1, Main features of HAProxy
The reliability and stability are very good, which can be comparable to the hardware level F5 load balancing equipment;
● up to 40000-50000 concurrent connections can be maintained at the same time, the maximum number of requests processed per unit time is 20000, and the maximum processing capacity can reach 10Git/s;
● support up to 8 load balancing algorithms and session maintenance;
● support the function of virtual machine host, so as to realize more flexible web load balancing;
● support unique functions such as connection rejection and fully transparent proxy;
● strong ACL support for access control;
● its unique elastic binary tree data structure increases the complexity of the data structure to 0 (1), that is, the search speed of data will not decrease with the increase of data entries;
● support the keepalive function of the client, reduce the waste of resources caused by multiple handshakes between the client and haproxy, and allow multiple requests to be completed in one tcp connection;
● support TCP acceleration and zero replication function, similar to mmap mechanism;
● support response buffering;
● support RDP protocol;
● source based stickiness, similar to nginx's ip_hash function, which always schedules requests from the same client to the same upstream server within a certain period of time;
● better statistical data interface, whose web interface displays the statistical information of data received, sent, rejected, error and other data of each server in the back-end cluster;
● detailed health status detection. The web interface has the health detection status of the upstream server, and provides certain management functions;
● flow based health assessment mechanism;
● http based authentication;
● management interface based on command line;
● log analyzer, which can analyze logs.
2, Eight common load balancing strategies of HAProxy
● roundrobin: indicates simple polling.
● static RR: indicates the weight.
● leastconn: indicates that the least connected person will handle it first.
● source: indicates the source IP according to the request, which is similar to the IP of Nginx_ Hash mechanism.
● ri: indicates the URI according to the request.
●rl_param: it means to lock every HTTP request according to the HTTP request header.
● RDP cookie(name): it means that each TCP request is locked and hashed according to the cookie(name).
3, Differences among LVS, Nginx and HAproxy
LVS realizes soft load balancing based on Linux operating system, while HAProxy and Nginx realize soft load balancing based on third-party applications;
LVS is a 4-layer IP load balancing technology, which can not realize forwarding based on directory and URL. Both HAProxy and Nginx can implement layer 4 and layer 7 technologies. HAProxy can provide a comprehensive load balancing solution for TCP and HTTP applications;
Because LVS works in the fourth layer of ISO model, its status monitoring function is single, while HAProxy has richer and more powerful functions in status monitoring, and can support port, URL, script and other status detection methods;
HAProxy is powerful, but its overall performance is lower than LVS load balancing in layer 4 mode.
Nginx is mainly used for Web servers or cache servers.
4, Building Web cluster with Haproxy
| server name | IP address |
|---|---|
| Haproxy server | 192.168.73.88 |
| Nginx server 1 | 192.168.73.188 |
| Nginx server 2 | 192.168.73.166 |
| client | 192.168.73.200 |
1. Close the firewall and transfer the software package required to install Haproxy to the / opt directory
systemctl stop firewalld setenforce 0 haproxy-1.5.19.tar.gz
2. Compile and install Haproxy
yum install -y pcre-devel bzip2-devel gcc gcc-c++ make tar zxvf haproxy-1.5.19.tar.gz cd haproxy-1.5.19/ make TARGET=linux2628 ARCH=x86_64 make install
3. Haproxy server configuration
mkdir /etc/haproxy
cd /opt/haproxy-1.5.19/examples
cp haproxy.cfg /etc/haproxy/
cd /etc/haproxy/
vim haproxy.cfg
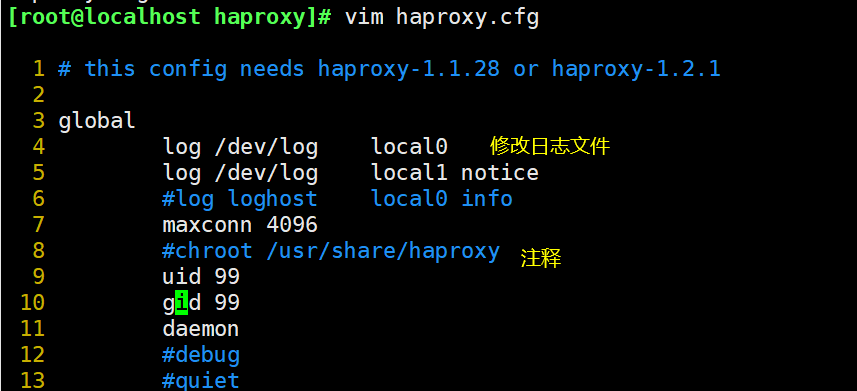
global
--------4~5 that 's ok------Modify, configure logging, local0 It is a log device and is stored in the system log by default
log /dev/log local0 info
log /dev/log local0 notice
#log loghost local0 info
maxconn 4096 #For the maximum number of connections, consider the ulimit -n limit
--------8 that 's ok------notes, chroot The running path is the root directory set by the service itself. Generally, this line needs to be commented out
#chroot /usr/share/haproxy
uid 99 #User UID
gid 99 #User GID
daemon #Daemon mode
defaults
log global #Define log is the log definition in global configuration
mode http #The mode is http
option httplog #Log in http log format
option dontlognull #Do not record health check log information
retries 3 #Check the number of failures of the node server. If there are three consecutive failures, the node is considered unavailable
redispatch #When the server load is very high, it will automatically end the connection that has been queued for a long time
maxconn 2000 #maximum connection
contimeout 5000 #Connection timeout
clitimeout 50000 #Client timeout
srvtimeout 50000 #Server timeout
--Delete all below listen term--,add to
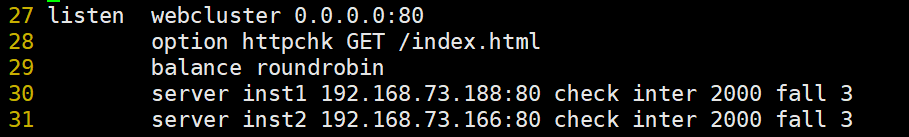
listen webcluster 0.0.0.0:80 #Define an application called webcuster
option httpchk GET /index.html #Check the index of the server HTML file
balance roundrobin #The load balancing scheduling algorithm uses the polling algorithm roundrobin
server inst1 192.168.73.188:80 check inter 2000 fall 3 #Define online nodes
server inst2 192.168.73.166:80 check inter 2000 fall 3
4. Add haproxy system service
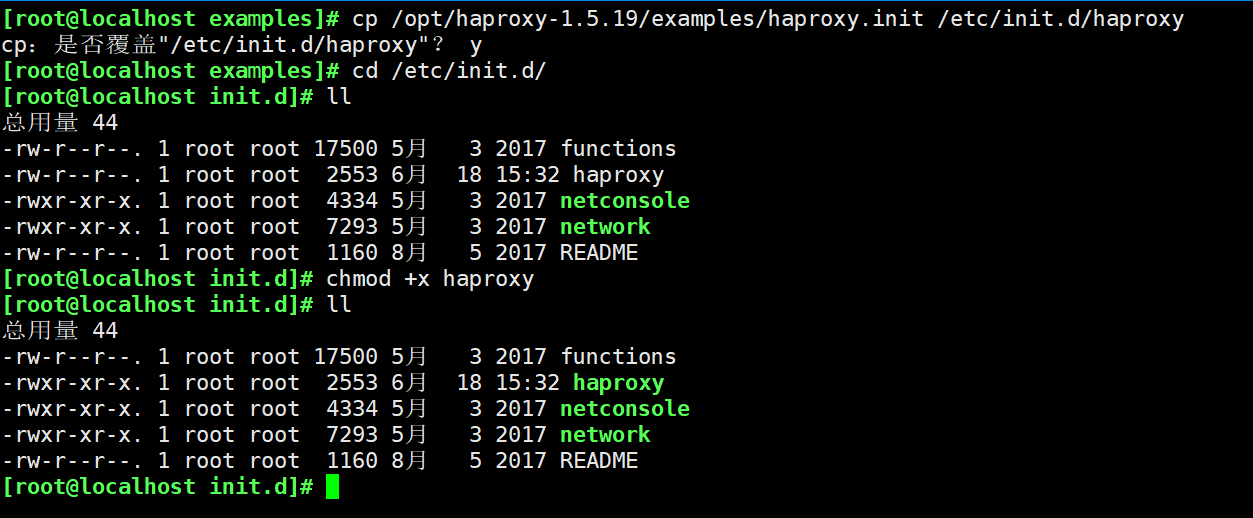
cp /opt/haproxy-1.5.19/examples/haproxy.init /etc/init.d/haproxy chmod +x haproxy chkconfig --add /etc/init.d/haproxy ln -s /usr/local/sbin/haproxy /usr/sbin/haproxy service haproxy start or /etc/init.d/haproxy start

5. Node server deployment (either nginx or apache)
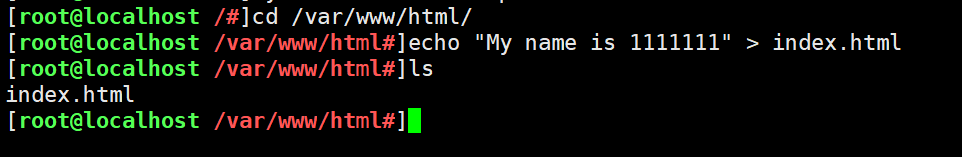
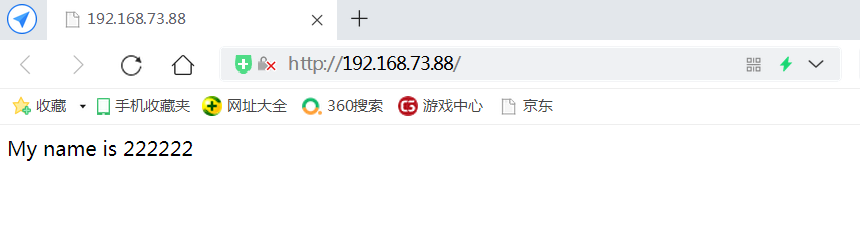
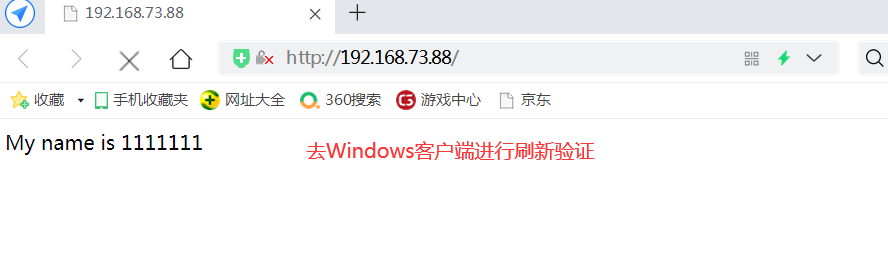
systemctl stop firewalld setenforce 0 yum install -y pcre-devel zlib-devel gcc gcc-c++ make useradd -M -s /sbin/nologin nginx cd /opt tar zxvf nginx-1.12.0.tar.gz -C /opt/ cd nginx-1.12.0/ ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx --user=nginx --group=nginx && make && make install make && make install --192.168.73.166--- echo "this is kgc web" > /usr/local/nginx/html/test.html --192.168.73.188--- echo "this is benet web" > /usr/local/nginx/html/test.html ln -s /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx /usr/local/sbin/ nginx #Start nginx service -------------------------Or use httpd Service to test, more convenient--------------------------- systemctl stop firewalld setenforce 0 yum install -y httpd systemctl start httpd ----------------------192.168.73.166---------------------- cd /var/www/html/ echo "My name is 1111111" > index.html ----------------------192.168.73.188---------------------- cd /var/www/html/ echo "My name is 2222222" > index.html

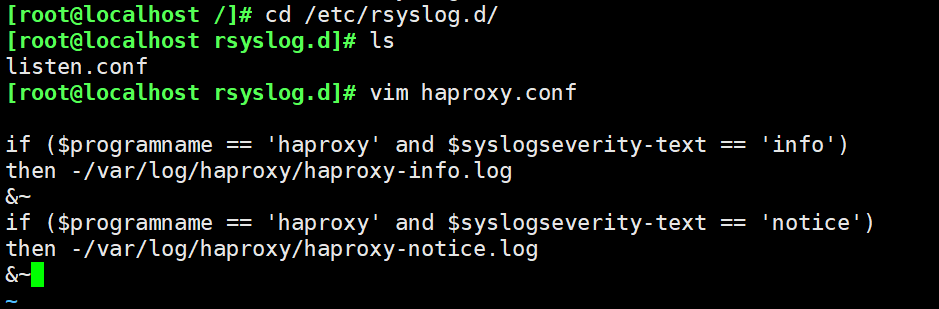
6. Log definition
By default, the log of haproxy is output to the syslog of the system, which is not very convenient to view. In order to better manage the log of haproxy, we generally define it separately in the production environment. The info and notice logs of haproxy need to be recorded in different log files.
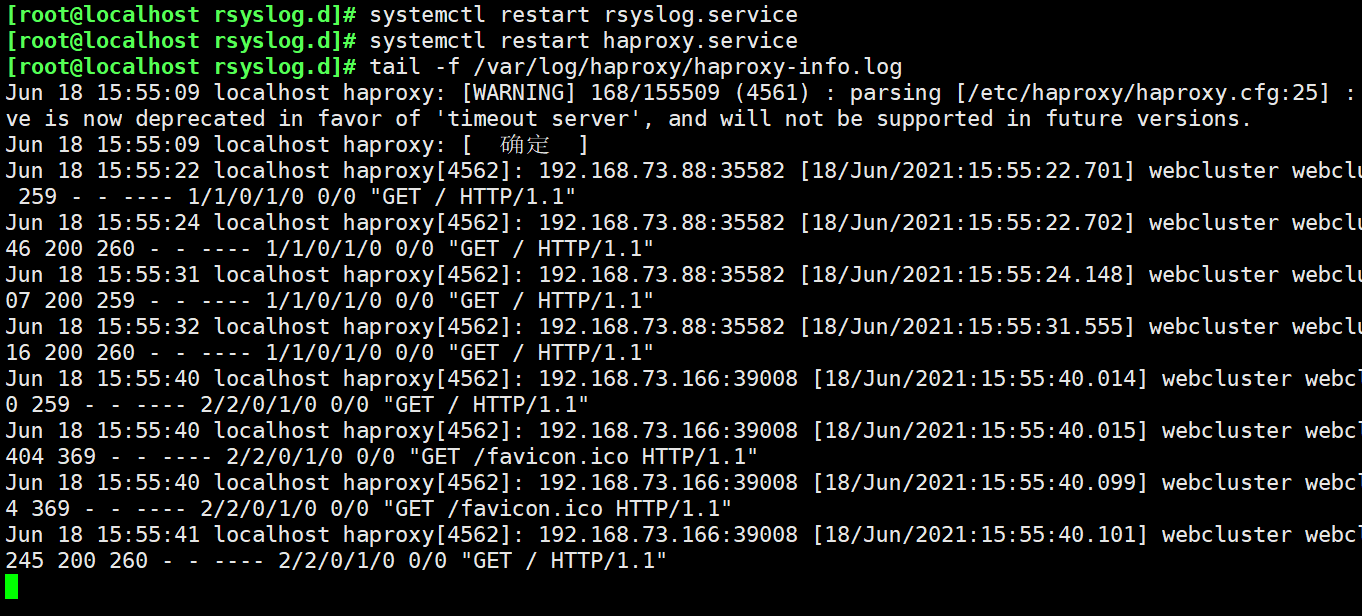
vim /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg global log /dev/log local0 info log /dev/log local0 notice service haproxy restart #The rsyslog configuration needs to be modified to facilitate management. Define the configuration related to haproxy independently to haproxy Conf and put it in / etc / rsyslog D /, all configuration files in this directory will be loaded automatically when rsyslog is started. vim /etc/rsyslog.d/haproxy.conf if ($programname == 'haproxy' and $syslogseverity-text == 'info') then -/var/log/haproxy/haproxy-info.log &~ if ($programname == 'haproxy' and $syslogseverity-text == 'notice') then -/var/log/haproxy/haproxy-notice.log &~ #explain: This part of the configuration will haproxy of info Log to/var/log/haproxy/haproxy-info.log Next, the notice Log to/var/log/haproxy/haproxy-notice.log Down. “&~"Indicates that after the log is written to the log file, rsyslog Stop processing this message. systemctl restart rsyslog.service tail -f /var/log/haproxy/haproxy-info.log #View the access request log information of haproxy