In the previous article Analysis of the whole process of using hystrix from feign In, the workflow of springboot startup is explained in detail through a figure. I haven't enjoyed it yet. Today, I will analyze the instantiation process of beans and how spring solves circular dependency in detail. The following figure related to bean instantiation is slightly supplemented.
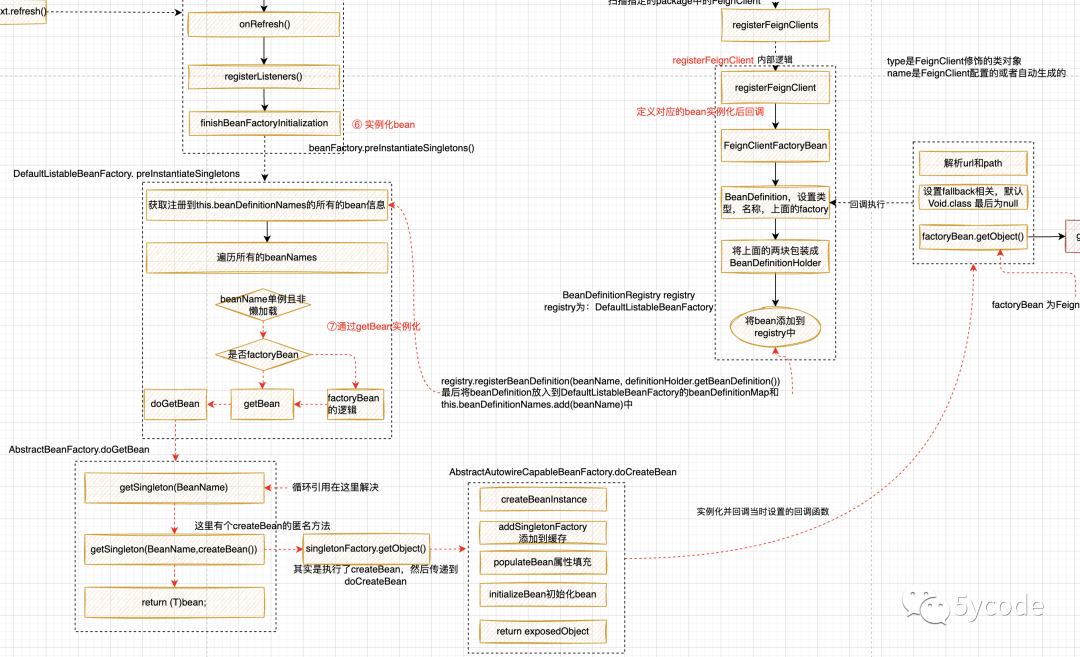
Refresh refresh
-
Invokebeanfactoryprocessors process beanFactory
-
First, the configclass is parsed (all metadata is parsed)
-
Load beanDefinition from resources and Registrar
-
finishBeanFactoryInitialization
public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext extends DefaultResourceLoader implements ConfigurableApplicationContext {
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
......
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
......
}
}
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
//The beanFactory here is DefaultListableBeanFactory
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}
}
In the DefaultListableBeanFactory, the getBean is booted
public class DefaultListableBeanFactory extends AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory implements ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, BeanDefinitionRegistry, Serializable {
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
//beanDefinitionNames is the beanName registered after parsing
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
//Special handling for FactoryBean
} else {
//Focus on
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
}
}
Let's take a look at AbstractBeanFactory and the class relationship
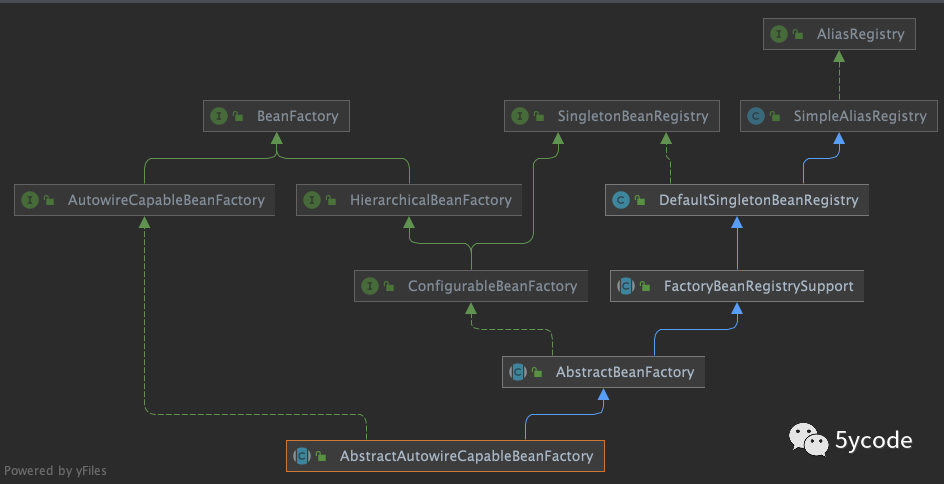
public abstract class AbstractBeanFactory extends FactoryBeanRegistrySupport implements ConfigurableBeanFactory {
@Override
public Object getBean(String name) throws BeansException {
//From getBean to doGetBean
return doGetBean(name, null, null, false);
}
protected <T> T doGetBean(String name, @Nullable Class<T> requiredType, @Nullable Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)throws BeansException {
//① Get the singleton class from the cache (focus on reading)
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
} else {
//If it is a circular reference of multiple cases, throw the exception directly
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
//Other processing
}
if (!typeCheckOnly) {
//Tag bean creation
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
}
try {
RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// ② Get singleton bean (focus on writing)
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
//Create a bean, an anonymous method, which is called in getSingleton
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
});
//bean fetch
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
}catch (BeansException ex) {
cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);
throw ex;
}
return (T) bean;
}
}
In the above code, there are two
-
One is to ① get the singleton class from the cache (focusing on reading), getSingleton(beanName);
-
It's meaningless to just look here. It should be combined with the creation process.
-
② get the singleton bean (focus on writing), and finally follow the createBean logic in the anonymous method
public class DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry extends SimpleAliasRegistry implements SingletonBeanRegistry {
//① Cache the mapping of singleton object, bean name and instance
private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
//② Cache the factory of the singleton object, and the mapping of the bean name and the corresponding factory
private final Map<String, ObjectFactory<?>> singletonFactories = new HashMap<>(16);
//③ Cache the early singleton object. After instantiation, the uninitialized cache (in spring, it is in the state of being created)
private final Map<String, Object> earlySingletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);
//④ The collection of registered singleton instances has only bean name
private final Set<String> registeredSingletons = new LinkedHashSet<>(256);
//⑤ Cache of bean being created, set collection
private final Set<String> singletonsCurrentlyInCreation =Collections.newSetFromMap(new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16));
//Focus on reading
@Override
@Nullable
public Object getSingleton(String beanName) {
return getSingleton(beanName, true);
}
//Pay attention to reading. Here is the widely circulated three-level cache
@Nullable
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
// Quick check for existing instance without full singleton lock
//At this time, get the instance from ① and return it directly, which is the so-called first level cache
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
// When the instance is not obtained and is being created
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
//At this time, get the bean instance from earlySingletonObjects
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
/Still no instance was obtained, allowEarlyReference Incoming is true
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
//Lock the singletonObjects at this time
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
// Double check. Get it again from ① at this time
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
// Double check. Get it again from ③ at this time
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
//Get the Bean Factory from ②
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
//If it is not empty, it will be put into ③ and removed from ② at the same time
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
//Focus on creating
public Object getSingleton(String beanName, ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory) {
Assert.notNull(beanName, "Bean name must not be null");
//Lock the singletonObjects of the current object
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
//Check again for
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
//It will be put into ⑤ here
beforeSingletonCreation(beanName);
boolean newSingleton = false;
boolean recordSuppressedExceptions = (this.suppressedExceptions == null);
if (recordSuppressedExceptions) {
this.suppressedExceptions = new LinkedHashSet<>();
}
try {
//Obtain the object through the factory, which is the return createBean(beanName, mbd, args) in the anonymous method;
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
newSingleton = true;
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
//If the creation is successful, continue to execute. If the exception is thrown, don't go down
singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null) {
throw ex;
}
}
finally {
//It will be removed from ⑤ here
afterSingletonCreation(beanName);
}
//After successful creation, it will be removed from singletonFactories and earlySingletonObjects
if (newSingleton) {
//This will be put into ① and ④ and removed from ② and ③
addSingleton(beanName, singletonObject);
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
}
protected void beforeSingletonCreation(String beanName) {
if (!this.inCreationCheckExclusions.contains(beanName) && !this.singletonsCurrentlyInCreation.add(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
}
protected void addSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
this.singletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
this.earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
this.registeredSingletons.add(beanName);
}
}
}
The final code points to the doCreateBean in AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory, which can be said to be the core of spring to create a singleton. It can be divided into three steps:
- ① createBeanInstance creates an instance (internal reflection mechanism)
- Here is another key point: active cache addSingletonFactory, which will be added to the cache
- ② populateBean automatic attribute filling
- ③ Initialize bean initializeBean
Operation mechanism of L3 cache
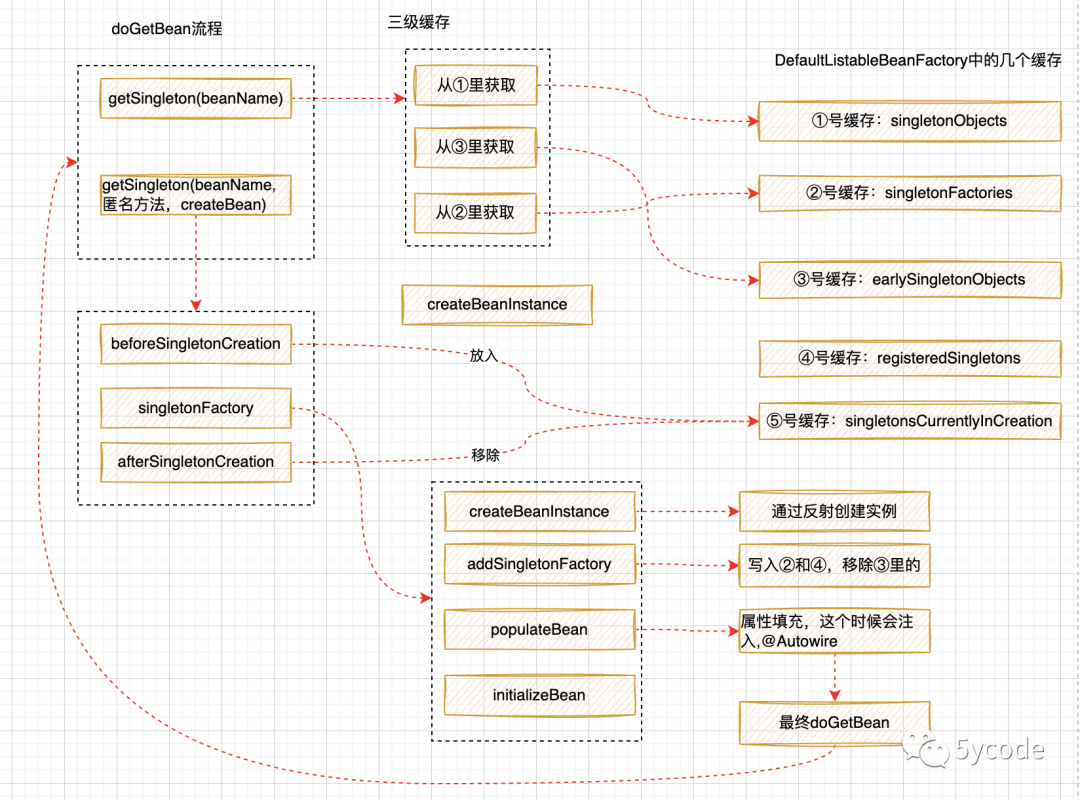
From the above, we can see that after the instance is created, spring will add the object to the cache, and then do dependency filling and initialization
The specific codes are as follows:
public abstract class AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory extends AbstractBeanFactory implements AutowireCapableBeanFactory {
protected Object createBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)throws BeanCreationException {
RootBeanDefinition mbdToUse = mbd;
Class<?> resolvedClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
if (resolvedClass != null && !mbd.hasBeanClass() && mbd.getBeanClassName() != null) {
mbdToUse = new RootBeanDefinition(mbd);
mbdToUse.setBeanClass(resolvedClass);
}
try {
//Before instantiation, BeanPostProcessors have the opportunity to return a proxy object
Object bean = resolveBeforeInstantiation(beanName, mbdToUse);
if (bean != null) {
return bean;
}
}
try {
//Where beans are created without BeanPostProcessors intervention
Object beanInstance = doCreateBean(beanName, mbdToUse, args);
return beanInstance;
}
}
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args)
throws BeanCreationException {
// Instantiate the bean.
BeanWrapper instanceWrapper = null;
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
instanceWrapper = this.factoryBeanInstanceCache.remove(beanName);
}
if (instanceWrapper == null) {
//① Create bean instance
instanceWrapper = createBeanInstance(beanName, mbd, args);
}
Object bean = instanceWrapper.getWrappedInstance();
Class<?> beanType = instanceWrapper.getWrappedClass();
if (beanType != NullBean.class) {
mbd.resolvedTargetType = beanType;
}
// Allows post processors to modify the merged bean definition
synchronized (mbd.postProcessingLock) {
if (!mbd.postProcessed) {
try {
applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName);
}
mbd.postProcessed = true;
}
}
// Actively cache singletons to resolve circular references
boolean earlySingletonExposure = (mbd.isSingleton() && this.allowCircularReferences &&
isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName));
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
//Here, it will be written to ② ④ of DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry and removed from ③, where the cache is formed
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, mbd, bean));
}
// Initializing an instance of a bean
Object exposedObject = bean;
try {
//② Attribute filling
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
//③ Initialize bean
exposedObject = initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd);
}
if (earlySingletonExposure) {
Object earlySingletonReference = getSingleton(beanName, false);
if (earlySingletonReference != null) {
if (exposedObject == bean) {
exposedObject = earlySingletonReference;
}
else if (!this.allowRawInjectionDespiteWrapping && hasDependentBean(beanName)) {
String[] dependentBeans = getDependentBeans(beanName);
Set<String> actualDependentBeans = new LinkedHashSet<>(dependentBeans.length);
for (String dependentBean : dependentBeans) {
if (!removeSingletonIfCreatedForTypeCheckOnly(dependentBean)) {
actualDependentBeans.add(dependentBean);
}
}
}
}
return exposedObject;
}
protected BeanWrapper createBeanInstance(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable Object[] args) {
// Make sure bean class is actually resolved at this point.
Class<?> beanClass = resolveBeanClass(mbd, beanName);
//Omit a bunch of special treatment
//Handle when there is an object to be injected in the constructor
Constructor<?>[] ctors = determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors(beanClass, beanName);
if (ctors != null || mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR ||
mbd.hasConstructorArgumentValues() || !ObjectUtils.isEmpty(args)) {
return autowireConstructor(beanName, mbd, ctors, args);
}
// There is no special treatment, and the parameterless constructor is used for instantiation
return instantiateBean(beanName, mbd);
}
protected BeanWrapper instantiateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
try {
Object beanInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
beanInstance = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, this),
getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
//Using cglibsubclassing instantiationstrategy
beanInstance = getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(mbd, beanName, this);
}
BeanWrapper bw = new BeanWrapperImpl(beanInstance);
initBeanWrapper(bw);
return bw;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Instantiation of bean failed", ex);
}
}
//Attribute filling
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
//Give instantiaawarebeanpostprocessors the opportunity to modify the state of the bean, especially the injection of fields, before setting the properties
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
return;
}
}
}
}
PropertyValues pvs = (mbd.hasPropertyValues() ? mbd.getPropertyValues() : null);
//Resolve Autowire. At this time, the dependent object may not have been instantiated
int resolvedAutowireMode = mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode();
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME || resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Injection by name
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// By type injection
if (resolvedAutowireMode == AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != AbstractBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = null;
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
if (pvs == null) {
pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
}
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
//Attribute resolution
PropertyValues pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessProperties(pvs, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
pvsToUse = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvsToUse == null) {
return;
}
}
pvs = pvsToUse;
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
if (filteredPds == null) {
filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
}
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
//Finally, attribute injection is completed
if (pvs != null) {
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
}
protected Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, @Nullable RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedAction<Object>) () -> {
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
return null;
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
//Implement the method of realizing Aware interface
invokeAwareMethods(beanName, bean);
}
Object wrappedBean = bean;
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//Call the before method before instantiation
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
try {
//Call the init method method
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, mbd);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
(mbd != null ? mbd.getResourceDescription() : null),
beanName, "Invocation of init method failed", ex);
}
if (mbd == null || !mbd.isSynthetic()) {
//Call after method
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
}
return wrappedBean;
}
protected void autowireByName(
String beanName, AbstractBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw, MutablePropertyValues pvs) {
String[] propertyNames = unsatisfiedNonSimpleProperties(mbd, bw);
for (String propertyName : propertyNames) {
if (containsBean(propertyName)) {
//To getBean according to the attribute name, the logic is very simple, which directly starts the injected getBean process
Object bean = getBean(propertyName);
pvs.add(propertyName, bean);
registerDependentBean(propertyName, beanName);
}
}
}
protected void autowireByType(
String beanName, AbstractBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw, MutablePropertyValues pvs) {
TypeConverter converter = getCustomTypeConverter();
if (converter == null) {
converter = bw;
}
Set<String> autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);
String[] propertyNames = unsatisfiedNonSimpleProperties(mbd, bw);
for (String propertyName : propertyNames) {
try {
//Resolved attribute type
PropertyDescriptor pd = bw.getPropertyDescriptor(propertyName);
//Only objects of non Object type can be injected
if (Object.class != pd.getPropertyType()) {
MethodParameter methodParam = BeanUtils.getWriteMethodParameter(pd);
// Do not allow eager init for type matching in case of a prioritized post-processor.
boolean eager = !(bw.getWrappedInstance() instanceof PriorityOrdered);
DependencyDescriptor desc = new AutowireByTypeDependencyDescriptor(methodParam, eager);
//It is complicated to resolve the dependent beans here. The resolveDependency is DefaultListableBeanFactory
Object autowiredArgument = resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, converter);
if (autowiredArgument != null) {
pvs.add(propertyName, autowiredArgument);
}
for (String autowiredBeanName : autowiredBeanNames) {
registerDependentBean(autowiredBeanName, beanName);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Autowiring by type from bean name '" + beanName + "' via property '" +
propertyName + "' to bean named '" + autowiredBeanName + "'");
}
}
autowiredBeanNames.clear();
}
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, propertyName, ex);
}
}
}
}
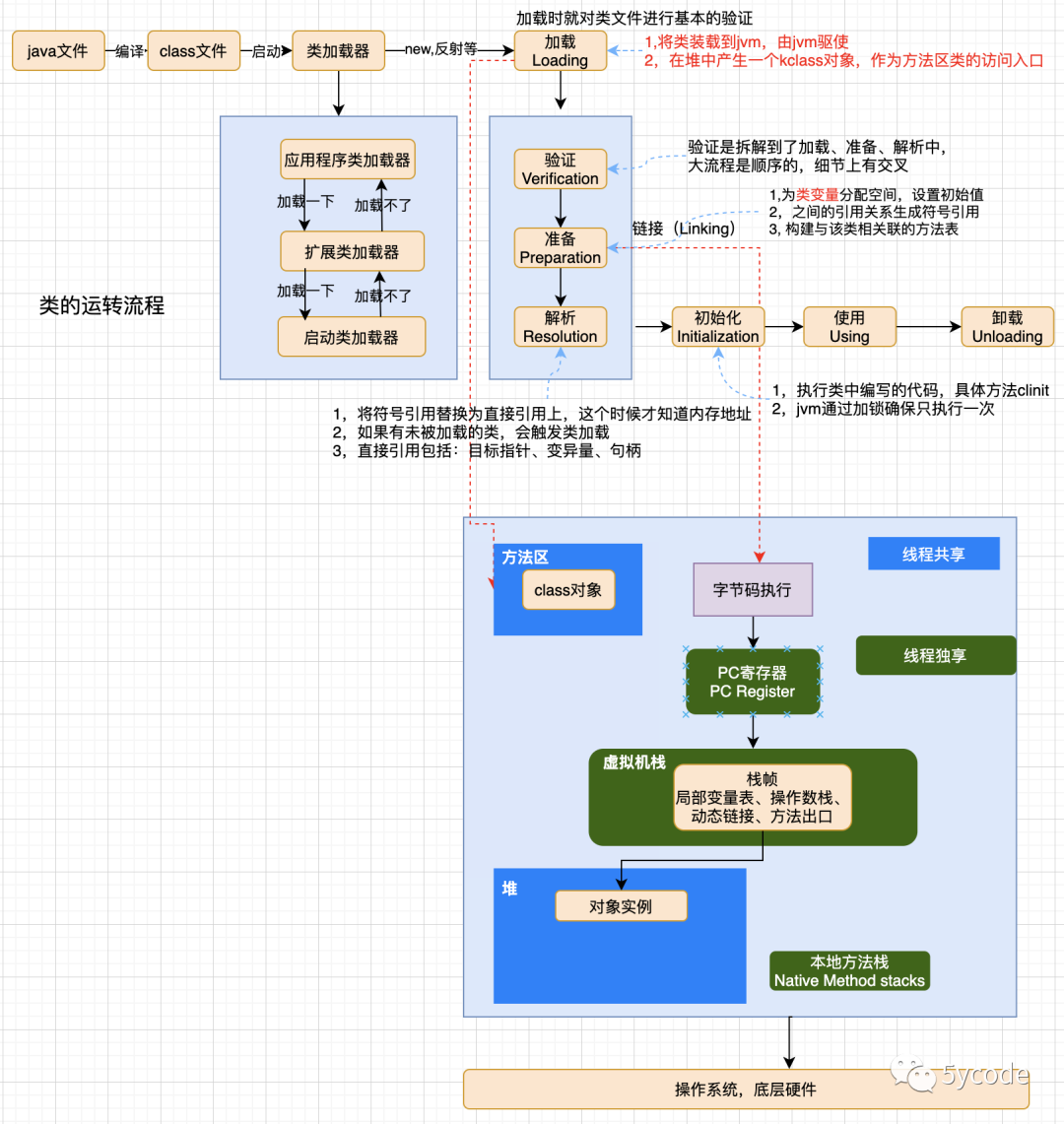
spring takes over the class loading process through its own mechanism, and automatically loads dependent properties through configuration.
ps: a flow chart of class loading is attached:
The following code is instantiated through reflection
public class CglibSubclassingInstantiationStrategy extends SimpleInstantiationStrategy {
}
public class SimpleInstantiationStrategy implements InstantiationStrategy {
@Override
public Object instantiate(RootBeanDefinition bd, @Nullable String beanName, BeanFactory owner) {
// Don't override the class with CGLIB if no overrides.
if (!bd.hasMethodOverrides()) {
Constructor<?> constructorToUse;
//Omit get class constructor
//Specify constructor instantiation class through BeanUtils
return BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructorToUse);
}
else {
// Must generate CGLIB subclass.
return instantiateWithMethodInjection(bd, beanName, owner);
}
}
}
public abstract class BeanUtils {
public static <T> T instantiateClass(Constructor<T> ctor, Object... args) throws BeanInstantiationException {
Assert.notNull(ctor, "Constructor must not be null");
try {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(ctor);
if (KotlinDetector.isKotlinReflectPresent() && KotlinDetector.isKotlinType(ctor.getDeclaringClass())) {
return KotlinDelegate.instantiateClass(ctor, args);
}
else {
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = ctor.getParameterTypes();
Assert.isTrue(args.length <= parameterTypes.length, "Can't specify more arguments than constructor parameters");
Object[] argsWithDefaultValues = new Object[args.length];
for (int i = 0 ; i < args.length; i++) {
if (args[i] == null) {
Class<?> parameterType = parameterTypes[i];
argsWithDefaultValues[i] = (parameterType.isPrimitive() ? DEFAULT_TYPE_VALUES.get(parameterType) : null);
}
else {
argsWithDefaultValues[i] = args[i];
}
}
//Notice here that ctor is a constructor and instantiated through reflection
return ctor.newInstance(argsWithDefaultValues);
}
}
}
Property population code trace
public class AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor extends InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter implements MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor, PriorityOrdered, BeanFactoryAware {
//Attribute resolution
public PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) {
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}
public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Collection<InjectedElement> checkedElements = this.checkedElements;
Collection<InjectedElement> elementsToIterate =
(checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements);
if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
}
private class AutowiredFieldElement extends InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement {
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Field field = (Field) this.member;
Object value;
if (this.cached) {
try {
value = resolvedCachedArgument(beanName, this.cachedFieldValue);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
// Unexpected removal of target bean for cached argument -> re-resolve
value = resolveFieldValue(field, bean, beanName);
}
}
else {
value = resolveFieldValue(field, bean, beanName);
}
if (value != null) {
ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field);
field.set(bean, value);
}
}
@Nullable
private Object resolveFieldValue(Field field, Object bean, @Nullable String beanName) {
DependencyDescriptor desc = new DependencyDescriptor(field, this.required);
desc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());
Set<String> autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<>(1);
Assert.state(beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");
TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();
Object value;
try {
//Back to BeanFactory
value = beanFactory.resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(null, beanName, new InjectionPoint(field), ex);
}
synchronized (this) {
if (!this.cached) {
Object cachedFieldValue = null;
if (value != null || this.required) {
cachedFieldValue = desc;
registerDependentBeans(beanName, autowiredBeanNames);
if (autowiredBeanNames.size() == 1) {
String autowiredBeanName = autowiredBeanNames.iterator().next();
if (beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(autowiredBeanName, field.getType())) {
cachedFieldValue = new ShortcutDependencyDescriptor(
desc, autowiredBeanName, field.getType());
}
}
}
this.cachedFieldValue = cachedFieldValue;
this.cached = true;
}
}
return value;
}
}
}
}
public class InjectionMetadata {
public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Collection<InjectedElement> checkedElements = this.checkedElements;
Collection<InjectedElement> elementsToIterate =
(checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements);
if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
}
}
autowireByType code trace
public class DefaultListableBeanFactory extends AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory implements ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, BeanDefinitionRegistry, Serializable {
public Object resolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String requestingBeanName,@Nullable Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {
//analysis
result = doResolveDependency(descriptor, requestingBeanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
return result;
}
@Nullable
public Object doResolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, @Nullable String beanName,@Nullable Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, @Nullable TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException {
InjectionPoint previousInjectionPoint = ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(descriptor);
try {
if (instanceCandidate instanceof Class) {
//Type type resolution
instanceCandidate = descriptor.resolveCandidate(autowiredBeanName, type, this);
}
Object result = instanceCandidate;
return result;
}
finally {
ConstructorResolver.setCurrentInjectionPoint(previousInjectionPoint);
}
}
}
Finally, getBean is returned in the DependencyDescriptor
public class DependencyDescriptor extends InjectionPoint implements Serializable {
public Object resolveCandidate(String beanName, Class<?> requiredType, BeanFactory beanFactory)throws BeansException {
//Finally, it returns to getBean
return beanFactory.getBean(beanName);
}
}
A conclusion can be drawn from the above. When injecting through Autowire, if beanName is not specified, the cost is still relatively high.
To sum up:
- After the instantiation is completed, spring adds the instance to the cache;
- Then, dependency injection is adopted. At this time, the non instantiated classes are not in the cache, and they will go directly to doCreateBean;
- When it has been created, it will be returned directly when getBean is created, and doCreateBean will not be executed
- Through such a mechanism, the circular dependency is solved.