catalogue
1. Storage structure and definition of single linked list
2.5 finding table length function
2.6 search function by location
2.10 create linked list - head interpolation / front interpolation
2.11 create linked list tail insertion method
1. Storage structure and definition of single linked list
storage structure
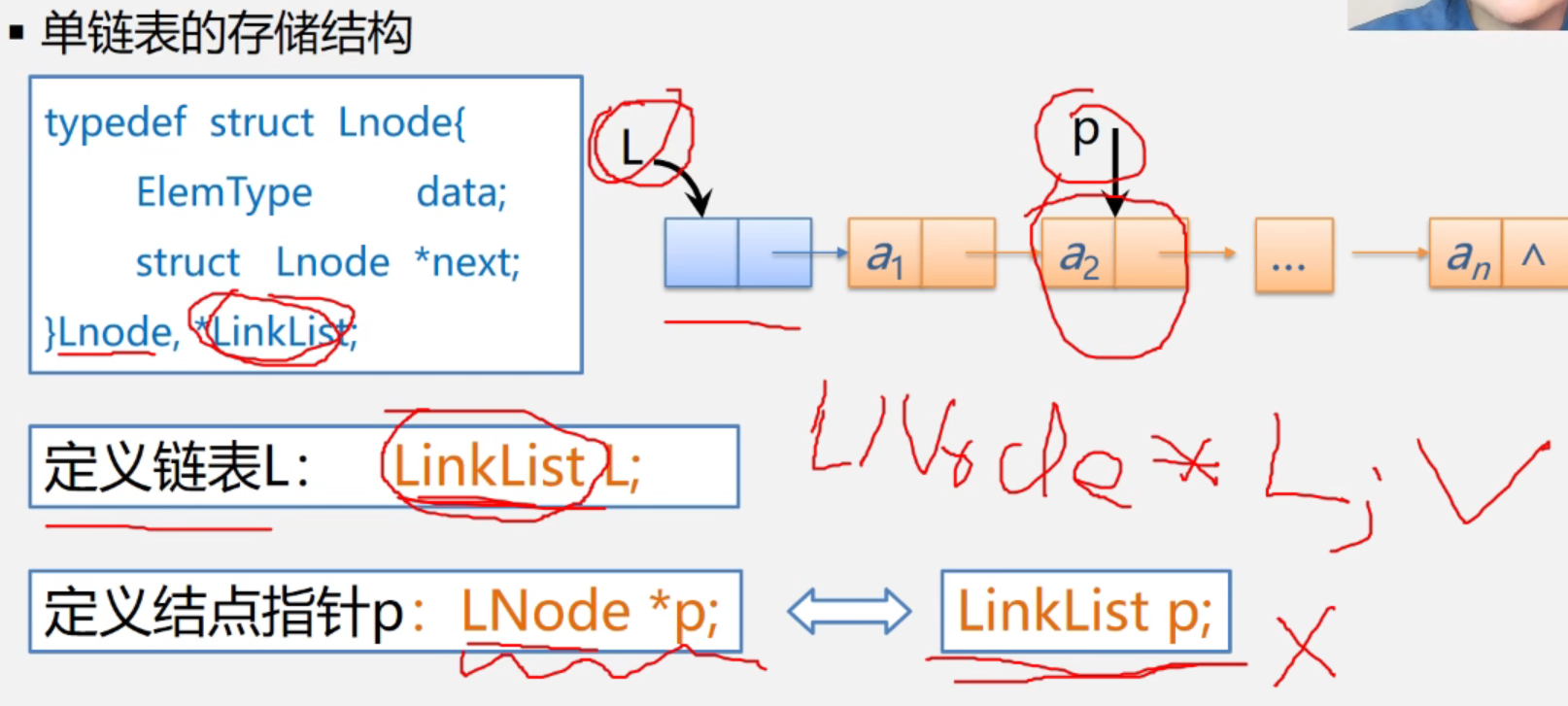
Typedef Description: typedef int status. The first is the type, and the second is the given object. In the following example, a pointer Linklist is given, and then Linklist can be directly used to represent the pointers to nodes similar to L and p in the figure. Linklist L = Lnode *L, simpler.
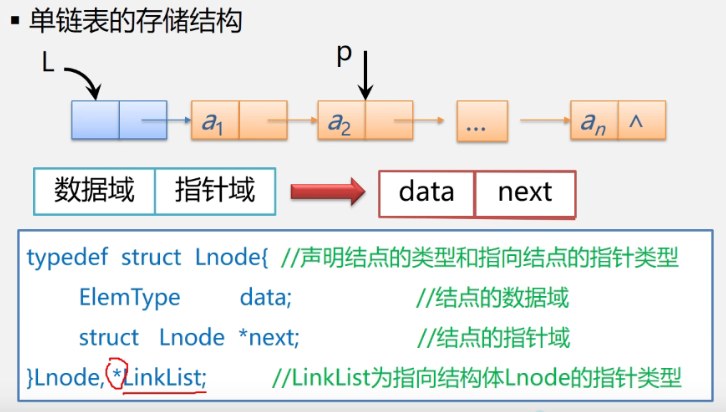
Function definition
Linklist is generally used for linked list and LNode is used for defining pointer. Actually, it's all right, but I'm more used to it.
Example: Student transcript
For unified operation, data fields are generally defined separately. In this way, there are only data field and pointer field in Lnode.
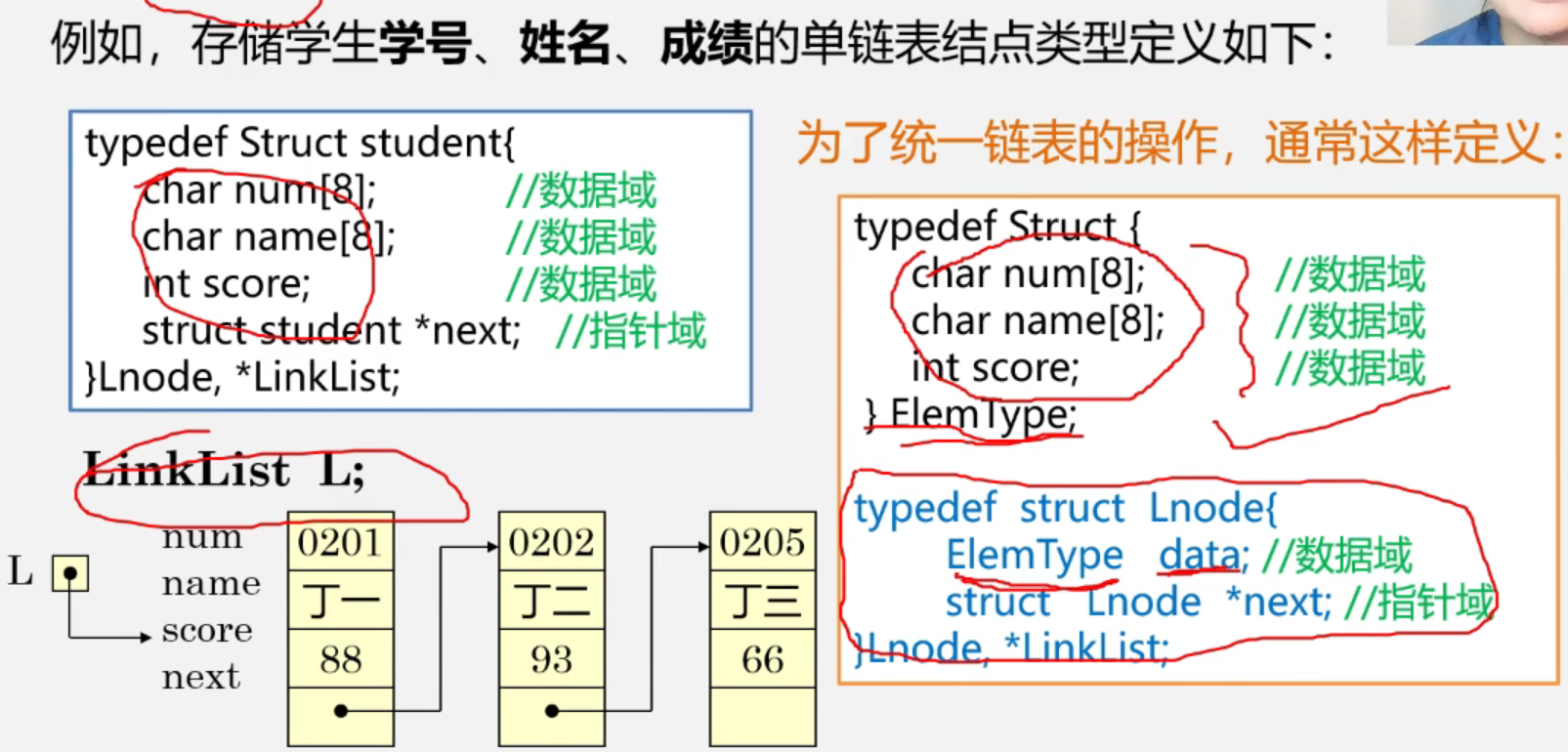
2. Function definition
2.1 initialization function
Note: Linklist itself is a pointer, so you don't need to add *. The int * used in the previous sequential storage is an int pointer.
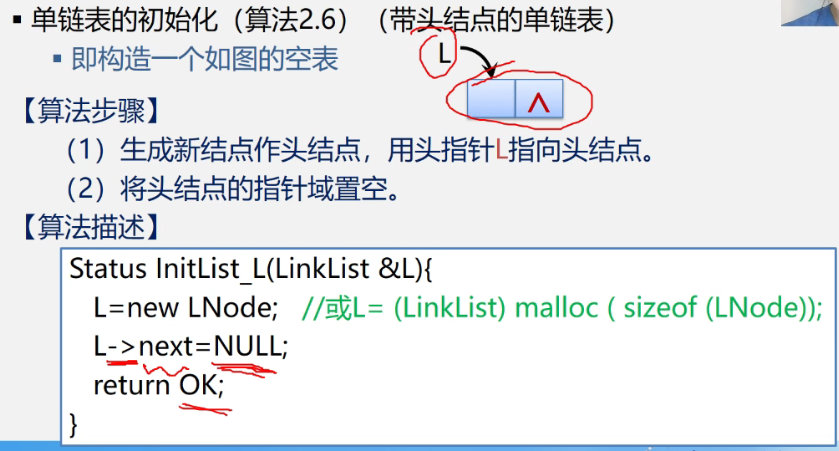
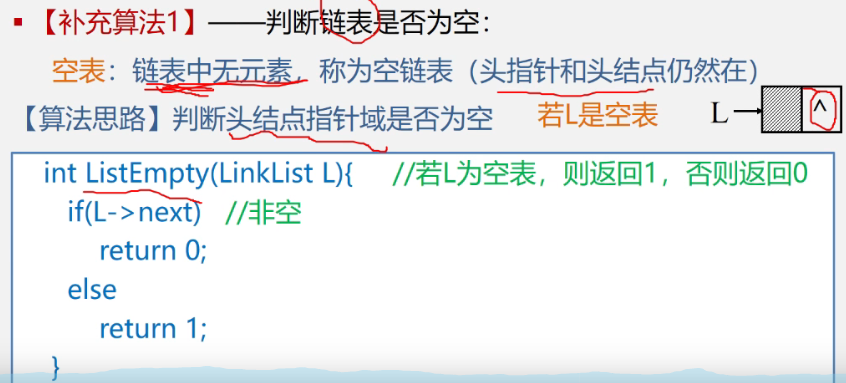
2.2 empty judgment function
2.3 destruction function
thinking
Use a new pointer to point to the head node, then make the original pointer point to the next node, delete the area pointed by the new pointer, and so on.
Release operation:
C++: new with delete p
C: malloc(sizeof()) with free(p)
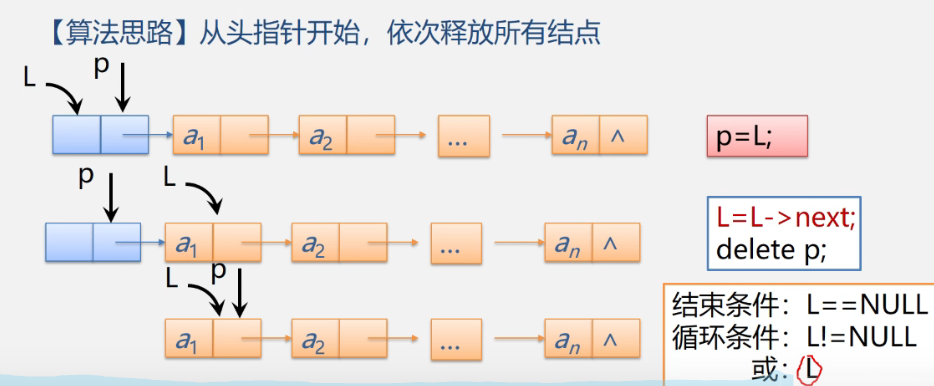
Code (C + +)
Note: when defining a new pointer p, it is written as Linklist *p, which is not standardized. Node pointer definition should be Lnode *p
Status DestroyList_L(Linklist &L){
Lnode *p;
while(L){
p=L;
L=L->next;
delete p;//free(p);
}
return OK;
}2.4 emptying function
thinking
Step by step is simpler than step by step, but the code implementation is more complex. So still use the teacher's method.
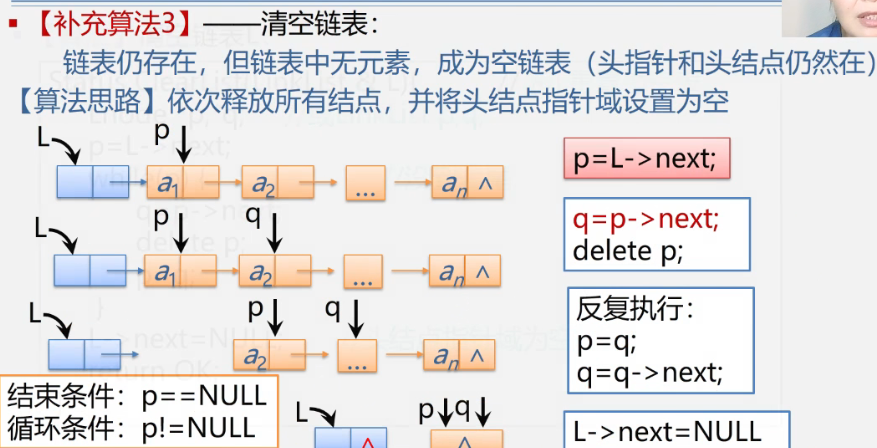
code
Status ClearList(Linklist &L){
Lnode *p,*q;
p = L->next;
while(p){
q = p->next;
delete p;
p = q;
}
L->next = NULL;
return OK;
}2.5 finding table length function
Start from the first element node and cycle back to the next field. If p is not empty, the table length is + 1
code
Status ListLength(Linklist L){
Lnode *p;
p = L->next;
int i=0;
while(p){
i++;
p = p->next;
}
return i;
}2.6 search function by location
Train of thought

code
Status GetElem(Linklist L, int i, Elemtype &e){
Lnode *p;
p = L->next;
int j = 1;
while(p&&j<i){
j++;
p = p->next;
}
if(!p||j>i) return ERROR;//! p means i is too large and not found. J > i means i is too small. It may be 0 or negative
e = p->data;
return e;
}2.7} find function by value
Code (return address pointer)
Lnode *LocateElem(Linklist L, Elemtype e){
Lnode *p;
p = L->next;
while(p && p->data!=e)
p = p->next;
if(!p) return ERROR;
return p;
}Code (return location)
Status LocateElem(Linklist L, Elemtype e){
Lnode *p;
p = L->next;
int i = 1;
while(p && p->data!=e){
p = p->next;
i++;
}
if(!p) return ERROR;
return i;
}Time complexity O(n)
2.8 insert function
thinking
Reasonable position of insertion: 1-n+1. If it is inserted in bit n+1, the pointer p should be in bit n after passing through the loop. Therefore, when initializing, p=L head node and j=0 (bit 0) can be inserted into the first bit.
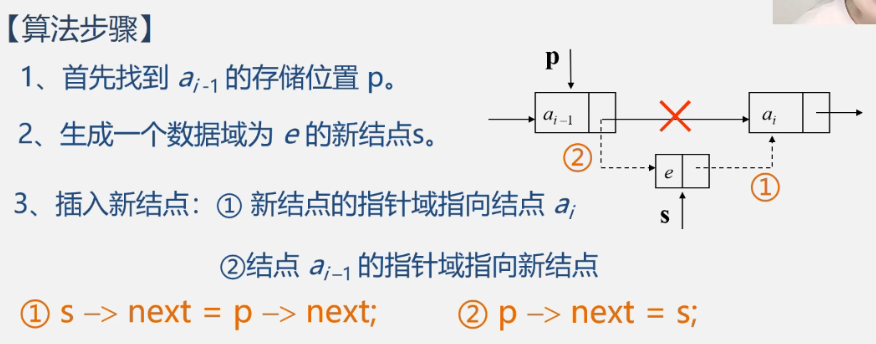
code
Status ListInsert(Linklist &L, int i, Elemtype e){
Lnode *p = L;//Initialization is on the header node L, not the first element node
int j = 0;
while(p && j<i-1){
j++;
p = p->next;
}
if(!p||j>i) return ERROR;//If the length exceeds + 1 or i is not a positive number, an error will be reported
s = new Lnode; s->data = e;//Create a new node space storage e
s->next = p->next;
p->next = s;//Re bridging
return OK;
}Time complexity O(n) because you need to find it from scratch
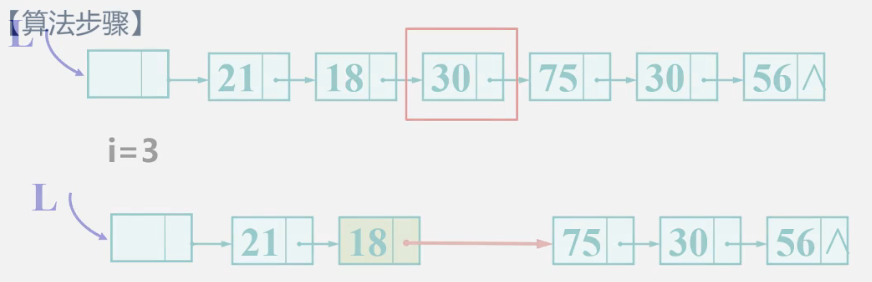
2.9 delete function
thinking
Before deleting bit i, connect the next of bit i-1 to bit i+1, and then release it.
code
Status DeleteElem(Linklist &L, int i, Elemtype &e){//**ElemType & E optional**
Lnode *p = L;
Lnode *s;
int j = 0;
while(p->next && j<i-1){
j++;
p = p->next;//p is now the direct precursor of the i-th bit to be deleted
}
if(!(p->next)||j>i-1) return ERROR;
s = p->next; //Pos i tion s of the record to be deleted
p->next = p->next->next; //Re bridging from i-1 to i+1
e = s->data; //**Optional * * the deleted value of the record, which can be used to view
delete s;
return OK;
}Time complexity O(n) because you need to find it from scratch
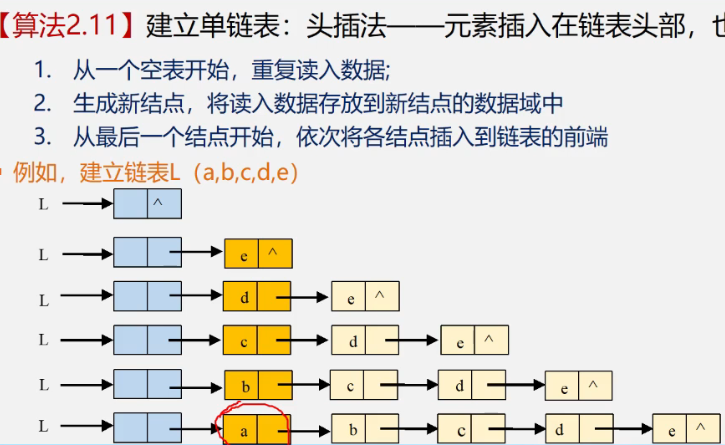
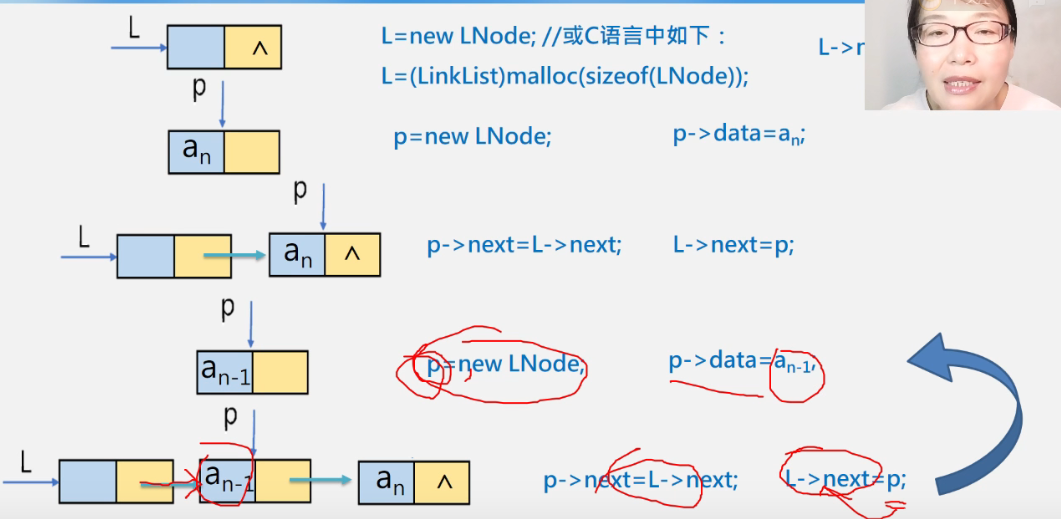
2.10 create linked list - head interpolation / front interpolation
thinking
code
void CreateList(Linklist &L, int n){
L = new Lnode; //L = (Linklist)malloc(sizeof(Lnode));
L->next = NULL;
for(i = n; i > 0; i--){
p = new Lnode; //L = (Lnode*)malloc(sizeof(Lnode));
cin>>p->data; //scanf(&p->data);
p->next = L->next;
L->next = p; //Re bridging
}
}Time complexity O(n), executed n+1 times in for.
2.11 create linked list tail insertion method
thinking
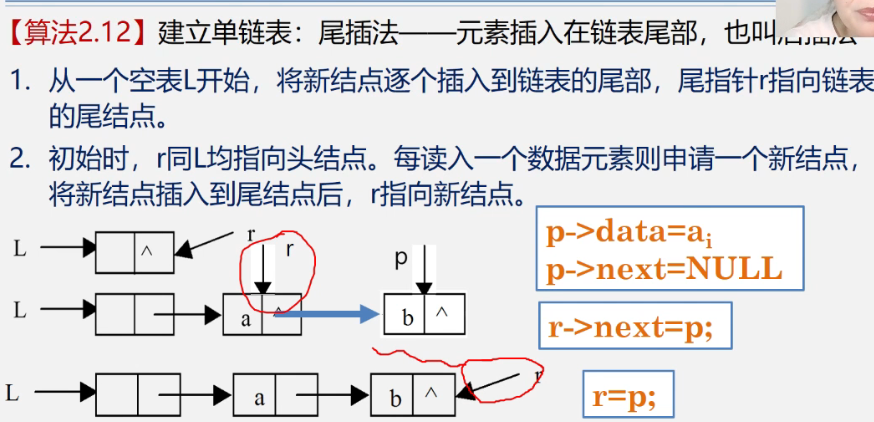
Code
void CreateList(Linklist &L, int n){
L = new Lnode; // L = (Linklist)malloc(sizeof(Lnode));
L->next = NULL;
Lnode *r = L;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++){
p = new Lnode; cin>>p->data; p->next = NULL;
r->next = p; //Connect p to the end
r = p; //r points last
}
}