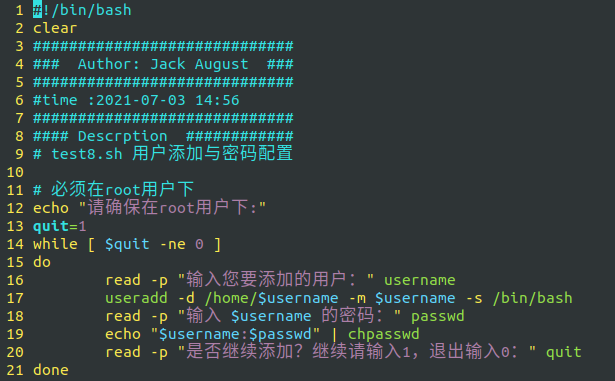
Script execution:
bash test8.sh enter the user and corresponding password to add and switch: