reference
Install Let's Encrypt certificate through Certbot to realize HTTPS access of the whole station
College army - upgrade blog application from HTTP protocol to HTTPS for free
certbot official website address
- Open the home page and select your own system version first (the web server I use here is nginx and the system is centos7) Transmission gate
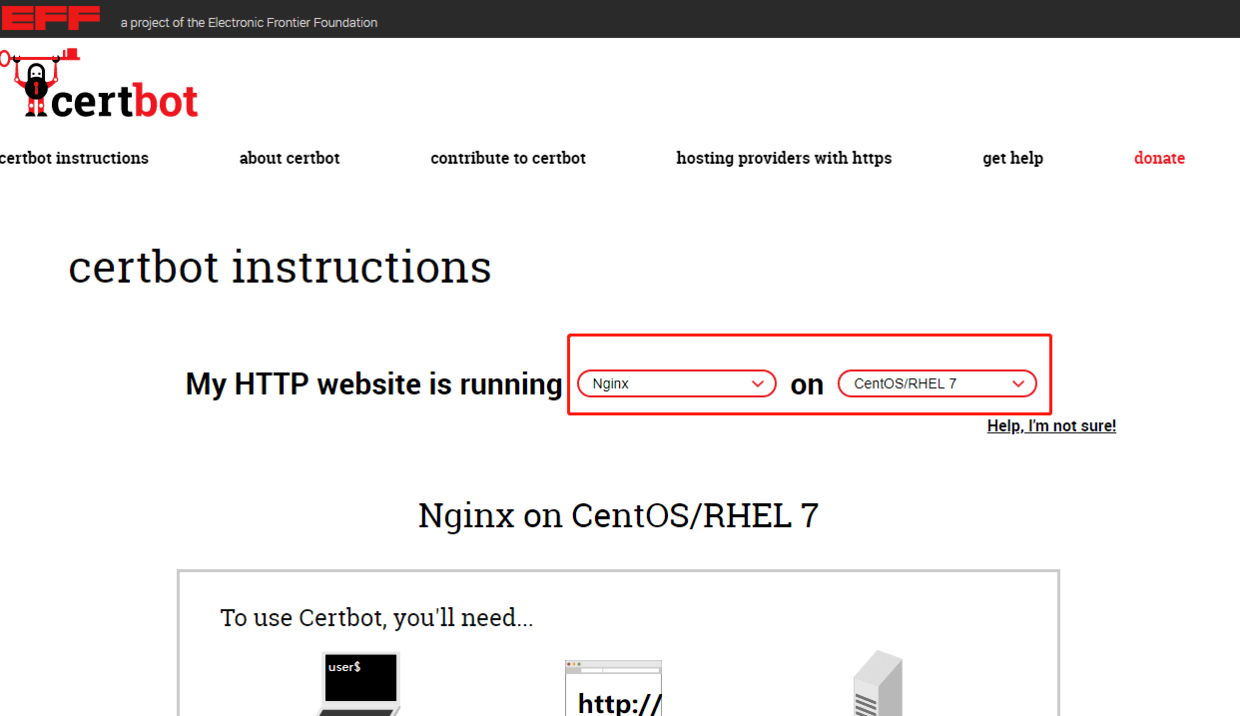
- You can execute commands according to the operation documents provided on the official website
# Install the certbot client tool sudo yum install certbot python2-certbot-nginx # Automatically detect nginx configuration and determine which websites need to be configured with ssl (all nginx configuration information will be listed) sudo certbot --nginx # Set crontab scheduling tasks to automatically update ssl certificates echo "0 0,12 * * * root python -c 'import random; import time; time.sleep(random.random() * 3600)' && certbot renew -q" | sudo tee -a /etc/crontab > /dev/null
The following records the whole process of installing certbot
System environment
Server: Alibaba cloud server
System: centos 7
web server: nginx
Install the pagoda (after installing the pagoda, the main configuration file of nginx is located at / www/server/nginx/conf /)
The overall process is operated according to the process on the official website, but various problems will be encountered. The problems are as follows:
- Install the certbot client tool (this process is normal). During the installation process, press enter if you want to enter directly. Select Yes, enter Y, and then press enter
sudo yum install certbot python2-certbot-nginx
- An error occurred while configuring ssl, as follows:
sudo certbot --nginx
Important error messages are as follows:
pkg_resources.ContextualVersionConflict: (cryptography 2.1 (/usr/lib64/python2.7/site-packages), Requirement.parse('cryptography>=2.3'), set(['PyOpenSSL']))
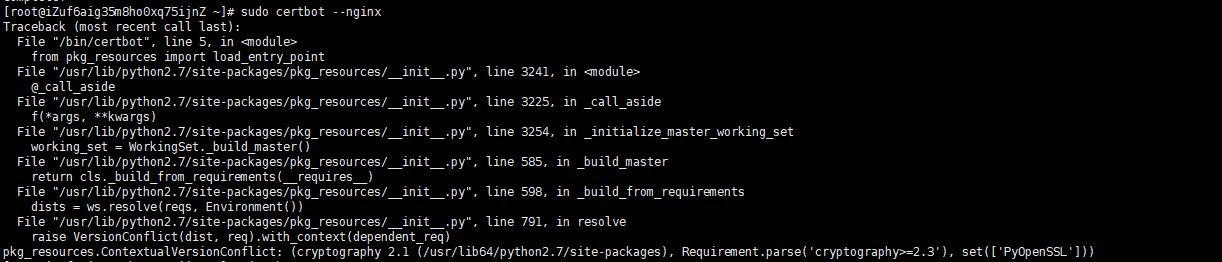
Check the PyOpenSSL version information and find that it is really the reason why the version is too low
pip show PyOpenSSL
Solution: update the corresponding python package
pip install -U PyOpenSSL pip install -U cryptography
Execute the following command again
sudo certbot --nginx
The error message is as follows:
ImportError: cannot import name UnrewindableBodyError
Solution: install the corresponding python package
# Update pip pip install --upgrade pip # Uninstall urllib3 pip uninstall urllib3 # Download again pip install urllib3
Execute the following command again
sudo certbot --nginx
The error message is as follows:
ImportError: No module named urllib3.exceptions
Solution: download the corresponding pyOpenSSL package directly
yum -y install http://cbs.centos.org/kojifiles/packages/pyOpenSSL/16.2.0/3.el7/noarch/python2-pyOpenSSL-16.2.0-3.el7.noarch.rpm
Execute the following command again
sudo certbot --nginx
Continue to report errors as follows:
Error while running nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf -t.
nginx: [emerg] open() "/etc/nginx/nginx.conf" failed (2: No such file or directory)
nginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test failed
The nginx plugin is not working; there may be problems with your existing configuration.
The error was: MisconfigurationError('Error while running nginx -c /etc/nginx/nginx.conf -t.\n\nnginx: [emerg] open() "/etc/nginx/nginx.conf" failed (2: No such file or directory)\nnginx: configuration file /etc/nginx/nginx.conf test failed\n',)
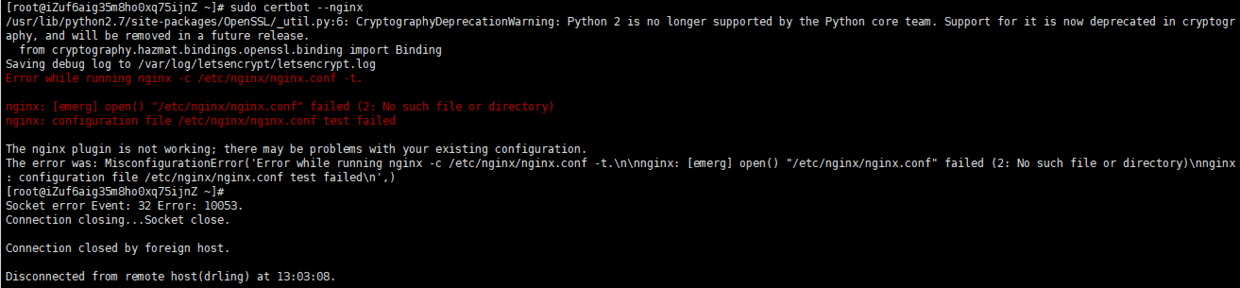
The reason is: pagoda installs the main configuration file of nginx in / www/server/nginx/conf / directory, but certbot scans / etc / nginx / nginx by default Conf file, so the configuration file of nginx cannot be found
Solution: specify the configuration directory of nginx and execute the following command
sudo certbot --nginx --nginx-server-root=/www/server/nginx/conf/
Unfortunately, however, errors are still reported. The error information is as follows:
An unexpected error occurred: TypeError: from_buffer() cannot return the address of the raw string within a str or unicode or bytearray object
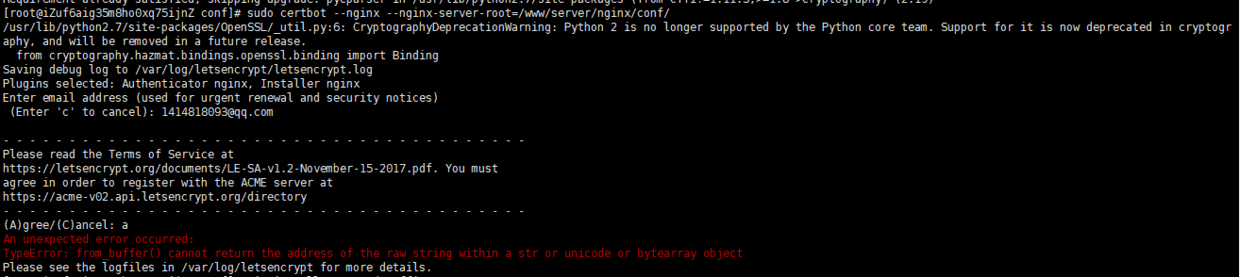
Solution: update cffi package and execute the following command
pip install --upgrade cffi
After installation, execute the following command again
sudo certbot --nginx --nginx-server-root=/www/server/nginx/conf/
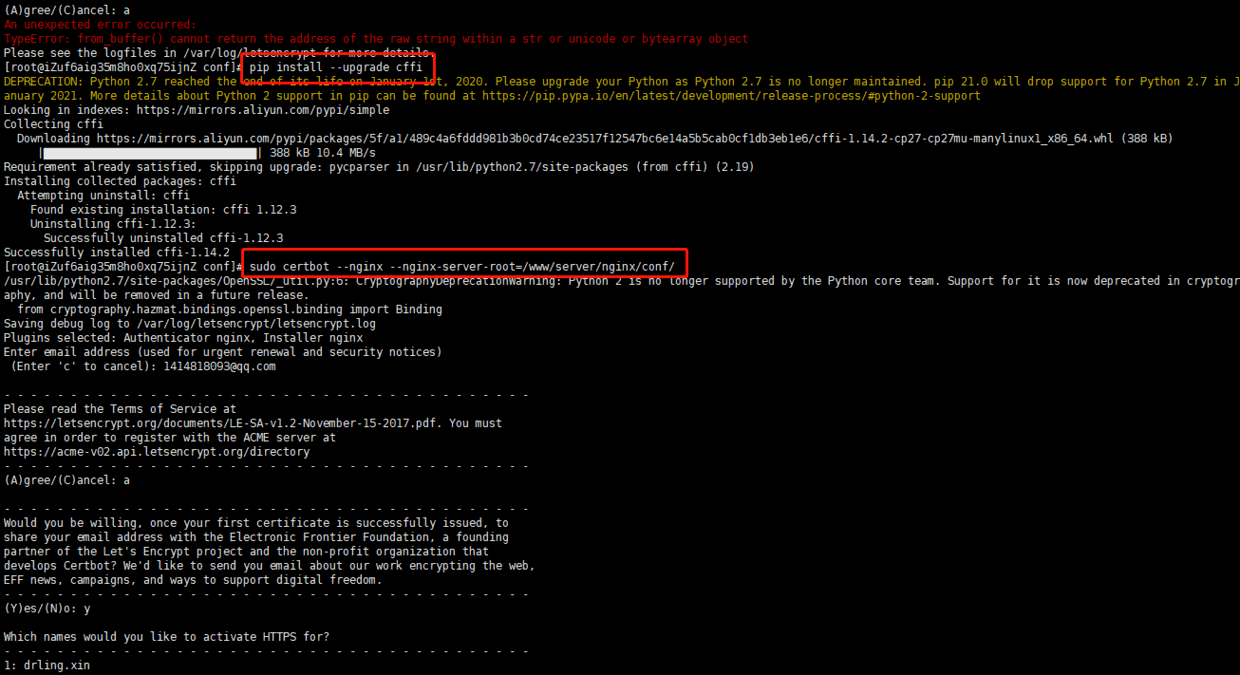
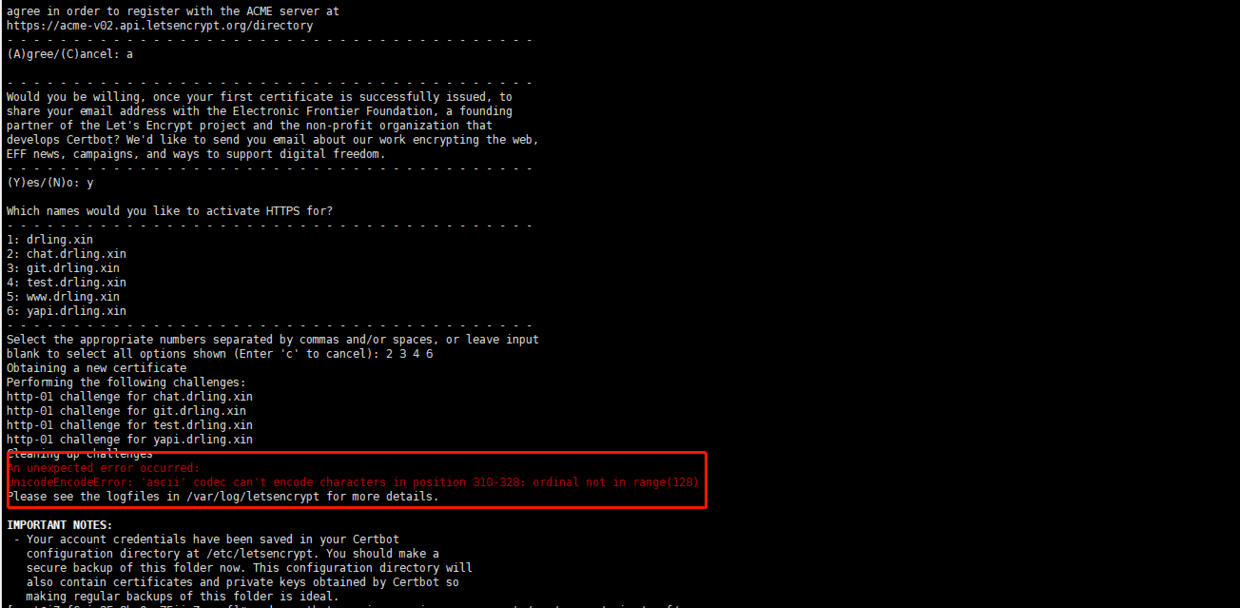
The error information is as follows:
An unexpected error occurred: UnicodeEncodeError: 'ascii' codec can't encode characters in position 310-328: ordinal not in range(128)
About ascii error reporting, this article has a detailed introduction Install Let's Encrypt certificate through Certbot to realize HTTPS access of the whole station
The solution is: check whether the nginx configuration file you choose to configure contains Chinese. Just remove all Chinese
After removing, execute the following command again
sudo certbot --nginx --nginx-server-root=/www/server/nginx/conf/
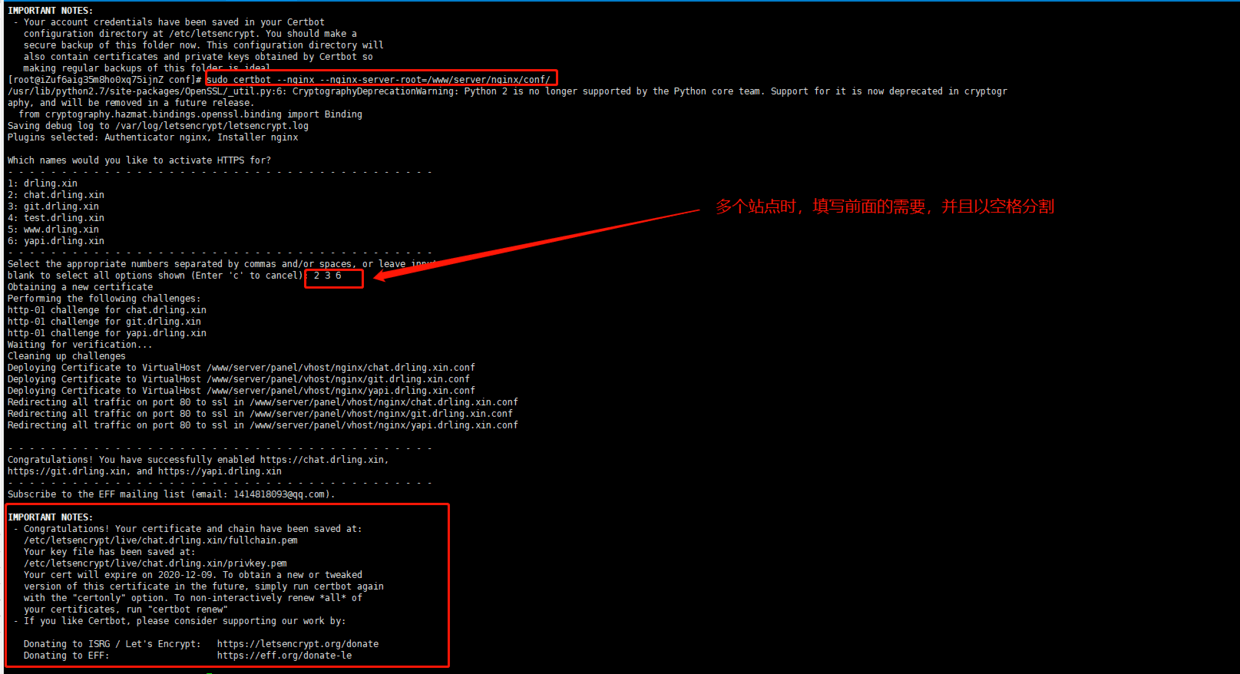
be accomplished!
Compare the nginx configuration before ssl configuration
nginx information before ssl is not configured
server
{
server_name www.pudongping.com;
index index.php index.html index.htm default.php default.htm default.html;
root /www/wwwroot/www.pudongping.com;
location ~ ^/(\.user.ini|\.htaccess|\.git|\.svn|\.project|LICENSE|README.md)
{
return 404;
}
}
Configuration information after configuring ssl (https is mandatory redirection by default in the configuration file)
server
{
server_name www.pudongping.com;
index index.php index.html index.htm default.php default.htm default.html;
root /www/wwwroot/www.pudongping.com;
location ~ ^/(\.user.ini|\.htaccess|\.git|\.svn|\.project|LICENSE|README.md)
{
return 404;
}
listen 443 ssl; # managed by Certbot
ssl_certificate /etc/letsencrypt/live/www.pudongping.com/fullchain.pem; # managed by Certbot
ssl_certificate_key /etc/letsencrypt/live/www.pudongping.com/privkey.pem; # managed by Certbot
include /etc/letsencrypt/options-ssl-nginx.conf; # managed by Certbot
ssl_dhparam /etc/letsencrypt/ssl-dhparams.pem; # managed by Certbot
}
server
{
if ($host = www.pudongping.com) {
return 301 https://$host$request_uri;
} # managed by Certbot
listen 80;
server_name www.pudongping.com;
return 404; # managed by Certbot
}
Automatically update certificates
Since the default validity period of Let's Encrypt is 90 days, if your application needs to provide long-term services in the production environment and update the certificate after the certificate expires, we can update the certificate through the certbot renew command. You can test whether the command is effective through the following command:
sudo certbot renew --dry-run
If you see the following words in the output, it is effective:
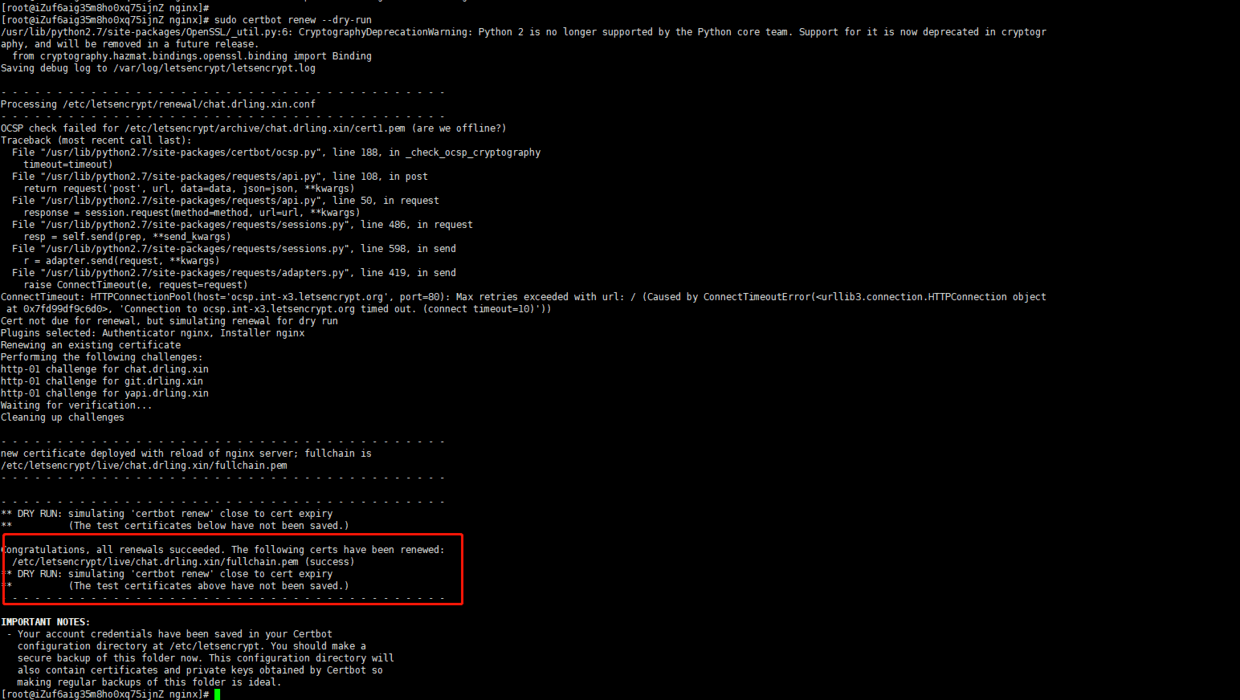
Of course, manual maintenance is impractical in the real environment. We can use cronab to write a scheduled task, forcibly update this certificate every month, and then restart Nginx:
0 0 1 * * certbot renew 5 0 1 * * service nginx restart
Or directly execute the orders provided by the official
echo "0 0,12 * * * root python -c 'import random; import time; time.sleep(random.random() * 3600)' && certbot renew -q" | sudo tee -a /etc/crontab > /dev/null
About catalog
- The configuration file directory of Certbot is in / etc/letsencrypt
- The log default path of Certbot is / var/log/letsencrypt
- Corresponding to the website The path of the PEM file is in / etc/letsencrypt/live / website name / privkey pem