1. Connect to our server via ssh
By default, docker is installed on your system. If it is not installed, please search other tutorials and install it first
2. View the network card name
Use the nmcli command to view your network card name
root@debian:~# nmcli
enp2s0: connected to Wired connection 2
...
inet4 192.168.1.6/24
route4 192.168.1.0/24
...
The network card name here is enp2s0, and the IP address is 192.168.1.6. Everyone's is different. Remember that it will be used later
3. Enable network card hybrid mode
sudo ip link set eth0 promisc on
4. Set up MAC VLAN network
Note that this step must be based on your actual situation, otherwise the setting will fail
docker network create -d macvlan --subnet=192.168.1.0/24 --gateway=192.168.1.1 -o parent=enp2s0 macnet
The subnet mask 192.168.1.0/24, gateway 192.168.1.1 and network card name enp2s0 in the command should be changed according to your actual situation in the first step. The value of gateway is the IP of your router. Generally, it is the first network segment where your host is located, that is, 192.168 XXX. one
For example, what you found in the first step is 192.168.22.3/24 and eth0, which should be set to the following code
docker network create -d macvlan --subnet=192.168.22.0/24 --gateway=192.168.22.1 -o parent=eth0 macnet
After setting, you can use the docker network ls command to view. Here you can see that the network macnet has been established successfully
root@debian:~# docker network ls NETWORK ID NAME DRIVER SCOPE de29daef40a1 bridge bridge local f961f2a52dd9 host host local 2cfd9f6843a7 macnet macvlan local a8a1bb1e628d none null local
5. Pull the openwrt image
Here, the image in the Dock image warehouse is used OpenWrt-Rpi-Docker You can choose the version of this image if you have other habits
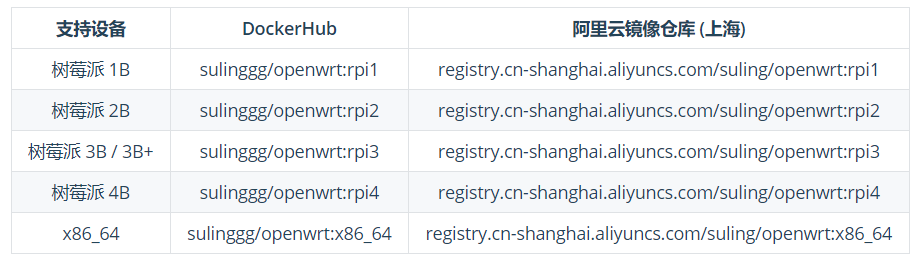
Since my platform is x86, I use the following commands. Everyone can choose according to the actual situation
docker pull sulinggg/openwrt:x86_64
After the image is pulled successfully, we can execute the docker images command to view the existing image
root@debian:~# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE sulinggg/openwrt x86_64 5ce79834d1ba 2 days ago 460MB
6. Create and start the container
docker run -d --restart always --name openwrt --network macnet --privileged sulinggg/openwrt:x86_64 /sbin/init
--The restart always parameter indicates that the container is always restarted when it exits, so as to keep the service available as far as possible
--The name openwrt parameter defines the name of the container
-d parameter definition makes the container run in Daemon mode
--The network macnet parameter defines to join the container to the maxnet network
--The privileged parameter defines that the container runs in privileged mode
sulinggg/openwrt:x86_64 is the Docker image name
/sbin/init defines the commands to be executed after the container is started
After the installation is successful, use the command to view the installation
root@debian:~# docker run -d --restart always --name openwrt --network macnet --privileged sulinggg/openwrt:x86_64 /sbin/init 7be08241566d293f7ab8fd81e7ee4a2e47efdb77bd2288d3aa7e292f6941bd15 root@debian:~# docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 7be08241566d sulinggg/openwrt:x86_64 "/sbin/init" 32 seconds ago Up 31 seconds openwrt
status displays UP, indicating that the installation and startup are successful
7. Network configuration
It must be combined with the actual network situation and cannot copy the configuration, otherwise the previous efforts will be in vain
Use the command to enter the bash mode of docker
docker exec -it openwrt bash
Of which:
openwrt is the container name;
bash is the command executed after entering the container
After executing this command, we will enter the command line interface of OpenWrt
root@debian:~# docker exec -it openwrt bash bash-5.1#
First, we need to edit OpenWrt's network configuration file
vim /etc/config/network
We need to change the Lan port settings:
config interface 'lan'
option type 'bridge'
option ifname 'eth0'
option proto 'static'
option ipaddr '192.168.123.100'
option netmask '255.255.255.0'
option ip6assign '60'
option gateway '192.168.123.1'
option broadcast '192.168.123.255'
Of which:
All 192.168.123 X needs to be modified according to the network segment where the IP is located in step 1. Fill in the IP of the router in the option gateway. If the IP obtained in step 1 is 192.168.1.6 and the router IP is 192.168.1.1, it needs to be modified as follows:
config interface 'lan'
option type 'bridge'
option ifname 'eth0'
option proto 'static'
option netmask '255.255.255.0'
option ip6assign '60'
option ipaddr '192.168.1.8'
option gateway '192.168.1.1'
option dns '192.168.123.1'
Note that the option proto name here remains the default and does not need to be modified. When I installed it, I repeated it several times to find the problem
8. Restart the network and update the configuration
/etc/init.d/network restart
9. Reset openwrt management password
passwd
Enter the password twice as prompted
bash-5.1# passwd Changing password for root New password: Retype password: passwd: password for root changed by root
10. Enter the control panel to configure the soft path
Enter the IP in option ipaddr in step 7 in the browser to enter the control panel. If the parameter of option ipaddr is 192.168.1.8, you can enter it in the browser http://192.168.1.8 Enter the control panel.
Well, the installation of openwrt is completed. I will describe in detail how to configure the side route in the following articles