CentOS Stream 9 configures sshd_ Configure AllowUsers to implement SSH access control
1, Description of several popular versions of CentOS
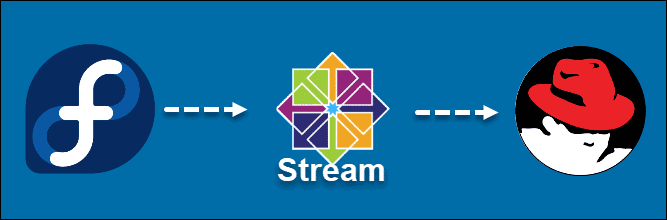
(the picture can be zoomed in)
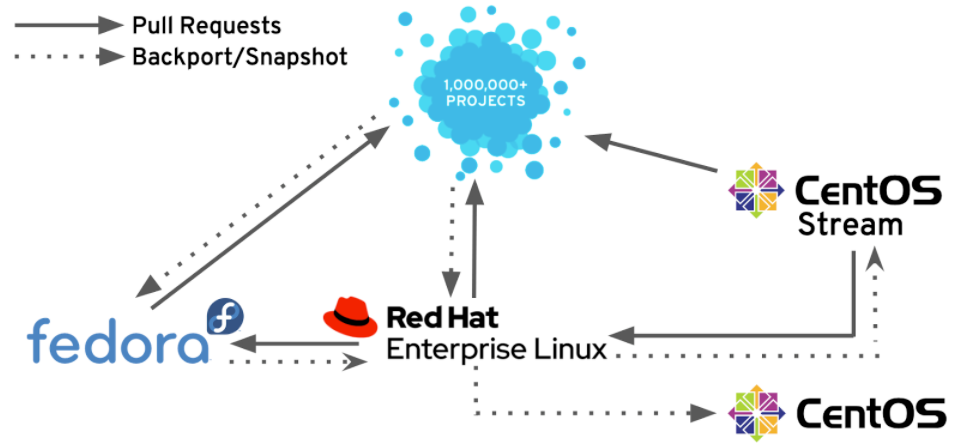
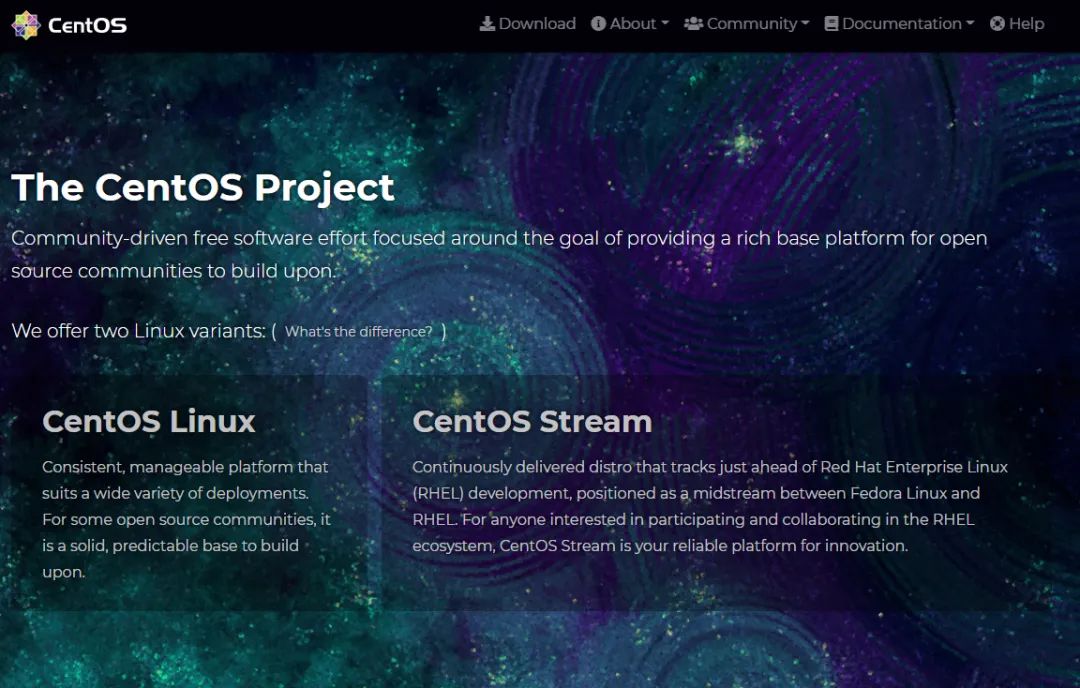
CentOS Linux and CentOS Stream
(the picture can be zoomed in)
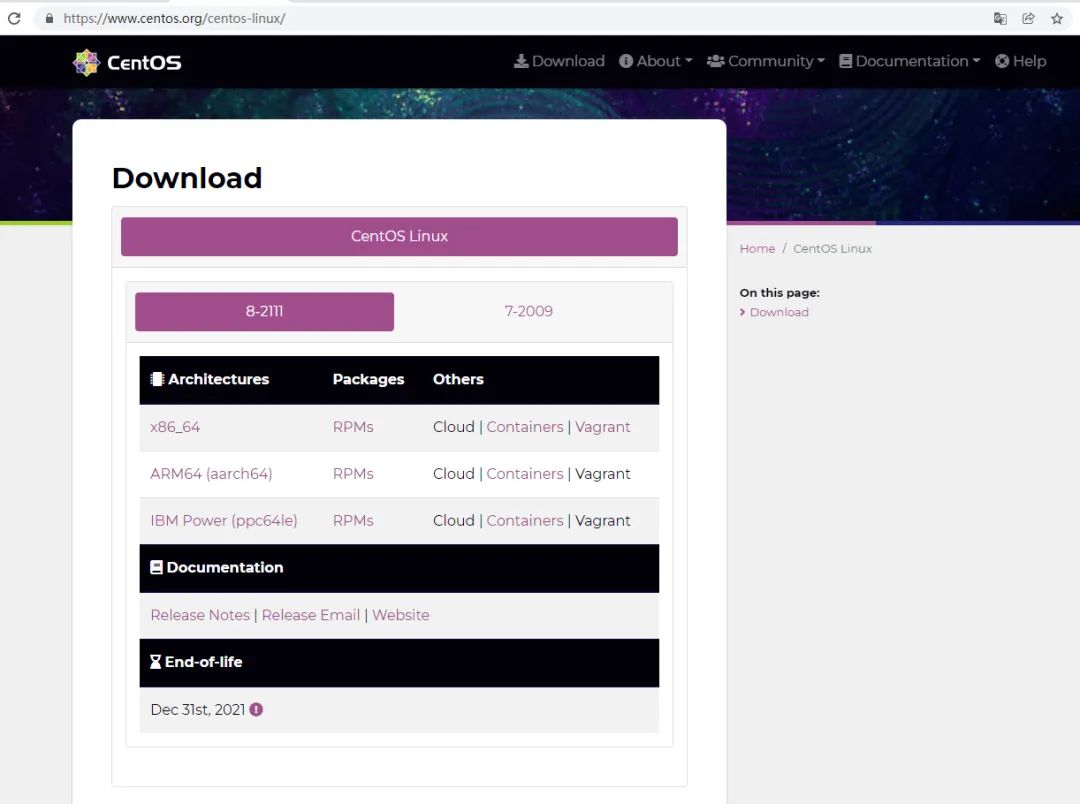
- CentOS Linux currently has two major versions
-- CentOS Linux 7
-- CentOS Linux 8
(the picture can be zoomed in)
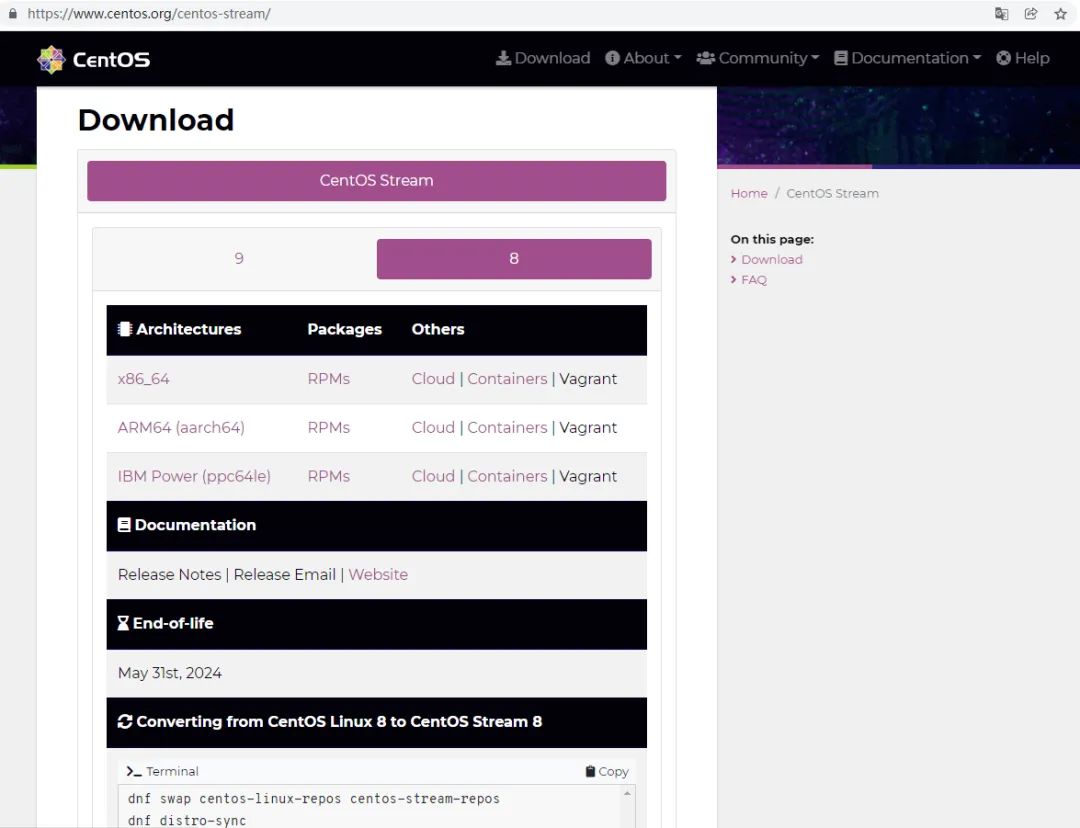
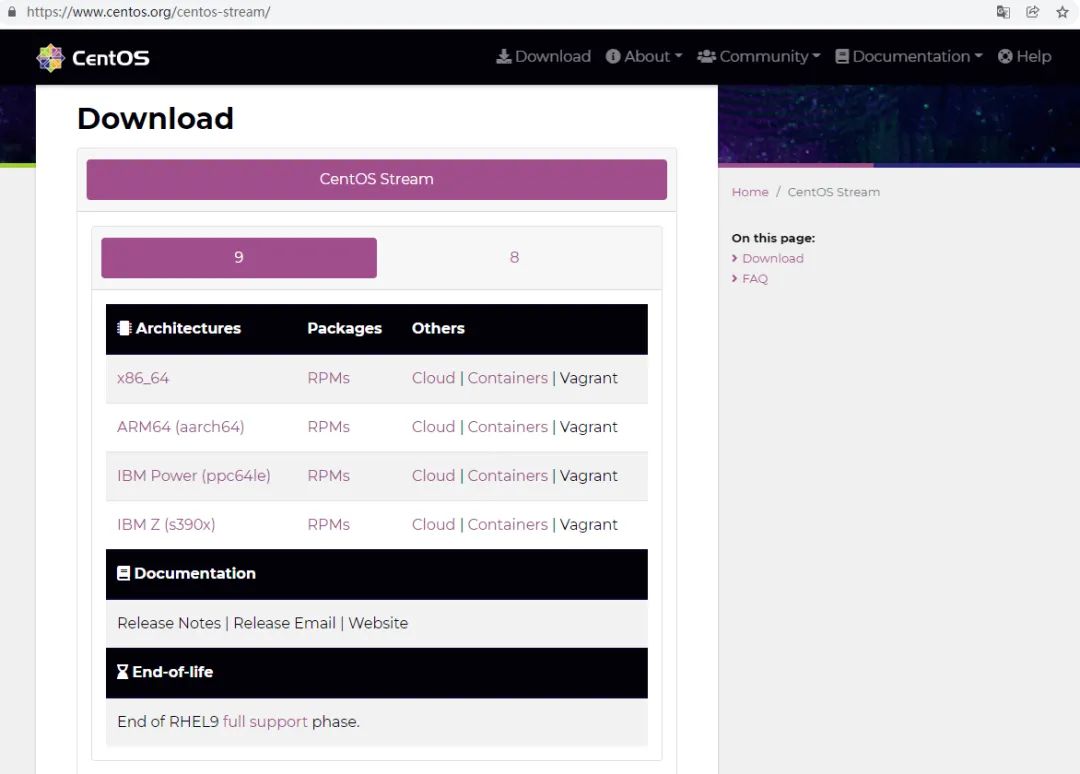
- CentOS Stream currently has two major versions
-- CentOS Stream 8
-- CentOS Stream 9
(the picture can be zoomed in)
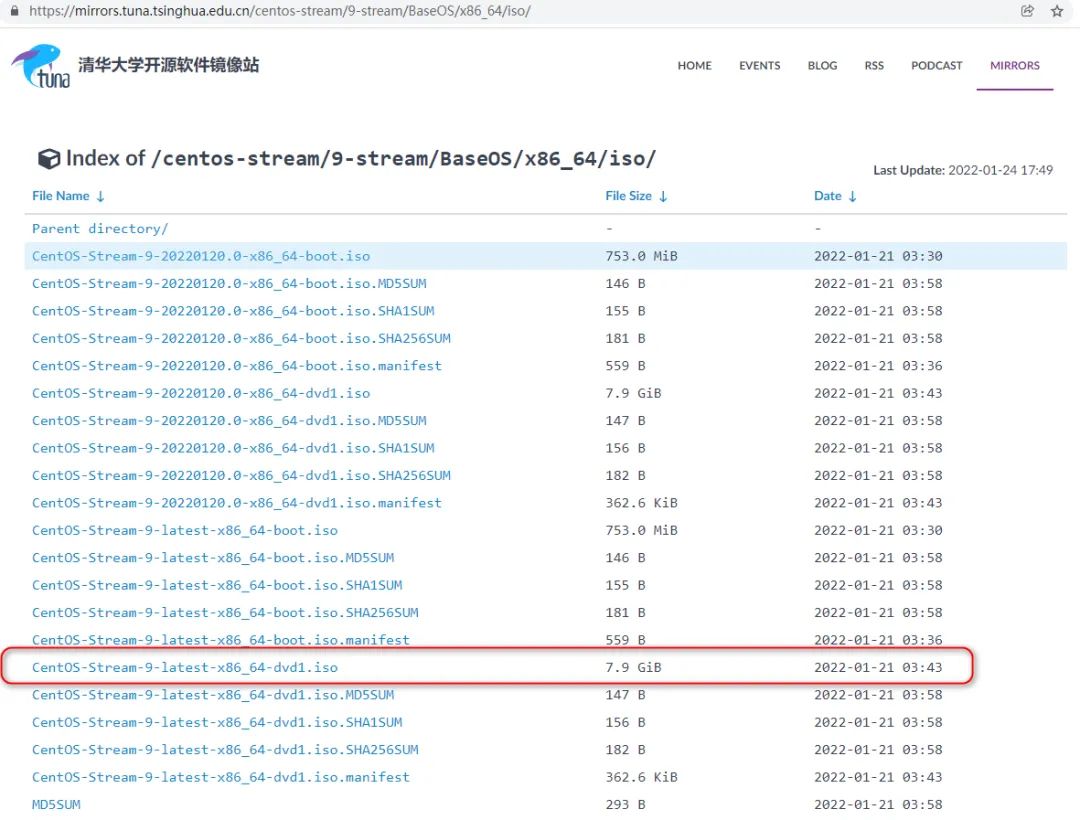
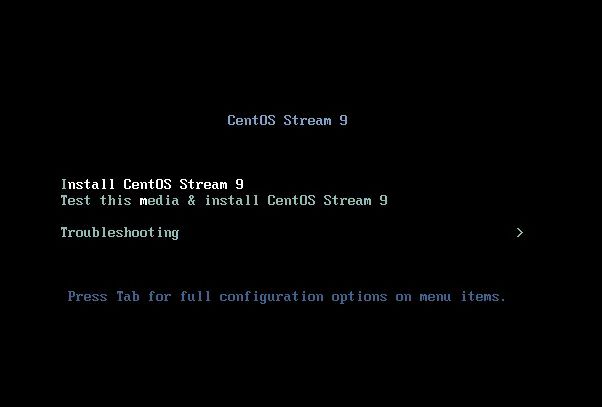
2, CentOS Stream 9 system installation experience
(the picture can be zoomed in)
(the picture can be zoomed in)
1. Screenshot of installation process
(the picture can be zoomed in)
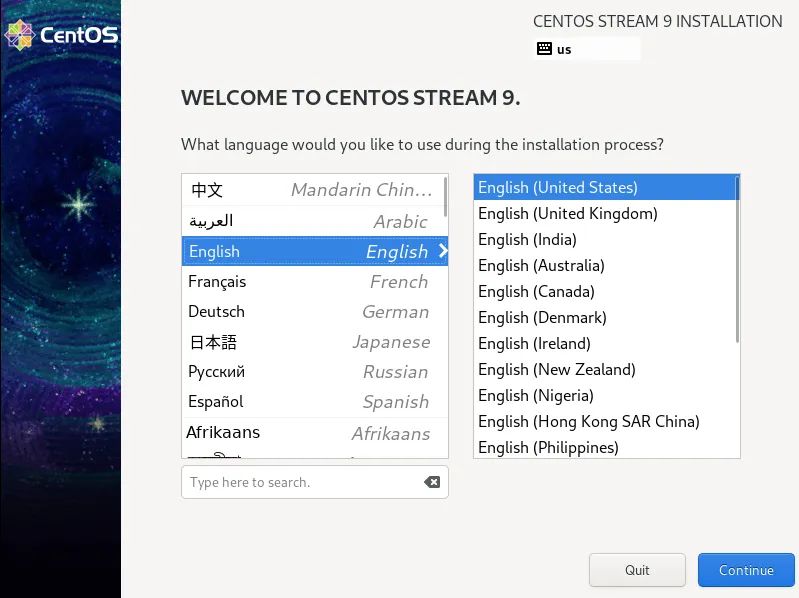
(the picture can be zoomed in)
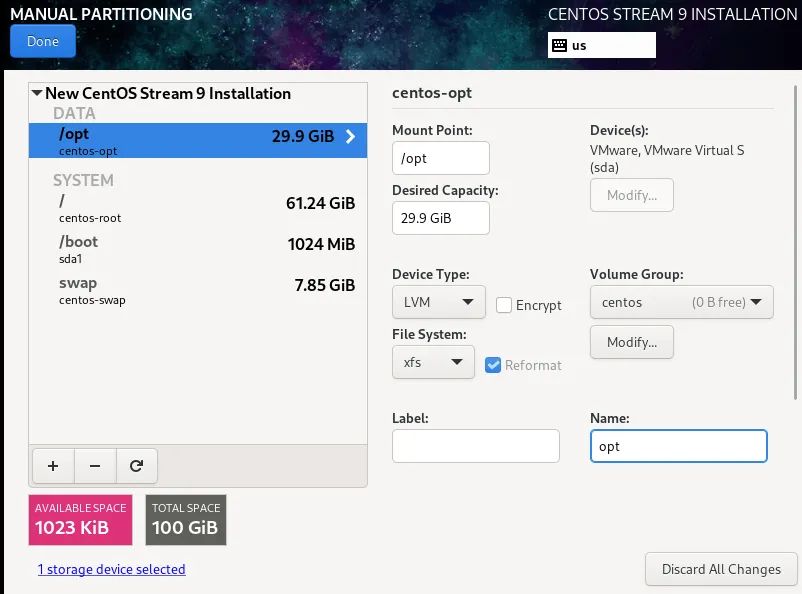
(the picture can be zoomed in)
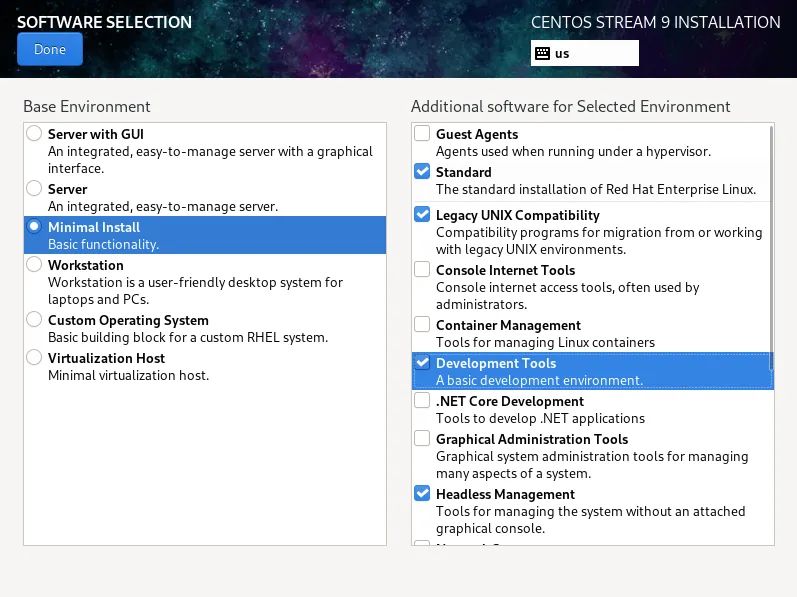
(the picture can be zoomed in)
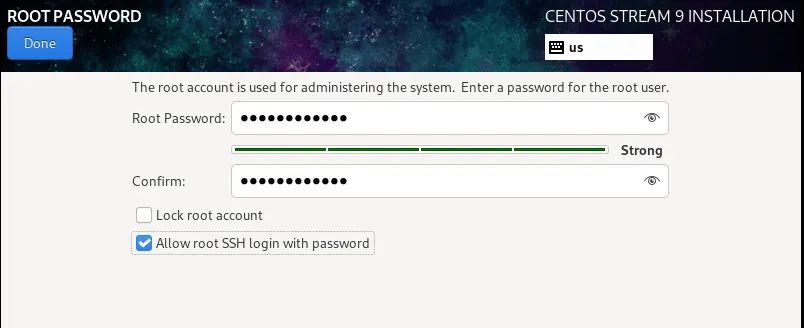
(the picture can be zoomed in)
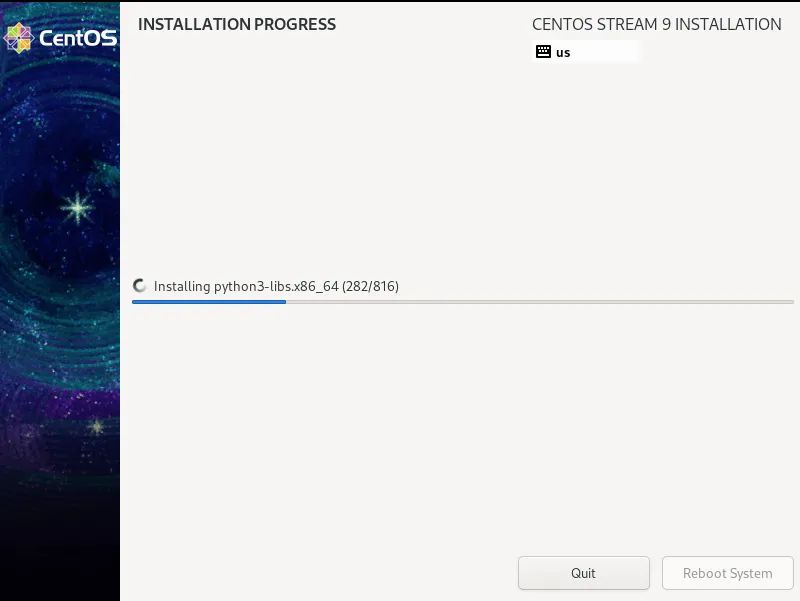
(the picture can be zoomed in)
(the picture can be zoomed in)
2. Close SELINUX after installation
getenforce setenforce 0 sed -i 's/^SELINUX=.*$/SELINUX=disabled/' /etc/selinux/config cat /etc/selinux/config
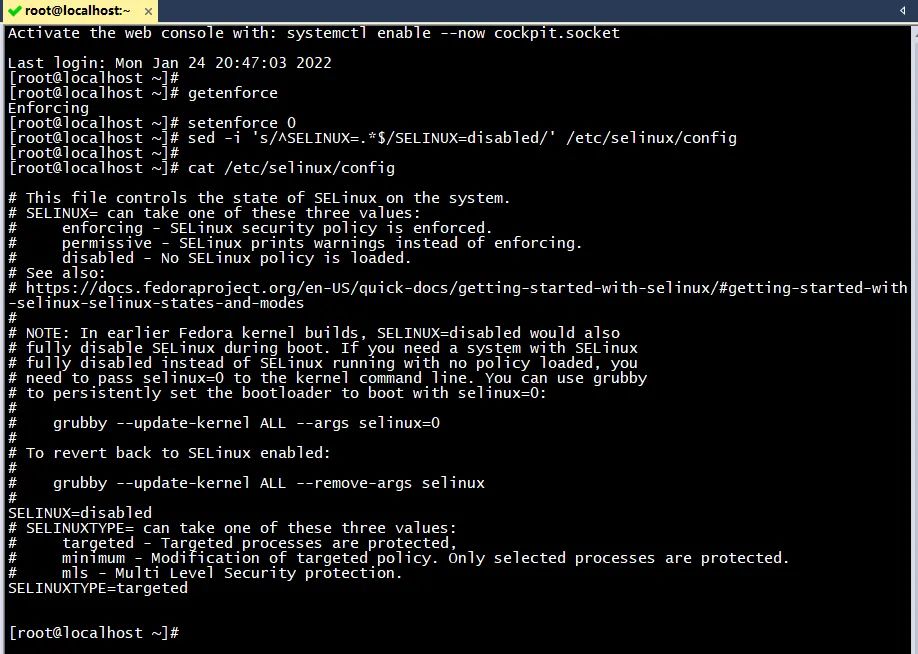
(the picture can be zoomed in)
Let's get to the point
3, CentOS Stream 9 configures sshd_ Configure AllowUsers to implement SSH access control
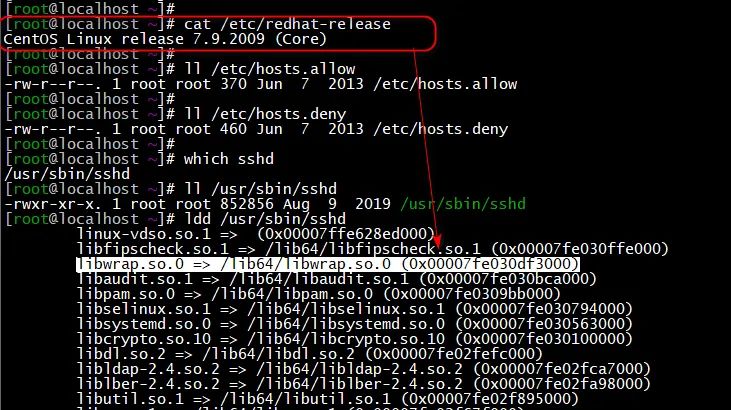
1. CentOS Stream 9 does not have / etc / hosts by default allow
In CentOS Stream 9 system
ll /etc/hosts.allow ldd /usr/sbin/sshd
You can find no libwrap so. 0 library file
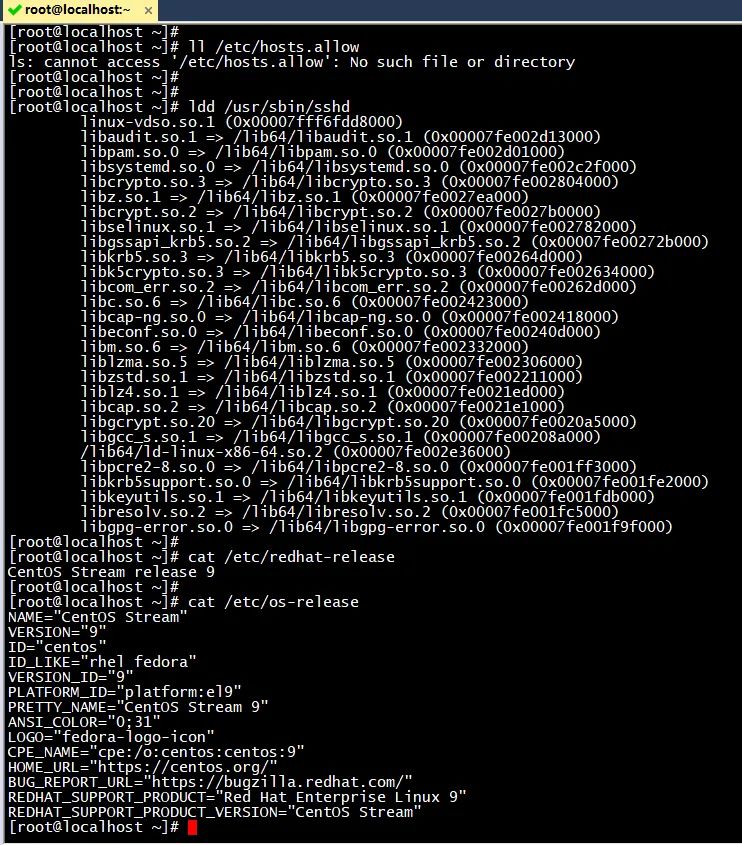
(the picture can be zoomed in)
There is no / etc / hosts.in the system Allow and / etc / hosts Deny file
Compare CentOS7 system
Refer to the following two articles for details
Using tcp_wrapper implements IP access control of SSH login
On the problem of bypassing fortress machines in enterprise network security
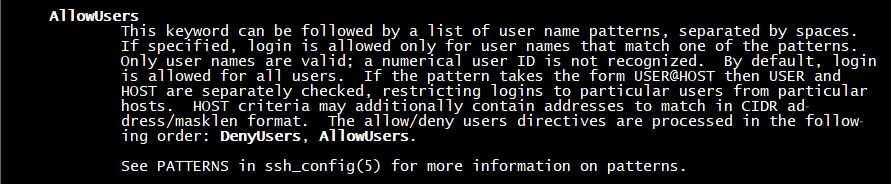
2,man sshd_config
man sshd_config view AllowUsers parameter configuration description
AllowUsers
This keyword can be followed by a list of user name patterns, separated by spaces.
If specified, login is allowed only for user names that match one of the patterns.
Only user names are valid; a numerical user ID is not recognized. By default, login
is allowed for all users. If the pattern takes the form USER@HOST then USER and
HOST are separately checked, restricting logins to particular users from particular
hosts. HOST criteria may additionally contain addresses to match in CIDR ad‐
dress/masklen format. The allow/deny users directives are processed in the follow‐
ing order: DenyUsers, AllowUsers.
(the picture can be zoomed in)
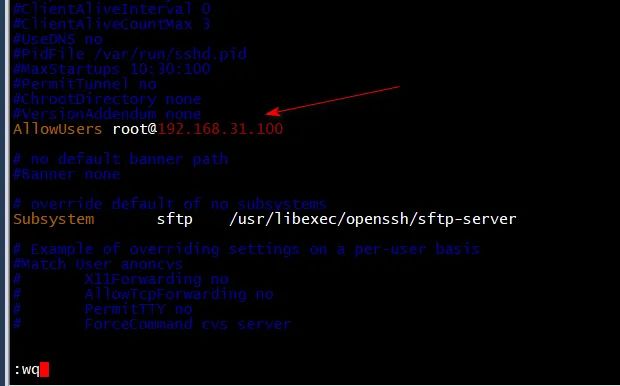
3. SSH access control configuration steps and Practice
vi /etc/ssh/sshd_config Add the following line, only 192 are allowed.168.31.100+root User login AllowUsers root@192.168.31.100 systemctl restart sshd
(the picture can be zoomed in)
(the picture can be zoomed in)
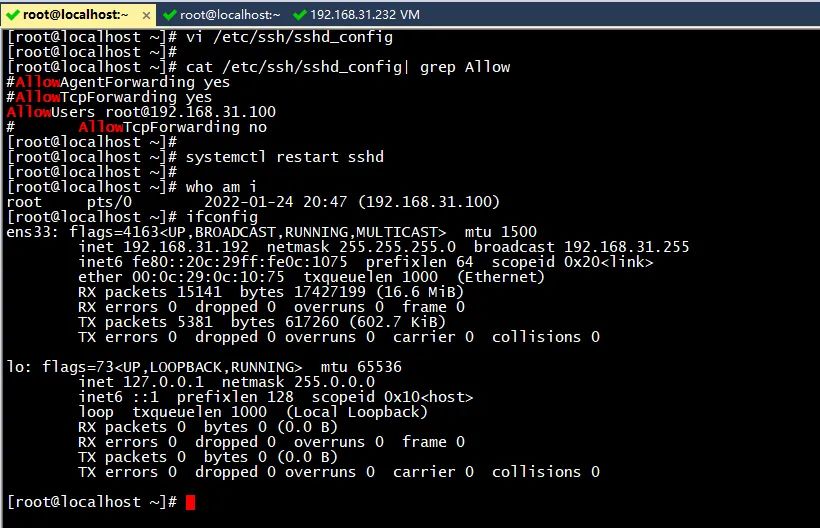
Authentication: 192.168.31.232 try SSH login to CentOS Stream 9 192.168.31.192
Entering the correct password will also prompt login failure
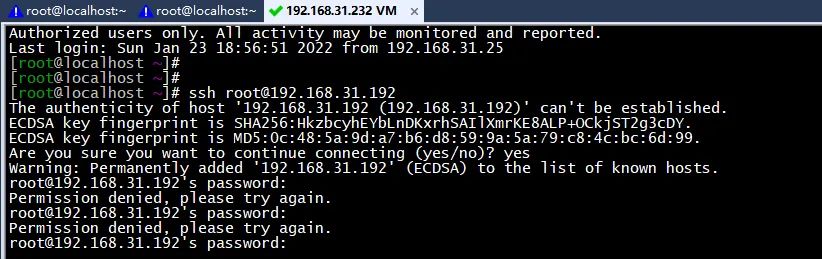
(the picture can be zoomed in)
Viewing logs on the CentOS Stream 9 server
tail -f /var/log/secure You can see the following log Jan 24 21:07:47 localhost sshd[1447]: User root from 192.168.31.232 not allowed because not listed in AllowUsers
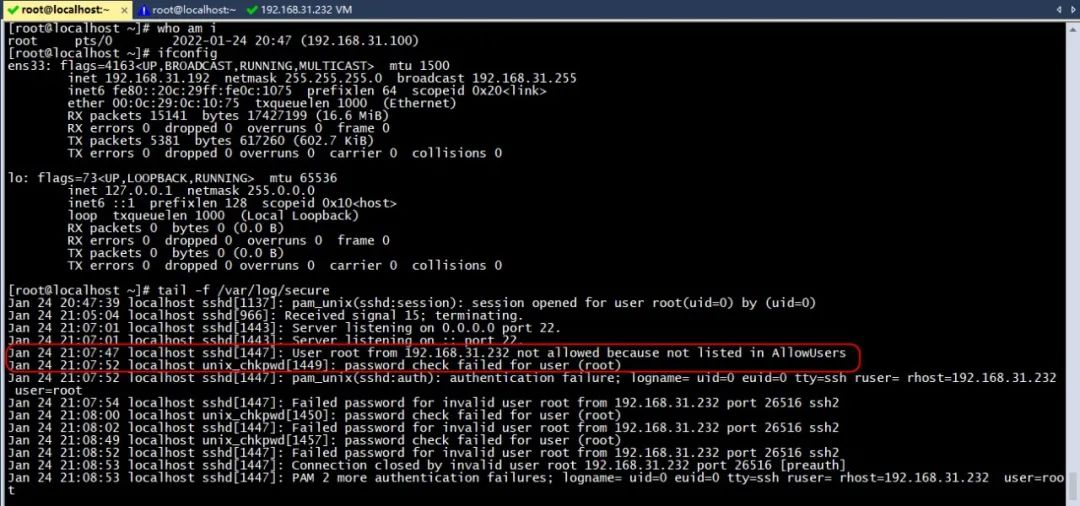
(the picture can be zoomed in)
In this way, SSH access control can be realized
When the line AllowUsers is commented out and the sshd service is restarted, you can log in normally
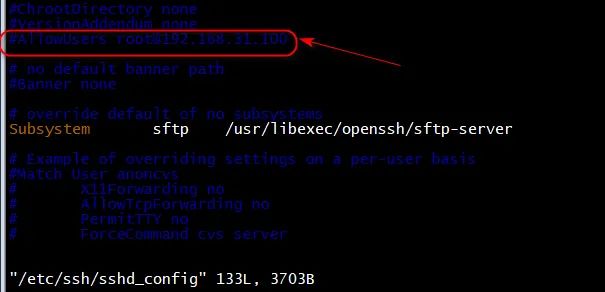
(the picture can be zoomed in)
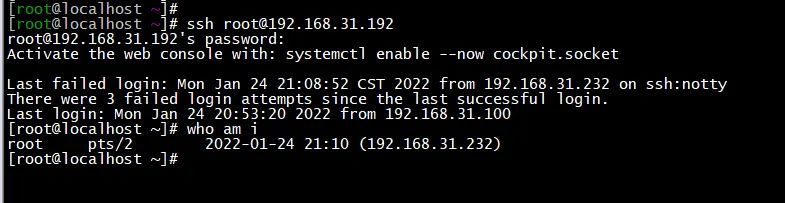
(the picture can be zoomed in)
Tips:
CentOS Linux 8 will no longer support / etc / hosts Allow and / etc / hosts deny
1,CentOS Linux 8
2,CentOS Stream 9
3,CentOS Stream 8
The above three systems can realize SSH access control according to the method in this paper