
Author: Han Xinzi@ShowMeAI
Tutorial address: http://www.showmeai.tech/tutorials/56
Article address: http://www.showmeai.tech/article-detail/77
Notice: All Rights Reserved. Please contact the platform and the author for reprint and indicate the source
1.Python list
Sequence is the most basic and common data structure in Python. Each element in the sequence is assigned a number - [its position, or index]. The first index is 0, the second index is 1, and so on.
Sequences can perform operations, including indexing, slicing, adding, multiplying, and checking members.
In addition, Python has built-in methods to determine the length of the sequence and the largest and smallest elements.
List is the most commonly used Python data type and can appear as a comma separated value within square brackets.
The data items of the list do not need to have the same type.
To create a list, simply enclose the different data items separated by commas in square brackets. As follows:
list1 = ['python', 'ShowMeAI', 1997, 2022] list2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ] list3 = ["a", "b", "c", "d"]
Like the index of a string, the list index starts at 0. The list can be intercepted, combined, etc.
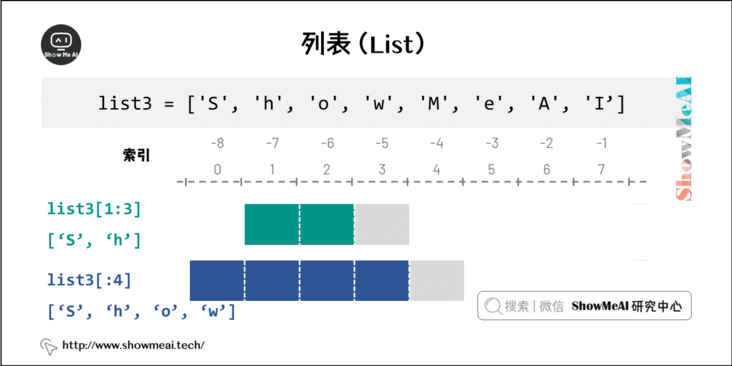
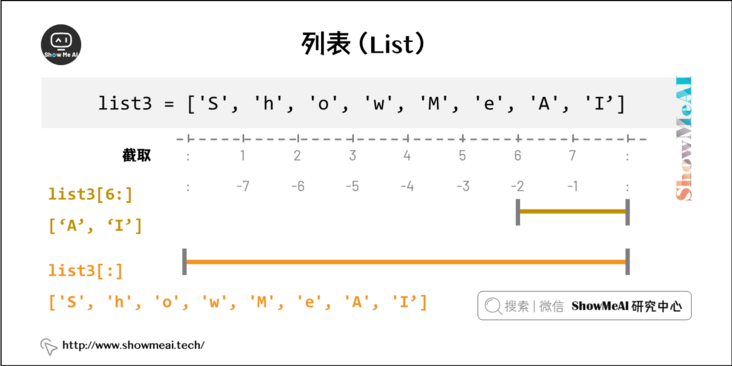
2. Access the values in the list
Use the subscript index to access the values in the list. Similarly, you can intercept the sub list in the form of square brackets.
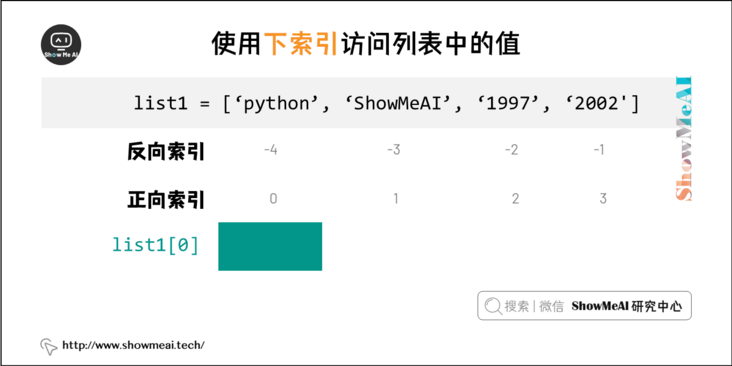
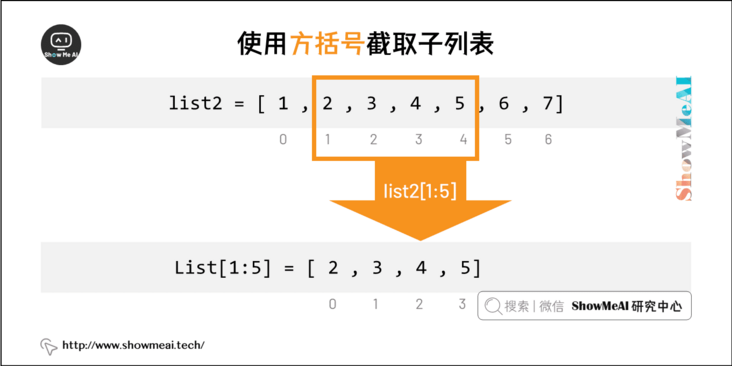
The following is the sample code (the code can be found in Online Python 3 environment Running in:
list1 = ['python', 'ShowMeAI', 1997, 2022]
list2 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 ]
print("list1[0]: ", list1[0])
print("list2[1:5]: ", list2[1:5])Execution result of the above code:
list1[0]: python list2[1:5]: [2, 3, 4, 5]
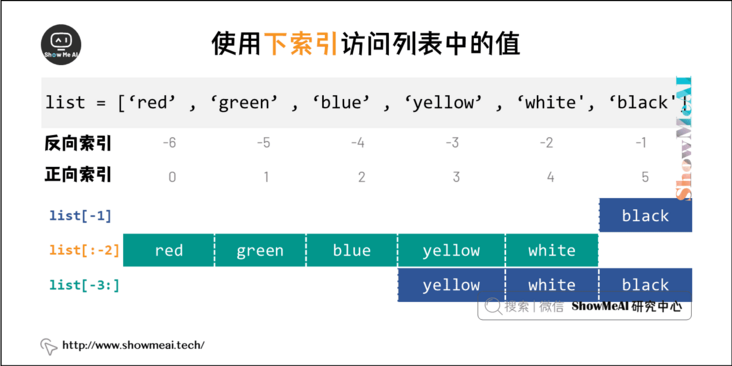
The following is the sample code (the code can be found in Online Python 3 environment Running in:
list = ['red', 'green', 'blue', 'yellow', 'white', 'black'] print( list[-1] ) print( list[:-2] ) print( list[-3:] )
Operation results
black ['red', 'green', 'blue', 'yellow'] ['yellow', 'white', 'black']
3. Update list
You can modify or update the data items of the list, or you can use the append() method to add the list items, as shown below (the code can be found in the Online Python 3 environment Running in:
list = [] ## Empty list
list.append('Google') ## Add elements using append()
list.append('ShowMeAI')
print(list)Execution result of the above code:
['Google', 'ShowMeAI']
4. Delete list elements
You can use the del statement to delete the elements of the list, as shown below (the code can be found in the Online Python 3 environment Running in:
list1 = ['python', 'ShowMeAI', 1997, 2022]
print(list1)
del list1[2]
print("After deleting the element with index 2 : ")
print(list1)Execution result of the above code:
['python', 'ShowMeAI', 1997, 2022] After deleting the element with index 2 : ['python', 'ShowMeAI', 2022]
Note: we will discuss the use of the remove() method later
5.Python list script operator
The operators for list pairs + and are similar to strings+ Number is used for combined list and number is used for repeated list.
As follows:
| Python expression | result | describe |
|---|---|---|
| len([1, 2, 3]) | 3 | length |
| [1, 2, 3] + [4, 5, 6] | [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6] | combination |
| ['Hi!'] * 4 | ['Hi!', 'Hi!', 'Hi!', 'Hi!'] | repeat |
| 3 in [1, 2, 3] | True | Does the element exist in the list |
| for x in [1, 2, 3]: print x, | 1 2 3 | iteration |
6.Python list interception
Examples of Python list interception are as follows:
>>>L = ['Google', 'ShowMeAI', 'Baidu'] >>> L[2] 'Baidu' >>> L[-2] 'ShowMeAI' >>> L[1:] ['ShowMeAI', 'Baidu'] >>>
Description:
| Python expression | result | describe |
|---|---|---|
| L[2] | 'Baidu' | Read the third element in the list |
| L[-2] | 'ShowMeAI' | Reads the penultimate element in the list |
| L[1:] | ['ShowMeAI', 'Baidu'] | Intercept the list from the second element |
7.Python list functions & Methods
Python contains the following functions:
| Serial number | function | effect |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | len(list) | Number of list elements |
| 2 | max(list) | Returns the maximum value of a list element |
| 3 | min(list) | Returns the minimum value of a list element |
| 4 | list(seq) | Convert tuples to lists |
# Example 1: length
list1, list2 = [123, 'ShowMeAI', 'google'], [456, 'abc']
print("Length of the first list : ", len(list1))
print("Length of the second list : ", len(list2))result
Length of the first list : 3 2nd list length : 2
# Example 2: max min
list1, list2 = ['Baidu', 'ShowMeAI', 'google'], [456, 789, 200]
print("Maximum value of the first list : ", max(list1))
print("Minimum value of the first list : ", min(list1))
print("Maximum value of the second list : ", max(list2))
print("2nd list min : ", min(list2))result
Maximum value of the first list : google Minimum value of the first list : Baidu Maximum value of the second list : 789 2nd list min : 200
# Example 3: transfer list
aTuple = (123, 'ShowMeAI', 'google', 'Baidu');
aList = list(aTuple)
print("List element : ")
print(aList)result
List element : [123, 'ShowMeAI', 'google', 'Baidu']
Python includes the following methods:
| Serial number | method | effect |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | list.append(obj) | Add a new object at the end of the list |
| 2 | list.count(obj) | Count the number of times an element appears in the list |
| 3 | list.extend(seq) | Append multiple values in another sequence at the end of the list at one time (expand the original list with the new list) |
| 4 | list.index(obj) | Find the index position of the first match of a value from the list |
| 5 | list.insert(index, obj) | Insert object into list |
| 6 | list.pop([index=-1]) | Removes an element from the list (the default last element) and returns the value of that element |
| 7 | list.remove(obj) | Removes the first occurrence of a value in the list |
| 8 | list.reverse() | Elements in reverse list |
| 9 | list.sort(cmp=None, key=None, reverse=False) | Sort the original list |
aList = ['Baidu', 'ShowMeAI', 'google']
print("aList : ", aList)
aList.append( 'ByteDance' )
aList += ['ShowMeAI']
print("after append and+Calculated aList : ", aList)
print("Statistics ShowMeAI number : ", aList.count('ShowMeAI'))
aList.extend(['Taobao', 'Tencent'])
print("after extend Later aList : ", aList)
print("use index lookup Taobao Index location of: ", aList.index('Taobao'))
aList.insert( 3, 'DiDi')
print("stay index Position of 3 insert After element aList : ", aList)
print("aList pop Out of element: ", aList.pop())
aList.remove('ShowMeAI')
print("aList use remove Delete the first matching ShowMeAI after: ", aList)
aList.reverse()
print("aList use reverse Results after reverse order: ", aList)
aList.sort()
print("aList use sort Sorted results: ", aList)result
aList : ['Baidu', 'ShowMeAI', 'google'] after append and+Calculated aList : ['Baidu', 'ShowMeAI', 'google', 'ByteDance', 'ShowMeAI'] Statistics ShowMeAI number : 2 after extend Later aList : ['Baidu', 'ShowMeAI', 'google', 'ByteDance', 'ShowMeAI', 'Taobao', 'Tencent'] use index lookup Taobao Index location of: 5 stay index Position of 3 insert After element aList : ['Baidu', 'ShowMeAI', 'google', 'DiDi', 'ByteDance', 'ShowMeAI', 'Taobao', 'Tencent'] aList pop Out of element: Tencent aList use remove Delete the first matching ShowMeAI after: ['Baidu', 'google', 'DiDi', 'ByteDance', 'ShowMeAI', 'Taobao'] aList use reverse Results after reverse order: ['Taobao', 'ShowMeAI', 'ByteDance', 'DiDi', 'google', 'Baidu'] aList use sort Sorted results: ['Baidu', 'ByteDance', 'DiDi', 'ShowMeAI', 'Taobao', 'google']
8. Video tutorial
Please click to station B to view the version of [bilingual subtitles]
Data and code download
The code for this tutorial series can be found in github corresponding to ShowMeAI Download in, you can run in the local python environment. Babies who can surf the Internet scientifically can also directly use Google lab to run and learn through interactive operation!
The Python quick look-up table involved in this tutorial series can be downloaded and obtained at the following address:
Extended references
ShowMeAI related articles recommended
- Introduction to python
- python installation and environment configuration
- python basic syntax
- python basic data type
- python operator
- python conditional control and if statement
- python loop statement
- python while loop
- python for loop
- python break statement
- python continue statement
- python pass statement
- python string and operation
- python list
- python tuple
- python dictionary
- python collection
- python function
- python iterators and generators
- python data structure
- python module
- python file reading and writing
- python file and directory operation
- python error and exception handling
- python object oriented programming
- python namespace and scope
- python time and date
ShowMeAI series tutorial recommendations
- Illustrated Python Programming: a series of tutorials from getting started to mastering
- Graphic data analysis: a series of tutorials from introduction to mastery
- Fundamentals of graphic AI Mathematics: a series of tutorials from introduction to mastery
- Illustrated big data technology: a series of tutorials from introduction to mastery
