1, Message queue
1. Definition of Message queue
The most common way of communication between services is to directly call each other to communicate. Messages can reach the other end immediately after they are sent from one end, which is called instant messaging (synchronous communication)
After a message is sent from one end, it first enters a container for temporary storage. When certain conditions are met, it is sent by this container to the other end, which is called delayed message communication (asynchronous communication)
① I. problem thinking
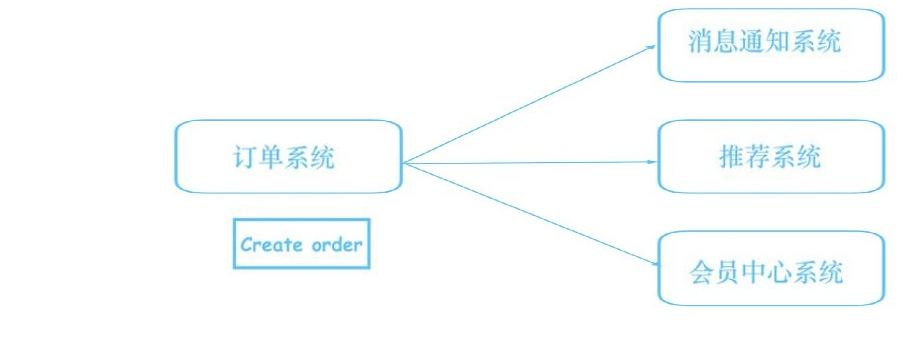
Suppose that after we place an order on Taobao, the background of Taobao needs to do these things:
- Message notification system: inform the merchant that you have a new order, please deliver it in time
- Recommendation system: update the user's portrait and re recommend the products that the user may be interested in
- Membership system: update users' points and grade information
createOrder(...) {
//Complete order service
doCreateOrder(...);
//Call other service interfaces
sendMsg(...); updateUserInterestedGoods(...); updateMemberCreditInfo(...);
}
② . existing problems
If you need to add a new line of code at the end of the original order, you need to add another line of code at the end of the original order
Lack of buffer: if the member system happens to be in a very busy or down state when creating an order, updating the member information will fail at this time. We need a place to temporarily store messages that cannot be consumed
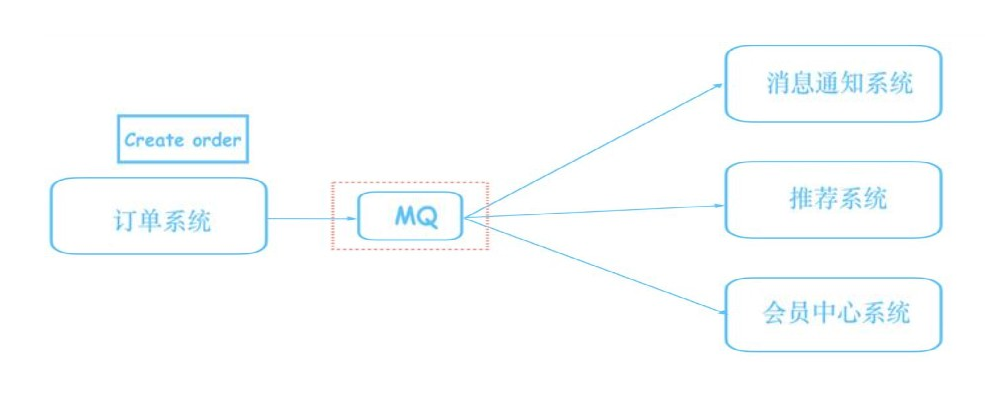
③ . optimization scheme
We need a message middleware to realize the functions of decoupling and buffering
Email case analysis:
There are a large number of users registering your software. Under the condition of high concurrency, some problems begin to appear in the registration request
For example, the email interface can't bear it, or a large amount of calculation during information analysis makes the cpu full, which will lead to the situation that although the user data records are quickly added to the database, they are stuck when sending email or analyzing information
This leads to a substantial increase in the response time of requests and even timeout, which is a little uneconomical In this case, these operations are generally put into the message queue (producer consumer model). The message queue can process them slowly, and the registration request can be completed quickly, which will not affect users' use of other functions
2. Message queue related
①,AMQP
An application layer standard advanced message queuing protocol providing unified messaging service is a general application layer protocol
Asynchronous communication can be realized by both sending and receiving sides following this protocol This protocol specifies the format and working mode of the message
| characteristic | ActiveMQ | RabbitMQ | Kafka | RocketMQ |
| PRODUCER-COMSUMER | support | support | support | support |
| PUBLISH-SUBSCRIBE | support | support | support | support |
| REQUEST-REPLY | support | support | - | support |
| API completeness | high | high | high | Low (static configuration) |
| Multilingual support | Support, JAVA preferred | Language independent | Support, JAVA preferred | support |
| Single machine swallowing volume | 10000 class | 10000 class | Class 100000 | Single 10000 class |
| Message delay | - | microsecond | millisecond | - |
| usability | High (master-slave) | High (master-slave) | Very high (distributed) | high |
| Message loss | - | low | Theoretically, it will not be lost | - |
| Duplicate message | - | Controllable | In theory, there will be repetition | - |
| Completeness of documents | high | high | high | in |
| Provide quick start | have | have | have | nothing |
| First deployment difficulty | - | low | in | high |
③, RabbitMq
RabbitMQ is a Message Queuing service that implements AMQP(Advanced Message Queuing Protocol) advanced message queuing protocol. It uses Erlang language
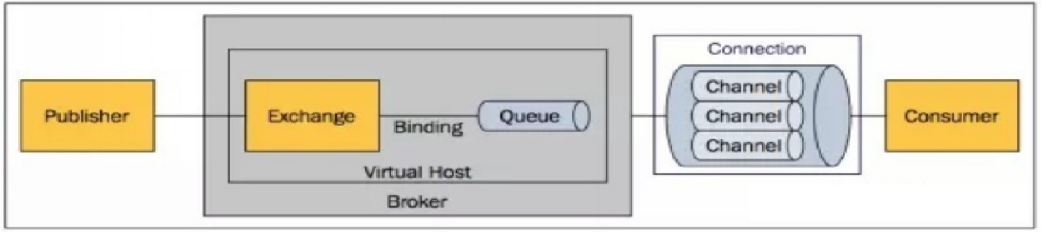
Server(Broker): a process that receives client connections and implements the message queuing and routing functions of AMQP protocol
Virtual Host: the concept of Virtual Host, which is similar to permission control group. A Virtual Host can have multiple exchanges and queues Exchange: the switch receives the messages sent by the producer and routes the messages to the Queue in the server according to the Routing Key
ExchangeType: the switch type determines the behavior of routing messages. There are three types of Exchange in RabbitMQ: fanout, direct and topic Message queue: message queue, used to store messages that have not been consumed by consumers
Message: it is composed of header and body. Header is a collection of various attributes added by the producer, including whether the message is persisted, what is the priority, which message Queue receives it, etc Body is the data content that really needs to be sent
BindingKey: binding keyword, which binds a specific Exchange to a specific Queue
2, Docker installation and deployment RabbitMQ
1. Pull image
Note that when obtaining images, you should obtain the management version instead of the last version. Only the management version has the management interface
docker pull rabbitmq:management
2. New rabbitmq folder
mkdir rabbitmq
Operation:
docker run -d \
--name my-rabbitmq \
-p 5672:5672 -p 15672:15672 \
-v /home/rabbitmq:/var/lib/rabbitmq \
--hostname my-rabbitmq-host \
-e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_VHOST=my_vhost \
-e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER=admin \
-e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS=admin \
--restart=always \
rabbitmq:management
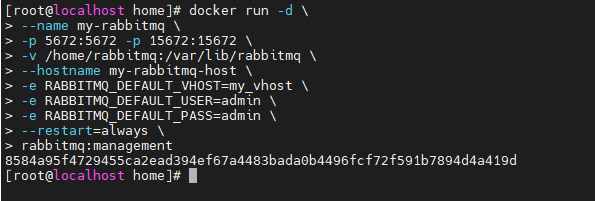
--hostname: host name (an important note of RabbitMQ is that it stores data according to the so-called "node name", which is the host name by default)
-e: Specify environment variables:
RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_VHOST: default virtual machine name
RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER: default user name
RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS: the password of the default user name
3. Enter the management background
Account password: admin
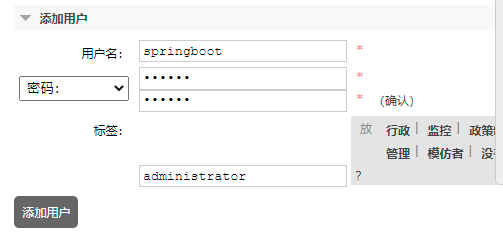
Create a new user and set it as an administrator,
Assign users access to virtual hosts
3, Set up RabbitMQ project
1. springboot project construction
(1) . create an empty Maven parent project, delete src,
pom. New in XML, which means that it is not packaged, but only provides dependencies
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>rabbitMQ</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<modules>
<module>provider</module>
<module>consumer</module>
</modules>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<spring-boot.version>2.4.1</spring-boot.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-boot.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
</project>(2) . new sub project
① . create a new provider sub project
pom.xml: inherit parent project
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>rabbitMQ</artifactId>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.mwy</groupId>
<artifactId>provider</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>provider</name>
<description>provider</description>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.4.1</version>
<configuration>
<mainClass>com.mwy.provider.ProviderApplication</mainClass>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>repackage</id>
<goals>
<goal>repackage</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>②. New consumer subproject
pom.xml: inherit parent project
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>rabbitMQ</artifactId>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.mwy</groupId>
<artifactId>consumer</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>consumer</name>
<description>consumer</description>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.4.1</version>
<configuration>
<mainClass>com.mwy.consumer.ConsumerApplication</mainClass>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>repackage</id>
<goals>
<goal>repackage</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>(3) . related dependencies
① Add pom dependency in rabbitMQ parent project
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
(4) yml file configuration
server:
port: 8080
spring:
application:
name: xx
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.42.148
password: 123456
port: 5672
username: springboot
virtual-host: my_vhost
2. Producer provider
① . create a new RabbitConfig class
package com.mwy.provider;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class RabbitConfig {
@Bean
public Queue firstQueue() {
return new Queue("firstQueue");
}
}② . create a new Sender class
package com.mwy.provider;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class Sender {
@Autowired
private AmqpTemplate rabbitTemplate;
public void sendFirst() {
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("firstQueue", "Hello World");
}
}③ , test class ProviderApplicationTests
package com.example.provider;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class ProviderApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private Sender sender;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
sender.sendFirst();
}
}At this point, a queue will be added to RabbitMQ Management
3. Consumer
① . yml file configuration
server:
port: 8081
spring:
application:
name: consumer
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.42.148
password: 123456
port: 5672
username: springboot
virtual-host: my_vhost
②,Receiver
package com.example.consumer;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Slf4j
@RabbitListener(queues = "firstQueue")
public class Receiver {
@RabbitHandler
public void process(String msg) {
log.warn("Received:" + msg);
}
}4. Custom data sending
(1) Producer provider
①,Uset
package com.example.provider;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User implements Serializable {
private String username;
private String userpwd;
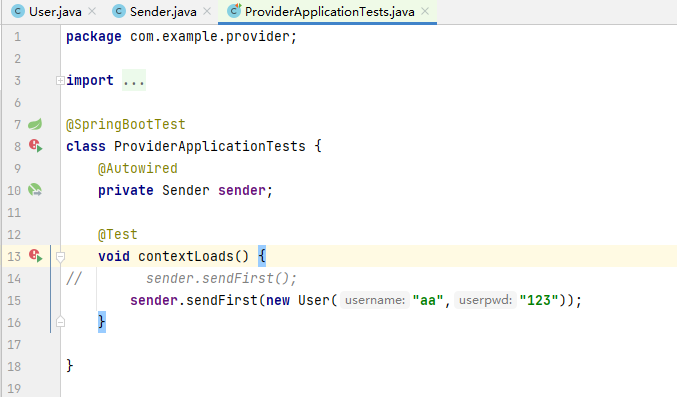
}②,Sender
public void sendFirst(User user) {
amqpTemplate.convertAndSend("firstQueue", user);
}
③ , test
(2) Consumer
①,Uset
package com.example.consumer;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User implements Serializable {
private String username;
private String userpwd;
}②,Receiver
package com.example.consumer;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitHandler;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Slf4j
@RabbitListener(queues = "firstQueue")
public class Receiver {
// @RabbitHandler
// public void process(String msg) {
// log.warn("received:" + msg);
// }
@RabbitHandler
public void process(User user) {
log.warn("Received:" + user);
}
}There are still mistakes,
producer:
Sender
public void sendFirst(String json) {
amqpTemplate.convertAndSend("firstQueue", json);
}
Test class ProviderApplicationTests
package com.example.provider;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import lombok.SneakyThrows;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class ProviderApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private Sender sender;
@Test
@SneakyThrows
void contextLoads() {
// sender.sendFirst();
// sender.sendFirst(new User("aa","123"));
User u=new User("aa","123");
ObjectMapper objectMapper=new ObjectMapper();
sender.sendFirst(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(u));
}
}consumer:
Receiver
@RabbitHandler
@SneakyThrows
public void process(String json) {
ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
objectMapper.readValue(json,User.class);
log.warn("receive:" + json);
}