explain:
Today, I found a useful tool that can rename local files or folders in batches and replace them in batches.
Just. macos, linux and window s.
Installation and use documents of each platform
Tool usage:
The rest of me will touch and search to learn how to use this tool on windows.
1. windows installation:
Find the tags directory of the project, and then I now a latest version.
For example, download address: https://github.com/ayoisaiah/f2/releases/tag/v1.6.7
I choose win64 bit to download here.
After downloading and decompressing, put it in the fixed drive letter and add the directory to the environment variable.
2. Usage view:
1. View usage notes
win+R enters cmd, and then enter:
f2 -h
E:\>f2 -h
DESCRIPTION:
F2 is a command-line tool for batch renaming multiple files and directories quickly and safely
USAGE:
f2 FLAGS [OPTIONS] [PATHS...]
AUTHOR:
Ayooluwa Isaiah <ayo@freshman.tech>
VERSION:
v1.6.7
FLAGS:
-f, --find <pattern>
Search pattern. Treated as a regular expression by default unless --string-mode is also used. If omitted, it defaults to the entire file name (including the extension).
-r, --replace <string>
Replacement string. If omitted, defaults to an empty string. Supports built-in and regex capture variables. Learn more about variable support here: https://github.com/ayoisaiah/f2/wiki/Built-in-variables
-u, --undo
Undo the last operation performed in the current working directory if possible. Learn more: https://github.com/ayoisaiah/f2/wiki/Undoing-a-renaming-operation
OPTIONS:
-l, --replace-limit <integer>
Limit the number of replacements to be made on the file name (replaces all matches if set to 0). Can be set to a negative integer to start replacing from the end of the file name.
-s, --string-mode
Opt into string literal mode. The presence of this flag causes the search pattern to be treated as a non-regex string.
-E, --exclude <pattern>
Exclude files/directories that match the given search pattern. Treated as a regular expression. Multiple exclude patterns can be specified.
-x, --exec
Execute the batch renaming operation. This will commit the changes to your filesystem.
-R, --recursive
Recursively traverse all directories when searching for matches. Use the --max-depth flag to control the maximum allowed depth (no limit by default).
-m, --max-depth <integer>
Positive integer indicating the maximum depth for a recursive search (set to 0 for no limit).
--sort <sort>
Sort the matches according to the provided '<sort>'.
Allowed sort values:
'default': alphabetical order
'size': file size
'mtime': file last modified time
'btime': file creation time (Windows and macOS only)
'atime': file last access time
'ctime': file metadata last change time
--sortr <sort>
Same as --sort but presents the matches in the reverse order.
-i, --ignore-case
When this flag is provided, the given pattern will be searched case insensitively.
-q, --quiet
Activate silent mode which doesn't print out any information including errors
-e, --ignore-ext
Ignore the file extension when searching for matches.
-d, --include-dir
Include directories when searching for matches as they are exempted by default.
-D, --only-dir
Rename only directories, not files (implies --include-dir)
-H, --hidden
Include hidden directories and files in the matches (they are skipped by default). A hidden file or directory is one whose name starts with a period (all operating systems) or one whose hidden attribute is set to true (Windows only)
-F, --fix-conflicts
Automatically fix conflicts based on predefined rules. Learn more: https://github.com/ayoisaiah/f2/wiki/Validation-and-conflict-detection
--allow-overwrites
Allow the overwriting of existing files
-h, --help
show help
-v, --version
print the version
DOCUMENTATION:
https://github.com/ayoisaiah/f2/wiki
WEBSITE:
https://github.com/ayoisaiah/f2
Corresponding Chinese translation explanation:
Flag:
-f, --find <pattern>
Search mode. By default, it is treated as a regular expression unless it is also used --string-mode. If omitted, it defaults to the entire file name (including the extension).
-r, --replace <character string>
Replace string. If omitted, it defaults to an empty string. Supports built-in and regular expression capture variables. Learn more about variable support here: https://github.com/ayoisaiah/f2/wiki/Built-in-variables
-u,--undo
If possible, undo the last action performed in the current working directory. Learn more: https://github.com/ayoisaiah/f2/wiki/Undoing-a-renaming-operation
Options:
-l, --replace-limit <integer>
Limit the number of file name replacements (if set to 0, all matches are replaced). Can be set to a negative integer to replace from the end of the file name.
-s, --string-mode
Select string text mode. The presence of this flag causes the search pattern to be treated as a non regular expression string.
-E, --exclude <pattern>
Exclude files that match the given search pattern/catalogue Treat as regular expressions. You can specify multiple exclusion modes.
-x, --exec
Perform a batch rename operation. This will commit the changes to your file system.
-R, --recursion
Recursively traverses all directories when searching for matches. use --max-depth Flag to control the maximum depth allowed (there is no limit by default).
-m, --max-depth <integer>
A positive integer indicates the maximum depth of recursive search (set to 0 to no limit).
--sort <sort>
According to the information provided“<sort>"Sort matches.
Allowed sort values:
"Default: alphabetical order
"Size: file size
'mtime': Last modification time of file
'btime': File creation time (only) Windows and macOS)
'atime': File last accessed
'ctime': Last change time of file metadata
--sortr <sort>
And --sort Same, but displays matches in reverse order.
-i, --ignore-case
When this flag is provided, the given pattern is searched case insensitive.
-q, --be quiet
Activate silent mode that does not print any information, including errors
-e, --ignore-ext
Ignore file extensions when searching for matches.
-d, --include-dir
Include directories when searching for matches because they are exempt by default.
-D, --only-dir
Rename directories only, not files (implied) --include-dir)
-H, --hide
Include hidden directories and files in the match (they are skipped by default). Hidden files or directories are files or directories whose names begin with a period (all operating systems) or whose hidden properties are set to true File or directory for (only) Windows)
-F, --fix-conflicts
Automatically fix conflicts based on predefined rules. Learn more: https://github.com/ayoisaiah/f2/wiki/Validation-and-conflict-detection
--allow-overwrites
Allow existing files to be overwritten
-h, --help
Show help
-v, --version
Print version
2. Prepare a catalog file
To view the prepared file tree:
Note:
Under Windows: tree /f, under linux: tree -f
E:\photos\f2-demo>tree /f
volume data Folder for PATH list
The volume serial number is 2 EC0-3153
E:.
├─76296_Top charming beauty ecstatic breast hotel human body art photo wallpaper
│ 0.jpg
│
├─76474_Pure double ponytail beautiful rail photo mobile phone wallpaper
│ 0.jpg
│ 1.jpg
│ 2.jpg
│ 3.jpg
│ 4.jpg
│ 5.jpg
│ 6.jpg
│ 7.jpg
│ 8.jpg
│
├─77478_Healing Department beauty sexy off shoulder private room photo mobile phone wallpaper
│ 0.jpg
│ 1.jpg
│ 2.jpg
│
├─78727_Home playful beauty private house sexy photo mobile phone wallpaper
│ 0.jpg
│ 1.jpg
│
├─79401_Christmas vitality beauty lovely photo mobile wallpaper
│ 0.jpg
│ 1.jpg
│ 2.jpg
│ 3.jpg
│ 4.jpg
│ 5.jpg
│
├─80835_Long hair beauty pure and gentle photo mobile phone wallpaper
│ 0.jpg
│ 1.jpg
│ 2.jpg
│ 3.jpg
│ 4.jpg
│ 5.jpg
│
├─82663_Pure oxygen beauty home eye care photo mobile phone wallpaper
│ 0.jpg
│ 1.jpg
│ 2.jpg
│ 3.jpg
│ 4.jpg
│
└─85483_Pure and lovely beauty private house sexy and playful photo mobile phone wallpaper
0.jpg
1.jpg
3. Common search test
1) , search folder or file name contains the results of beauty
f2 -f beauty -d -R
Search results include folders. You need to add -d references. By default, folders are not included.
I found and modified several subdirectories here, named them and added "beauty", so I found them.
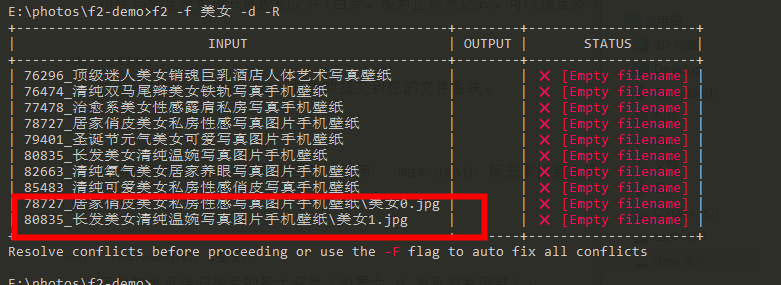
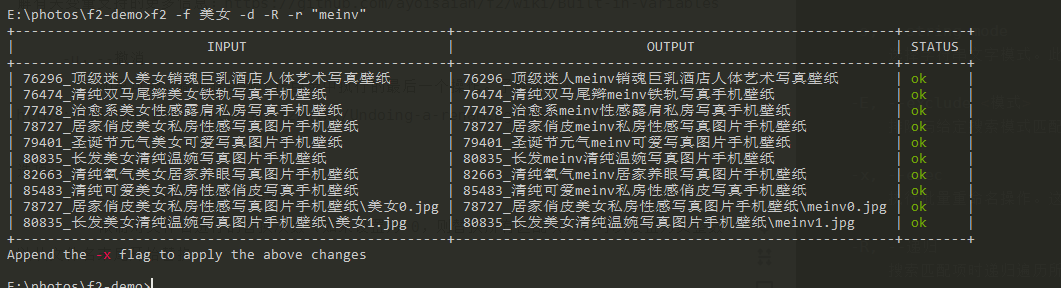
2) Replace search results with preview:
f2 -f beauty -d -R -r "meinv"
At this time, the local file will not be changed. Add - x to perform the replacement.
# After execution, the preview interface will not be displayed, and the local file name and folder will be modified directly f2 -f beauty -d -R -r "meinv" -x


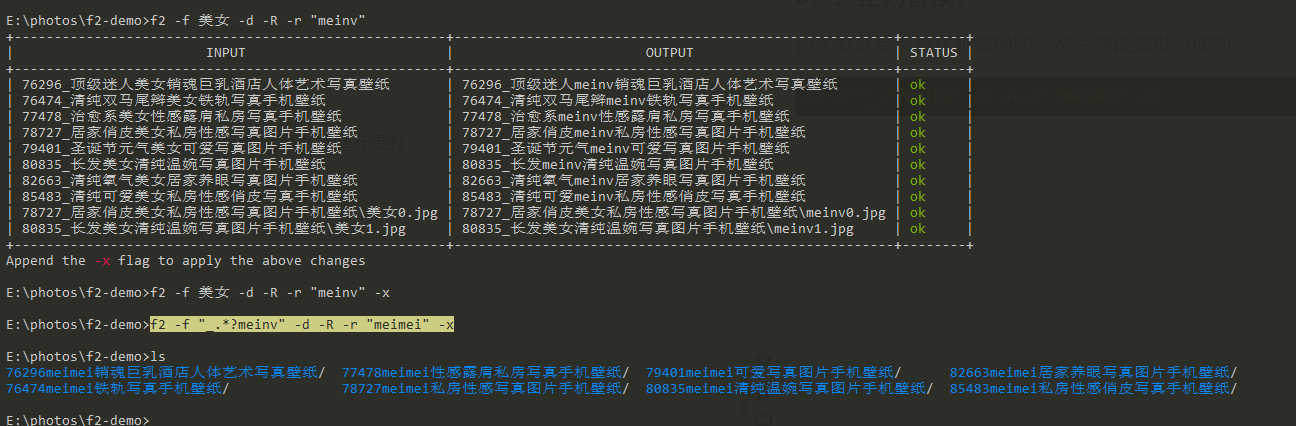
3) . regular replacement:
Since regular substitution is supported by default, it is very convenient to test
f2 -f "_.*?meinv" -d -R -r "meimei" -x
The comparison shows that the underlined and meinv direct directories have been replaced with meimei.
Summary:
For more usage, it depends on your own needs. I think it is completely easy to rename regular files in a directory.
However, for a directory, there are too many subdirectories or many files [for example, millions, the performance is unknown]
However, for batch renaming or part of it, it is simply convenient to fly.