react source code analysis 12 Status update process
Video Explanation (efficient learning): Enter learning
setState&forceUpdate
Several ways to trigger status update in react:
- ReactDOM.render
- this.setState
- this.forceUpdate
- useState
- useReducer
Let's focus on this Setstate and this Forceupdate, hook in Chapter 13
-
this. Call this in setstate updater. Enqueuesetstate is mainly used to add update to updateQueue
//ReactBaseClasses.js Component.prototype.setState = function (partialState, callback) { if (!(typeof partialState === 'object' || typeof partialState === 'function' || partialState == null)) { { throw Error( "setState(...): takes an object of state variables to update or a function which returns an object of state variables." ); } } this.updater.enqueueSetState(this, partialState, callback, 'setState'); };//ReactFiberClassComponent.old.js enqueueSetState(inst, payload, callback) { const fiber = getInstance(inst);//fiber instance const eventTime = requestEventTime(); const suspenseConfig = requestCurrentSuspenseConfig(); const lane = requestUpdateLane(fiber, suspenseConfig);//priority const update = createUpdate(eventTime, lane, suspenseConfig);//Create update update.payload = payload; if (callback !== undefined && callback !== null) { //Assignment callback update.callback = callback; } enqueueUpdate(fiber, update);//update join updateQueue scheduleUpdateOnFiber(fiber, lane, eventTime);//Schedule update }enqueueUpdate is used to add update to the updateQueue queue
//ReactUpdateQueue.old.js export function enqueueUpdate<State>(fiber: Fiber, update: Update<State>) { const updateQueue = fiber.updateQueue; if (updateQueue === null) { return; } const sharedQueue: SharedQueue<State> = (updateQueue: any).shared; const pending = sharedQueue.pending; if (pending === null) { update.next = update;//Form a circular linked list with yourself } else { update.next = pending.next;//Add to the end of the linked list pending.next = update; } sharedQueue.pending = update; }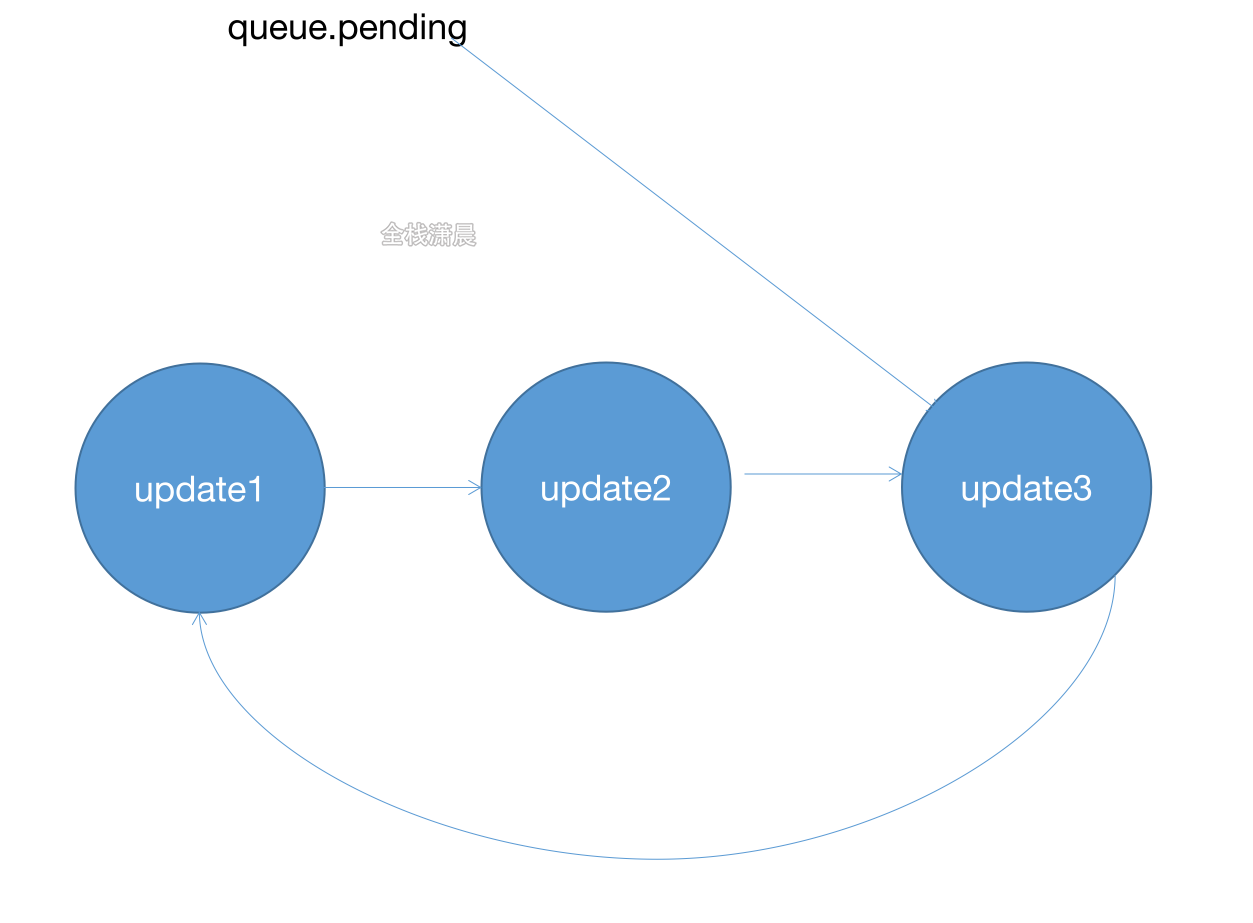
-
this.forceUpdate and this It is the same as setstate, but it will assign the tag ForceUpdate
//ReactBaseClasses.js Component.prototype.forceUpdate = function(callback) { this.updater.enqueueForceUpdate(this, callback, 'forceUpdate'); };//ReactFiberClassComponent.old.js enqueueForceUpdate(inst, callback) { const fiber = getInstance(inst); const eventTime = requestEventTime(); const suspenseConfig = requestCurrentSuspenseConfig(); const lane = requestUpdateLane(fiber, suspenseConfig); const update = createUpdate(eventTime, lane, suspenseConfig); //tag assignment ForceUpdate update.tag = ForceUpdate; if (callback !== undefined && callback !== null) { update.callback = callback; } enqueueUpdate(fiber, update); scheduleUpdateOnFiber(fiber, lane, eventTime); }, };If ForceUpdate is marked, the component Update in the render phase will be judged according to checkHasForceUpdateAfterProcessing and checkShouldComponentUpdate. If the Update tag is ForceUpdate, checkHasForceUpdateAfterProcessing is true. When the component is PureComponent, checkShouldComponentUpdate will shallow compare state and props, so when using this ForceUpdate will be updated
//ReactFiberClassComponent.old.js const shouldUpdate = checkHasForceUpdateAfterProcessing() || checkShouldComponentUpdate( workInProgress, ctor, oldProps, newProps, oldState, newState, nextContext, );Overall process of status update
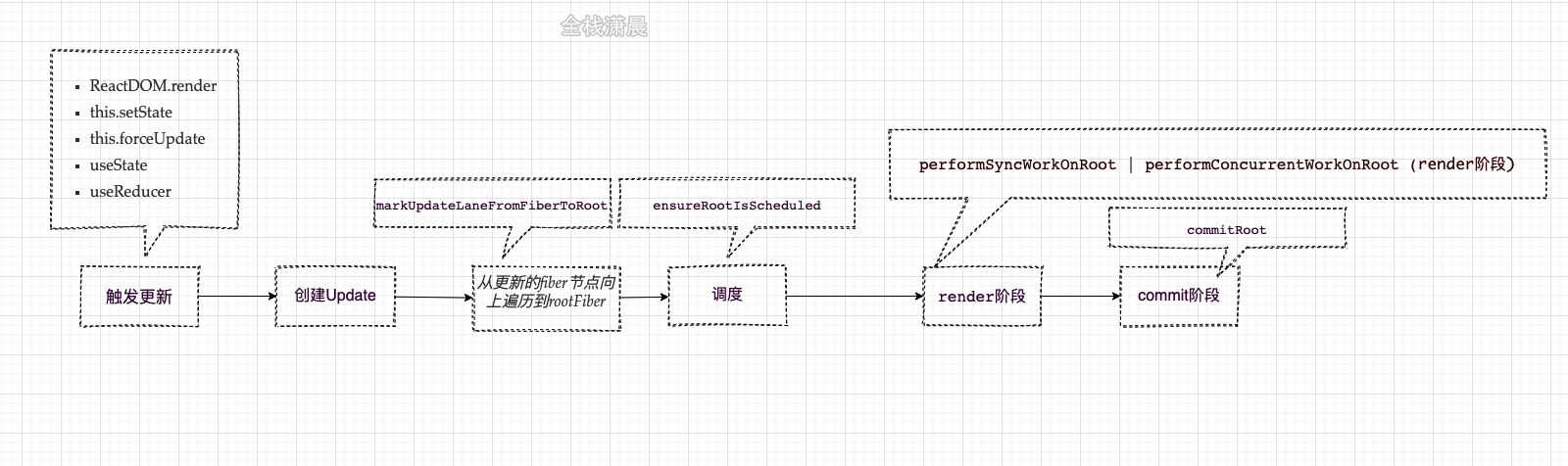
Update&updateQueue
After the update is triggered by HostRoot or ClassComponent, an update will be created in the function createUpdate, and the update will be calculated in beginWork in the later render stage. The update corresponding to functional component is described in Chapter 11. It is somewhat different from the update structure of HostRoot or ClassComponent
//ReactUpdateQueue.old.js
export function createUpdate(eventTime: number, lane: Lane): Update<*> {//Create update
const update: Update<*> = {
eventTime,
lane,
tag: UpdateState,
payload: null,
callback: null,
next: null,
};
return update;
}
We mainly focus on these parameters:
-
lane: priority (Chapter 12)
-
tag: type of update, such as UpdateState and ReplaceState
-
Payload: the payload of ClassComponent is the first parameter of setState, and the payload of HostRoot is reactdom The first parameter of render
-
callback: the second parameter of setState
-
Next: connect the next Update to form a linked list. For example, when multiple setstates are triggered at the same time, multiple updates will be formed, and then connect with next
For HostRoot or ClassComponent, use initializeUpdateQueue to create an updateQueue during mount, and then mount the updateQueue to the fiber node
//ReactUpdateQueue.old.js
export function initializeUpdateQueue<State>(fiber: Fiber): void {
const queue: UpdateQueue<State> = {
baseState: fiber.memoizedState,
firstBaseUpdate: null,
lastBaseUpdate: null,
shared: {
pending: null,
},
effects: null,
};
fiber.updateQueue = queue;
}
- baseState: initial state. Based on this state, a new state will be calculated according to Update
- firstBaseUpdate and lastBaseUpdate: the head and tail of the linked list formed by Update
- shared.pending: the newly generated update will be saved in shared. Net as a one-way circular linked list On pending, when calculating the state, the circular linked list will be cut off and linked after lastBaseUpdate
- effects: update whose callback is not null
Traverse upward from the fiber node triggering the update to rootFiber
In the markUpdateLaneFromFiberToRoot function, it will traverse upward from the node triggering the update to rootFiber, and the traversal process will deal with the priority of the node (Chapter 15)
//ReactFiberWorkLoop.old.js
function markUpdateLaneFromFiberToRoot(
sourceFiber: Fiber,
lane: Lane,
): FiberRoot | null {
sourceFiber.lanes = mergeLanes(sourceFiber.lanes, lane);
let alternate = sourceFiber.alternate;
if (alternate !== null) {
alternate.lanes = mergeLanes(alternate.lanes, lane);
}
let node = sourceFiber;
let parent = sourceFiber.return;
while (parent !== null) {//Start from the node triggering the update and traverse upward to rootFiber
parent.childLanes = mergeLanes(parent.childLanes, lane);//Merge childLanes priority
alternate = parent.alternate;
if (alternate !== null) {
alternate.childLanes = mergeLanes(alternate.childLanes, lane);
} else {
}
node = parent;
parent = parent.return;
}
if (node.tag === HostRoot) {
const root: FiberRoot = node.stateNode;
return root;
} else {
return null;
}
}
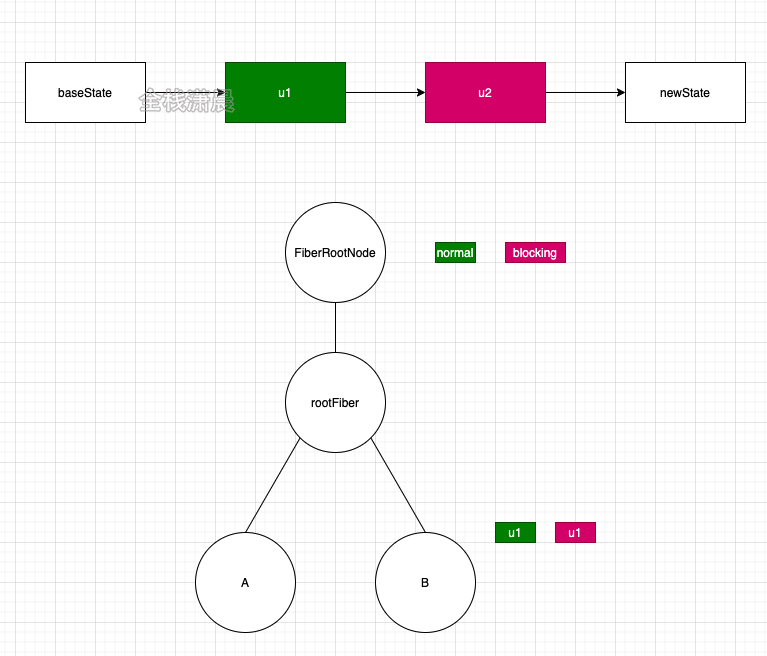
For example, node B triggers an update. Node B is marked as normal update, that is, u1 in the figure, and then traverses upward to the root node, marking a normal update on the root node. If node B triggers another userBlocking update at this time, it will also traverse upward to the root node, marking a userBlocking update on the root node.
If the update priority of the current root node is normal, both u1 and u2 participate in the status calculation. If the update priority of the current root node is userBlocking, only u2 participates in the calculation
dispatch
In ensureroot isscheduled, scheduleCallback will schedule the start function performSyncWorkOnRoot or performcurrentworkonroot of the render phase with a priority
//ReactFiberWorkLoop.old.js
if (newCallbackPriority === SyncLanePriority) {
// The task has expired and the render phase needs to be executed synchronously
newCallbackNode = scheduleSyncCallback(
performSyncWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root)
);
} else {
// The render phase is executed asynchronously according to the task priority
var schedulerPriorityLevel = lanePriorityToSchedulerPriority(
newCallbackPriority
);
newCallbackNode = scheduleCallback(
schedulerPriorityLevel,
performConcurrentWorkOnRoot.bind(null, root)
);
}
Status update
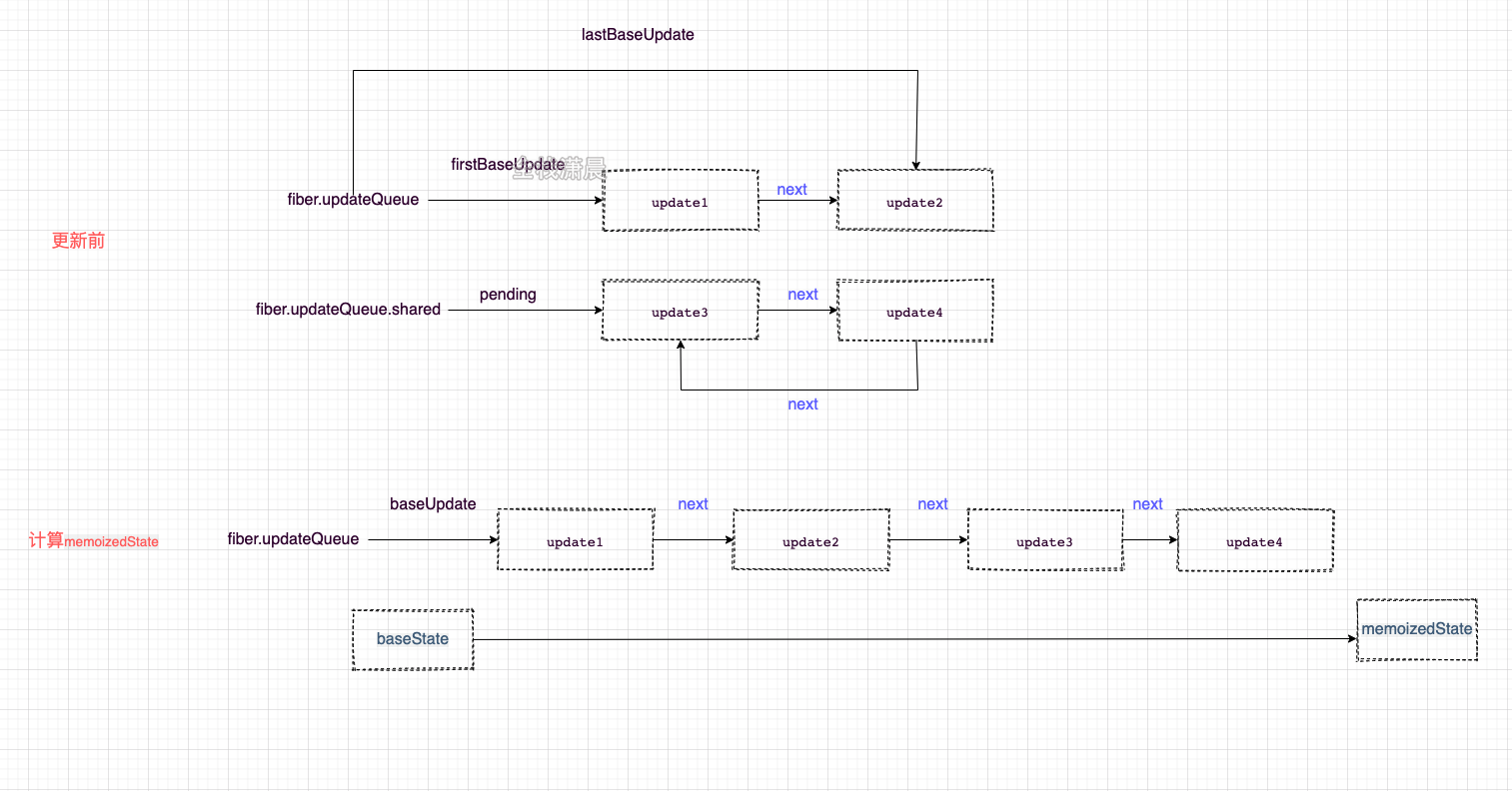
The classComponent status calculation takes place in the processUpdateQueue function and involves many linked list operations. The figure is more straightforward
-
Initial fiber There are firstBaseUpdate (update1) and lastBaseUpdate (update2) on the updatequeue single linked list, which are connected by next
-
fiber. updateQueue. There are update3 and update4 on the shared circular linked list, which are connected with each other by next connection
-
When calculating state, first set fiber updateQueue. The shared circular linked list is' cut open 'to form a single linked list, which is connected to fiber baseUpdate is formed after updatequeue
-
Then traverse the linked list and calculate the memoizedState according to the baseState
Status update with priority
Similar to git submission, c3 here means high priority tasks, such as user departure events, data requests, synchronously executed code, etc.
-
Through reactdom The application created by render has no concept of priority. Compared with git submission, it is equivalent to commit first and then submit c3
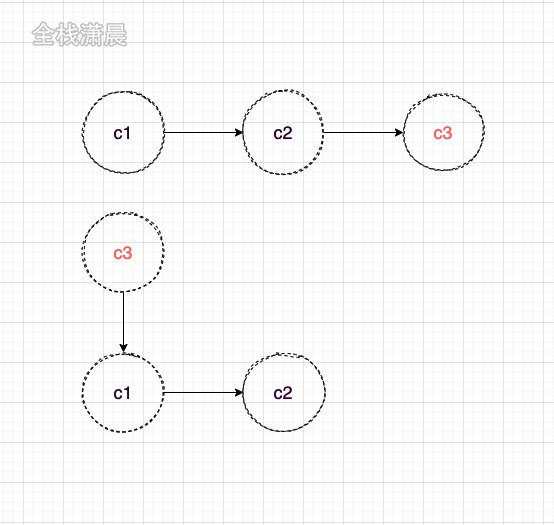
-
In the concurrent mode, similar to git rebase, the previous code is temporarily stored, developed on the master, and then rebased to the previous branch
The priority is scheduled by the Scheduler. Here we only care about the priority ranking during status calculation, that is, the calculation in the function processUpdateQueue. For example, there are four updates c1-c4 at the beginning, of which c1 and c3 are high priority
- In the first render, low priority update s will be skipped, so only c1 and c3 are added to the state calculation
- In the second render, the update (c1) before the update (c2) skipped in the first will be taken as the baseState, and the skipped update and the subsequent update (c2, c3, c4) will be recalculated as the baseUpdate
In concurrent mode, componentWillMount may be executed multiple times, which is inconsistent with the previous version
Attention, fiber updateQueue. Shared exists in workInprogress Fiber and current Fiber at the same time. The purpose is to prevent state loss caused by high priority interrupting the ongoing calculation. This code also occurs in processUpdateQueue

Look at the demo_ Priority of 8
Now let's look at the function that calculates the state
//ReactUpdateQueue.old.js
export function processUpdateQueue<State>(
workInProgress: Fiber,
props: any,
instance: any,
renderLanes: Lanes,
): void {
const queue: UpdateQueue<State> = (workInProgress.updateQueue: any);
hasForceUpdate = false;
let firstBaseUpdate = queue.firstBaseUpdate;//First Update of updateQueue
let lastBaseUpdate = queue.lastBaseUpdate;//Last Update of updateQueue
let pendingQueue = queue.shared.pending;//Uncomputed pendingQueue
if (pendingQueue !== null) {
queue.shared.pending = null;
const lastPendingUpdate = pendingQueue;//The last update of an uncomputed ppendingQueue
const firstPendingUpdate = lastPendingUpdate.next;//First uncalculated update queue
lastPendingUpdate.next = null;//Cut open the circular linked list
if (lastBaseUpdate === null) {//Add pendingQueue to updateQueue
firstBaseUpdate = firstPendingUpdate;
} else {
lastBaseUpdate.next = firstPendingUpdate;
}
lastBaseUpdate = lastPendingUpdate;
const current = workInProgress.alternate;//Do the same on current
if (current !== null) {
const currentQueue: UpdateQueue<State> = (current.updateQueue: any);
const currentLastBaseUpdate = currentQueue.lastBaseUpdate;
if (currentLastBaseUpdate !== lastBaseUpdate) {
if (currentLastBaseUpdate === null) {
currentQueue.firstBaseUpdate = firstPendingUpdate;
} else {
currentLastBaseUpdate.next = firstPendingUpdate;
}
currentQueue.lastBaseUpdate = lastPendingUpdate;
}
}
}
if (firstBaseUpdate !== null) {
let newState = queue.baseState;
let newLanes = NoLanes;
let newBaseState = null;
let newFirstBaseUpdate = null;
let newLastBaseUpdate = null;
let update = firstBaseUpdate;
do {
const updateLane = update.lane;
const updateEventTime = update.eventTime;
if (!isSubsetOfLanes(renderLanes, updateLane)) {//Determine whether priority is enough
const clone: Update<State> = {//The priority is not enough. Skip the current update
eventTime: updateEventTime,
lane: updateLane,
tag: update.tag,
payload: update.payload,
callback: update.callback,
next: null,
};
if (newLastBaseUpdate === null) {//Save skipped update
newFirstBaseUpdate = newLastBaseUpdate = clone;
newBaseState = newState;
} else {
newLastBaseUpdate = newLastBaseUpdate.next = clone;
}
newLanes = mergeLanes(newLanes, updateLane);
} else {
//It will not be calculated until newLastBaseUpdate is null, so as to prevent the updateQueue from not completing the calculation
if (newLastBaseUpdate !== null) {
const clone: Update<State> = {
eventTime: updateEventTime,
lane: NoLane,
tag: update.tag,
payload: update.payload,
callback: update.callback,
next: null,
};
newLastBaseUpdate = newLastBaseUpdate.next = clone;
}
newState = getStateFromUpdate(//Calculate state based on updateQueue
workInProgress,
queue,
update,
newState,
props,
instance,
);
const callback = update.callback;
if (callback !== null) {
workInProgress.flags |= Callback;//Callback flag
const effects = queue.effects;
if (effects === null) {
queue.effects = [update];
} else {
effects.push(update);
}
}
}
update = update.next;//Next update
if (update === null) {//Reset updateQueue
pendingQueue = queue.shared.pending;
if (pendingQueue === null) {
break;
} else {
const lastPendingUpdate = pendingQueue;
const firstPendingUpdate = ((lastPendingUpdate.next: any): Update<State>);
lastPendingUpdate.next = null;
update = firstPendingUpdate;
queue.lastBaseUpdate = lastPendingUpdate;
queue.shared.pending = null;
}
}
} while (true);
if (newLastBaseUpdate === null) {
newBaseState = newState;
}
queue.baseState = ((newBaseState: any): State);//New state
queue.firstBaseUpdate = newFirstBaseUpdate;//New first update
queue.lastBaseUpdate = newLastBaseUpdate;//New last update
markSkippedUpdateLanes(newLanes);
workInProgress.lanes = newLanes;
workInProgress.memoizedState = newState;
}
//...
}